
Phylum Chordata belongs to the Kingdom Animalia and includes all the vertebrates, i.e., animals with a backbone, and several invertebrates, i.e., organisms without a backbone. They possess a bilaterally symmetrical body and are divided into three different sub-phyla.
Explore more: Kingdom Animalia
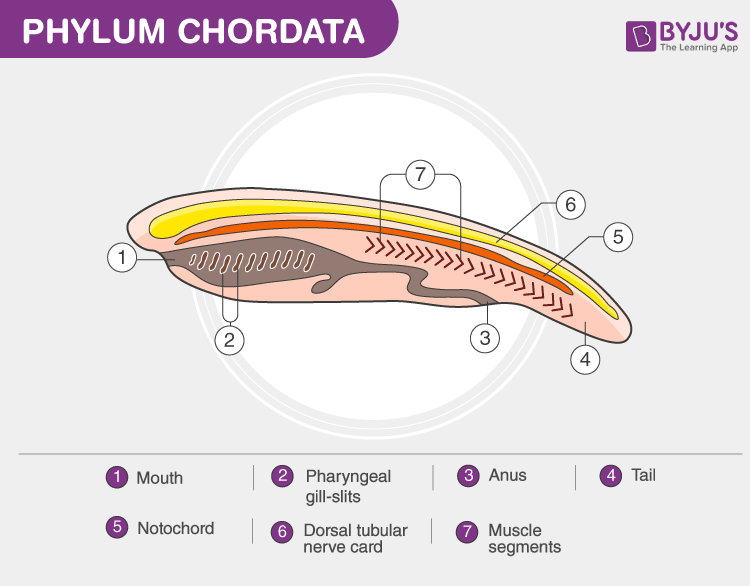
Let us have a detailed look at the characteristics and classification of the phylum Chordata.
Characteristics Of Phylum Chordata
Phylum Chordata possesses the following characteristic features:
Notochord
It is a longitudinal, cartilaginous rod running between the nerve cord and the digestive tract. It acts as a support for the nerve cord and is replaced by the vertebral column after the embryonic stage in all vertebrates.
Dorsal Nerve Cord
It is a bundle of nerves running along the “back” and splits into the brain and the spinal cord. It is hollow and lies dorsal to the notochord.
Pharyngeal Slits
They are the openings which allow the entry of water through the mouth without entering the digestive system viz. they connect mouth and throat. All Chordates have these openings on the lateral sides of the pharynx at some stage of their life.
Post anal Tail
It is an extension of the body to the anus. In chordates, the tail is composed of skeletal muscles which help in locomotion in fish-like species. It is absent in most of the adult Chordates.
Other characteristics of chordates include:
- Bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomic and segmented body.
- The body design is complex and well-differentiated.
- The body has an organ system level of organization.
Also Read: Animal Kingdom
Classification Of Phylum Chordata
Phylum Chordata is classified into three subphyla, namely
- Urochordata (tunicates),
- Cephalochordata (lancelets)
- Vertebrata (vertebrates).
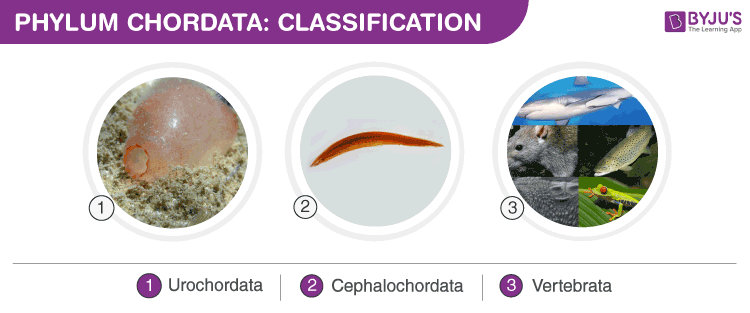
Classification Of Phylum Chordata into three Sub-Phyla
The subphylum Urochordata and Cephalochordata are collectively known as protochordates, which are marine animals. They are invertebrates but they share attributes of chordates.
Urochordata
- The adults are fixed to the substratum.
- It is also known as Tunicate because the body of an adult is enclosed within a tunic made up of cellulose-like substance known as tunicin.
- Notochord can be seen only in the larval stage and disappears in adults.
- The nerve cord present in larva is replaced by a dorsal ganglion in adults.
- The larva can move and undergoes a metamorphosis.
For e.g., Ascidia, Salpa, Doliolum.
Cephalochordata
- The atrium is present.
- Motile adult and larval stage.
- The tail is present throughout life.
- They show progressive metamorphosis.
- The notochord is found throughout life.
- Numerous well-developed pharyngeal gill slits are present.
For e.g., Lancelets possess the notochord and nerve cord throughout their life. However, they lack the brain and bony vertebral column like Branchiostoma.
Vertebrata
The characteristic features of vertebrates include:
- These are advanced chordates and have cranium around the brain.
- The notochord is replaced by a vertebral column in adults. This is why it is said that ‘all vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates’.
- A high degree of cephalization is observed.
- The epidermis is multi-layered.
- They consist of three types of muscles-striped, unstriped and cardiac.
- They have a well-developed coelom.
- The alimentary canal is complete.
- The heart is three or four-chambered.
- They have well-developed respiratory and excretory systems.
- Endocrine glands are present in all.
- They are unisexual and reproduce sexually, hagfish being an exception.
For e.g., humans.
Subphylum Vertebrata is further classified into seven classes. They are:
- Cyclostomata
- Chondrichthyes
- Osteichthyes
- Amphibia
- Reptilia
- Aves
- Mammalia
Examples of Phylum Chordata
Examples of phylum Chordata include the following:
Lampreys
This chordate belongs to the sub-phylum Vertebrata. It is a fish devoid of jaws and spends its larval stages as a filter-feeder. It gets transformed into a parasite as it grows into an adult.
Sea Squirt
It is a Urochordate with a barrel-shaped body attached to the substratum. The larva is tadpole-like and possesses a notochord. They bear a dorsal nerve, pharyngeal slits and a post-anal tail.
Also Read: Arthropoda
Learn more in detail about the phylum Chordata, its characteristics, classification and other related topics at BYJU’S Biology.

A very nice and great site, given to me what my lecturers lack the time to give.
it help me alot
Your lectures and your notes are really helpful to me.
It is very useful at this time
Thank you so much. Great information. Very brief and easily understood.
Tusion centre from jammu and kashmir