Flashcards for NEET Biology are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for Mineral Nutrition. These flashcards on Mineral Nutrition are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. This is helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams during last-minute revision. Flashcards For NEET Biology – Mineral Nutrition, covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Biology. Solve NEET Biology MCQs to check your understanding and outperform in the exam.
Download PDF of NEET Biology Flashcards for Mineral Nutrition
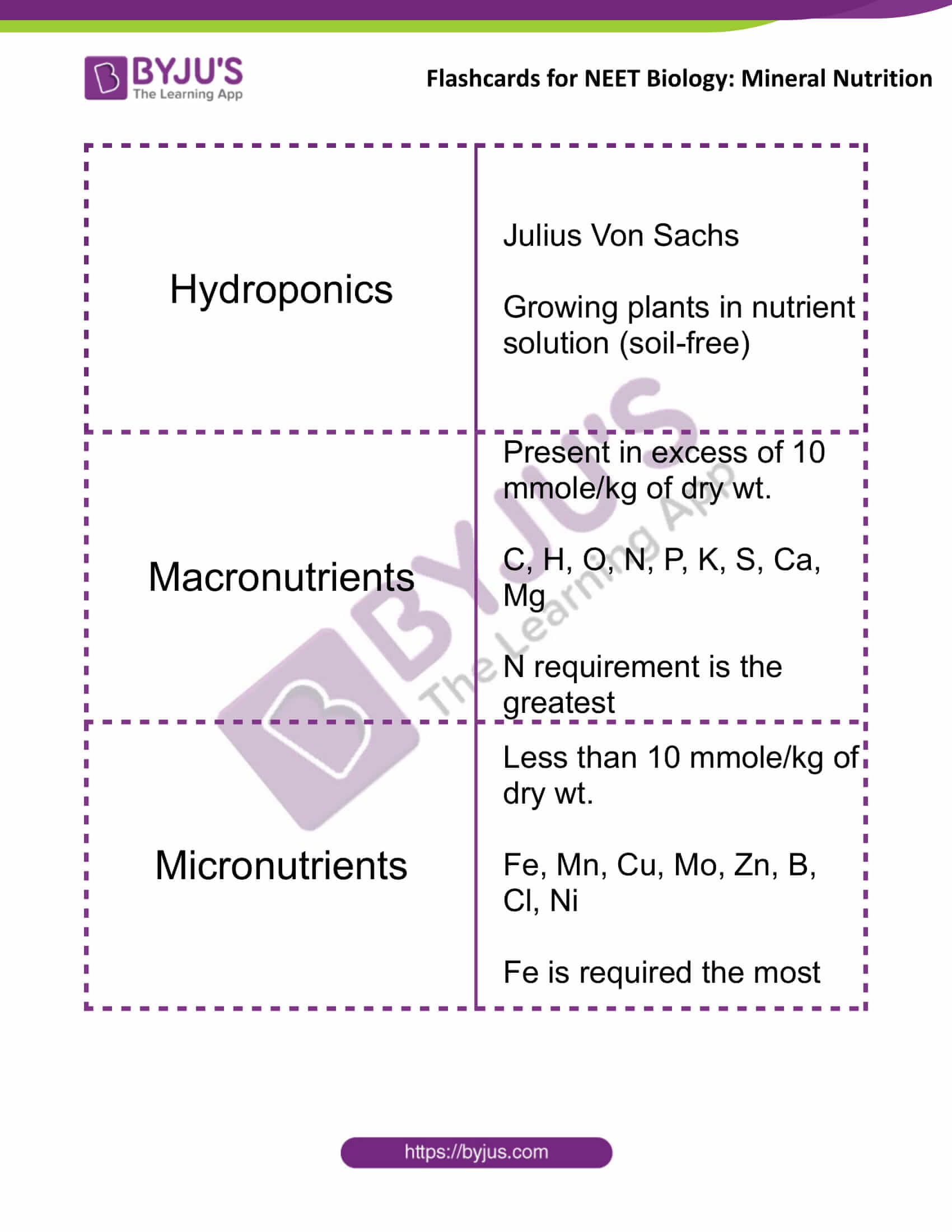
| Hydroponics | Julius Von Sachs
Growing plants in nutrient solution (soil-free) |
| Macronutrients | Present in excess of 10 mmole/kg of dry wt.
C, H, O, N, P, K, S, Ca, Mg N requirement is the greatest |
| Micronutrients | Less than 10 mmole/kg of dry wt.
