TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS1 Related B. GS2 Related POLITY 1. SC scraps NOTA option for RS polls SOCIAL ISSUES 1. ILO report flags wage inequality in India GOVERNANCE 1. SC suggests way to cleanse political parties INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS 1. Taliban plans to take part in Afghan talks C. GS3 Related ENVIRONMENT 1. Centre rules out total ban on firecrackers DISASTER MANAGEMENT 1. Centre releases Rs. 600 cr., 89,540 tonnes of grains for Kerala ECONOMY 1. Opening up trade with India a priority for the U.S. 2. Centre moots overseas UDAN 3. Trade deficit is greater concern than declining rupee: NITI chief D. GS4 Related E. Editorials INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS 1. Beyond words, India – Pak Relations POLITY 1. Strengthening the federal link ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY 1. Clearing the path F. Tidbits G. Prelims Fact H. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions I. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
A. GS1 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
B. GS2 Related
1. SC scraps NOTA option for RS polls
- The Supreme Court on Tuesday scrapped the use of NOTA (none of the above) option for Rajya Sabha polls, saying it would usher back the “Satan of defections.”
- A three-judge Bench, led by Chief Justice of India Dipak Misra, held that the option is meant only for universal adult suffrage and direct elections and not elections held by the system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote as done in the Rajya Sabha.
- The option of NOTA may serve as an elixir in direct elections but in the election to the Council of States, it would not only undermine the purity of democracy but also serve the Satan of defection and corruption.
- The court pointed out that in the voting in Rajya Sabha elections, there is a whip and the elector is bound to obey the command of the party.
- The party discipline in this kind of election is of extreme significance, for that is the fulcrum of the existence of parties.
- It is essential in a parliamentary democracy. The thought of cross-voting and corruption is obnoxious.
- The court held that NOTA in an indirect election would not only run counter to the discipline expected from an elector under the Tenth Schedule but also be counterproductive to the basic grammar of the law of disqualification on the ground of defection.
Background : NOTA
- “NOTA” or ‘None of the Above’ has been provided as an option to the voters of India in most elections.
- Through the usage of NOTA, a citizen can choose not to vote for any candidates who are contesting the elections.However, NOTA in India does not guarantee dismissal of the winning candidate.
- Therefore, it’s only a method to give a negative feedback.
- NOTA does not hold any electoral value even if the maximum votes are for NOTA, the candidate with maximum vote share will still be the winner.
1. ILO report flags wage inequality in India
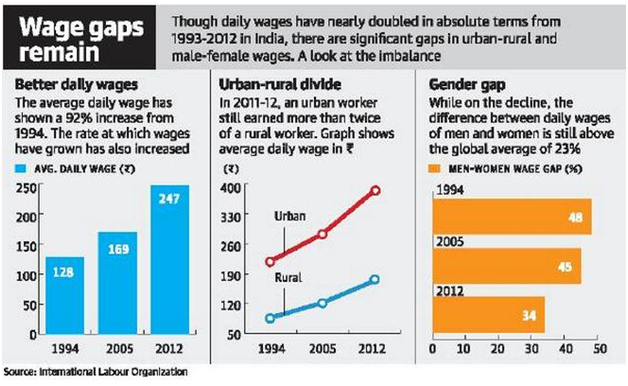
- Real average daily wages in India almost doubled in the first two decades after economic reforms, but low pay and wage inequality remains a serious challenge to inclusive growth, the International Labour Organization warned in its India Wage Report.
- The ILO has called for stronger implementation of minimum wage laws and strengthening of the frameworks for collective bargaining by workers.
- This is essential to combat persistent low pay in some sectors and to bridge the wage gaps between rural and urban, male and female, and regular and casual workers.
- Overall, in 2009-10, a third of all of wage workers were paid less than the national minimum wage, which is merely indicative and not legally binding. That includes 41% of all casual workers and 15% of salaried workers.
- In 2011-12, the average wage in India was about Rs. 247 rupees a day, almost double the 1993-94 figure of Rs. 128.
- However, average labour productivity (as measured by GDP per worker) increased more rapidly than real average wages.
- Thus, India’s labour share — or the proportion of national income which goes into labour compensation, as opposed to capital or landowners — has declined.
- The rise in average wages was more rapid in rural areas, and for casual workers.
- However, these groups started at such a low base that a yawning wage gap still remains.
