All humans undergo a sexual mode of reproduction, which involves the production of an offspring by the fusion of male and female gametes. In sexual reproduction, the newborn baby will be identical to their parents.
Let’s have a glance at reproduction, its process, types and its significance.
What is Reproduction?
Reproduction is a biological process by which a living organism gives birth to its own offspring, which is biologically similar to their parents. This biological process permits and assures the continuity of life on the planet earth.
Explore more: Reproduction
Modes of Reproduction
There are basically two modes of reproduction:
Sexual mode of Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves the production of an offspring by the fusion of male and female gametes.
Asexual mode of Reproduction
Asexual reproduction refers to the type of reproduction in which only a single organism gives rise to a new individual.
Reproduction in Humans
In humans, reproduction occurs after the formations of male and female gametes, which later fertilize to give rise to an embryo. The complete process of fertilization in humans is called internal fertilization as it occurs within the body of a female.
As human beings are viviparous organisms, we give birth directly to the young ones, instead of laying eggs.
Process of Reproduction in Humans
Sexual reproduction involves a set of events, which are divided into three different stages:
- Pre-fertilization
The different stages in Pre-Fertilization events are:
Gametogenesis
The formation of male and female gametes or sex cells or reproductive cells.
Cell Division
During the formation of gametes, both male and female undergo a meiotic cell division.
Also Refer: Why is Cell Division Necessary?
Transfer of Gametes
The male gametes are called sperms whereas the female gametes are called egg or ovum. In humans, only the male gametes are motile and female gametes are non motile, hence, the male gametes should be transferred into the female’s body for the further process of fertilization. This is done by fusion or copulation and the process is called gametangiogamy.
- Fertilization
After the transfer and fusion of male and female gametes, fertilization occurs with the formation of a diploid zygote.
Also Refer: Fertilization and implantation
- Post-fertilization
Post-fertilization is a series of events in sexual reproduction, which occurs after the fertilization and development of the zygote. The different stages in post-fertilization events are:
Development of zygote
After fertilization, the zygote is formed. The zygote divides mitotically to form 2, 4, 8, 16 celled stages. These cells are known as blastomeres.
Embryogenesis
This stage is also known as embryonic development or the development of an embryo. At this stage, the actual development of a baby begins. This period is called the gestational period.
Between Eight to ten weeks, the embryo develops into a fetus
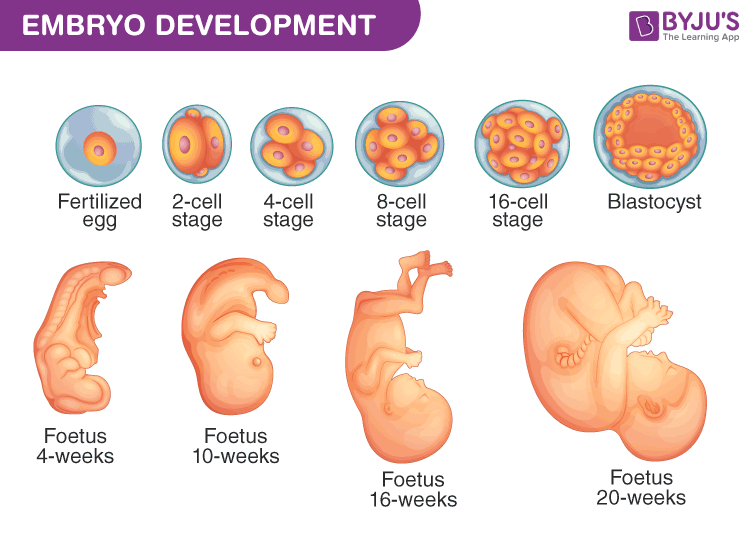
The table provided below explains complete stages involved from embryonic development till the delivery of a baby.
|
Weeks after Fertilization |
Embryonic Development |
|
3rd Week |
In the beginning of the third gestational week, there is a formation of clusters of cells and three germinal layers. |
|
4th Week or 1st month |
Heart is the first organ to start functioning. Along with the heart functioning, the fetal arm buds and optic pits become visible. |
|
5th Week |
In the fifth week, the embryo grows approx. 4mm and begins to curve into a C-shape. At this stage, the fetal liver, pancreas, gallbladder, spleen, the inner part of the ear and the pharyngeal arches start developing. |
|
6th Week |
In the sixth week, the embryo grows from 4 mm to 9 mm in length and the baby’s external features begin to form – eyes and nose, leg buds and hand, stomach and kidney also start developing. |
|
7th Week |
In the seventh week, the baby continues to grow fast from 9mm to 13mm, along with the lengthening of arms and legs. There is the development of internal organs like lungs, primary sex organs and lymphatic system. |
|
8th Week or 2nd Month |
At 7th week, the baby’s hair follicles start developing, along with the external ear, nipples and most of the internal and external organs start developing by this time. |
|
1st-trimester |
By the end of the third month, all the major organ systems are well developed and the genital organs are visible. |
|
5th Month |
During the fifth month, the baby starts moving and hairs start appearing on the head. |
|
24 weeks or 6 months |
By the end of the 2nd trimester, the baby’s eyelashes are formed, eyelids separate and the body gets covered with fine hair. |
|
9th month |
By the end of the 9th month, the fetus fully develops and is ready for birth. |
Also Refer: Embryo development
This article concludes with an introduction to reproduction and how reproduction happens in humans. To know more about the reproduction, types, different stages and other related topics, keep visiting our website at BYJU’S Biology.

Comments