Stress Hormones in PlantsAbscisic AcidStress Hormones in HumansAdrenalin and NoradrenalineCortisol
Stress Hormone
“Stress hormones are the hormones which are released during stress and they modify the internal environment of an organism in response to stress.”
Stress Hormones in Plants
Phytohormones are chemical compounds that regulate the various physiological processes in plants. They are produced in very less quantity. Plants are exposed to various kinds of stress like drought, salinity, heat, cold etc.
Plant hormones play an essential role during stress condition and help plant in adapting to adverse environmental conditions. Several phytohormones like Jasmonates, Salicylates and ABA interact together and act in hormone signal transduction cascade or “crosstalk” between hormones to form a defence network against environmental stresses.
Why is Abscisic acid called a Stress Hormone?
The stress hormone name in plants is Abscisic acid (ABA). It acts as a plant growth inhibitor and regulates abscission and dormancy. The naturally occurring Abscisic acid is dextrorotatory (+), synthetic ABA used commercially is a racemic mixture. ABA transport occurs through the xylem, phloem and parenchyma cells.
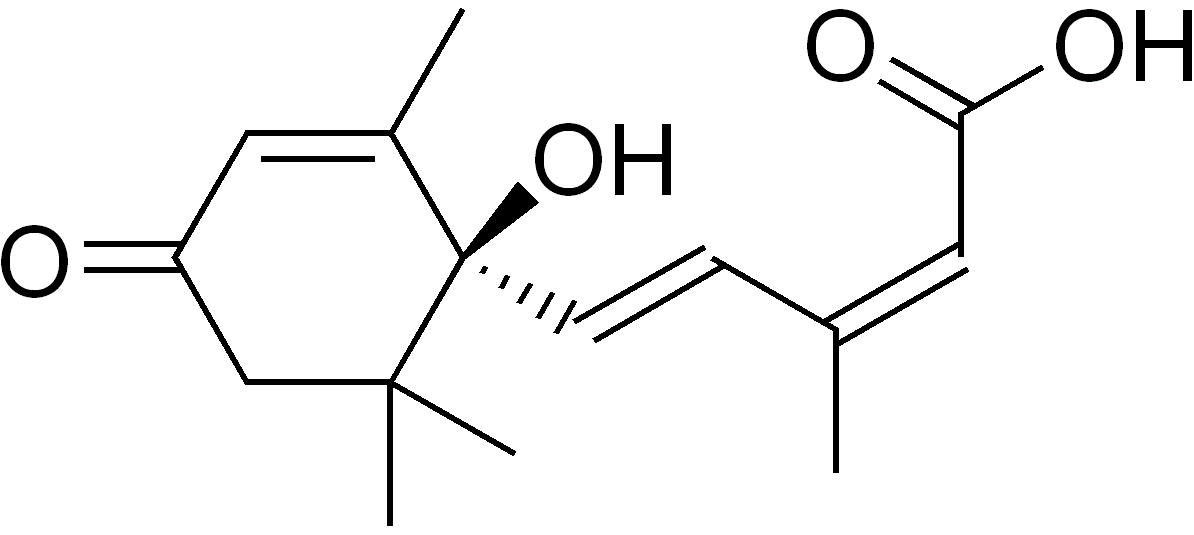
Fig. Abscisic acid chemical structure(ABA)
Abscisic acid is called a stress hormone because the synthesis of the hormone is stimulated by environmental stresses like drought, water logging etc. It plays an important role in tolerating abiotic stress. There are various developmental and physiological processes where ABA plays a critical role:
- ABA stimulates closure of stomata during high salinity, water stress and reduces water loss by transpiration. ABA interacts with other phytohormones like Jasmonates, nitric oxide and signalling molecules to induce stomatal closure
- ABA induces seed dormancy and thereby helps seeds to withstand desiccation and other unfavourable conditions for the growth. Seeds can be kept in storage for a longer duration
- ABA plays an important role in the growth and modification of root during nitrogen deficiency and drought. It regulates the gene expression, required for root growth maintenance and water uptake
- ABA regulates protein-encoding genes and biosynthesis of lipids and storage proteins
- ABA plays an essential role during signal transduction pathway during the stress response
- Abscisic acid is involved in the synthesis of dehydrins, osmoprotectants and protective proteins
- ABA stimulates long term growth by regulating stress-responsive genes
Stress Hormones in Humans
Hormones that are secreted in response to stress and emergency situation are known as stress hormones. These are responsible for initiating a series of reactions to stress referred to as “fight or flight” responses.