- Thus, the average wage of casual workers — who make 62% of the earning population — was only Rs. 143 a day.
- Daily wages in urban areas (Rs. 384) also remain more than twice as high as those in rural areas (Rs. 175), the report said.
- Regional disparities in average wages have actually increased over time, with wages rising more rapidly in high-wage States than in low-wage ones.
- The gender wage gap decreased from 48% in 1993-94 to 34% in 2011-12, but still remains high by international standards.
- And of all worker groups, the average wages of casual rural female workers was the lowest, at just Rs. 104 a day.
- The ILO also highlighted the lack of timely data as a hindrance, pointing out that its analysis — and the decisions of Indian policy makers — was dependent on 2011-12 data from the Employment and Unemployment Survey (EUS) of the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO), as that was the last year in which the survey was done.
- State-specific and comparative studies on wages are needed, said the ILO, urging collaborative work between government agencies, academic institutions and expert organisations.
Background :ILO
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency dealing with labour problems, particularly international labour standards, social protection, and work opportunities for all.
- The ILO has 187 member states: 186 of the 193 UN member states plus the Cook Islands are members of the ILO.
- In 1969, the organisation received the Nobel Peace Prize for improving peace among classes, pursuing decent work and justice for workers, and providing technical assistance to other developing nations.
- The ILO registers complaints against entities that are violating international rules; however, it does not impose sanctions on governments.
1. SC suggests way to cleanse political parties
- The Supreme Court proposed to make political parties accountable for criminalising politics by welcoming in “crooks” who may later win elections on party ticket and grab power.
- The five-judge Constitution Bench, led by Chief Justice of India Dipak Misra, suggested it could direct the Election Commission to insist that parties get new members to declare in an affidavit their criminal antecedents and publish them so that the entire country knows how many criminals there are in a party.
- The court said the EC could de-register a party or withdraw its symbol if it refused to comply.
- The suggestion was made by the Bench in a bid to prevent criminals from entering politics or later contesting elections to become parliamentarians, legislators and Ministers.
- The court is hearing a batch of petitions to ban persons charged with heinous criminal charges from contesting elections.
- The suggestion from the Bench faced stiff opposition from the government. Attorney-General K.K. Venugopal said the court’s proposal amounted to disqualifying a prospective candidate.
- The Bench has been steadfast during the past days that it cannot legislate and change the written law.
- Thus, it was as an alternative measure that the Bench suggested: making the political party accountable for giving memberships to persons with a criminal record.
- Each political party may incorporate a clause in their membership form requiring a member to file an affidavit disclosing his criminal antecedents.
- If not, they will face deregistration by the Election Commission.
- The Bench, including Justices D.Y. Chandrachud, A.M. Khanwilkar and Indu Malhotra, based its proposal on the power of the Election Commission to conduct an election and register/de-register political parties under Article 324 of the Constitution and Section 29A of the Representation of the People Act of 1951, respectively.
- The court invoked The Election Symbols (Reservation and Allotment) Order of 1968.
- Chief Justice Misra pointed to how Section 29A requires a party to swear to uphold the principles of socialism, secularism, democracy, sovereignty, unity and integrity of India.
Category: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. Taliban plans to take part in Afghan talks
- The Taliban plans to take part in Afghanistan peace talks in Moscow on September 4.
- Russia had invited 12 countries, including the U.S., to international talks, which come as Moscow is taking a more prominent role on Afghanistan.
- Moscow supported an Afghan government offer of a three-month ceasefire, and regretted that the Taliban rejected the offer .
- Abdul Kayum Kuchai, Afghanistan’s Ambassador in Moscow, welcomed the Taliban’s involvement in the talks. Russia conducted international talks on Afghanistan in April last year.
C. GS3 Related
1. Centre rules out total ban on firecrackers
- The Centre ruled out a national ban on firecrackers and suggested the production of “green crackers”, community cracker bursting in major cities and a freeze on the production of series crackers or laris as alternative measures to curb pollution during Diwali.
- The Centre told the Supreme Court that crackers could even be burst in areas pre-designated by the State governments.
- The Supreme Court was hearing a bunch of applications seeking a complete nationwide ban on the use, manufacture, licensing, sale, resale or distribution of firecrackers and sparklers of any kind in a bid to combat pollution on an emergency basis.
- In its turn, the Tamil Nadu government, represented by senior advocate Shekhar Naphade, echoed the Centre.