Fe, Mn, Cu, Mo, Zn, B, Cl, Ni Fe is required the most |
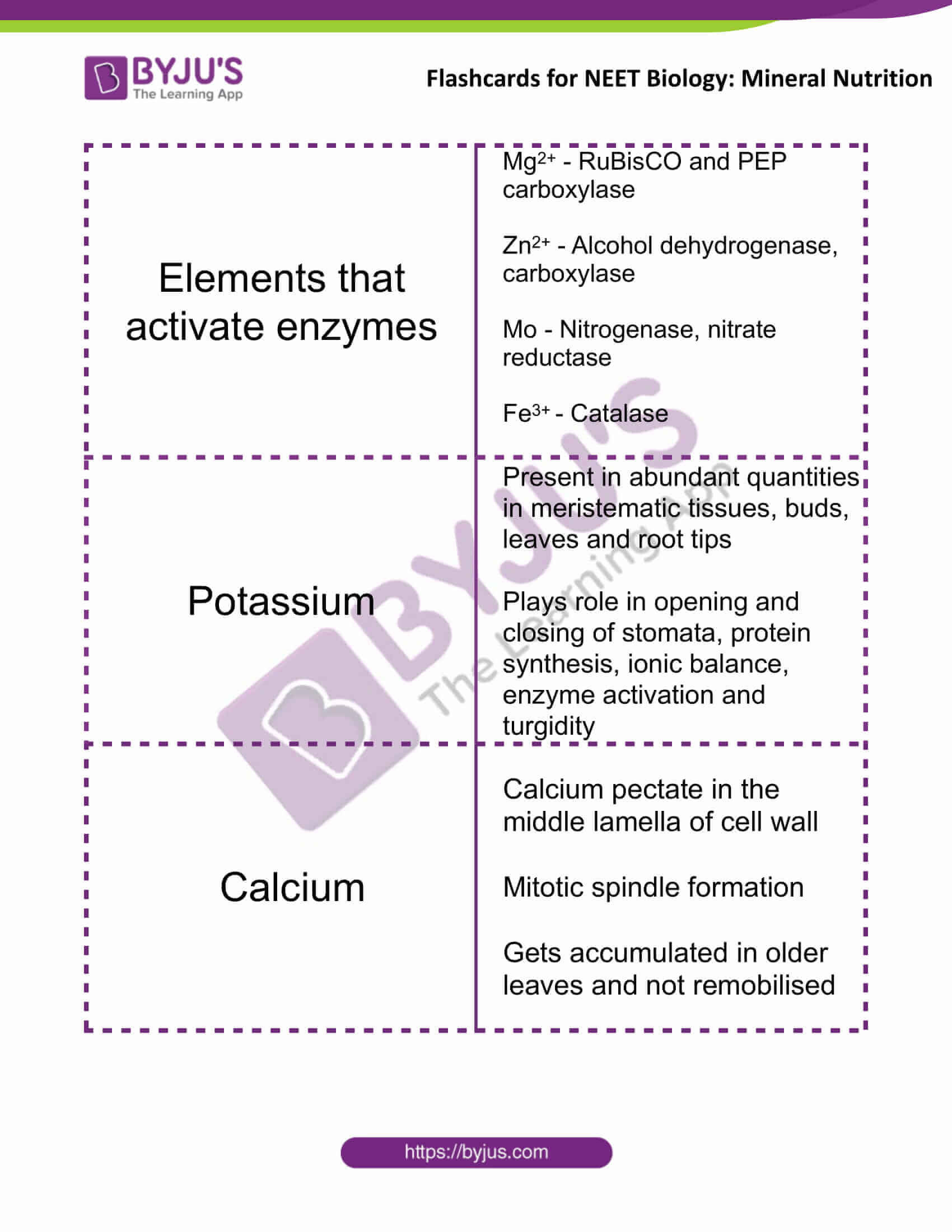
| Elements that activate enzymes | Mg2+ – RuBisCO and PEP carboxylase
Zn2+ – Alcohol dehydrogenase, carboxylase Mo – Nitrogenase, nitrate reductase Fe3+ – Catalase |
| Potassium | Present in abundant quantities in meristematic tissues, buds, leaves and root tips
Plays role in opening and closing of stomata, protein synthesis, ionic balance, enzyme activation and turgidity |
| Calcium | Calcium pectate in the middle lamella of cell wall
