Table of Contents:
Download Complete Chapter Notes of Biological Classification
Download Now
Rhizopus is a genus of saprophytic and parasitic fungi. They are found in moist or damp places. They are found on organic substances like vegetables, fruits, bread, jellies, etc. The vegetative structure is made up of coenocytic (multinucleated) and branched hyphae. They are used to produce various chemicals and alcoholic products. Some species of rhizopus cause plant diseases and may cause infection in humans too, known as mucormycosis.
Classification and Examples
Rhizopus is a genus under the phylum Zygomycota. They are classified by the production of zygospores during sexual reproduction.
They are commonly known as black bread mould, pin mould, etc.
| Domain | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom | Fungi |
| Phylum | Zygomycota |
| Class | Zygomycetes |
| Order | Mucorales |
| Family | Mucoraceae |
| Genus | Rhizopus |
Some common species of Rhizopus include:
Rhizopus stolonifer – It is also known as black bread mould. Commercially used in the production of chemicals, e.g. cortisone, fumaric acid, etc. Causes fruit rot disease.
Rhizopus oryzae – Alcoholic beverages are produced
Rhizopus microsporus – It is used to get fermented soybean products
Rhizopus Structure with Diagram
- They are fast-growing fungi and have a cottony appearance
- The body of rhizopus consists of branched mycelium. The mycelium is coenocytic and composed of three types of hyphae; stolon, rhizoids and sporangiophores
- Stolon is the internodal region, it is aerial, forms an arch and touches the substratum forming nodal region
- Rhizoids are formed where the stolon touches the substratum at nodes. They are branched, anchor the mycelium to the substratum and absorb food
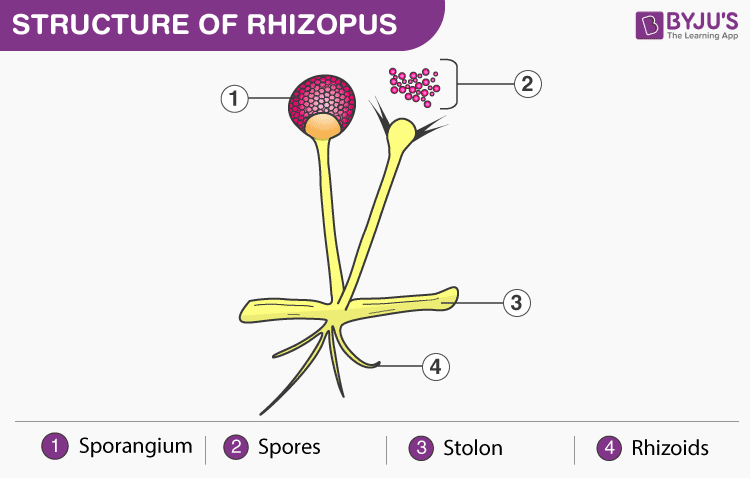
- Sporangiophores are the aerial and reproductive mycelia. They are branched and consist of sporangiospores terminally
- The cell wall is made up of chitin. The cytoplasm is multinucleated and consists of other cell organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vacuoles and oil droplets
- They reproduce by vegetative, asexual and sexual methods
Also see: MCQs on Rhizopus
Life Cycle of Rhizopus
Rhizopus reproduce by all the three processes, i.e. vegetative, asexual and sexual
Vegetative reproduction is by fragmentation and each of the fragments of a stolon develops separately making a complete mycelium
Asexual reproduction is by the formation of sporangiospores and chlamydospores
1.Formation of Sporangiospores: Sporangiospores are formed terminally in sporangia of aerial mycelium called sporangiophores. They are formed under favourable conditions.
- Sporangiophores develop from the upper side of the rhizoidal node
- The apical part swells up forming sporangium, as nuclei and cytoplasm move apically
- The cytoplasm of sporangium differentiates into the denser peripheral region with more nuclei and the central columella region with fewer nuclei and more vacuoles
- Sporangiospores develop inside sporangium. They are multinucleated and non-motile
- The wall of sporangium ruptures after maturation and sporangiospores come out as a powdery mass
- After getting suitable condition and substratum, each spore germinates into a new mycelium
2.Formation of Chlamydospores: Chlamydospores are formed during unfavourable conditions. An intercalary segment of mycelium develops due to the formation of septae and accumulation of protoplasm. It is thick-walled and detaches from the mycelium once it dries. They remain dormant until the favourable conditions return and then germinate to form a new mycelium.
Sexual reproduction is by fusion of two compatible hyphae. Most of the Rhizopus species (R. stolonifer) are heterothallic, i.e. having different mycelium for + and – mating strains. R. sexualis is homothallic.
- The compatible hyphae come together. In both the mycelia, a small outgrowth develops. It is known as progametangia
- Nuclei and cytoplasm move towards the apical region and progametangia make contact
- The apical region is separated from the rest of the hyphae by septae formation. This is known as gametangia
- Gametangia conjugate to form a multinucleated structure
- Plasmogamy is followed by karyogamy and diploid (2n) zygote is formed. It is known as zygospore. Rest of the unpaired nuclei degenerate
- Zygospores enlarge and become thick-walled and resistant to adverse environmental conditions. On getting favourable conditions, zygospores germinate
- The inner wall of zygospore develops into promycelium forming germ sporangiophore, with germ sporangium formed apically
- Meiosis occurs and haploid meiospores are formed. They come out after rupture of the germ sporangium wall and develop into new mycelia
Economic Importance
Many Rhizopus species are commercially used to produce various chemicals and alcoholic products.
- R. oryzae is used in the production of cortisone and lactic acid
- R. oryzae is also used for biosorption of heavy metals in wastewater
- R. stolonifer is used to produce lactic acid, fumaric acid and cortisone
- R. delemar is used to produce biotin and fumaric acid
- Tempeh, a traditional soybean fermented product of Asia, is prepared using Rhizopus species
- Many traditional alcoholic beverages, e.g. Parakari (cassava product), is prepared using Rhizopus
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the common name for rhizopus?
Rhizopus is a genus of fungi. It is commonly called bread mould.
Why rhizopus is called Bread Mould?
Rhizopus species generally grow on bread, hence, the name bread mould. Rhizopus stolonifer is specifically called black bread mould as it is a black mould that grows on bread.
Where is rhizopus found?
Rhizopus is a genus of saprophytic fungi which commonly grows on jellies, syrups, leather, bread, etc. They are also found as parasites in animals causing fungal infection, e.g. zygomycosis in humans.
Does rhizopus reproduce sexually as well as asexually?
Yes, Rhizopus reproduce asexually as well as sexually. Asexual reproduction is by the formation of sporangiospores and chlamydospores. Sexual reproduction is by fusion of two compatible hyphae. They can either be heterothallic, i.e. having different mycelium for + and – mating strains or homothallic.
Which class does Rhizopus belong to?
Rhizopus belongs to the class Zygomycetes of the phylum Zygomycota.
Also Explore:
NEET Flashcards: The Living World
NEET Flashcards: Biological Classification
NEET Flashcards: Plant Kingdom
NEET Flashcards: Morphology Of Flowering Plants
NEET Flashcards: Anatomy Of Flowering Plants
Recommended Video:


Comments