- Naphade summed up his arguments in favour of restrained use of firecrackers but not a blanket ban by submitting that whatever human beings do contributes to environmental pollution.
- The Union Ministry of Environment submitted a five-page affidavit to the Supreme Court suggesting ways to deal with the pollution problem and chalking out short-term measures to combat pollution during Diwali.
Effect of Firecrackers
- One of them is that the fumes produced by the crackers would kill insects and mosquitoes found after the rains.
- The fumes that these crackers produce are harmful to the the environment and us.
Elements involved
Copper: Causes irritation in the respiratory tract.
Cadmium: Reduces the oxygen carrying capacity of blood, leading to anaemia.
Lead: Lead in the body has a harmful effect on the nervous system.
Magnesium: Magnesium fumes cause a condition known as metal fume fever.
Zinc: Causes metal fume fever and also induces vomiting.
Sodium: Sodium is a highly reactive element and combines with moisture to cause burns.
HEALTH
- The bursting of crackers during Diwali is primarily responsible for an increase in concentration of dust and pollutants.
- The fine dust that settles after bursting crackers is rich in pollutants like oxides of sulphur and nitrogen, metal dust and organic pollutants.
- Even the tiny sparklers, torches and flower pots which are otherwise considered to create no noise at all generate thick smoke that can affect the respiratory tract of young children.
- The suspended particulate matter (SPM) levels rise significantly during Diwali. This causes throat, nose and eye related problems which can later develop into adverse health issues.
- Firecrackers have much more severe effects in people with heart, respiratory or nervous system disorders.
- They can aggravate problems for people suffering from colds, allergies or coughs and can also cause congestion of the throat and chest.
- They can also cause water contamination and acid rains.
- They result in air pollution that creates carcinogenic Sulphur compounds and airborne arsenic effect.
- The green light produced in fireworks displays comes from barium, which is radioactive and poisonous.
- The blue colour produced from copper compounds comes from dioxins linked to cancer.
ENVIRONMENT
Fire Hazards: Sometimes rockets set fire to huts, heaps of dry grass and even houses.
Noise Pollution: Firecrackers make more noise than the allowed decibel limit.
Air Pollution:
- Smog caused by firecrackers is harmful when inhaled. It also causes reduced visibility.
- The Central Pollution Control Board of India has also banned firecrackers with a decibel level of more than 125 at a distance of 4mts from the bursting point.
- The sound of bursting crackers can be quite traumatic to pets, as they cannot bear loud sounds.
Child Labour
- Most fireworks are made by factories that employ children as labourers.
- These young children are forced to handle the toxic substances that go into these firecrackers.
- As a result, they contract diseases associated with these substances.
- Limited access to medical aid means that many of them die in their teens.
1. Centre releases Rs. 600 cr., 89,540 tonnes of grains for Kerala
- Central assistance of Rs. 600 crore was released to the Kerala government on Tuesday.
- This includes Rs. 500 crore announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Rs. 100 crore announced by Union Home Minister Rajnath Singh.
- The National Crisis Management Committee, chaired by Cabinet Secretary P.K Sinha, was informed by the Kerala government that the situation was improving now but there were some isolated pockets still under water.
- The Centre has also approved 89, 540 tonnes of additional grains for Kerala.
- It has also started sending 80 tonnes of pulses (dals) every day to the State. This is in addition to the 100 MT of pulses supplied earlier.
- The decision came in response to Kerala Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan’s letter to Prime Minister Narendra Modi, requesting 1.18 lakh tonnes of foodgrains.
- The centre, under the National Food Security Act, already provides Kerala 1.18 lakh tonnes of foodgrains.
- In addition to it, it has been decided to provide 89,540 tonnes of foodgrains to the State to extend the coverage to entire State.
- Under the National food security Act, 52.3% of the rural population and 39.5% of the urban population receive subsidised food grains—wheat is sold at Rs. 2 per kg and rice at Rs. 3 per kg.
- With the additional foodgrains, the coverage will be hundred percent.
- For now, the State does not have to foot the bill. As per the provisions, this special assistance can be extended for 90 days.
Measures taken by the various government agencies
- Public Sector Oil Marketing Companies have contributed Rs. 25 crore to the Chief Minister’s Relief Fund in Kerala.
- The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas has opened special points in the flood affected areas of the state for LPG distribution.
- Permission has also been granted, in coordination with the State Government, for non-certified vehicles to carry LPG cylinders.