Mitotic spindle formation Gets accumulated in older leaves and not remobilised |
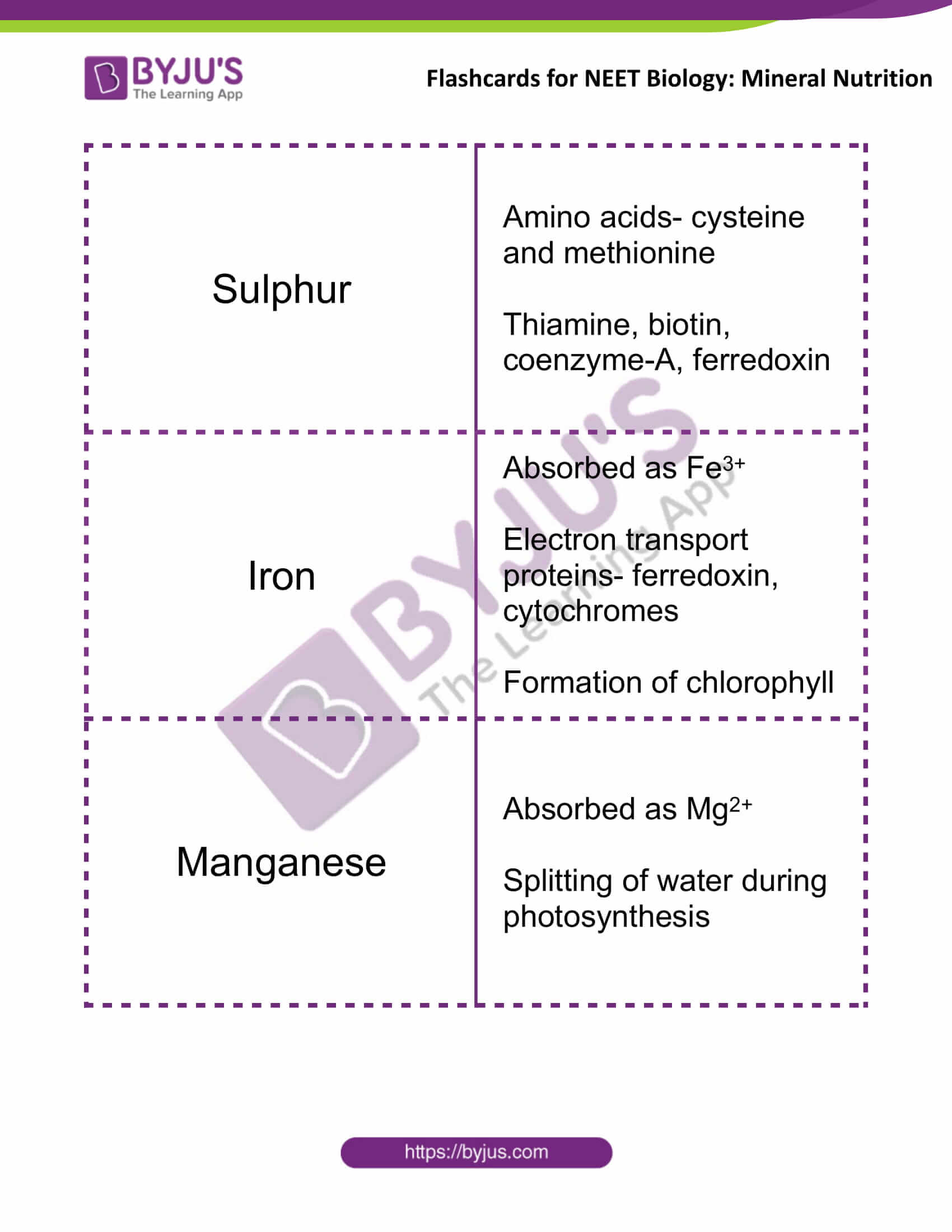
| Sulphur | Amino acids- cysteine and methionine
Thiamine, biotin, coenzyme-A, ferredoxin |
| Iron | Absorbed as Fe3+
Electron transport proteins- ferredoxin, cytochromes Formation of chlorophyll |
| Manganese | Absorbed as Mg2+
Splitting of water during photosynthesis |
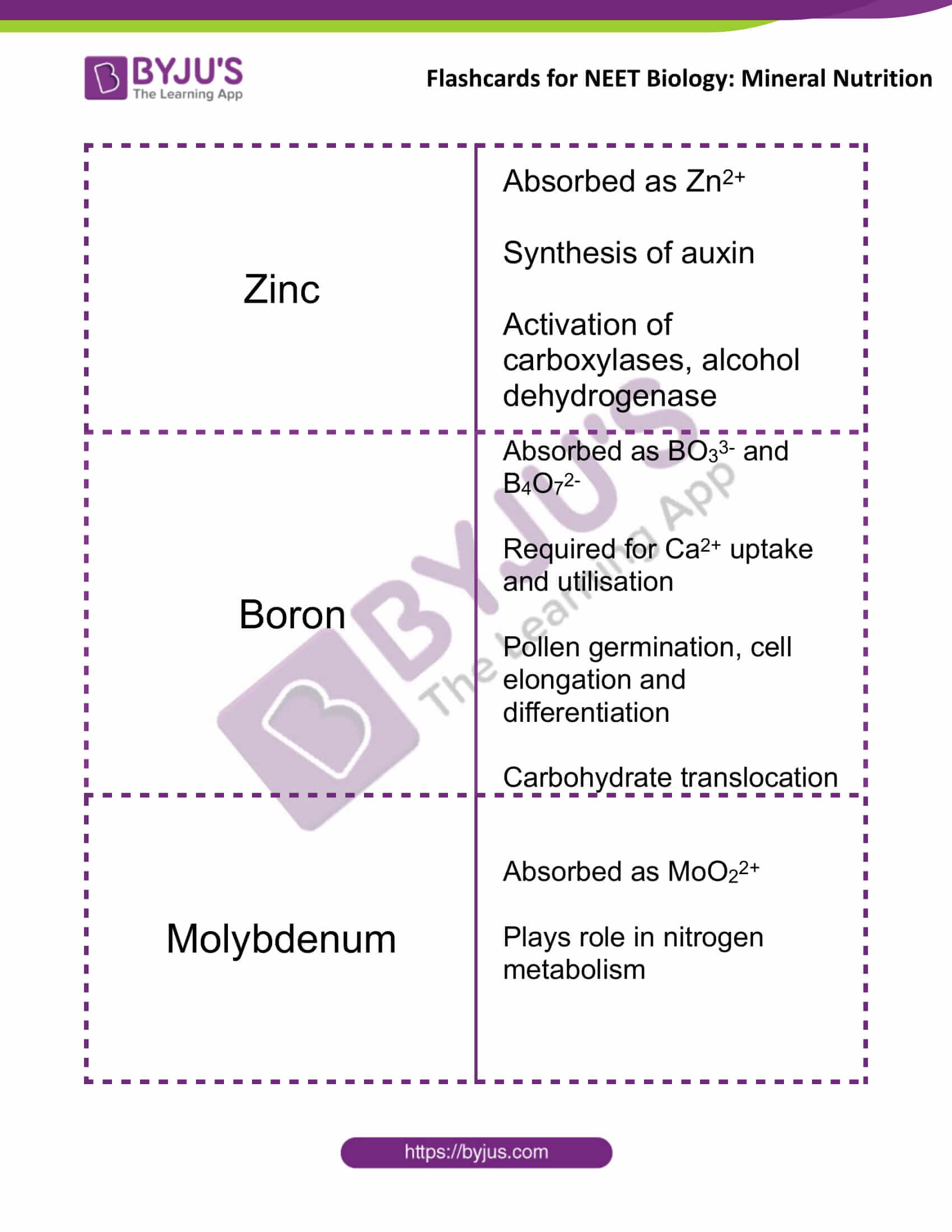
| Zinc | Absorbed as Zn2+
Synthesis of auxin Activation of carboxylases, alcohol dehydrogenase |
| Boron | Absorbed as BO33- and B4O72-
