Throughout the history of mankind, there have always been two sets of opposing beliefs, ideas, teachings or theories about the creation and the end of the Universe. One group thought that it existed eternally without any overall change (no specific beginning or ending). The other group vouched that the Universe was created at some special point in time, and it will ultimately end at a particular point in time. Just like these polarising thoughts, cosmology is also divided into two thoughts on the origin and end of our Universe.
|
Table of Contents |
|---|
Theories on the Universe
The Universe is just space, time, matter and energy. It includes all the familiar entities like stars, galaxies, and all other versions of matter. Apart from visible matter, it is dominated by dark matter and dark energy. We don’t have the slightest clue what they are. Even though these unknown factors exist, cosmologists have come up with many theories that explain the nature of our Universe. The Big Bang Theory is the most accepted scientific description of the evolution of the Universe. As per this origin theory, time and space emerged from a singularity 13.7 billion years ago. As a result of inflation, it is still expanding. Even though the physical dimension of the Universe is not known, the rate of cosmic expansion suggests that it should have a diameter of about 23 trillion light-years.
Among all the theories about the evolution of the Universe, the Big Bang has the most viable postulates that are compatible with the available observational characteristics of the cosmos. However, there are a bunch of physicists and cosmologists who are against it. The most famous theory that tries to counter the inflation postulates is the Steady-State Theory. Here, the overall density of the Universe stays constant even if the space is expanding. This result is only possible when there is a continuous generation of matter at a very high rate. This theory got out of the hype with the observation of the cosmic microwave background radiation. The model has no clarification regarding this omnipresent entity.
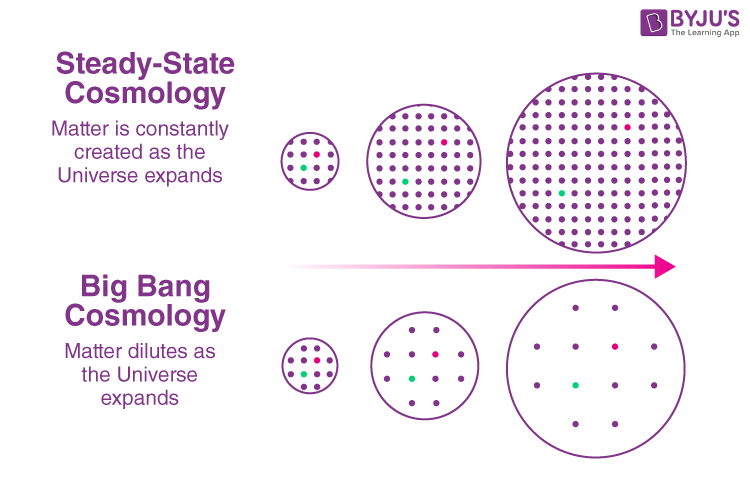
What is the Steady-State Theory?
In cosmology, the Steady-State Theory is a theoretical model in which the Universe is constantly expanding but with a fixed average density. In this Universe model, matter is always created to form galaxies and stars at the same speed as the old ones become destroyed. Their relative distances and recession velocity increase to nullify the overall change in the density. There is no overall beginning or end for a steady-state Universe. When we take any point within view on a grand scale, the overall average density and order of galaxies are always the same. In this model, the matter density in the expanding space-time stays constant as a reason for the ceaseless creation of matter. Thus, acting as an ideal principle suggests that the visible Universe is physically the same at any place and time.
The video explains the basic concepts of stars

Evolution of the Steady-State Theory
Edwin Hubble discovered cosmological expansion by observing the characteristics of the movement of galaxies. Albert Einstein had put forward a static model of the Universe. The work of Hubble made this static model unstable. Father Georges Lemaître was the first person to suggest a concept that is similar to the modern Big Bang theory. It is a model where the Universe has a finite timeline with a definite beginning and end. It is a dynamic Universe model where there is a continuous expansion, cooling, and creation of structures through gravitational and other collapses.
In 1948, Fred Hoyle, Thomas Gold and Hermann Bondi published the most influential papers on the Steady-State Universe model. Later, William Duncan MacMillan and a few others proposed similar models.
The Steady-State Theory suggests that the over appearance and density of the Universe do not change over time even if the Universe is continuously expanding. On the grand scale, the Universe has a particular end or beginning. It also suggests that the matter is being created continuously to replace the old ones to create the balance that a static Universe needs. During the 20th century, the steady-state archetype had a considerable influence on the scientific community. It was backed up by some famous personalities in the field. However, as more observational results came in, it lost its prowess and withered away into just a thought experiment. Most astronomers and cosmologists disregarded this Universe model as the observational results point to a hot and vigorous Big Bang model (distinct beginning).
|
Related Topics |
|---|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Steady-State Theory?
In cosmology, the steady-state theory is a theoretical model in which the Universe is constantly expanding but with a fixed average density. In this Universe model, matter is always created to form stellar bodies at the same speed as the old ones become destroyed or their relative distance and recession velocity increase. There is no overall beginning or end for a steady-state Universe. When we take any point within view on a grand scale, the overall average density and order of galaxies are always the same. In this model, the matter density in the expanding space-time stays constant as a reason for the ceaseless creation of matter. Thus, acting as an ideal principle suggests that the visible Universe is physically the same at any place and time.
What is the significance of the Big Bang Theory?
The Big Bang Theory is the most accepted scientific description of the evolution of the Universe. As per this origin theory, time and space emerged from a singularity 13.7 billion years ago. As a result of inflation, it is still expanding. Among all the theories about the evolution of the Universe, the Big Bang has the most viable postulates that are compatible with the available observational characteristics of the cosmos.
Who were the pioneers of the Steady-State Theory?
In 1948, Fred Hoyle, Thomas Gold and Hermann Bondi published the most influential papers on the Steady-State Universe model.
Who is known as the father of the Big Bang model?
Georges Lemaître, the Belgian cosmologist, is known as the father of the Big Bang model.
Who discovered that the Universe is continuously expanding?
Edwin Hubble discovered cosmological expansion by observing the characteristics of the movement of galaxies.
How did the Steady-State Theory lose its importance?
During the 20th century, the steady-state archetype had a considerable influence on the scientific community. It was backed up by some famous personalities in the field. However, as more observational results came in, it lost its prowess and withered away into just a thought experiment. Most astronomers, cosmologists, and cosmologists disregarded this Universe model as the observational results point to a hot and vigorous Big Bang model (distinct beginning).
Stay tuned to BYJU’S and Fall in Love with Learning!
Comments