- The Ministry has also made available 3.2 lakh LPG cylinders and 2.2 lakh regulators.
- The Railways have so far supplied 24 lakh litres of drinking water in addition to 2.7 lakh water bottles. Another 14 lakh litres water is currently available at Ernakulam.
- The Railways have also made arrangements for supply of bed sheets and blankets.
- Trains on all sections have resumed. It is also transporting relief materials from various States to Kerala free of cost, the statement said.
- The Health Ministry will supply three crore chlorine tablets in addition to one crore tablets supplied earlier.
- Thirty tonnes of bleaching powder and 1.76 lakh sanitary pads have also been sent.
- Additional quantities will also be sent in the next few days. No major outbreak of disease has been reported so far.
- As per the State government’s requirement, essential spices, salt, tea and coffee are also being supplied by the Ministry of Food Processing Industries.
National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC)
- Cabinet Secretary, who is the highest executive officer, heads the NCMC.
- Secretaries of all the concerned Ministries /Departments as well as organizations are the members of the Committee The NCMC gives direction to the Crisis Management Group as deemed necessary.
- The Secretary, Ministry of Home Affairs is responsible for ensuring that all developments are brought to the notice of the NCMC promptly.
- The NCMC can give directions to any Ministry/Department/Organization for specific action needed for meeting the crisis situation.
Crisis Management Group
- The Central Relief Commissioner in the Ministry of Home Affairs is the Chairman of the CMG, consisting of senior officers (called nodal officers) from various concerned Ministries.
- The CMG’s functions are to review every year contingency plans formulated by various Ministries/Departments/Organizations in their respective sectors, measures required for dealing with a natural disasters, coordinate the activities of the Central Ministries and the State Governments in relation to disaster preparedness and relief and to obtain information from the nodal officers on measures relating to above.
- The CMG, in the event of a natural disaster, meets frequently to review the relief operations and extend all possible assistance required by the affected States to overcome the situation effectively. The Resident Commissioner of the affected State is also associated with such meetings.
UAE offers Rs. 700 cr. in aid to Kerala
- The UAE government has promised Rs. 700 crore assistance for Kerala’s post-flood reconstruction effort even as the State on Tuesday sought a Rs. 2,600 crore special package from the Centre to cope with the deluge that has left 228 dead and displaced over 14 lakh people.
- Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan chaired a meeting of the Cabinet, which decided to seek the special package under the Centrally sponsored schemes.
- On the offer of aid, Mr. Vijayan told reporters that Abu Dhabi Crown Prince and Deputy Supreme Commander Sheikh Mohammed bin Zayed Al Nahyan had communicated the decision to Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- The offer reflects the concern that Gulf nations have for Kerala and Malayalis, the Chief Minister said while thanking UAE President Sheikh Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan and the Crown Prince.
- Meanwhile, the Centre has released Rs. 600 crore announced during the visits of Mr. Modi and Home Minister Rajnath Singh.
- Though rains have eased over the last two days, vast swathes of land remain under water in Ernakulam, Thrissur, Pathanamthitta, Alappuzha and Kollam districts, with 32 persons still reported missing.
2018 Kerala floods
- Kerala received heavy monsoon rainfall on the mid evening of August 8 resulting in dams filling to capacity; in the first 24 hours of rainfall the state received 310 mm (12 in) of rain.
- Almost all dams have been opened since the water level has risen close to overflow level due to heavy rainfall, flooding local low-lying areas.
- For the first time in the state’s history, 35 of its 42 dams have been opened.
- Most of the regions affected by this monsoon were classified as ecologically-sensitive zones (ESZs) by the the Western Ghats Ecology Expert Panel, the Gadgil Committee.
- Most of the recommendations and directions by the commitee was either neglected or rejected.
- Chairman of the committee Madhav Gadgil accused the state government and its irresponsible environmental policy for the recent landslides and floods. He called it a man-made calamity.
1. Opening up trade with India a priority for the U.S.
- Opening up trade with India is a key priority of the Trump administration, a senior official of the U.S. State Department has said.
- Briefing reporters on the administration’s Asia-Pacific policy, Principal Deputy Assistant Secretary for South and Central Asian Affairs Alice G. Wells — the highest-ranking official for the region — also welcomed Pakistan Prime Minister Imran Khan’s statement in support of peace in South Asia.
- Wells will be participating in the Indian Ocean Conference in Vietnam’s capital Hanoi on August 27-28, organised by think tank India Foundation.
