TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS1 Related B. GS2 Related INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS 1. River and rice deals put India-China ties on an upswing C. GS3 Related ECOLOGY 1. Threat to Bannerghatta zone D. GS4 Related E. Editorials INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS 1. Shanghai Cooperation Organization: The quest for multilateralism F. Tidbits 1. New route to clean wastewater 2. What caused Dec. 1, 2015 Chennai downpour? 3. India, Uzbekistan review bilateral ties 4. ‘India backed Maldives in UN’ 5. Even small dams have severe impact on river ecology G. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions H. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
A. GS1 Related
Nothing here for today!
B. GS2 Related
Category: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. River and rice deals put India-China ties on an upswing
- In a significant move, China agreed to provide India hydrological data of the Brahmaputra river in flood season, months after Beijing stopped the practice, crucial to predict floods.
- The two countries also signed an agreement under which China has agreed to import non-Basmati rice from India which is likely to bridge the ballooning trade deficit to a certain extent.
- The two Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs) were signed after Prime Minister Narendra Modi held detailed discussions with Chinese President Xi Jinping on bilateral and global issues, which will add vigour to the India-China friendship after their informal summit in Wuhan.
- India has allowed China’s state-owned Bank of China to open its branch in Mumbai.
73-day standoff
- Last year, China stopped sharing data soon after the 73-day standoff between the Indian and Chinese troops at Doklam over Chinese military’s plans to build a road close to India’s Chicken Neck corridor connecting the north-eastern States.
Hydrological information
- The first MoU was inked between China’s Ministry of Water Resources and India’s Ministry of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation upon provision of hydrological information of the Brahmaputra river in flood season.
- The agreement enables China to provide hydrological data in flood season from May 15 to October 15 every year.
- It also enables the Chinese side to provide hydrological data if water level exceeds the mutually agreed level during non-flood season.
- China, an upstream country, shares the scientific study of the movement, distribution and quality of water data for the river.
- Originating from Tibet, the Brahmaputra is one of the major rivers in China. From Tibet, it flows down to India and later enters Bangladesh where it joins the Ganga.
Rice export
- The second MoU was signed between China’s General Administration of Customs and India’s Department of Agriculture, Cooperation and Farmers Welfare on Phytosanitary requirements for exporting rice from India to China, one of the world’s biggest rice markets.
- The 2006 Protocol on Phytosanitary Requirements for Exporting Rice from India to China has been amended to include the export of non-Basmati varieties of rice from India.
- At present, India can only export Basmati rice to China.
- The pact on non-Basmati rice may help in addressing India’s concerns over widening trade deficit which has been in China’s favour.
- China has been promising to address the issue of trade deficit with India which has been seeking a greater market access for its goods and services in China.
- Trade deficit with China stood at $ 36.73 billion during April-October this fiscal. India’s trade deficit with China has marginally dipped to $51 billion in 2016-17 from $52.69 billion in the previous fiscal.
Afghanistan
- India and China agreed that they would jointly move forward in identifying a specific project in the area of capacity building in Afghanistan. The move could upset Pakistan.
- During the informal summit between Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Chinese President Xi Jinping in Wuhan in April, the two leaders had agreed to undertake a joint India-China economic project in Afghanistan.
- This will be a first such project in the war-torn country where China has tacitly backed Pakistan.
New starting point
- India and China have expanded on the spirit of the Wuhan informal summit, with Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Chinese President Xi Jinping agreeing to a string of official engagements, including a fresh round of boundary talks and new mechanism to step up exchange of films.
- Xi accepted Mr. Modi’s invitation for another informal summit in India next year and described Wuhan as a new starting point in India-China relations.
C. GS3 Related
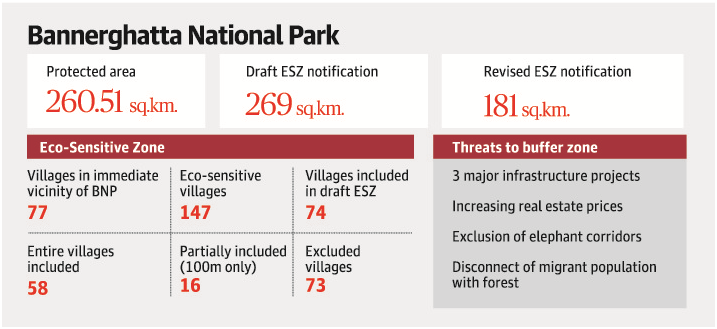
1. Threat to Bannerghatta zone
- At least 73 eco-sensitive villages, of which 22 are red list villages, have been left out of the buffer zone of the Bannerghatta National Park, which remains ’s last big, urban forest.
