This article will go through Sir Isaac Newton’s Laws of Motion, which revolutionised our understanding of the physical world centuries ago. This article explores Newton’s three laws and provides a deep understanding of their implications. Starting with Newton’s First Law of Motion, also known as the Law of Inertia, we delve into how objects behave when at rest or in uniform motion. Moving on to Newton’s Second Law of Motion, we unravel the relationship between mass, acceleration and external forces. Next, we explore Newton’s Third Law of Motion, shedding light on the concept of action and reaction. A concise summary of Newton’s laws offers a recap of the key concepts, while numerical examples in the Laws of Motion Numericals section demonstrate practical applications. Finally, our Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) section covers additional queries, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of Newton’s Laws of Motion.
Newton’s First Law of Motion
Newton’s First Law of Motion, also known as the Law of Inertia, is a fundamental principle that describes the behaviour of objects in the absence of external influences. The term “Law of Inertia” emphasizes the concept of inertia, which refers to the property of massive objects to resist changes in their state of motion. This idea stems from the observation that objects naturally maintain their current state of rest or motion, resisting any changes unless acted upon by an external force.
By naming the first law of motion the “Law of Inertia,” Newton highlighted this inherent property of objects and laid the groundwork for understanding how forces can cause changes in motion. Newton’s first law of motion states that objects persist in their current state of motion unless compelled to do otherwise by an external force. Whether an object is at rest or in uniform motion, it will continue in that state unless a net external force acts upon it.

One crucial insight provided by Newton’s First Law is that the object will maintain a constant velocity in the absence of a net force resulting from unbalanced forces acting on an object. If the object is already in motion, it will continue moving at the same speed and direction. Likewise, if the object is at rest, it will remain stationary. However, introducing an additional external force will cause the object’s velocity to change, responding to the magnitude and direction of the force applied.
Understanding Newton’s First Law of Motion sets the stage for a deeper exploration of the subsequent laws that govern the complexities of motion. By comprehending this fundamental principle, we gain crucial insights into how objects behave independently and how external forces influence their motion. The first law of motion provides a strong foundation for further understanding the dynamics and behaviour of objects in the physical world.
Newton’s Second Law of Motion
This section will explore Newton’s Second Law of Motion, which provides a deeper understanding of how bodies respond to external forces.
The second law of motion describes the relationship between the force acting on a body and the resulting acceleration. According to Newton’s second law, the force acting on an object is equal to the product of its mass and acceleration.
Mathematically, we express Newton’s Second Law as follows:
Here, F represents the force, m is the object’s mass and a is the acceleration produced. This equation reveals that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force applied in the same direction as the force and inversely proportional to the object’s mass.

By understanding Newton’s Second Law, we can determine how much an object will accelerate when subjected to a specific net force. The equation highlights the intricate relationship between force, mass, and acceleration, providing a quantitative framework for analysing the dynamics of objects in motion.
In the second law equation, a proportionality constant is represented by the letter “k.” When using the SI unit system, this constant is equal to 1. Therefore, the final expression simplifies to:
The concise and powerful expression of Newton’s Second Law showcases the fundamental principle that governs the relationship between force and acceleration in physics. With this law, we gain a quantitative understanding of how external forces impact the motion of objects based on their mass and the resulting acceleration they experience.
By exploring Newton’s Second Law of Motion, we deepen our insights into the mechanics of motion, setting the stage for further exploration of the principles that govern the complexities of physical phenomena.
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
This section will discuss Newton’s Third Law of Motion, revealing a fascinating relationship between forces exerted by interacting bodies.
Newton’s Third Law of Motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. When two bodies interact, they apply forces on each other that are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. This law highlights the concept that forces always occur in pairs.

To illustrate this principle, consider the example of a book resting on a table. As the book applies a downward force equal to its weight on the table, the table, in turn, exerts an equal and opposite force on the book. This occurs because the book slightly deforms the table’s surface, causing the table to push back on the book, much like a compressed spring releasing its energy.
This third law of motion has profound implications, including conserving momentum. Momentum is a property of moving objects determined by an object’s mass and velocity. According to Newton’s third law, the total momentum of an isolated system remains constant. This means that in any interaction, the total momentum before and after the interaction remains the same, regardless of the forces involved.
Understanding Newton’s third law of motion deepens our comprehension of the interconnectedness and equilibrium within the physical world. It provides a framework for analysing and predicting the effects of forces in various scenarios, from everyday interactions to complex mechanical systems.
As we delve further into the subsequent sections on the laws of motion, we will continue building upon the foundational principles of inertia, force, and action-reaction relationships.
Exploring the Fundamentals of Force and Laws of Motion with Engaging Videos
Unveiling the Laws of Motion: Exploring Galileo’s Insights

Master Newton’s Laws of Motion and Solve Your Doubts – Mission Midterm Series

Forces of Motion: Newton’s Laws and the Power of Inertia

Mastering Force and Laws of Motion: A Comprehensive Marathon Session for Students