- Delegates from 43 countries, including China, India, Singapore, Australia and Vietnam, are scheduled to participate in the event.
- This annual conference hosted by the India Foundation and our partners in Singapore, Sri Lanka, and Bangladesh has become an important touch point for nations bordering the Indian Ocean, and it showcases India’s rising leadership role in the region.
- Strategic objective
- With respect to Indo-American cooperation, trade with India and opening up trade with India is a key strategic objective for this administration
- The bilateral trade is now at about $126 billion, an increase of more than $10 billion from last year.
- The defence contracts from India for U.S firms now total $18 billion.
- State governments will be able to encourage tourism on preferred international air routes by offering subsidy to domestic airlines for a period of three years.
- The Ministry of Civil Aviation has prepared a draft scheme document for “UDAN International” and invited comments from stakeholders till September 4.
- The scheme is designed for State governments that are keen to promote air connectivity on international routes identified by them and for which they are willing to provide subsidy to airlines.
- The airlines will bid on the percentage of flight capacity for which they require financial assistance, provided that the figure doesn’t exceed 60% of the flight capacity. The entity that quotes the lowest amount will be awarded subsidy for a particular route.
- However, the government will grant financial aid only for the actual number of passenger seats that are unsold, even if the airline had sought subsidy for a higher percentage of seating capacity at the time of bidding.
- An airline that is awarded a particular route will have exclusive rights to a subsidy on that route for a period of three years.
- The key difference between this scheme and the regional connectivity scheme (RCS) for domestic routes is that there is no capping of fares.
- Under RCS, fares are capped at Rs. 2,500 for one hour of flight on a fixed wing aircraft in order to make air travel affordable, which was why the scheme was called Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik (UDAN).
- So far, Assam has proposed to offer Rs. 100 crore per year for flights to Kathmandu, Dhaka, Singapore, Bangkok, Kuala Lumpur and Yangon.
- Andhra Pradesh has also expressed its keenness to the Civil Aviation Ministry to encourage tourism.
3. Trade deficit is greater concern than declining rupee: NITI chief
- NITI Aayog Vice-Chairman Rajiv Kumar said on Tuesday that he was more concerned about the rising trade deficit than the falling rupee, and called for efforts to push exports.
- Rupee should remain in its natural value, some countries depreciate their currency deliberately. It will be very difficult for India to try and push up the rupee.
- There is a constituency that benefits from strong rupee.The constituency should be put on back foot. The rupee on August 16 had slumped to a life-time low of 70.32 on strong demand for the U.S. dollar.
- Kumar further said that economic policymaking should not focus only on fiscal deficit number, arguing that large economies like USA, China and European Union do not give much importance to fiscal deficit.
- At a time when private investment was low, then the aggregate demand can be brought up by public spending.
- Some revenue expenditure can be just brought to zero. The main worry is trade deficit.
D. GS4 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
E. Editorials
Category: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. Beyond words, India – Pak Relations
Context:
Since the Prime Minister Imran Khan’s swearing-in ceremony in Pakistan, there have been many substantive exchanges between New Delhi and Islamabad.
Details:
- In his first statement after the Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf emerged as the single largest party, Mr. Khan singled out India as a foreign policy relationship he hoped to work on, offering to walk “two steps for every one step” that India took.
- Indian Prime Minister responded with a phone call, and they spoke of a shared vision of “peace and development”.
- The Indian High Commissioner presented the Pakistan PM a cricket bat with the signatures of the Indian team members.
- The new appointee on the Pakistan Cricket Board has said that resuming bilateral cricket is high on the leader’s agenda for improving people-to-people ties.
- A delegation led by a Minister in Pakistan’s caretaker government came to Delhi to attend Atal Bihari Vajpayee’s funeral.
- The Pakistan’s new Foreign Minister, Shah Mehmood Qureshi, said Mr. Khan had received a congratulatory letter from Mr. Modi calling for the two countries to pursue “constructive engagement”.
- Khan tweeted that trade and resolution of differences through dialogue are the “best way” to “uplift the people in the subcontinent”.
All these gestures confirm that both the Prime Ministers are at least sticking by diplomatic courtesy against the backdrop of an otherwise bitter relationship.
Existing Situation:
- There appears to be very little trust in any quarter of both capitals. Both leaders face political realities that could inhibit them from taking any major risks.