- Red list comprises villages that are adjacent to the forest and are highly eco-sensitive.
- While a movement has started in the city, rather successfully, to curb mining projects close to the forest, the pressure on the buffer zone may be a bigger threat to the eco-sensitive national park.
- Using a 2016 Indian Institute of Science report that puts villages in the region in five categories of eco-sensitivity, just 58 of 147 villages in the top two levels of eco-sensitivity had been included in the draft ESZ.
- A further 16 are partially included (that is, only 100 metres into the village), while 73 are excluded.
- The Ministry of Environment and Forests does allow for buffer zone to be reduced to 100 metres in densely populated areas, and this makes sense in the context of the northern edge where Bengaluru lies.
- But, there is no logical reason, apart from vested interests, to exclude villages with low built-up area in the central and southern boundaries of the park.
- The buffer zone will do little in protecting the area, or the elephants that either use it as a refuge or as a transit passage.
- The findings will be presented to the Supreme Court, which is hearing the matter on eco-sensitive zones.
- Protecting this meagre buffer zone may be more than a challenge, finds the study.
- This could lead to an increased man-elephant conflict, as the principle of ESZ to provide a contiguous corridor for wildlife is undermined in Bannerghatta.
D. GS4 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
E. Editorials
Category: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. Shanghai Cooperation Organization: The quest for multilateralism
- India has been at the forefront of vigorously engaging with numerous world powers, multilateral institutions as well as regional groupings
- Membership to the Shanghai Cooperation Organization will strengthen India’s relations with Central Asia.
- Many of the economic and political issues challenging economies across the world are essentially both global and regional. The forces of globalization and regionalization are unceasingly restructuring the contours of the prevailing international economic order.
Context
- Multilateralism provides the most holistic structure for political and economic relations in the world. For example, international problems, especially sustaining rules for trade and investment, inherently involve numerous countries concurrently.
- These international problems cannot be dealt with effectively within the national domain or even bilaterally.
- The problems are frequently so profuse and extraordinary that domestic goals cannot be accomplished without coordinated multilateral action.
- In the past seven decades, there have been abundant developments on multilateral action to create fair, just and lasting solutions to critical matters of peace and political, economic and social security.
Background of Shanghai Cooperation Organization:
- What started off as the “Shanghai 5” in 1996 for security and border peace between Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, China, Russia and Tajikistan has metamorphosed into the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), which today has an ambitious regional and global vision, coupled with a strong economic mandate.
- The expansion of SCO last year to include India and Pakistan now makes this a powerful and strategic regional grouping, accounting for 40% of the world’s population, almost 20% of its gross domestic product (GDP) and 22% of the world’s land mass.
- This is the first time that India will participate as a full member of this grouping. In his acceptance speech at the summit in 2017, where India was inducted as a full member, Prime Minister Narendra Modi recalled India’s historic ties with the grouping as an observer over the past 12 years: “We may have gotten the membership now but our relations with this group are long, around 12 years long.
- The relationship we share with the members of SCO are historical. We will continue to work together.”
Significance
- For India, membership of this grouping will strengthen its relations with Central Asian republics and provide a new opportunity to pursue the “Connect Central Asian Policy”.
- The SCO would also be a new channel to enhance bilateral ties with China and Russia in addition to robust engagement through Brics (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) and bilateral mechanisms.
The key goals of the SCO
- strengthening mutual trust and neighbourliness;
- promoting effective cooperation in politics,
- trade,
- the economy,
- research,
- technology and culture,
- education,
- energy,
- transport,
- tourism, and
- environmental protection;
- Making joint efforts to maintain and ensure peace, security and stability in the region; and moving towards the establishment of a democratic, fair and rational new international political and economic order.
- All the key goals of the SCO prove that the sustenance and celebration of an effective multilateral organization will significantly benefit the consolidation and expansion of these bilateral relationships.
- To summarize, the sum of their multilateral interactions will be greater than the sum of their bilateral interactions and engagements. In this sense, the SCO platform provides new meaning for its member countries.
India and Shanghai Cooperation Organization
- India has been at the forefront of vigorously engaging with numerous world powers, multilateral institutions as well as regional groupings. India’s aptitude to endure and confidently influence multilateral processes will have an unswerving bearing on its emergence as a great power.
- It is essential to take note of the developments and
Way forward for India at SCO.
