B-Cell receptors
B-Cell receptors are protein molecules attached to the B-Cell surface. The principal element of a B cell is to create antibodies against the foreign organisms that enter our body. These are known as B lymphocytes or simply the B-Cells. These cells form an essential part of creating immunity. Moreover, it establishes resistance to unfavourable conditions. They commence from the bone marrow of our body. They also flow through our blood and lymphatic system.
See also: Types of Receptors
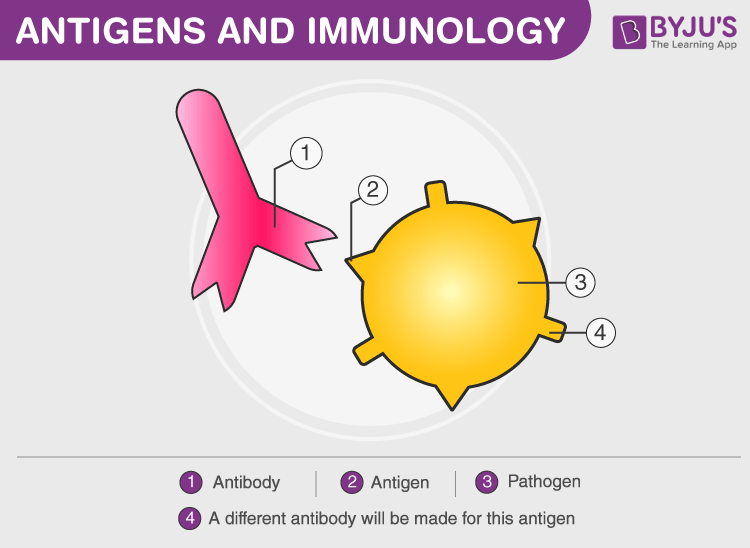
Antibodies
The antibody is otherwise called immunoglobulin(Ig). These are Y-shaped proteins delivered by our plasma cells. Moreover, it is a huge structure that ties to unfamiliar particles and attacks them.
Antigens are unfamiliar particles such as viruses, bacteria or toxins. They attack our body and have the ability to bring about a reaction from our complex immune system. Furthermore, these frameworks gather bigger particles for a specific resistant reaction. Subsequently, antigens invigorate the development of antibodies with the help of our immune system.
Significant differences between B-Cell Receptors and Antibody
B-Cell Receptors |
Antibodies |
| These are cell surface receptors that are attached to the plasma membrane. | The B-Cells produce protein structures called antibodies. |
| The B-cell receptors attach to free moving antigens. | They bind to the foreign organism/pathogen and activate the Immune System. |
Also see: Immunity and Immune System
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the differences between B-Cell receptors and T-Cell receptors?
T-cell receptors can not identify free antigens. These T-cell receptors can recognize an antigen if it is associated with the MHC (Major Histocompatibility Complex) molecule. In contrast, B-Cell receptors recognize the free moving antigens.
What are immunoglobulins?
Immunoglobulins are glycoproteins that are found in five different variables. IgA, IgD, IgE, IgM and IgG are those variants. They specifically bind to antigens and create an immune response. The immunoglobulins are nothing but antibodies that get attached to the B-Cell receptors.
Is antibody also a receptor?
The initial antibodies made by the B cells are embedded equally into the plasma layer. Here, they act as receptors for antigen.

Also Read: Differences between T-Cells and B-Cells
Visit BYJU’S Biology for more interesting topics.
Comments