- Modi, who dealt with the Pathankot airbase attack just days after his visit to Lahore in December 2015, may well prefer to avoid such overtures, especially with Lok Sabha elections due in less than a year.
- Khan, who commands a thin majority in Parliament, and has frequently criticised his predecessors for close ties with India, may choose to remain conservative.
Way forward:
- Well-chosen words, however, will not be enough. The steps needed are clear.
- To kick start, the situation at the Line of Control urgently needs attention, and a restoration of the ceasefire would be a major move forward for both countries.
- Khan could earn Pakistan an economic breather if he adheres to the international Financial Action Task Force’s demands on ending terror financing. He would earn more goodwill by directly addressing India’s concerns on the support to terrorists in Pakistan, and those being pushed over the LoC.
- These actions could set up an even bolder move, no matter how unlikely it currently seems: for Mr. Modi to agree to restore the SAARC process by attending the long-delayed summit due in Islamabad this year.
- Much work, preferably behind the scenes, is needed if both the Prime Ministers hope to realise any of the objectives they have spoken of over the past month. India and Pakistan must build on diplomatic courtesy to restore equilibrium to ties
1. Strengthening the federal link
There must be recognition of the potential of State Finance Commissions in building regional equity
Context:
There has been inadequate appreciation of the significance of this institution by the Union, States as well as the professional community.
What is State Finance Commission?
The State Finance Commission (SFC) is a unique institution created by the 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments (CAs) to rationalise and systematise State/sub-State-level fiscal relations in India.
- It has few parallels in other federal systems.
- Its primary task is to rectify growing horizontal imbalances in the delivery of essential public services to citizens.
- Article 243I of the Constitution mandated the State Governor to constitute a Finance Commission within one year of the CAs (before April 24, 1994) and thereafter every five years.
Issue:
- The fifth generation SFCs ought to have submitted reports by now, with around 140 reports available in the public domain.
- Till date, only Assam, Himachal Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Kerala have submitted their fifth SFC reports.
- Many States are yet to cross the third SFC stage.
- The large majority has violated the mandate of the Constitution with impunity.
- The seriousness, regularity, acceptance of recommendations and their implementation which characterise the Union Finance Commissions (UFCs) are conspicuously absent when it comes to SFCs.
- The UFC has been widely acknowledged as a professional and quasi-judicial body when compared to the SFC.
- A cursory survey of the composition of SFCs would reveal the overwhelming presence of serving and/or retired bureaucrats rather than academics. The States have to bear their share of the blame for this.
Details:
In order to properly compare UFCs and SFCs, certain facts have to be put in perspective.
- For historical reasons, UFCs, particularly from the third, have chosen a restrictive role of staying away from plan and investment allocations. SFCs normally could not do this although some have chosen the UFC path. Now that the Planning Commission has been dismantled, the 15th UFC has to spell out its decision-making domain.
- It is important to disabuse the notion among several politicians, policy makers and even experts that SFCs and the local governments they deal with have an inferior constitutional status when compared to the UFC. This is wrong.
- The SFC is undoubtedly modelled on the UFC created under Article 280 and exemplified in Articles 243I and 243Y.
- While the UFC is tasked with rectifying vertical and horizontal imbalances at the Union-State level, the SFC has to perform the same with reference to State/sub-State-level institutions.
- The Constitution treats a local government on a par with a State government, especially when it comes to sharing of financial resources.
What are the link roles?
- The task of the SFC to correct horizontal imbalances is extremely onerous when compared with the UFC as SFCs have to consider nearly 2.5 lakh local governments to promote minimum essential services in rural and urban areas.
- SFC is the institutional agency to implement the golden rule of cooperative federalism that every citizen should be assured minimum public goods irrespective of her choice of residence.
- Article 280(3) has been amended to take measures to augment the resources of panchayats and municipalities on the basis of the recommendations “made by the finance commission of the state”. These affirm the organic link between local governments and SFCs to fiscal federalism.
- It is only when inter-State disparities are reduced by the UFCs through their inter-se distribution criteria and intra-State disparities are reduced by SFCs through the horizontal distribution criteria that the Indian federation becomes a sustainable and inclusive nation-state.
- UFCs had no data problem in reviewing the finances of the Union and States. On the other hand, local governments with no proper budgetary system are in deep disarray and, because of that, SFCs face a crucial problem of reliable data.
- Several sufficient conditions remain unfulfilled in the case of SFCs.
