Pythagoras Theorem (also called Pythagorean Theorem) is an important topic in Mathematics, which explains the relation between the sides of a right-angled triangle. The sides of the right triangle are also called Pythagorean triples. The formula and proof of this theorem are explained here with examples.
Pythagoras theorem is basically used to find the length of an unknown side and the angle of a triangle. By this theorem, we can derive the base, perpendicular and hypotenuse formulas. Let us learn the mathematics of the Pythagorean theorem in detail here.

Pythagoras Theorem Statement
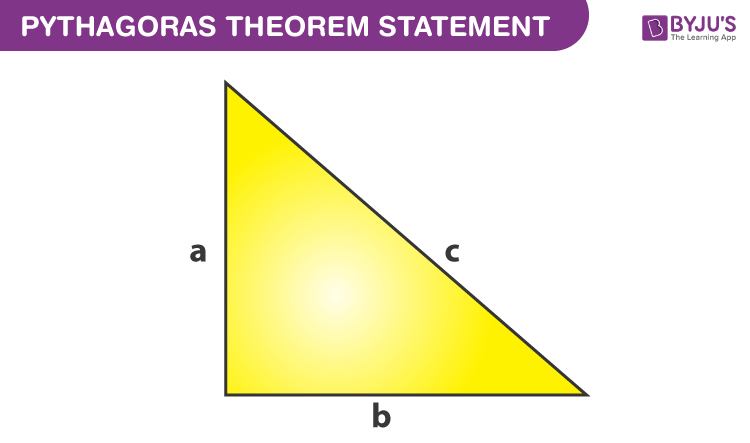
Pythagoras theorem states that “In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides“. The sides of this triangle have been named Perpendicular, Base and Hypotenuse. Here, the hypotenuse is the longest side, as it is opposite to the angle 90°. The sides of a right triangle (say a, b and c) which have positive integer values, when squared, are put into an equation, also called a Pythagorean triple.
History
The theorem is named after a Greek Mathematician called Pythagoras.
Pythagoras Theorem Formula
Consider the triangle given above:
Where “a” is the perpendicular,
“b” is the base,
“c” is the hypotenuse.
According to the definition, the Pythagoras Theorem formula is given as:
| Hypotenuse2 = Perpendicular2 + Base2
c2 = a2 + b2 |
The side opposite to the right angle (90°) is the longest side (known as Hypotenuse) because the side opposite to the greatest angle is the longest.
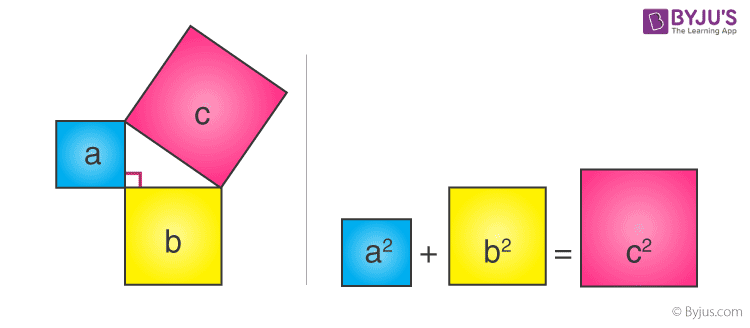
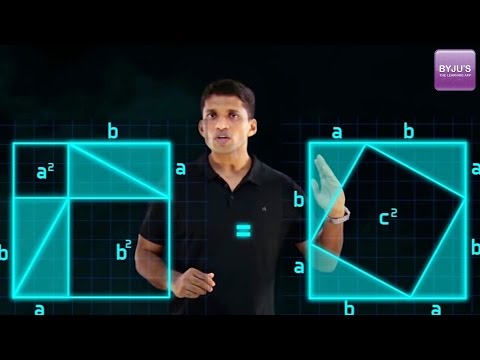
Consider three squares of sides a, b, c mounted on the three sides of a triangle having the same sides as shown.