- In line with the foreign policy priorities of India on SCO countries, the aim should be to further enhance connectivity, given the existing strong cooperation bilaterally with existing member countries.
- For example, connectivity through Chabahar will help India’s trade and economic relations with Central Asian republics. Other sectors, such as education, tourism and even medical tourism, can be focused upon to further strengthen the SCO platform.
- Economic cooperation, energy, connectivity, education, tourism, agriculture, trade and investment, amongst other security and anti-terrorism concerns, are expected to be on the summit agenda.
- India’s interest in seeking membership of this multilateral grouping shows that foreign policy will no longer be driven by political necessities alone, but also by economic diplomacy.
- Indian industry has the responsibility of guiding the country’s engagement with SCO member countries to deepen the ecosystem with this multilateral grouping.
- Strong engagements with the Brics business council.
- Robust institutional relationships in the region: and the foundation of bilateral relations with SCO member countries would be a starting point on this journey to forge meaningful economic partnerships and a strong regional synergy for inclusive development, stability and prosperity in the region.
F. Tidbits
1. New route to clean wastewater
- Self-propelling nanomotors, just 200 nanometres in size, could be used for wastewater management in chemical industries.
- The nanomotor can be used for transporting catalysts needed in harsh chemical environments and removing unwanted chemicals in water.
- Nanorods (rod shaped nanomotors) are made using ammonium heptamolybdate tetrahydrate and dispersed in the solution to be treated. When hydrazine sulphate is added to water, it reacts with the nanorods producing nitrogen gas. This leads to an osmotic stress in the fluid and causes the nanorods to move along the direction of the gas evolved.
- This nanomotor is amongst the fastest reported active nanoparticles.
- Another type of nanomotor in the form of a sphere (using titanium dioxide, heptamolybdate and gold) can also be used for delivering a catalyst to a particular area of interest by using visible light.
- The nanospheres were found to move away from visible light.
- The catalyst triggers a reaction and the pollutants get adsorbed on the nanospheres leading to quickly removal of organic pollutants from water.
- The solution can then be filtered, dried and the nanosphere can be retrieved.
2. What caused Dec. 1, 2015 Chennai downpour?
- On December 1, 2015 Chennai and its surrounding regions experienced an unprecedented, heavy rainfall.
- In a region where the average rainfall during the season is expected to be 8-10 mm per day, one of the rain gauges in the city recorded an abnormally high, 494 mm, rainfall over 24 hours that day.
- This led to death of nearly 250 people, and Chennai was declared a ‘disaster zone’.
- There have been attempts to explain this phenomenon of how clouds remained stationary over this region, continuously giving rain over 24 hours.
- In a first, a paper published in Monthly Weather Review links the presence of the Eastern Ghats to this phenomenon,
Cold pool
- When clouds give out water droplets, the droplets evaporate mid-air, as they fall down. This cools the surrounding air, forming a cold pool of air which sinks down and flows horizontally.
- The gusty cold wind that heralds an approaching thunderstorm is nothing but a cold pool, which plays a pivotal role in cloud dynamics.
- Unlike the Western Ghats, which run close to the west coast of India, the Eastern Ghats are nearly 200 km away from the coast. Therefore, the link between the mountains’ orography and the rainfall over the region is not obvious, and this is the first study to link the two.
- The cold pool was obstructed by the Eastern Ghats from flowing downward. Hence it piled up and remained stationary over the Chennai region.
- The reason for the clouds remaining stationary was that there was a balance between the piling of cold pool along the mountain and the winds from the bay.
Dust storms
- Cold pools are known to play an important role in the dust storms (Aandhi) that form in northern India.
- They form by the evaporation of raindrops. This process is more efficient in the drier and warmer environment as there is lot of scope of evaporation.
- So, the cold pools that form in these conditions, are deeper and more vigorous.
- The understanding gained from this analysis can be useful for improving the general weather forecast over this region.
3. India, Uzbekistan review bilateral ties
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi met Uzbekistan President Shavkat Mirziyoyev on the sidelines of the SCO Summit and the two leaders reviewed the full range of bilateral ties, especially ways to boost economic and cultural links.
- It is for the first time that an Indian Prime Minister is attending the summit after India along with Pakistan became a full-fledged member of the group jointly dominated by China and Russia, which has been increasingly seen as a counter to NATO.
4. ‘India backed Maldives in UN’
- India had assured the Maldives of its support for a non-permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council on at least three occasions, including one day before vote.