Required for Ca2+ uptake and utilisation Pollen germination, cell elongation and differentiation Carbohydrate translocation |
| Molybdenum | Absorbed as MoO22+
Plays role in nitrogen metabolism |
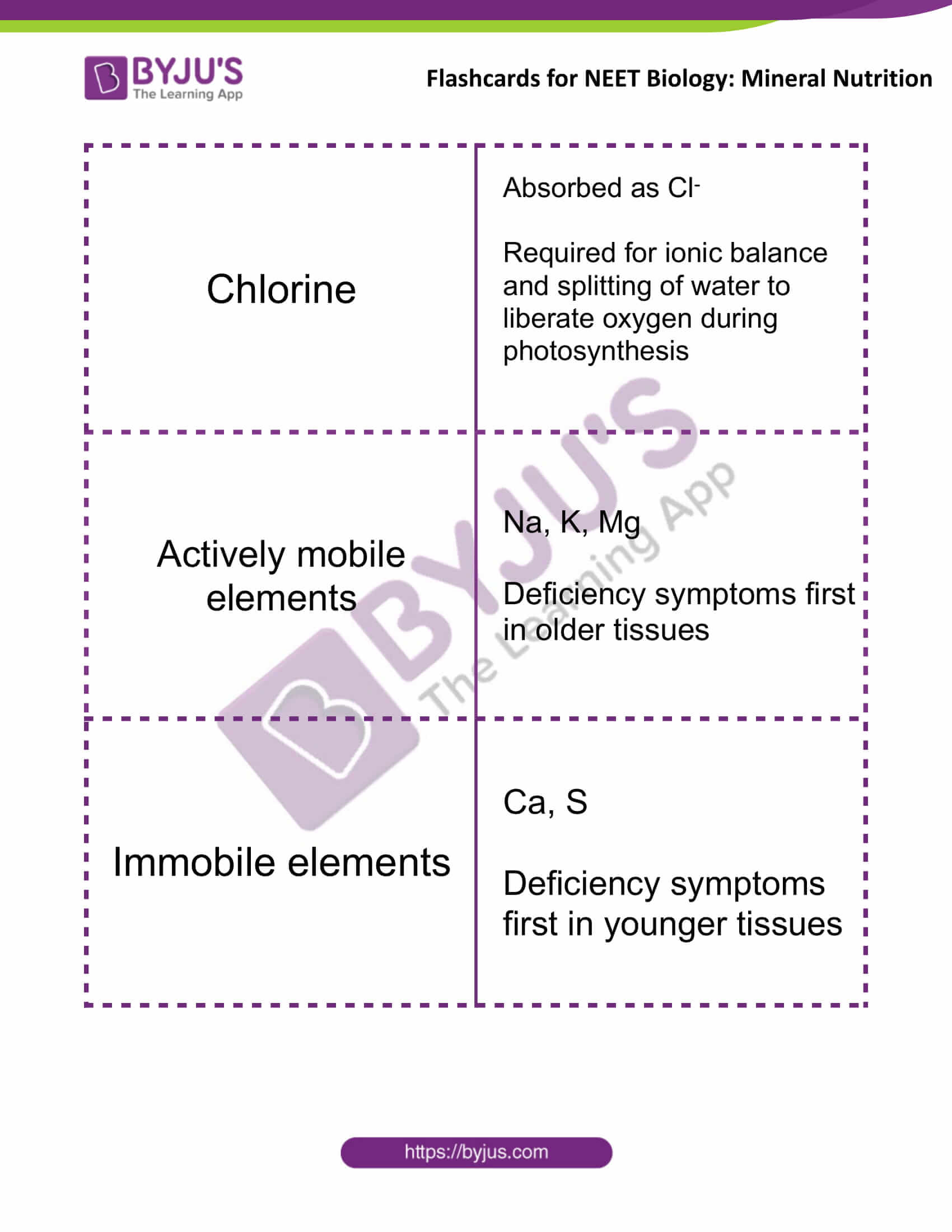
| Chlorine | Absorbed as Cl–
Required for ionic balance and splitting of water to liberate oxygen during photosynthesis |
| Actively mobile elements | Na, K, Mg
Deficiency symptoms first in older tissues |
| Immobile elements | Ca, S
Deficiency symptoms first in younger tissues |
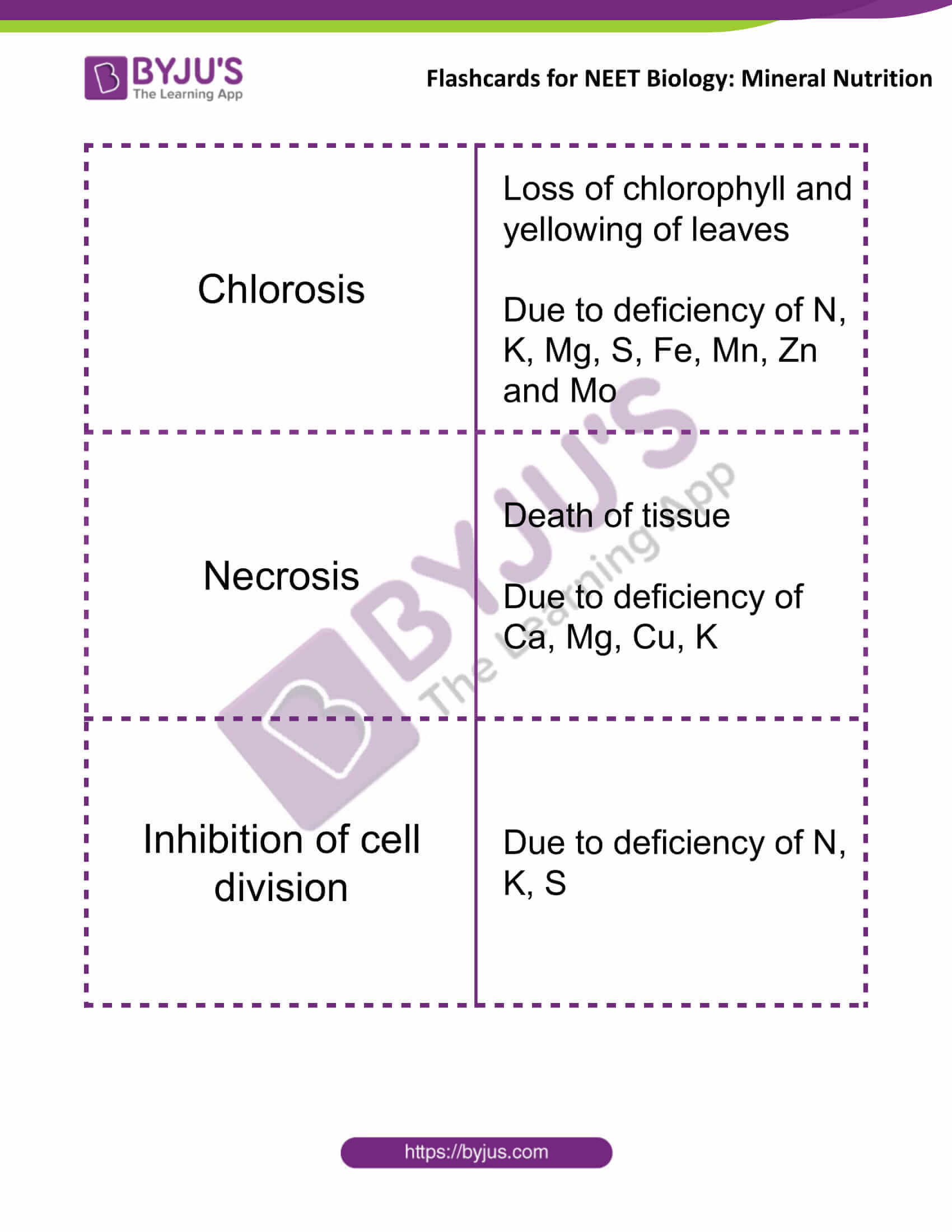
| Chlorosis | Loss of chlorophyll and yellowing of leaves
