Living organisms, which include humans, animals, plants, algae, fungi and other microorganisms reproduce as a law of nature, a means of ensuring the survival of the species and in the context of evolution. There are two major classifications of reproduction: sexual and asexual reproduction.

Each has its own advantages and disadvantages. Vertebrates, such as humans, exclusively follow sexual reproduction. Many simpler animals such as amoeba follow asexual reproduction.
Explore more: Reproduction
Let us have a look at the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction.
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction spans a variety of methods. The simplest single-celled organisms such as archaea, and bacteria, reproduce by binary fission. In this process, the cells simply divide in half, creating a clone of the parent. This method also holds the benefit of being very quick and energy-efficient. For example, bacteria that reproduce by binary fission can give rise to progeny every few hours. Multiple fission also exists, in which an organism splits into more than one offsprings. Certain species of algae and protozoans exhibit multiple fission.
Refer more: Asexual reproduction

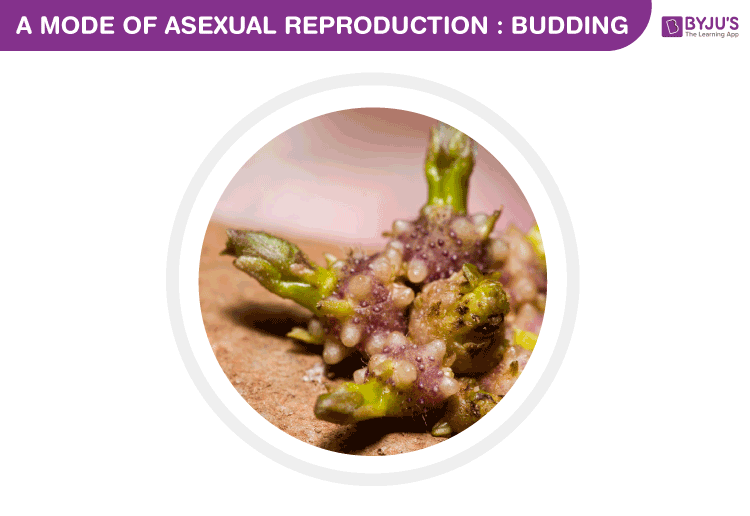
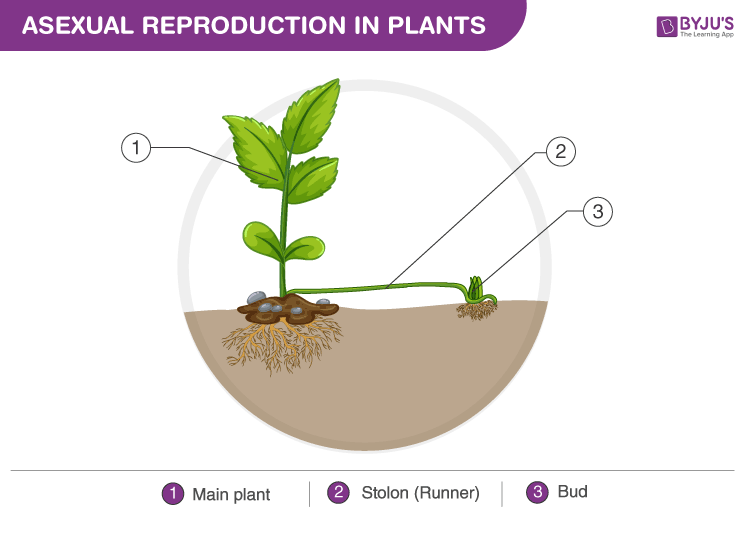
While in multicellular organisms, a similar method called fragmentation is observed. In this process, small pieces break off and grow into new organisms. Another method involves budding, which produces a completely new organism and remains attached to the original body or develops from the original body. A common thread in all this is that the offspring is a direct clone of the parent. The purpose of reproduction, as we’re well aware, is to propagate one’s own genes. Evolutionarily, asexual reproduction is a good bet for the species. It is quick, simple and the genes of the parent will not be diluted by those of another individual. Also, an organism that reproduces asexually can reproduce about twice as fast as one that reproduces sexually.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the combination of reproductive cells from two individuals to form a third unique offspring. Sexual reproduction produces offspring with a different combination of genes.
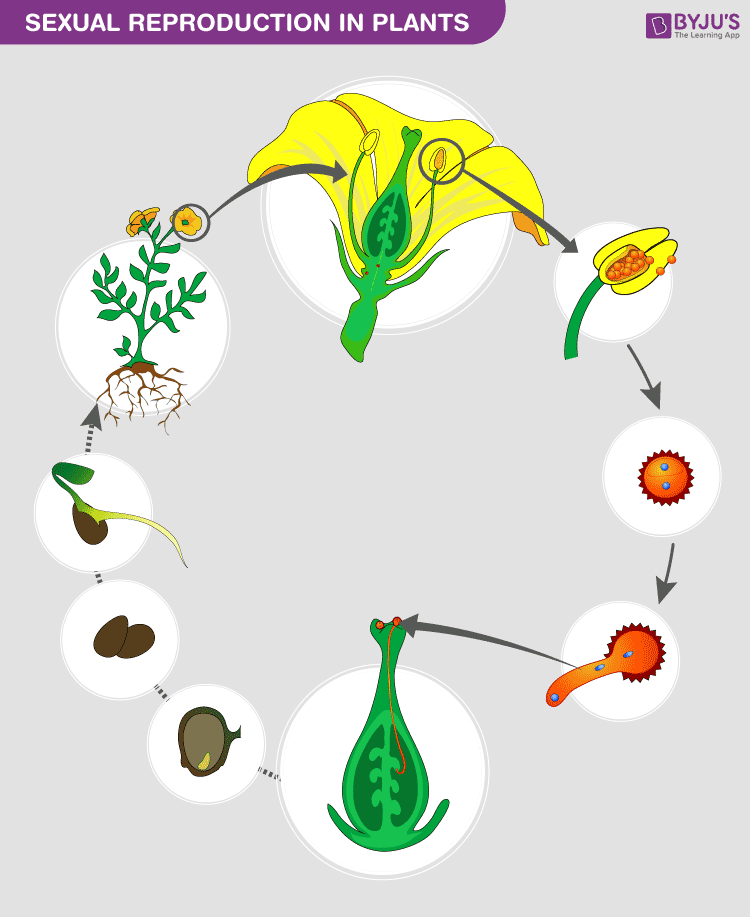
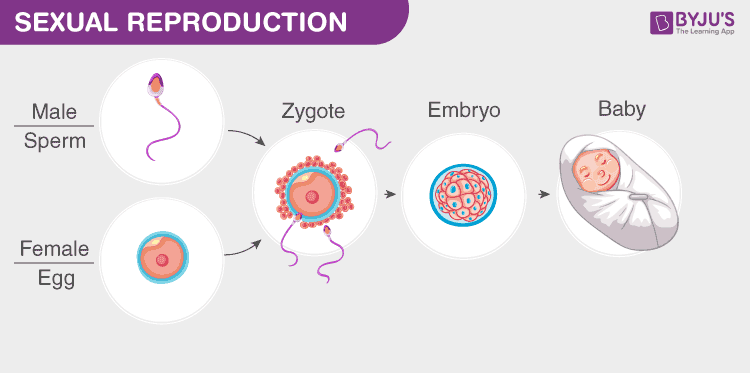
One must understand that sexual reproduction is a lot more complex than asexual reproduction. It includes the production of gametes, which have half the number of chromosomes compared to all other cells in the organism. They are produced by the process of meiosis, which produces haploid cells from diploid cells. There occurs crossing over and recombination of genes. Switching from chromosomes to chromosomes is a good way to ensure that the genes will remain active in a given population. Besides these, factors like gestation period also play an important role in sexual reproduction. The gestation period is the time required for the foetus to fully develop either internally (like in the mother’s womb) or externally (like an egg).
Also Read: Sexual Reproduction
Difference between Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
The differences between sexual and asexual reproduction are as follows:
| Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
|---|---|
| Occurs in prokaryotic microorganisms and in some eukaryotic unicellular and multicellular organisms, lower invertebrates and plants | Occurs almost in all types of multicellular organisms including humans, animals, and higher plants. |
| It is uniparental. | It is usually bi-parental. |
| Gametes are not formed. | Gametes are formed. |
| Somatic cells of parents are involved. | Germ cells of parents are involved. |