- The Maldives lost the vote for the Asia-Pacific seat to Indonesia by a large margin, winning only 46 of the 190 votes cast at the UN General Assembly for the two-year stint.
- Given a downslide in India-Maldives ties over the past year, however, India’s vote is particularly significant.
Secret ballot
- Though the External Affairs Ministry refused to comment on India’s stand at the vote, which is conducted by a secret ballot, it is understood that its recent assurance of support was received by the Maldivian mission at the United Nations from India’s Permanent Mission in New York.
- While the Maldives stood for the 2019-20 term, India has announced it will stand for the Security Council seat in 2021-22.
Background
- In January 2014, the India-Maldives joint statement issued after a meeting between President Abdulla Yameen and then Prime Minister Manmohan Singh, both countries had committed to supporting each other’s candidature for the UNSC non-permanent seats.
- Since then, however, relations between New Delhi and Male went into a tailspin over President Yameen’s decision to rush through a Free Trade Agreement with China and imposing an Emergency in the country in February that lasted several weeks and saw a crackdown on the Opposition parties.
- India objected strenuously, and even refused to entertain a special envoy sent by President Yameen to explain his decision.
- Meanwhile, the Maldives invited Pakistan’s Army Chief to Male and discussed joint patrols in the Indian ocean, once an exclusive domain of the Indian Navy.
Indonesia
- Adding to the uncertainty over which way India would vote was Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Indonesia last week, where the two sides upgraded their defence and strategic ties.
- Given the government’s emphasis on its “Act East” policy as well as strengthening ties with ASEAN, while not so much importance was given to SAARC (the Maldives is not part of the other sub-regional groups BIMSTEC and BBIN that India is promoting), it was widely believed that India would cast its lot with Indonesia over the Maldives.
5. Even small dams have severe impact on river ecology
- It seems to stand to reason that small dams cause less environmental problems than large ones.
- But the first study on small hydropower projects in India proves that they cause as severe ecological impacts as big dams, including altering fish communities and changing river flows.
- Such hydroprojects, which usually generate less than 25 megawatts of power and consist of a wall that obstructs a river’s flow, a large pipe that diverts the collected water to a turbine-driven powerhouse to generate electricity and a canal that releases the water back into the river, are touted to be better than large dams because they submerge fewer regions and barely impact river flow.
- Such projects receive financial subsidies — even carbon credits — for being greener.
- The results of the research show that changes in water flow in the dammed sections reduced the stream’s depth and width; water in these stretches was also warmer and had lower dissolved oxygen levels.
- These changes were most evident in the ‘de-watered’ zones and worsened in the dry seasons.
- This decrease in habitat quantity and quality showed in fish diversity too. The un-dammed stretches recorded a higher diversity of fish species, including endemics.
- The upstream and downstream stretches get disconnected and this impedes the river.
- Such small hydro-projects cropping up on rivers in the Ghats is a serious worry because they do not require environmental impact assessments.
- Regulations could include limiting the number of dams in a river basin or maintaining a minimum distance between dams on the same river stretch.
G. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
Question 1. Consider the following statements:
- Fundamental rights under Article 14 and 19 can be diluted to give effect to certain Directive Principles.
- If President of India reserves a bill for his own consideration and then approves, then Judicial Review would not be possible.
- Any law, relating to Schedule 9, can be curtailed on the grounds of violation of Fundamental Rights and it cannot be challenged.
Choose the correct option.
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- All of the above
- None of the above
See
Question 2. Indian Constitutional Assembly was criticized because:
- Initially it was not a Sovereign body.
- It was not a representative body.
- It is a bundle of borrowed material.
- It was dominated by Congress.
- It was dominated by Hindus.
Options:
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 3 and 5 only
- All of the above
See
Question 3. The main objective of Article 13 is to:
- To secure paramountcy of the Constitution in relation to Fundamental Rights
- To secure paramountcy of the Parliament in relation to Fundamental Rights
- To secure paramountcy of the Fundamental duties in relation to Article 368
- To secure paramountcy of the Parliament in relation to Constitution
See
Question 4. Which of the following were a part of Sher Shah Suri’s administration?
- Measurement of the sown land was done for revenue collection.
- Shiqdar was in charge of the general administration of a Pargana.
- Customs duty was imposed on the goods only at two places to promote trade and commerce.
Options:
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- All of the above
See
H. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
- Non-alignment as an instrument of foreign policy is to remain important in international politics of the day. Discuss.
- Democracy is the panacea to all the ills of governance. Critically analyse.
Also, check previous Daily News Analysis
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Current Affairs Webinar’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series
Comments