Due to deficiency of N, K, Mg, S, Fe, Mn, Zn and Mo |
| Necrosis | Death of tissue
Due to deficiency of Ca, Mg, Cu, K |
| Inhibition of cell division | Due to deficiency of N, K, S |
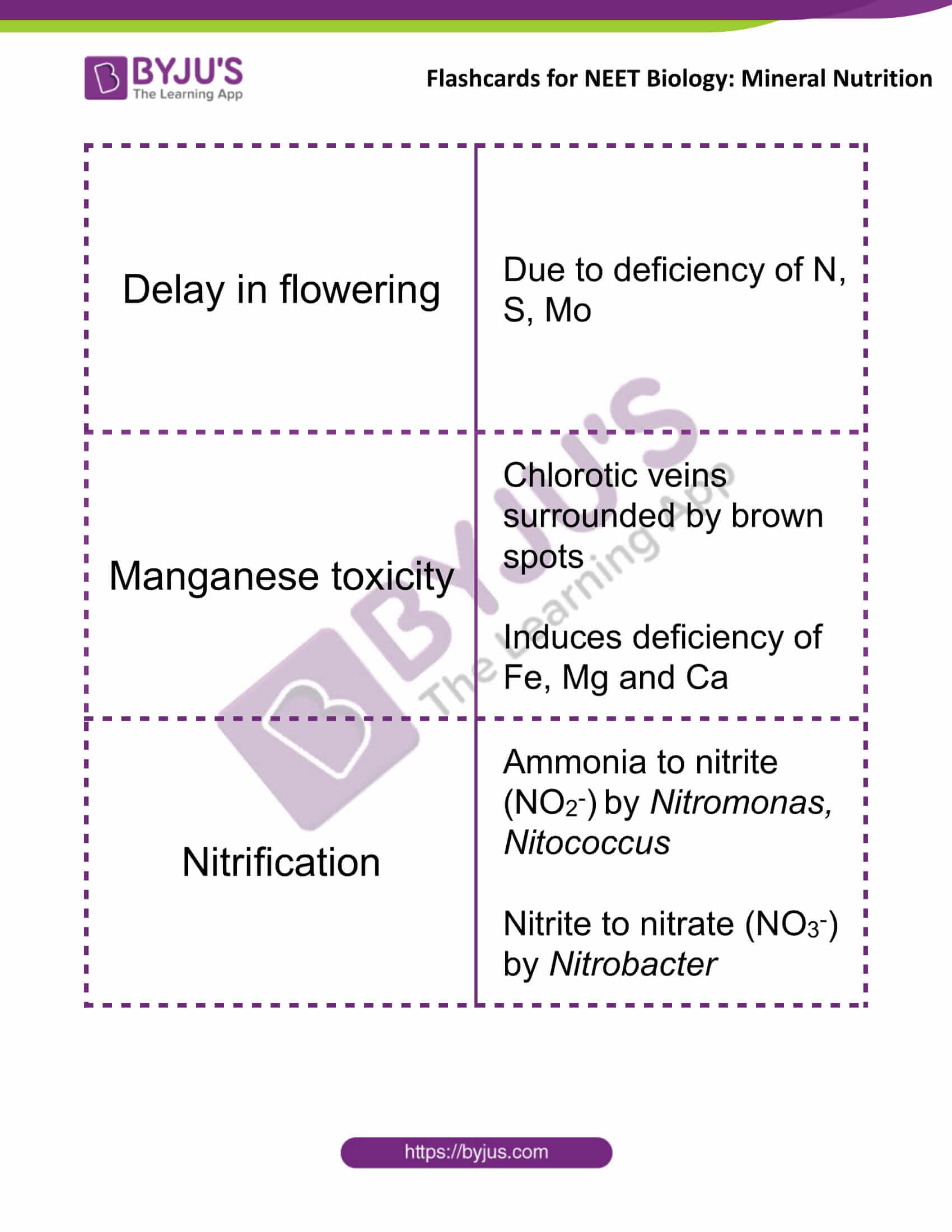
| Delay in flowering | Due to deficiency of N, S, Mo |
| Manganese toxicity | Chlorotic veins surrounded by brown spots
Induces deficiency of Fe, Mg and Ca |
| Nitrification | Ammonia to nitrite (NO2–) by Nitromonas, Nitococcus
Nitrite to nitrate (NO3–) by Nitrobacter |
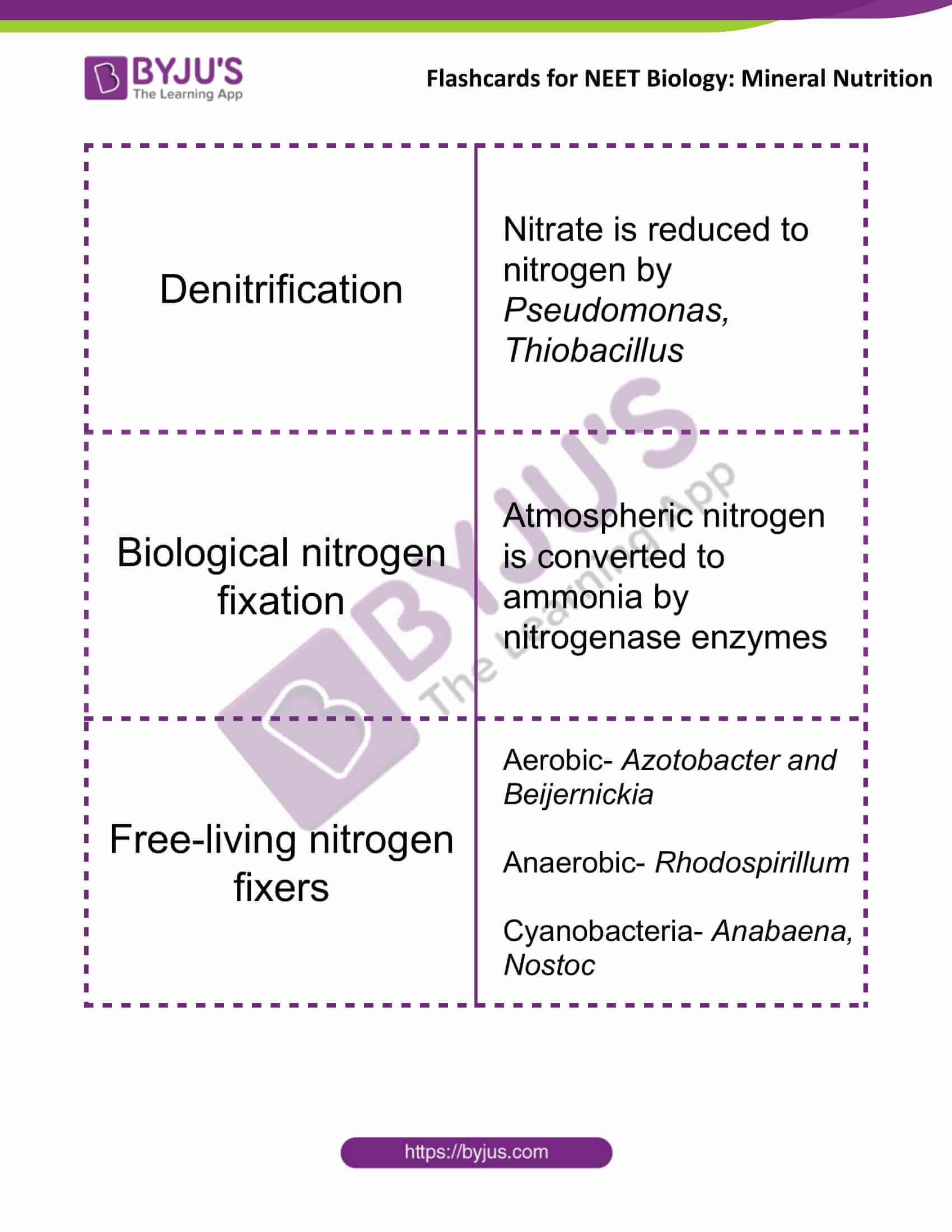