Explaining Everyday Phenomena with Newton’s Laws of Motion
Jack wonders why his wallet falls from the passenger seat to the floor while driving to work. How can we explain this phenomenon using physics?
We can explain this to Jack using Newton’s first law of motion. Due to its inertia, the wallet tends to maintain its state of motion. As the car accelerates or decelerates, the wallet continues moving forward with the same velocity before the car’s motion changes. However, when the car suddenly stops or changes direction, an external force (in this case, the force exerted by the car floor) acts on the wallet, causing it to slide off the seat and onto the floor. This is because the wallet resists changes in its state of motion, as Newton’s first law of motion described.
Using Newton’s laws, how can we explain the magician’s ability to pull a tablecloth from underneath dishes?
Newton’s first law of motion best explains the magician’s trick of pulling a tablecloth from underneath dishes. The magician carefully applies a negligible horizontal force to the tablecloth while quickly pulling it. According to Newton’s first law, objects at rest (the dishes and glasses) tend to remain in their state of motion or rest unless acted upon by an external force. In this case, the sudden pull of the tablecloth applies a minimal frictional force on the dishes and glasses. Since the tablecloth is made extremely slippery, it reduces the friction between the tablecloth and the dishes, allowing them to remain undisturbed and stay in their original state of motion or rest.
We gain insights into various phenomena by understanding and applying Newton’s laws of motion. We can explain seemingly perplexing situations like the movement of objects in a moving car or the magician’s illusionary tricks involving objects on a table. These laws provide a solid foundation for comprehending the principles governing motion in our everyday lives.
| Related Articles: |
Laws of Motion Summary
This section presents a visual summary of Newton’s Laws of Motion in the form of a flowchart. The flowchart provides an easy and digestible format to remember the key principles underlying the three laws of motion.
The flowchart highlights the three laws of motion established by Sir Isaac Newton:
- Newton’s First Law of Motion: The law of inertia states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue moving with a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force.
- Newton’s Second Law of Motion: This law relates the force acting on an object to its mass and acceleration. The force is equal to the product of mass and acceleration, where acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.
- Newton’s Third Law of Motion: The law of action and reaction states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. When one body exerts a force on another body, the second body simultaneously exerts a force of the same magnitude but in the opposite direction on the first body.
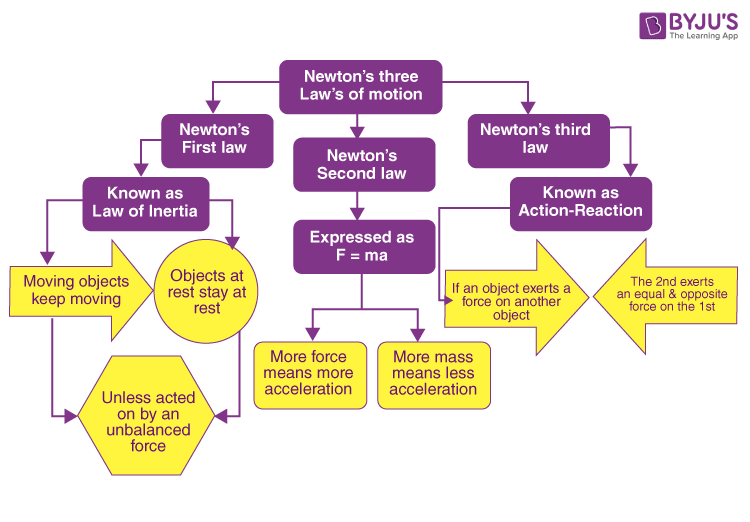
By referring to this flowchart, you can quickly grasp the fundamental principles of Newton’s Laws of Motion and understand how they govern the behaviour of objects in various scenarios. It serves as a useful tool for remembering Newton’s three laws of motion.
Laws of Motion Numericals
1. Suppose a bike with a rider on it having a total mass of 63 kg brakes and reduces its velocity from 8.5 m/s to 0 m/s in 3.0 seconds. What is the magnitude of the braking force?
Solution:
The combined mass of the rider and the bike = 63 kg
Initial Velocity = 8.5 m/s
Final Velocity = 0 m/s
The time in which the bike stops = 3 s
The net force acting on the body equals the rate of change of an object’s momentum.
The momentum of a body with mass m and velocity v is given by p = mv
Hence, the change in momentum of the bike is given by
Hence, the net force acting on the bike is given by
Substituting the value, we get
The magnitude of the braking force is -178.5 N.
2. Calculate the net force required to give an automobile of mass 1600 kg an acceleration of 4.5 m/s2.
We calculate the force using the following formula.
Substituting the values in the equation, we get
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Who discovered the three laws of motion?
Why are the laws of motion important?
What are Newton’s laws of motion all about?
What is the difference between Newton’s laws of motion and Kepler’s laws of motion?
What are some daily life examples of Newton’s 1st, 2nd and 3rd laws of motion?
- The motion of a ball falling through the atmosphere or a model rocket being launched up into the atmosphere are both excellent examples of Newton’s 1st law.
- Riding a bicycle is an excellent example of Newton’s 2nd law. In this example, the bicycle is the mass. The leg muscles pushing on the pedals of the bicycle is the force.
- You hit a wall with a certain amount of force, and the wall returns that same amount of force. This is an example of Newton’s 3rd law.
Stay tuned to BYJU’S and Fall in Love with Learning!



it is very helpful and useful i want to thank BY JU’S
Super
Good enough
nice
good
Thanks for the information
Very good super
Excellent
Good notes
really helpful, thanks!
Good information!
Nice exaplaination
The concepts are clear and easy to understand and to study. so, i feel comfortable with this app .
Good article
Good explanation of concept.
Good
Thanks
This really helped me😀
I will secure 🥇🏆
Super Explanation
Good to learn
This article cleared all my doubts about the laws of motion.
Thanks, BYJU’S.
The best content for visualization and it cleared all my doubts. I personally think that BYJU’S is the best app in terms of e-learning. Thanks to BYJU’S
Neat and Crisp Content!
Wow! Super and very useful content provided here.
A very useful content for making notes
Nice one
Thank you so much you helped in my project I ended up citing almost all my work from your website😅
Nice
It was nice 🙂
This was helpful
Very Nice Explanation!
Very interesting 🙌😍