Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Endocrine Gland – An overview
- Hypothalamus
- Pituitary Gland
- Pineal Gland
- Thyroid gland
- Parathyroid Gland
- Pancreas
- Adrenal Glands
- Gonads
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
An ecosystem is all about the interaction and dependency between living and non-living components. This interaction ensures the existence and survival of each organism. For better interaction, they need a well-defined coordinating system. Animals and plants have their own control and coordination mechanisms within their bodies. Let us see how endocrine glands help in chemical coordination in animals.

Also Read: Hormones
Endocrine Gland – An overview
Animals including humans have a complex living system. In the case of animals, they have the nervous system and endocrine system for control and coordination. The Endocrine System is responsible for chemical coordination. Numerous involuntary physiological activities are under the control of the endocrine system. It consists of glands which release hormones. Endocrine glands are also called ductless glands. Hormones play a vital role in various activities in the body including growth and development. They also support the nervous system.
Endocrine glands in animals are the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, the pineal gland, the thyroid, the parathyroid, the thymus, the pancreas, the adrenal gland and the gonads.
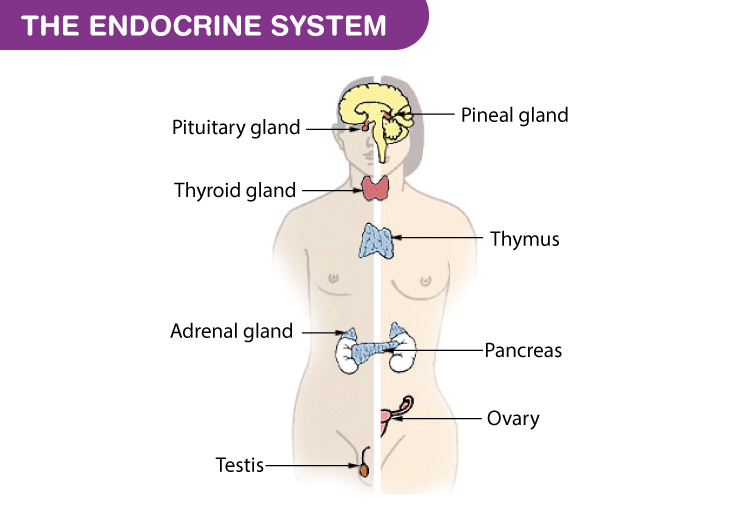
Also Refer: Endocrine Glands and its Disorders
Different endocrine glands along with the hormone they release are given below:
Hypothalamus
This gland is a part of the brain that consists of neurosecretory cells. They connect both the nervous and the endocrine system. The hypothalamus secretes various releasing hormones like gonadotropin-releasing hormones and growth hormone-releasing hormones. These hormones act on the pituitary gland to stimulate other glands.
Explore more: Hypothalamus
Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland is the master gland. It is a pea-sized gland that is located at the bottom of the brain. It controls and regulates other glands in the body. Hormones released by this gland are growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, LH, FSH etc.
Explore more: Pituitary gland
Pineal Gland
This gland is also located in the brain. It releases the hormone called melatonin which regulates the wake-up and sleep clock and helps in immunity etc.
Explore more: Pineal gland
Thyroid gland
This is a butterfly-shaped paired gland located in the neck region. It releases the hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones regulate body metabolism. Iodine is vital for thyroxine synthesis. Its deficiency leads to a disease called goitre.
Explore more: Thyroid gland
Parathyroid Gland
This gland is located near the Thyroid gland in the neck region. The hormone released by this gland is called Parathyroid hormone, which regulates calcium and phosphorus level in bones.
Explore more: Parathyroid Hormone
Pancreas
The pancreas is an endocrine as well as an exocrine gland. That is why the Pancreas is also known as a mixed gland. The pancreas secretes hormones like glucagon and insulin; these two hormones balance the blood sugar level in the body. Other hormones secreted are somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide.
Explore more: Pancreas
Adrenal Glands
Adrenal glands have two regions known as the adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla.
The cortex region of the adrenal gland secretes the hormones cortisol, aldosterone, and androgens while the medulla region secretes the hormones adrenaline and noradrenaline. Adrenaline is the hormone responsible for the fight or flight response of the body in times of emergency.
Explore more: Adrenal glands
Gonads
Gonads are reproductive glands present in males and females. The male gonad is the pair of testes which secretes the hormone testosterone. This is responsible for the secondary sexual characteristics in males. The female gonad consists of a pair of ovaries. They secrete two hormones estrogen and progesterone. Both of these regulate secondary sexual characteristics in females.
Explore more: Gonads
Frequently Asked Questions
Which endocrine gland plays important role in improving immunity?
The dorsal side of the heart contains the thymus gland, linked to immune system development. Thymosin hormone is secreted by it, which is essential for developing T-lymphocyte differentiation.
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
The primary function of the hypothalamus is to maintain the body as close to homeostasis as possible — the hypothalamus functions as a bridge between the nervous and endocrine systems. The network of hormone-producing organs and glands, the endocrine system, helps control body functions. The hypothalamus reacts by enhancing the appropriate endocrine activity to restore this balance. For example, the hypothalamus will tell the body to sweat if it obtains a signal that the internal temperature is too high.
To know more about hormone and their regulation, visit BYJU’S.

Comments