| Denitrification | Nitrate is reduced to nitrogen by Pseudomonas, Thiobacillus |
| Biological nitrogen fixation | Atmospheric nitrogen is converted to ammonia by nitrogenase enzymes |
| Free-living nitrogen fixers | Aerobic- Azotobacter and Beijernickia
Anaerobic- Rhodospirillum Cyanobacteria- Anabaena, Nostoc |
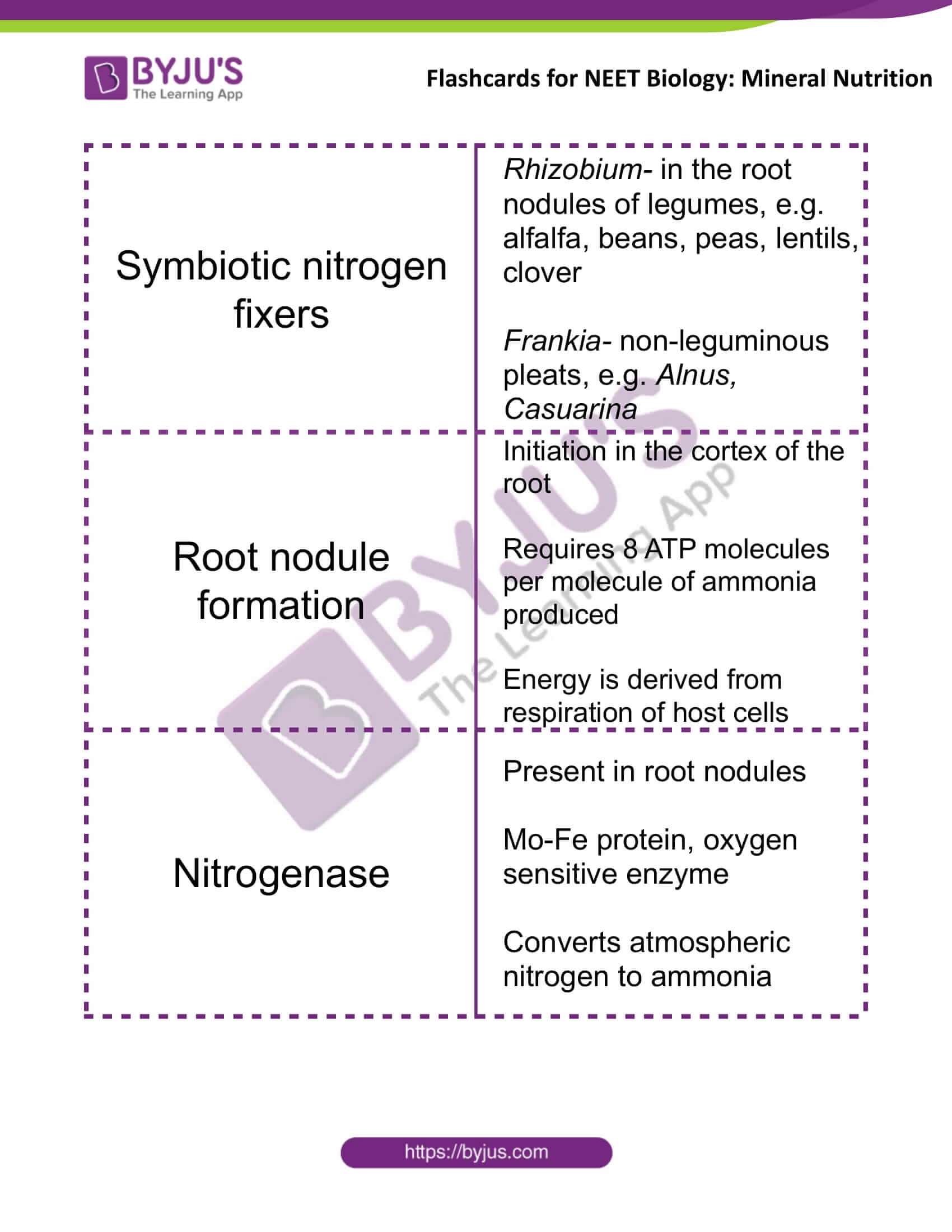
| Symbiotic nitrogen fixers | Rhizobium- in the root nodules of legumes, e.g. alfalfa, beans, peas, lentils, clover
Frankia- non-leguminous pleats, e.g. Alnus, Casuarina |
| Root nodule formation | Initiation in the cortex of the root