By Pythagoras Theorem –
Area of square “a” + Area of square “b” = Area of square “c”
Example
The examples of theorem and based on the statement given for right triangles is given below:
Consider a right triangle, given below:
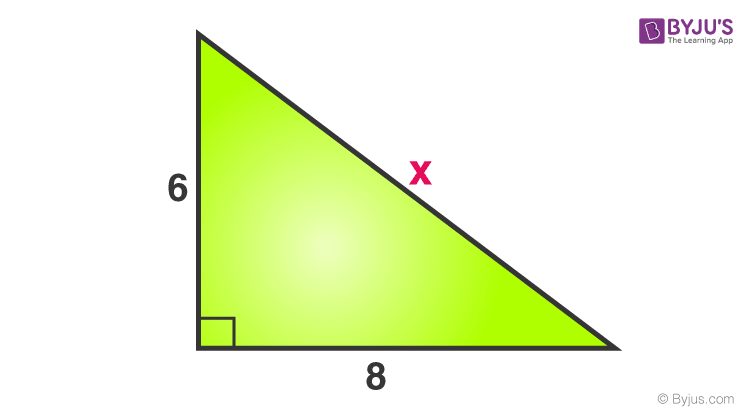
Find the value of x.
X is the side opposite to the right angle, hence it is a hypotenuse.
Now, by the theorem we know;
Hypotenuse2 = Base2 + Perpendicular2
x2 = 82 + 62
x2 = 64+36 = 100
x = √100 = 10
Therefore, the value of x is 10.
Pythagoras Theorem Proof
Given: A right-angled triangle ABC, right-angled at B.
To Prove- AC2 = AB2 + BC2
Construction: Draw a perpendicular BD meeting AC at D.
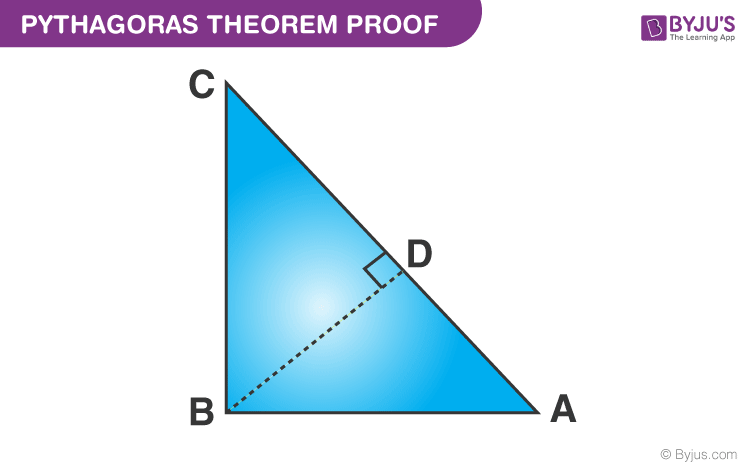
Proof:
We know, △ADB ~ △ABC
Therefore,
Or, AB2 = AD × AC ……………………………..……..(1)
Also, △BDC ~△ABC
Therefore,
Or, BC2= CD × AC ……………………………………..(2)
Adding the equations (1) and (2) we get,
AB2 + BC2 = AD × AC + CD × AC
AB2 + BC2 = AC (AD + CD)
Since, AD + CD = AC
Therefore, AC2 = AB2 + BC2
Hence, the Pythagorean theorem is proved.
Note: Pythagorean theorem is only applicable to Right-Angled triangle.
Video Lesson on Pythagoras Theorem
Applications of Pythagoras Theorem
- To know if the triangle is a right-angled triangle or not.
- In a right-angled triangle, we can calculate the length of any side if the other two sides are given.
- To find the diagonal of a square.
Useful For
Pythagoras theorem is useful to find the sides of a right-angled triangle. If we know the two sides of a right triangle, then we can find the third side.
How to use Pythagoras Theorem?
To use Pythagoras theorem, remember the formula given below:
c2 = a2 + b2
Where a, b and c are the sides of the right triangle.
For example, if the sides of a triangles are a, b and c, such that a = 3 cm, b = 4 cm and c is the hypotenuse. Find the value of c.
We know,
c2 = a2 + b2
c2 = 32+42
c2 = 9+16
c2 = 25
c = √25
c = 5 cm
Hence, the length of hypotenuse is 5 cm.
How to find whether a triangle is a right-angled triangle?
If we are provided with the length of three sides of a triangle, then to find whether the triangle is a right-angled triangle or not, we need to use the Pythagorean theorem.
Let us understand this statement with the help of an example.
Suppose a triangle with sides 10cm, 24cm, and 26cm are given.
