The Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women or CEDAW is a United Nations treaty against the discrimination faced by women in various forms worldwide. It is a crucial international convention and is important from the IAS exam perspective.
CEDAW UPSC Notes:- Download PDF Here
CEDAW
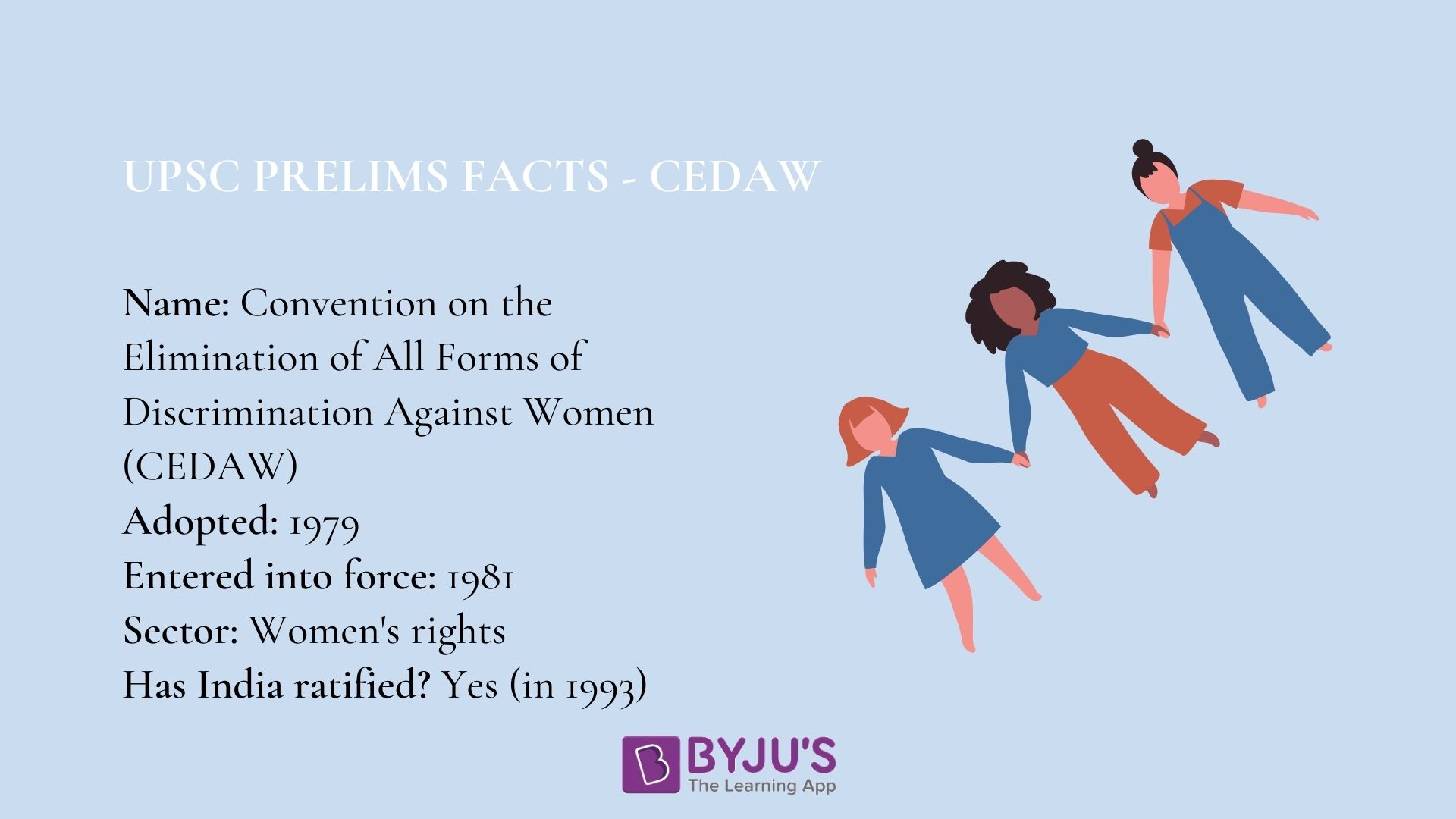
CEDAW was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) in 1979. It became effective in 1981 after the condition of 20 ratifications were fulfilled.
- It is considered by many as an international ‘bill of rights’ for women.
- It is one of the core international human rights treaties of the UN treaty system, which requires Member States to undertake legal obligations to respect, protect and fulfill human rights.
- It has been acceded to or ratified by 189 members.
- India signed CEDAW in 1980 and ratified it in 1993, with certain reservations.
- The US has signed the treaty but not ratified it.
- CEDAW is a treaty that is exclusively dedicated to gender equality.
- It also defines the meaning and nature of sex-based discrimination and gender equality.
- By becoming a party to the Convention, a country is legally obliged to take all appropriate measures to eradicate discrimination against women and promote gender equality.
- The obligation of the member pertains to both public as well as private life.
- This is important because one of the biggest hurdles to achieving equality has been the perception that the State should not interfere with the private life of an individual.
- CEDAW makes the States’ obligations to ensure that women are not discriminated against in the private realms of marriage and family life.
- CEDAW acknowledges that unequal power relations within the private sphere contribute greatly to gender inequality in all aspects of women’s lives, and it directs States to take measures to correct this power imbalance.
- The treaty is monitored by a 23-member expert committee called the Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination Against Women.
- The members are elected by state parties with the tenure of membership lasting four years.
- CEDAW requires that member states not only have an absence of discriminatory legal framework, but that their laws and policies should not be discriminatory in effect.
- It underscores the difference between formal equality and substantive equality between men and women.
- The CEDAW Convention provides strong standards on equality and non-discrimination for all women.
- It also provides critical normative standards that are intrinsically linked to the Agenda 2030 for sustainable development such as those related to food, health, education, housing, legal capacity, non-discrimination, political participation and equal family relations. SDG 5 talks about gender equality in the world by the year 2030.
To know more about Important Headquarters of International Organizations, check the linked article.
How CEDAW defines ‘discrimination against women’?
The Convention’s Article 1 declares the following:
“For the purposes of the present Convention, the term “discrimination against women” shall mean any distinction, exclusion or restriction made on the basis of sex which has the effect or purpose of impairing or nullifying the recognition, enjoyment or exercise by women, irrespective of their marital status, on a basis of equality of men and women, of human rights and fundamental freedoms in the political, economic, social, cultural, civil or any other field.”
Why is CEDAW Important?
CEDAW is important because it makes it the obligation of the member states to have non-discriminatory laws and policies. It also talks about substantive equality and not merely formal equality as mentioned above. Even in the 21st century, many women face routine discrimination in all matters of their lives such as healthcare, education, decent work, free marriage, equal pay for equal work, etc. They also face violence, even from family members and partners. They often have no voice in matters related to sexual and reproductive choices. It is important that governments in power make necessary laws that promote gender equality in the true sense of the word, and also empower women so that they can lead full lives to the best of their abilities and potential. This is not only a fundamental human right but also a necessity to realise the true economic and social development of society.
Frequently Asked Questions on CEDAW
Q 1. What is CEDAW and what is its objective?
Q 2. When was CEDAW established?
Also read: UN Women
Comments