Requires 8 ATP molecules per molecule of ammonia produced Energy is derived from respiration of host cells |
| Nitrogenase | Present in root nodules
Mo-Fe protein, oxygen sensitive enzyme Converts atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia |
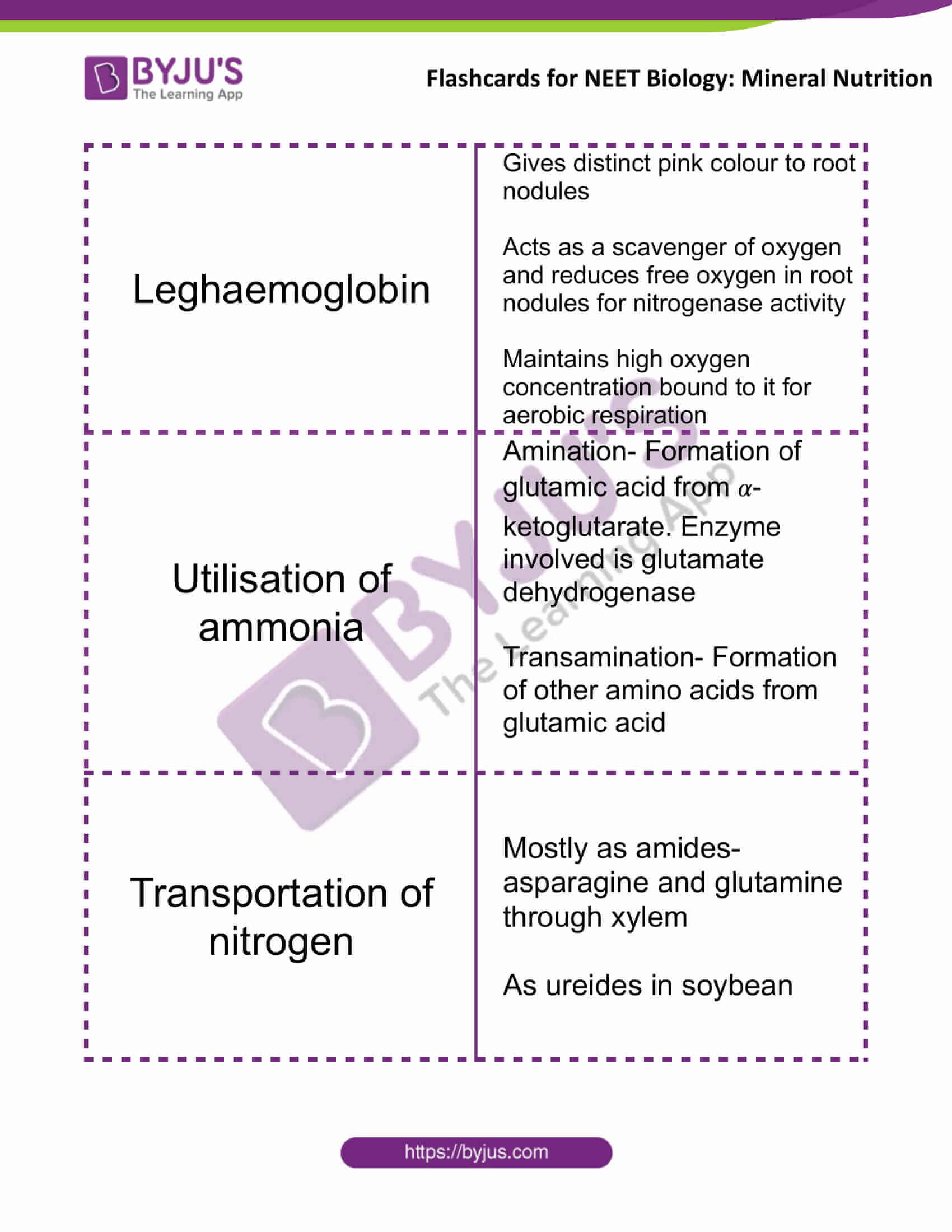
| Leghaemoglobin | Gives distinct pink colour to root nodules
Acts as a scavenger of oxygen and reduces free oxygen in root nodules for nitrogenase activity Maintains high oxygen concentration bound to it for aerobic respiration |
| Utilisation of ammonia | Amination- Formation of glutamic acid from 𝛼-ketoglutarate. Enzyme involved is glutamate dehydrogenase
Transamination- Formation of other amino acids from glutamic acid |
| Transportation of nitrogen | Mostly as amides- asparagine and glutamine through xylem
As ureides in soybean |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Biology, only at BYJU’S.
Also Check:
NEET Flashcards: Cell Cycle And Cell Division
NEET Flashcards: Transport In Plants
NEET Flashcards: Photosynthesis In Higher Plants
NEET Flashcards: Respiration In Plants
NEET Flashcards: Plant Growth And Development
Recommended Video:

Comments