Carbon cycle:
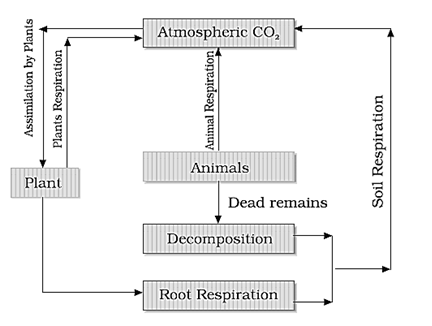
- The carbon cycle is mainly the conversion of carbon dioxide. This conversion is initiated by the fixation of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis.
- Such conversion results in the production of carbohydrate, glucose that may be converted to other organic compounds such as sucrose, starch, cellulose, etc.
- Here, some of the carbohydrates are utilised directly by the plant itself. During this process, more carbon dioxide is generated and is released through its leaves or roots during the day.
- The remaining carbohydrates not being utilised by the plant become part of the plant tissue. Plant tissues are either being eaten by the herbivorous animals or get decomposed by the microorganisms.
- The herbivores convert some of the consumed carbohydrates into carbon dioxide for release into the air through respiration.
- The micro-organisms decompose the remaining carbohydrates after the animal dies. The carbohydrates that are decomposed by the micro-organisms then get oxidised into carbon.
Oxygen cycle:
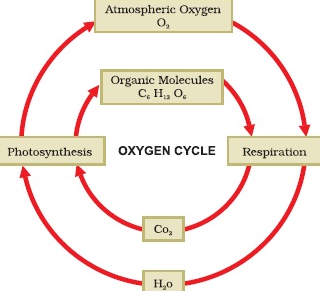
- The oxygen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle of oxygen. It is mainly involved in maintaining the level of oxygen in the atmosphere.
- Oxygen is the main by-product of photosynthesis. It is involved in the oxidation of carbohydrates with the release of energy, carbon dioxide and water.
- The cycling of oxygen is a highly complex process. Oxygen occurs in a number of chemical forms and combinations. It combines with nitrogen to form nitrates and with many other minerals and elements to form various oxides such as iron oxide, aluminium oxide and others.
- Much of oxygen is produced from the decomposition of water molecules by sunlight during photosynthesis and is released in the atmosphere through the transpiration and respiration processes of plants.
Further Reading:
|
Related Links |
|
Comments