Plants need water, minerals, and food for their growth and survival. Water and minerals are taken up by roots and leaves prepare the food. These are then transported to the other parts of the plants. When we talk about transport, there should be some means of transportation. Diffusion is the main pathway of transportation in plants.
Let us study about diffusion as a means of transport in plants in detail.
Diffusion In Plants
“Diffusion is the process of movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.”
Diffusion in Plants
Diffusion is a very important process for photosynthesis where carbon dioxide from the stomata diffuses into the leaves and finally into the cells. Also, during transpiration, the water and oxygen diffuse from the leaves into the environment.
It includes the movement of particles of a medium from the region of its higher concentration to the region of its lower concentration without the expenditure of energy. This process is slow and occurs mostly in gases and liquids. The rate of diffusion is affected by various factors like temperature and pressure, concentration gradient, separating membrane’s permeability etc.
Also Read: Diffusion
Diffusion as Means of Transport in Plants
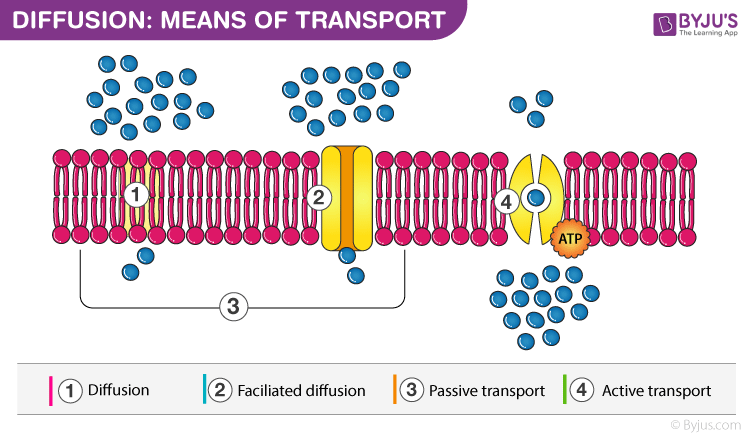
Transportation in plants is an important and natural phenomenon which takes place in all the higher plants. All plants require some essential organic material and inorganic material for the proper functioning of cells and tissues. This process is carried out by three means of transport.
- Diffusion
- Facilitated Diffusion
- Active Transport
Types of Diffusion in Plants
Diffusion in plants is of two major types:
Simple Diffusion
The diffusing molecules do not combine with the constituents of the membrane.
Facilitated Diffusion
The molecules diffuse through the membrane with the help of transporter proteins.
Also Read: Facilitated Diffusion
Factors affecting Diffusion in Plants
Following are the important factors affecting diffusion in plants:
Diffusion Pressure Gradient
The difference in the diffusion pressure determines the rate of diffusion. The rate of diffusion is directly proportional to the difference in concentration of the molecules in the two regions.
Temperature
The rate of diffusion is directly proportional to the increase in temperature.
Density
The rate of diffusion is inversely proportional to the square root of density of the gas.
Importance of Diffusion in Plants
The process of diffusion is important for the plants in the following ways:
- The exchange of gases through stomata takes place by the process of diffusion.
- Transpiration occurs by the principle of diffusion.
- The ions are absorbed by simple diffusion.
- The food material is translocated by this process.
- This process keeps the walls of the internal tissues of the plant moist.
- It is responsible for spreading the ions and molecules throughout the protoplast.
- Aroma of flowers is due to the diffusion of aromatic compounds to attract insects.
Also Read: Active Transport
Learn more about diffusion in plants, its types, importance and other related topics @ BYJU’S Biology.

This site provides me a lot of information, good website
it was very helpful I think the information is very complete
Good work