- The federalist development state of India can grow only through a process of evolutionary policy making which works towards cherished goals.
- The CAs left the task of adequately empowering local governments to discharge constitutional obligations to the States.
Conclusion:
The UFCs have failed to play a hand-holding role in placing decentralised governance properly in the cooperative federal map of India. The hard truth is that no UFC has done its homework in reading and analysing SFC reports. Without presenting a consolidated account of the reality at the sub-State level or highlighting which report went wrong, where and how, no UFC can legitimately guide States or contribute to improving the goals of constitutional amendments. All the terms of reference of UFCs (since the 11th) iterate the need for suggesting measures to augment the resources of panchayats and municipalities as a core task. Their well-designed grant scheme to incentivise States was not given a fair trial.
In sum, SFCs have not been provided with the necessary environment to play their rightful role in Indian fiscal federalism. A great opportunity to build regional equity in India has been undermined.
Category: ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
Context:
The Supreme Court had ordered to seal and close 27 resorts operating in corridors used by elephants in the Nilgiris.
Details:
- The Tamil Nadu government was ordered to seal or close down such resorts which were constructed on the elephant corridor in violation of law, within 48 hours.
- The court had stressed on the need to have elephant corridors across the country to reduce animal fatalities due to accidents and other reasons
Why should the elephant corridors be protected?
- It is a necessary step to restore the ecology of these spaces.
- Weak regulation of ecotourism is severely impacting important habitats, and affecting animals that have large home ranges, like elephants.
- Fragmentation of forests makes it all the more important to preserve migratory corridors.
- Forests that have turned into farms and unbridled tourism are blocking their paths, resulting in growing incidents of elephant-human conflict. These encounters claim the lives of about 450 people and lead to the death of nearly 100 elephants in retaliatory actions every year on average.
- A review of elephant corridors published by the Wildlife Trust of India jointly with the Environment Ministry’s Project Elephant last year indicates that there are 101 such identified pathways, of which almost 70% are used regularly. Nearly three-quarters of the corridors are evenly divided among southern, central and northeastern forests, while the rest are found in northwest Bengal and the northwestern region. Some of these passages are precariously narrow, at only a hundred metres wide.
- These landscape characteristics, and the evidence that there are an estimated 6,500 elephants in just the Brahmagiri-Nilgiris-Eastern Ghats ranges, call for complete protection of the routes they regularly use.
Importance of Elephant corridors:
- The movement of elephants is essential to ensure that their populations are genetically viable.
- It helps regenerate forests on which other species, including tigers.
- Ending human interference in the pathways of elephants is a conservation imperative, more so because the animals are then not forced to seek alternative routes that bring them into conflict with people.
Way forward:
- The District Collector’s report on 39 resorts in the Nilgiris points to their having come up right under the gaze of the Forest Department, the majority without the requisite permissions. This must be thoroughly investigated to check whether there was any wrongdoing.
- The grey area of mushrooming home- stay structures, which are just hotels on forest fringes, also deserves scrutiny.
- But more importantly, the effort should be to expand elephant corridors, using the successful models within the country, including acquisition of lands using private funds and their transfer to the government. More needs to be done to protect elephant corridors across the country
- Among the major factors affecting conservation, two need quick remedies: about 40% of elephant reserves are vulnerable, as they are not within protected parks and sanctuaries; and the corridors have no specific legal protection. Illegal structures in these pathways should be removed without delay.
F. Tidbits
Nothing here for today!!!
G. Prelims Fact
Nothing here for today!!!
H. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
Question 1. Consider the following statements:
- Cabinet Secretary heads the National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC).
- NCMC can give directions to any ministry, department or organization for specific action needed for meeting the crisis situation.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
See
Question 2. Consider the following statements:
- The Oxides and dioxides of sulphur and nitrogen are released during the burning of crackers.
- Oxides and Dioxodes of Sulphur and nitrogen are greenhouse gases.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
See
Question 3. Consider the following statements:
- In elections , None of the above is also known as “against all” or a “scratch” vote
- It means the voter is not interested in voting for any of the candidates.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
See
I. Practice Questions for UPSC Mains Exam
- Discuss the significance of State Finance Commission. Explain the challenges involved in its functioning.
- The recent Kerala floods pose a challenge to the existing mechanism of Disaster Management in India. Discuss the reasons for escalation of the disaster in Kerala.
Also, check previous Daily News Analysis
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Current Affairs Webinar’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series
Comments