The human eye is responsible for the most important function of the human body, the sense of sight. It consists of several distinct parts that work in coordination with each other. The most common eye diseases include myopia, hypermetropia, glaucoma and cataract.
The diagram of the eye is beneficial for Classes 10 and 12 and is frequently asked in the examinations. A brief description of the eye along with a well-labelled diagram is given below for reference.
Well-Labelled Diagram of Eye
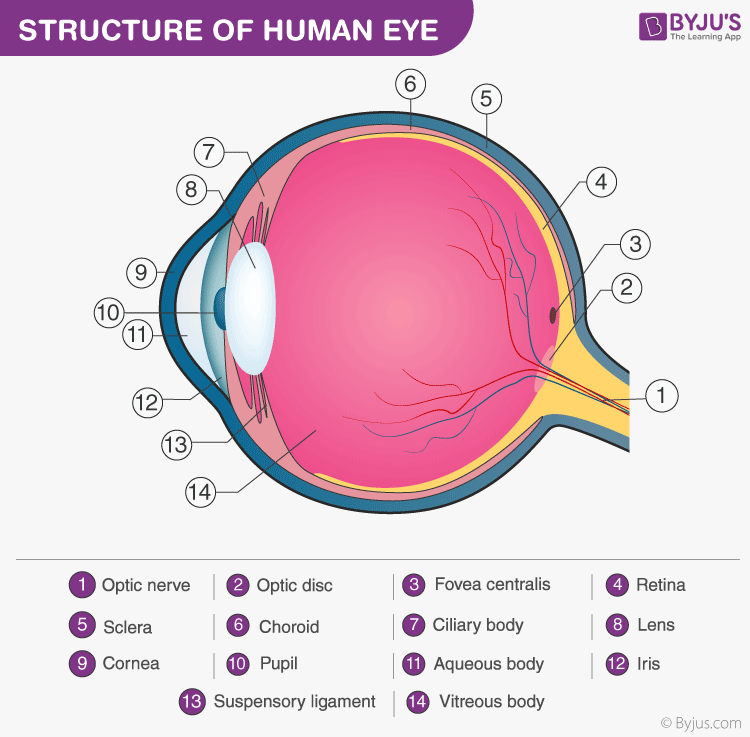
- The anterior chamber of the eye is the space between the cornea and the iris and is filled with a lubricating fluid, aqueous humour.
- The vascular layer of the eye, known as the choroid contains the connective tissue.
- The iris and the choroid are connected by the ciliary body.
- The Fovea is a minute pit located in the macula of the retina that provides clear vision.
- The Cornea is a dome-shaped tissue covering the front of the eye.
- Iris is the coloured part of the eye and controls the amount of light entering the eye by regulating the size of the pupil.
- The lens is located just behind the iris. Its function is to focus the light on the retina.
- The optic nerve transmits electrical signals from the retina to the brain.
- The Pupil is the opening at the centre of the iris. Its size changes with the amount of light.
- The retina lines the back of the eye and contains several photoreceptors.
- Vitreous humour is the fluid present in the centre of the eye and provides form and shape to the eye.
For facts about eye and more information on the diagram of eye, keep visiting BYJU’S website.
Recommended Video:
Related articles on eye:

Comments