What is Homologous series?
Homologous series is a series of compounds with similar chemical properties and some functional groups differing from the successive member by CH2. Carbon chains of varying lengths have been observed in organic compounds having the same general formula.
Table of Contents
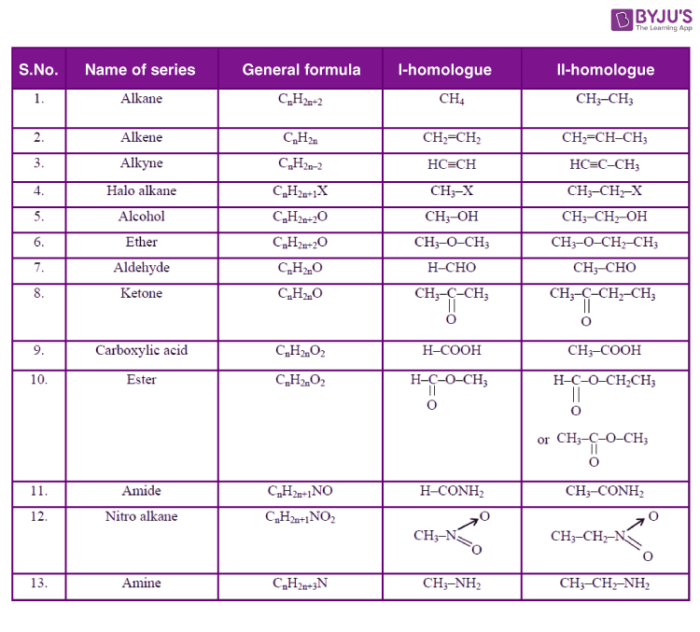
Such organic compounds that vary from one another by a repeating unit and have the same general formula form a series of compounds. Alkanes with general formula CnH2n+2, alkenes with general formula CnH2n and alkynes with general formula CnH2n-2 form the most basic homologous series in organic chemistry.
Examples of Homologous series
The successive members vary from each other by a CH2 unit. For example in CH4 and C2H6, the difference is -CH2 unit and the difference between C2H6 and C3H8 is also -CH2 unit. So CH4, C2H6, and C3H8 are homologs. The same thing can be observed in the case of alkenes in which the first member is ethene and the successive members are C3H6, C4H8, and C5H10. They differ from each other by a –CH2 unit. The Alkene formula is written as CnH2n.
All the members belonging to this series have the same functional groups. They have similar physical properties that follow a fixed gradation with increasing mass. The properties of CH3OH, C2H5OH, and C3H7OH are similar and follow a gradual change with increasing molecular mass of the successive members of the series. This is because, with the increase in the molecular mass of the compounds, the number of bonds also increases. Therefore, properties such as melting and boiling point, solubility, etc. that depend on the mass and the total number of bonds in a compound show a gradual change with an increase in molecular masses of the compounds. The Chemical properties of the members of a homologous series are the same due to the fact that they all have the same functional groups in them.
This series has enabled scientists and engineers to study different organic compounds systematically. They can predict the properties of organic compounds belonging to a particular homologous series based on the data available from the other members of the same series. The study of organic compounds has been simplified.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Write any 4 characteristics of homologous series of organic compounds?
The characteristics of homologous series are as follows-
The functional group of the members of the homologous series is the same.
The general formula is the same for all members.
Members have nearly identical chemical properties due to the same functional group.
Members have a general method of preparation in common.
How do you determine whether a series is homologous?
Each successive member differs from the others by a CH2 unit. For example, the difference between CH4 and C2H6 is -CH2 unit, and the difference between C2H6 and C3H8 is also -CH2 unit. As a result, CH4, C2H6, and C3H8 are homologs.
Why is it that the chemical properties of homologous series are always the same?
In organic chemistry, homologous series are groups of molecules that only differ in the number of methylene (CH2) groups. Because they share the same functional group, homologous series have similar chemical properties.
What are the two main distinctions between any two groups of homologous series?
The two main difference are as follows-
In terms of molecular mass, the difference in the molecular formula of any two adjacent homologues is 14 a.m.u.
It is distinguished by three atoms. It has one carbon and two hydrogen atoms that are different.
What are individual members of the homologous series called?
Individual members of such a series are known as homologues, and the phenomenon is known as homology.
Download the BYJU’S App and get in touch with our mentors for any further queries.
Read more:

tnx a lot