TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS1 Related B. GS2 Related Polity 1. Government backs varying ages for girls’ marriage 2. SC likely to hear curative pleas against Sec 377 on September 8 International Relations 1. Modi and Xi flag 'forward looking' ties after the close of the Doklam crisis 2. PM's '10 Noble Commitments' for BRICS members to achieve global transformation 3. PM Modi reaches Myanmar for first bilateral visit, to meet Suu Kyi tomorrow 4. ‘Undersea line from Iran to port cheap gas’ C. GS3 Related Economics 1. Policy soon to develop agri-clusters and boost farm exports: Prabhu 2. RBI includes HDFC Bank in the ‘too big to fail’ list 3. India to flag worry on pace of services talks at RCEP D. GS4 Related E. Prelims Fact F. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions G. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
A. GS1 Related
Nothing here for Today!!!
B. GS2 Related
1. Government backs varying ages for girls’ marriage
In news:
- NGO’s (Independent thought), petition before Supreme Court:
- Challenged Exception 2 to Section 375 (rape) of the Indian Penal Code, which permits “sexual intercourse with a girl child aged between 15 and 18 only on the ground that she is married”.
- The statutory exception to rape was violative of right to life, personal liberty, equality and is discriminatory.
- The Exception is part of the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act of 2013 and is contrary to the anti-child sex abuse law, Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act of 2012 (POCSO).
- Supreme court’s question to government:
- What is the logic behind keeping different minimum ages for marriage under different laws?
- Basis Information: The age of consent varies from the Indian Penal Code to the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act to the Hindu Marriage Act
- Government response: The legislature may have taken a conscious decision to retain the minimum age range for marriage between 15 and 18 for girls considering the socio-economic conditions of the country.
Section 375 in The Indian Penal Code
375.Rape.—A man is said to commit “rape” who, except in the case hereinafter excepted, has sexual intercourse with a woman under circumstances falling under any of the six following de-scriptions:—
(First) — Against her will.
(Secondly) —Without her consent.
(Thirdly) — With her consent, when her consent has been obtained by putting her or any person in whom she is interested in fear of death or of hurt.
(Fourthly) —With her consent, when the man knows that he is not her husband, and that her consent is given because she believes that he is another man to whom she is or believes herself to be lawfully married.
(Fifthly) — With her consent, when, at the time of giving such consent, by reason of unsoundness of mind or intoxication or the administration by him personally or through another of any stupefying or unwholesome substance, she is unable to understand the nature and consequences of that to which she gives consent.
(Sixthly) — With or without her consent, when she is under sixteen years of age. Explanation.—Penetration is sufficient to constitute the sexual intercourse necessary to the offence of rape.
(Exception) —Sexual intercourse by a man with his wife, the wife not being under fifteen years of age, is not rape.]
2. SC likely to hear curative pleas against Sec 377 on September 8
Context:
- Section 377 of the Indian Penal Code: a colonial era provision criminalising consensual sexual acts of Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual and Transgender (LGBT) adults in private.
- The Supreme Court is likely to hear curative petitions against Section 377.
- The fight against Section 377 got a major boost when a nine-judge Bench of the Supreme Court, while upholding the right to privacy as a fundamental right intrinsic to life and liberty, ripped apart a 2014 judgment dismissing the case against Section 377 of the Indian Penal Code, which criminalises consensual sexual acts of adults in private.
What is section 377?
- Section 377. Unnatural offences: Whoever voluntarily has carnal intercourse against the order of nature with any man, woman or animal shall be punished with imprisonment for life, or with imprisonment of either description for term which may extend to ten years, and shall also be liable to fine.
Petitioner’s contention: The petitioners have contended that homosexuality was not a mental disorder, but a normal and natural variant of human sexuality
List of Cases and their verdict:
- Naz Foundation v. Govt. of NCT of Delhi– is a landmark Indian case decided by a two-judge bench of the Delhi High Court, which held that treating consensual homosexual sex between adults as a crime is a violation of fundamental rights protected by India’s Constitution. The verdict resulted in the decriminalization of homosexual acts involving consenting adults, in the jurisdiction of the Delhi High court. This was later challenged in the Supreme Court of India.
- Suresh Kumar Koushal (2013) Case Observations:
- Supreme Court has upheld the validity of Section 377 of Indian Penal Code.
- LGBT “minuscule minority”: no need to challenge Section 377 because the LGBT community constitutes only a minuscule minority.
- National Legal Services Authority (2014) Case observations:
- Transgenders, even though insignificant in numbers, are entitled to human rights.
- Section 377 had been an instrument of harassment and abuse.
- Discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity must end. Sexual orientation is not only a freedom flowing from the right to privacy, but also a demanding of non-discriminatory treatment
- Adoption of the Yogyakarta Principles — norms on gender identity and sexual orientation adopted by human rights experts in 2006 in Indonesia.
- Latest: In the Aadhaar case the Supreme Court Observations are as follows:
- It has upheld the right to privacy as a fundamental right and an inherent component of human liberty and dignity.
- The nine-judge Bench has observed that the rationale behind the Koushal judgment is flawed and unsustainable.
- Rights of LGBT persons are real rights founded on sound constitutional doctrine and not “so-called rights” as the earlier Bench had described.
- Sexual orientation is an aspect of the right to privacy and an inalienable part of human dignity, freedom, and personal liberty.
Curative petition:
- The concept of Curative petition was evolved by the Supreme Court of India in the matter of Rupa Ashok Hurra vs. Ashok Hurra and Anr. (2002) where the question was whether an aggrieved person is entitled to any relief against the final judgement/order of the Supreme Court, after dismissal of a review petition.
- The Supreme Court in the said case held that in order to prevent abuse of its process and to cure gross miscarriage of justice, it may reconsider its judgements in exercise of its inherent powers.
- For this purpose the Court has devised what has been termed as a “curative” petition. In the Curative petition, the petitioner is required to aver specifically that the grounds mentioned therein had been taken in the review petition filed earlier and that it was dismissed by circulation. This has to be certified by a senior advocate. The Curative petition is then circulated to the three senior most judges and the judges who delivered the impugned judgement, if available. No time limit is given for filing Curative petition.
Requirements:
To entertain the curative petitions, the court has laid down certain specific condition:
- The petitioner will have to establish that there was a genuine violation of principles of natural justice and fear of the bias of the judge and judgement that adversely affected him.
- The petition shall state specifically that the grounds mentioned had been taken in the review petition and that it was dismissed by circulation.
- The curative petition must accompany certification by a senior lawyer relating to the fulfillment of the above requirements.
- The petition is to be sent to the three senior most judges and judges of the bench who passed the judgement affecting the petition, if available.
- If the majority of the judges on the above bench agree that the matter needs hearing, then it would be sent to the same bench (as far as possible).
- The court could impose “exemplary costs” to the petitioner if his plea lacks merit.
Category: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. Modi and Xi flag ‘forward looking’ ties after the close of the Doklam crisis
Context:
- 9th BRICS summit
- Venue: Xiamen , China
- India – China bilateral talks.
In news:
Highlights of the discussions held between Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Chinese President Xi Jinping on the sidelines of BRICS summit:
- India and China decided to open a new “forward looking” round of engagement, anchored by fresh mechanisms to ensure calm at the borders.
- Main focus: more on border Confidence Building Measures (CBMs), rather than on fresh ideas to resolve the festering boundary dispute between the two countries.
- Two leaders agreed that efforts should be made to ensure that “defence and security (personnel) must maintain strong contact and cooperation” at the borders.
BRICS:
- BRICS is the acronym for an association of five major emerging national economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
- Originally the first four were grouped as “BRIC” (or “the BRICs”), before the induction of South Africa in 2010.
- The BRICS members are all leading developing or newly industrialized countries, but they are distinguished by their large, sometimes fast-growing economies and significant influence on regional affairs; all five are G-20 members.
- The term does not include countries such as South Korea, Mexico and Turkey for which other acronyms and group associations were later created.
Financial structure: Currently, there are two components that make up the financial architecture of BRICS, namely, the New Development Bank (NDB) and the Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA). Both of these components were signed into treaty in 2014 and became active in 2015.
a) New Development Bank:
- The New Development Bank (NDB) is based in Shanghai.
- The New Development Bank (NDB), formerly referred to as the BRICS Development Bank, is a multilateral development bank operated by the BRICS states.
- The bank’s primary focus of lending will be infrastructure projects with authorized lending of up to $34 billion annually.
- South Africa will be the African Headquarters of the Bank named the “New Development Bank Africa Regional Centre”.
- The bank will have starting capital of $50 billion, with capital increased to $100 billion over time.
- Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa will initially contribute $10 billion each to bring the total to $50 billion.
b) BRICS CRA:
- The BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) is a framework for providing protection against global liquidity pressures.
- This includes currency issues where members’ national currencies are being adversely affected by global financial pressures.
- It is found that emerging economies that experienced rapid economic liberalization went through increased economic volatility, bringing uncertain macroeconomic environment.
- The CRA is generally seen as a competitor to the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and along with the New Development Bank is viewed as an example of increasing South-South cooperation.