The three main stress hormones in humans are:
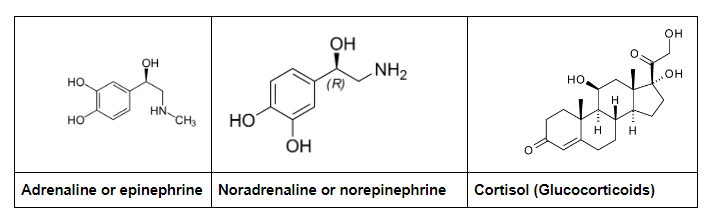
These stress hormones are rapidly secreted under stress and emergency situations. These are secreted from the adrenal gland, a pair of triangular-shaped gland present on kidneys.
- The centrally located adrenal medulla secretes two hormones commonly called as “catecholamines”, adrenalin and noradrenalin
- The outer part of adrenal cortex secretes hormones called “corticoids”, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. Cortisol is a major glucocorticoid present in the body
How do these stress hormones function during stress?
These stress hormones initiate various reactions in response to stress:
-
- Adrenalin and noradrenaline are responsible for immediate reaction under stress.
- They increase heartbeat, rate of respiration, increase alertness, pupillary dilation, piloerection (raising of hairs) and sweating
- Catecholamines also stimulate the breakdown of glycogen and thereby increasing blood glucose. The surge of energy which might be required to run away from a dangerous situation
- They also stimulate the breakdown of lipid and proteins
- They shift the blood flow away from areas which are less crucial under stress condition to areas like muscles which need it more during stress
- Depending on the stress condition it may take half an hour to two days to return to the normal resting state
- Adrenalin and noradrenaline are responsible for immediate reaction under stress.
- Cortisol takes more time (in minutes) to react to stress conditions. Release of cortisol is a multi-step process. The brain identifies the threat and signals hypothalamus to release corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), which in-turn directs pituitary to release adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH signals adrenal glands to release cortisol.
- It helps in maintaining fluid balance and blood pressure
- It suppresses the immune response and other physiological functions like digestive, reproductive and growth that are not crucial under stress
- It is a glucocorticosteroid, which regulates gluconeogenesis, lipolysis and proteolysis. It manages how the body uses carbohydrates, fats and proteins
- It increases blood sugar and boosts energy to handle stress condition
- It produces anti-inflammatory reactions to keep inflammation down
- In the long term stress situations, the continued increased level of cortisol may lead to various health problems like obesity, high blood pressure, diabetes, depression, anxiety and suppressed immunity
Learn more about different types of Plant Hormones and Chemical Coordination And Integration with BYJU’S.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are stress hormones in plants?
Plant stress hormones act during adverse conditions like drought, cold, salinity, etc. Abscisic acid (ABA) is one of the major plant stress hormone. It acts as plant growth inhibitor and also regulates abscission and dormancy.
What are some stress hormones in humans?
Stress hormones in humans initiate the ‘fight or flight’ responses. These include catecholamines and corticoids. The catecholamines include adrenaline and noradrenaline. The corticosteroids include mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids.
What is cortisol?
Cortisol is a major human stress hormone. It is a steroid hormone in the class glucocorticoid. It is produced by the zona fasciculata of the adrenal gland. Release of this hormone increases during stressful conditions.
Related Articles:


Comments