Clearly, 26 is the longest side.
It also satisfies the condition, 10 + 24 > 26
We know,
c2 = a2 + b2 ………(1)
So, let a = 10, b = 24 and c = 26
First we will solve R.H.S. of equation 1.
a2 + b2 = 102 + 242 = 100 + 576 = 676
Now, taking L.H.S, we get;
c2 = 262 = 676
We can see,
LHS = RHS
Therefore, the given triangle is a right triangle, as it satisfies the Pythagoras theorem.
Related Articles
Pythagorean Theorem Solved Examples
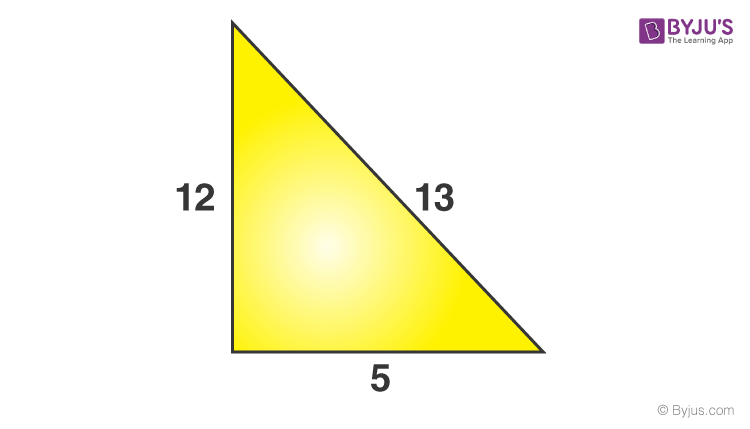
Problem 1: The sides of a triangle are 5, 12 & 13 units. Check if it has a right angle or not.
Solution: From Pythagoras Theorem, we have;
Perpendicular2 + Base2 = Hypotenuse2
P2 + B2 = H2
Let,
Perpendicular (P) = 12 units
Base (B)= 5 units
Hypotenuse (H) = 13 units {since it is the longest side measure}
LHS = P2 + B2
⇒ 122 + 52
⇒ 144 + 25
⇒ 169
RHS = H2
⇒ 132
⇒ 169
⇒ 169 = 169
L.H.S. = R.H.S.
Therefore, the angle opposite to the 13 units side will be a right angle.
Problem 2: The two sides of a right-angled triangle are given as shown in the figure. Find the third side.
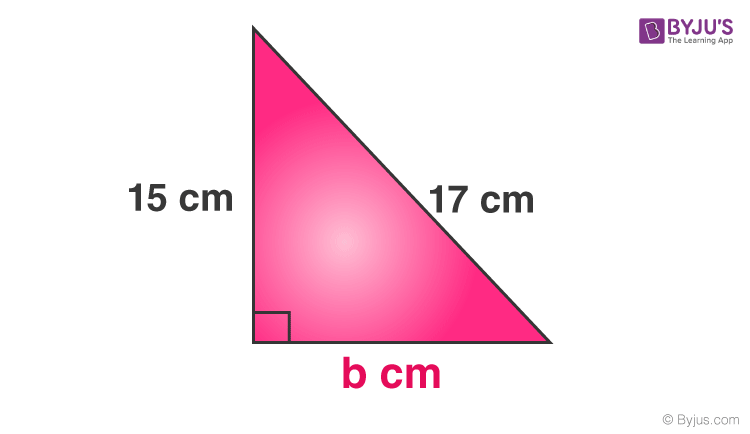
Perpendicular = 15 cm
Base = b cm
Hypotenuse = 17 cm
As per the Pythagorean Theorem, we have;
Perpendicular2 + Base2 = Hypotenuse2
⇒152 + b2 = 172
⇒225 + b2 = 289
⇒b2 = 289 – 225
⇒b2 = 64
⇒b = √64
Therefore, b = 8 cm
Problem 3: Given the side of a square to be 4 cm. Find the length of the diagonal.