- It was established in 2015 by the BRICS countries Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
- The legal basis is formed by the Treaty for the Establishment of a BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement, signed at Fortaleza, Brazil on 15 July 2014.
2. PM’s ’10 Noble Commitments’ for BRICS members to achieve global transformation
In news:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi suggested 10 commitments to be made by the five-member bloc for their role in global transformation. These are as follows:
- Creating a Safer World – By organised and coordinated action on three issues: Counter-terrorism, Cyber-security and Disaster Management
- Creating a Greener World – By taking concerted action on countering climate change through initiatives such as the International Solar Alliance
- Creating an Enabled World – By sharing and deploying suitable technologies to enhance efficiency, economy and effectiveness
- Creating an Inclusive World – By economic mainstreaming of our people including in the banking and financial system
- Creating a Digital World – By bridging the digital divide within and outside our economies
- Creating a Skilled World – By giving future-ready shills to millions of our youth
- Creating a Healthier World – By cooperating in research and development to eradicate diseases, and enabling affordable healthcare for all
- Creating an Equitable World – By providing equaity of opportunity to all, particularly through gender equality
- Creating a Connected World – By enabling free flow of goods, people and services
- Creating a Harmonious World – by promoting ideologies, practices and heritage that are centred on peaceful coexistence and living in harmony with nature
3. PM Modi reaches Myanmar for first bilateral visit, to meet Suu Kyi tomorrow
Context:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Myanamar.
In news:
- First bilateral visit to Myanmar.
- Aim: to chart out a roadmap for closer cooperation between the two countries in areas like security and counter-terrorism, trade and investment, infrastructure and energy, and culture.
- Key fact:
- Strategic importance: Myanmar shares a 1,640-km-long border with a number of northeastern states.
4. ‘Undersea line from Iran to port cheap gas’
In news:
Iran-India gas pipeline study: 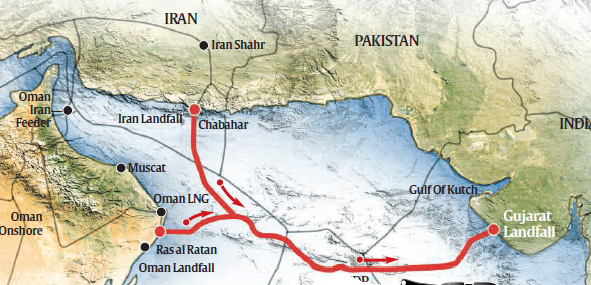
- A 1,300-km undersea pipeline from Iran, avoiding Pakistani waters, can bring natural gas from the Persian Gulf to India at rates less than the price of LNG available in the spot market.
- Cheaper fuel: Natural gas imported through the more than $4-billion pipeline would cost $5-5.50 per million British thermal unit at the Indian coast, cheaper than the rate at which some of the domestic fields supply gas.
- Cheaper than the ones which are shipped: Liquefied natural gas, or LNG, imported through ships costs about $7.50 per million British thermal unit.
- The cost of landed gas through an undersea pipeline will be at least $2 cheaper than importing LNG, saving about $1 billion annually.
- The pipeline is planned to carry 31.5 million standard cubic meters gas per day. The pipeline can first travel to Oman, and then onwards to Porbandar in the state of Gujarat.
- Iran-Pakistan-India pipeline:
- The subsea pipeline is being seen as an alternative to the on-land, Iran-Pakistan-India pipeline
- New Delhi has not been participating in talks on the 1,036-km Iran-Pakistan-India gas pipeline since 2007 citing security and commercial concerns. But, it has never officially pulled out of the $7.6 billion project.
C. GS3 Related
1. Policy soon to develop agri-clusters and boost farm exports: Prabhu
In news:
- New policy on the anvil: The government will soon bring out a policy to develop agricultural clusters and boost farm exports.
ICFA (Indian Council of Food and Agriculture):
- ICFA is a national level platform in India with a mandate for policy research, advocacy and enterprise development in food and agriculture sector.
- Besides, ICFA is engaged in business and trade facilitation, farm services and providing a platform for global partnerships.
- ICFA emerged out of the long felt need for a comprehensive approach to address issues in food and agriculture sector and tapping of emerging global business opportunities overcoming compartmentalized approach and absence of coordination and dialogue among various stake-holders.
- Currently in India, various stakeholders in the food and agriculture sector like the national and state governments, policy makers, research and academic bodies, extension agencies, value addition industry, NGOs, financial bodies, developmental institutions and farmers groups think in silos, often with contradictory approaches for the same ultimate cause.
