The ECG or electrocardiogram represents the electrical activity in a cardiac cycle. It is an important diagnostic tool to identify any deviations from the normal cardiac activity and heart-related problems.
Download the Complete Guide to NEET UG Prep
Download Now
QRS Complex
The QRS complex is the main spike seen in the standard ECG. It is the most obvious part of the ECG, which is clearly visible.
The QRS complex represents the depolarization of ventricles. It shows the beginning of systole and ventricular contraction.
Also Explore: Systole and Diastole
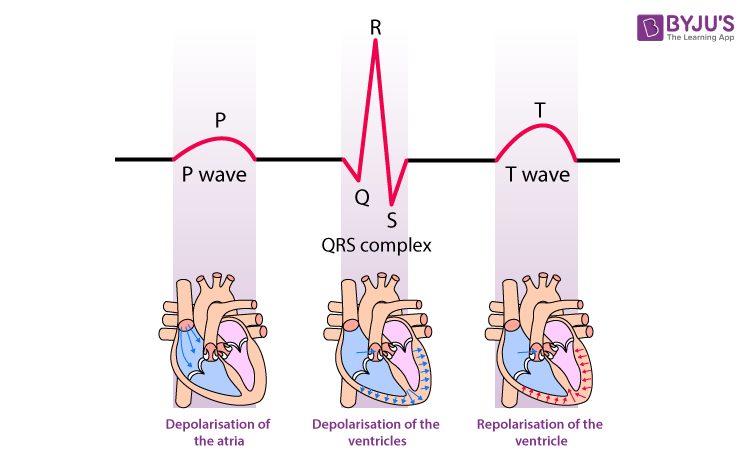
The QRS complex or wave starts with a small deflection downwards, represented by the point Q. It follows the P wave. After Q, there is a sharp peak, i.e. R and followed by deflection downwards, represented by S. By counting the number of QRS complexes in a minute, we can get the heartbeat rate of a person. The duration of the QRS complex is 80 to 120 ms when the heart is functioning properly.
Q-wave
Q wave represents the depolarization of the interventricular septum. It is represented as a small downward deflection. The P-wave is immediately followed by a Q-wave. Abnormality in Q-wave indicates the presence of infraction.
R-wave
The Q is followed by R-wave. This wave follows as an upward deflection. The R is then followed by an S-wave. Large amplitudes of R and S wave indicates left ventricular hypertrophy.
S-wave
R wave is followed by a deflection downwards, represented by S. The point where the QRS complex joins the ST segment is called the J-point. The J-point can also be defined as the first point of inflection of the upstroke of the S-wave.
Furthermore, any combinations of the Q, R and S waves can be termed as a QRS complex.
The other main components of an ECG are:
- P wave– It represents the depolarization of atria and represents atrial contraction. It precedes the QRS complex
- T wave– It represents the repolarization of ventricles and the end of the systole. It follows the QRS complex.
The action potential starts at the SA node present in the right atrium and from the atria it passes to the ventricles through the AV node and bundle of His.
Also see: Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Abnormalities in the QRS complex
The QRS complex has a great significance in clinical diagnosis. The amplitude, duration and morphology of the QRS complex are useful in diagnosing various heart ailments such as cardiac arrhythmias, ventricular hypertrophy, myocardial infarction and conduction abnormalities
- The widened or prolonged QRS complex indicates the bundle branch block or hyperkalemia.
- The increased amplitude of R shows cardiac hypertrophy.
- Abnormality in the Q wave indicates infarction.
This was in brief about the QRS complex and its significance. Get access to all the NEET Questions with explanation, only at BYJU’S.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the three main components of an ECG?
The three main components are P wave, QRS complex and T wave. The P represents depolarization of the atria, QRS complex denotes the depolarization of the ventricles and finally, the T wave represents repolarization of the ventricles.
What does the T wave represent?
The T wave represents the end of ventricular systole.
What is the duration of the QRS complex?
The duration of QRS complex in adults is typically 80 to 100 ms or 0.08 to 0.10 seconds. This duration might be slightly shorter in children. An increased QRS duration indicates hyperkalemia or intraventricular block.
See More:
| Important Notes for NEET – Body Fluids and Circulation |
| NEET Biology Flashcards |
| NEET MCQs |


Comments