Solution- Given;
Sides of a square = 4 cm
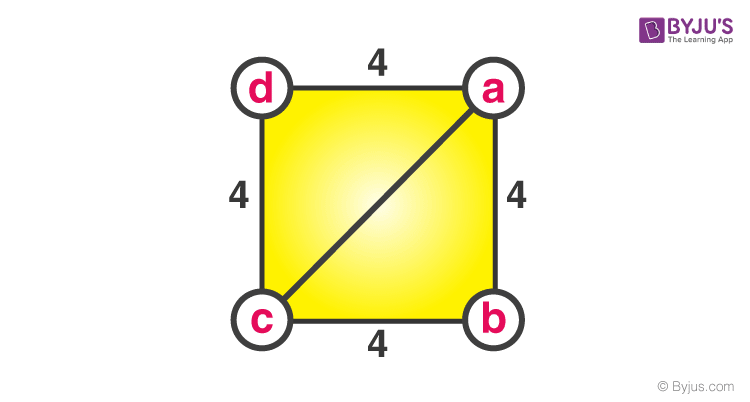
To Find- The length of diagonal ac.
Consider triangle abc (or can also be acd)
(ab)2 +(bc)2 = (ac)2
(4)2 +(4)2= (ac)2
16 + 16 = (ac)2
32 = (ac)2
(ac)2 = 32
ac = 4√2.
Thus, the length of the diagonal is 4√2 cm.
Practice Problems on Pythagoras Theorem
- In a right triangle ABC, right-angled at B, the lengths of AB and BC are 7 units and 24 units, respectively. Find AC.
- If the length of the diagonal of a square is 10 cm, then find the length of the side of the square.
- A triangle is given whose sides are of length 11 cm, 60 cm, and 61 cm. Check whether these are the sides of a right-angled triangle.
Stay tuned with BYJU’S – The Learning App to learn all the important mathematical concepts and also watch interactive videos to learn with ease.
Frequently Asked Questions on Pythagoras Theorem
What is the formula for Pythagorean Theorem?
The formula for Pythagoras, for a right-angled triangle, is given by; P2 + B2 = H2
What does Pythagoras theorem state?
Pythagoras theorem states that, in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the square of the other two sides.
What is the formula for hypotenuse?
The hypotenuse is the longest side of the right-angled triangle, opposite to right angle, which is adjacent to base and perpendicular. Let base, perpendicular and hypotenuse be a, b and c respectively. Then the hypotenuse formula, from the Pythagoras statement will be;
c = √(a2 + b2)
Can we apply the Pythagoras Theorem for any triangle?
No, this theorem is applicable only for the right-angled triangle.
What is the use of Pythagoras theorem?
Can the diagonals of a square be found using Pythagoras theorem?
Yes, the diagonals of a square can be found using the Pythagoras theorem, as the diagonal divides the square into right triangles.
Explain the steps involved in finding the sides of a right triangle using Pythagoras theorem.
Step 1: To find the unknown sides of a right triangle, plug the known values in the Pythagoras theorem formula.
Step 2: Simplify the equation to find the unknown side.
Step 3: Solve the equation for the unknown side.
What are the different ways to prove Pythagoras theorem?
There are various approaches to prove the Pythagoras theorem. A few of them are listed below:
Proof using similar triangles
Proof using differentials
Euclid’s proof
Algebraic proof, and so on.

I want all before year question papers of 10th cbse please send me as soon as possible my exams are going to be start
I could understand this concept very well even though I’m in sixth grade. I learnt this for my math project.
It was very helpful. thanks to Byju’ s.
Please explain about pythogorean theorem for side in detail for the project
I think that we children can use this website very well and it is also very helpful for us and I have used this website for the first time By the way I liked everything.
Yes I am satisfied this link 😊.
yes l am satisfied this link
Thanks to this website I will be the best student in my class thanks BYJUS I really appreciate it
Thank you very much byju’s for this. It really helped me in my math project.
Useful page and helped me understanding the concepts formulas I hope for much betterment
Hi , it is very useful page and thank you to byjus the are best learning app.
PLEASE DOWNLOAD THIS APP IT IS EXCELLENT APP
Very useful page for every students’. Thank you byjus!!
This link was very use ful for me 😊😊
I am very well satisfied with the explanation , helped me understand and grasp the concept well . This hep my math project also .Thank you 🙂
Thank you byju. It has helped me
Hi guys, Platform is awesome
According to this theorem, if a line divides any two sides of a triangle in the same ratio, then the line is parallel to the third side.
Check the proof of Basic Proportionality Theorem converse theorem here.
Very interesting, good job, and thanks for sharing such a good blog.