- ICFA aims to foster convergence and greater communication between different stakeholders and work towards bringing India aggressively into the loop of global trade and commerce.
- Headquartered in New Delhi, India, ICFA has drawn in the vast experience and expertise of a number of professionals cutting across various subsectors in the food and agriculture sector and has constituted a number of working groups and national councils to represent the interests of various stakeholders. It has also incorporated several state specific working groups.
2. RBI includes HDFC Bank in the ‘too big to fail’ list
In news:
- RBI has added HDFC Bank, the second largest private sector lender of the country – in the list of Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs).
- State Bank of India and ICICI Bank continue to be in that category.
Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs)
- Following the global financial crisis of 2008, it was observed that problems faced by certain large and highly interconnected financial institutions hampered the orderly functioning of the financial system, which in turn, negatively impacted the real economy.
- It was decided to identify such institutions and prescribe them higher capital requirements.
- The RBI has adopted a system by which banks are plotted into four buckets based on a lender’s systemic importance scores in ascending order.
- The banking regulator prescribes higher capital requirements — in terms of additional Common Equity Tier 1 (CET 1) capital — for such entities.
- RBI had started listing D-SIBs from August 2015. SBI and ICICI Bank were identified as D-SIB both in 2015 and 2016.
3. India to flag worry on pace of services talks at RCEP
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP):
- Proposed Free Trade Agreement (FTA) involving 16 Asia-Pacific nations.
- 10-member ASEAN bloc (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines. Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam) and its six FTA partners including India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia and New Zealand.
- RCEP ‘Guiding Principles and Objectives’: negotiations on trade in goods, trade in services, investment and other areas will be conducted in parallel to ensure a comprehensive and balanced outcome.
- India to raise the following issues at the forth-coming ministerial-level meeting:
- Slow pace of negotiations on services trade liberalization as opposed to ‘higher priority’ being accorded to commitments to open up goods trade in the region.
- No much progress: issues such as Intellectual Property Rights and investment liberalization.
‘RCEP Travel Card’: Idea mooted by India
- India is seeking support for its proposal on an ‘RCEP Travel Card’
- India is relatively strong in services with its vast pool of professionals including from sectors such as Information Technology, as well as in activities such as installation, trouble shooting, training, maintenance, investment management.
- Issues raised by other members: easing norms on temporary movement of people could lead to immigration of professionals from India and in turn loss of jobs for locals.
Free Trade Agreement: A free-trade area is the region encompassing a trade bloc whose member countries have signed a free-trade agreement (FTA). Such agreements involve cooperation between at least two countries to reduce trade barriers – import quotas and tariffs – and to increase trade of goods and services with each other.
The degree of economic integration can be categorized into seven stages:
- Preferential trading area
- Free trade area
- Customs union
- Common market
- Economic union
- Economic and monetary union
- Complete economic integration
D. GS4 Related
Nothing here for Today!!!
E. PRELIMS FACT
Nothing here for Today!!!
F. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
Question 1. Shanghai cooperation organization (SCO) is headquartered in which city?
- Shanghai
- Beijing
- Xinxiang
- Kabul
See
Question 2. Identify the correct statement.
- Raja Ampat is known for one of the world’s most biodiverse marine habitats.
- Raja Ampat lies in eastern part of Indonesian group of archipelago.
Choose the correct statement.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
See
Question 3. Identify the correct statement with reference to Latent TB?
- Drug resistant TB is known as Latent TB.
- Latent TB is a bacteria which is there in all of us, but it is our body’s immunity that converts the latent bacteria active.
- Recently announced National Strategic Plan focuses on Latent TB eradication.
- Both b and c
Question 4. Eczema and Callosities diseases associated with _______.
- Skin
- Lung
- Muscle tissues
- Bone
Question 5. ‘Larson C’ ice shelf has been in the news in recent times for which one of
the following reasons?
- A huge iceberg, expected to be one of the largest ever recorded, is poised to break off from this ice shelf that is located in Antarctica.
- It is one of the largest proven oil deposits beneath it in the Arctic.
- It is being subject to a man-made breakup (collapse) by Russia so as to open up the Northern Sea Route all year, making it a commercially viable route.
- None of the above
G. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
GS Paper II
- It is argued that the concept of marital rape is not suitable in the Indian context due to illiteracy, poverty, social customs, values, religious beliefs, and other factors. Do you agree with this view? Comment.
- “Sections 377 reflect prominent way in which the British left their stamp upon India’s criminal law, in a manner that is entirely inconsistent with a democratic, constitutional republic.” Analyze.
Also, check previous Daily News Analysis
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Current Affairs Webinar’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series
Comments