| No fertilization occurs. | Fertilization takes place. |
| No involvement of reproductive organs. | Presence of fully developed reproductive organs. |
| Only mitosis type of cell division occurs. | Both meiosis and mitosis type of cell division occurs. |
| The progeny and the parent are genetically identical. | The progenies will be genetically different from the parents. |
| Characteristics of only one parent are inherited. | Characteristics of both parents are inherited. |
| The genes and genetic material are just multiplied and passed on to new organisms from the parent. | The genetic material undergoes intermixing from both parents to form a new set of genetic material. |
| Multiplication is very rapid and takes less time. | Multiplication is not so rapid and takes a longer time to complete. |
| The number of offsprings produced may vary from two to many. | The number of offsprings produced is comparatively lower. |
| No evolutionary significance. | Has evolutionary significance in the population. |
| Bacterial fission, fragmentation, spore formation, budding of hydra are different types of asexual reproduction. | Syngamy, external fertilization, and conjugation are different types of sexual reproduction. |
Interesting Facts about Reproduction
- The record for the longest ever gestation period is held by the elephant which has around 640-660 days as compared to a human’s 280 days.
- The deep-sea male anglerfish bites on to the much larger females and then, the tissues start to fuse until the male fish looks like just a lump of tissue dangling from the female’s body. The male anglerfish receives nutrients and the female fish has access to male sperms to fertilize its eggs.
- Oysters are protandric creatures, this means that they can change from male to female over the course of their lifetime.
- Abiogenesis is a process that still remains a mystery. It speculates how the first-ever life arose from non-living matter such as carbon (Organic compounds.)
Learn more in detail about the differences between sexual and asexual reproduction and other related topics at BYJU’S Biology
Frequently Asked Questions
How is sexual reproduction different from asexual reproduction?
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes whereas asexual reproduction does not require male and female individuals and no fusion of gametes takes place.
What are the advantages of asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction has the following advantages:
- It requires less energy.
- It can occur in different environments.
- The reproduction process does not require a longer time.
- It requires only a single individual.
- Identical offspring is produced.
What is the advantage of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction?
Since sexual reproduction requires two individuals, it allows intermingling of genes which is beneficial for the individuals as well as the entire species. The organisms produced by asexual reproduction are genetically identical to each other.
What are the different types of asexual reproduction?
The different types of asexual reproduction include:
- Binary fission
- Budding
- Fragmentation
- Vegetative Propagation
What is vegetative propagation?
Vegetative propagation is a form of asexual reproduction that occurs in plants in which a new plant can be grown from any vegetative part of the parent plant. For eg., vegetative propagation by the stem in ginger, vegetative propagation by leaves in Bryophyllum.

This help me a lot, thanks
Thanks for helping me alot for exam
Thanks a lot for the information
thanks a lot
I am preparing for exams. Thanks, it really helped me
I like Byju’s learning app. It solves clear the solution