All living organisms in the ecosystem are classified into kingdoms and sub-kingdoms based on their characteristics. Similarly, plants are also classified into different sub-kingdoms based on certain characteristic features.
The general classification of plants is made on certain criteria such as:
- Botanical type
- Geographical or ecological communities
Classification of Plants
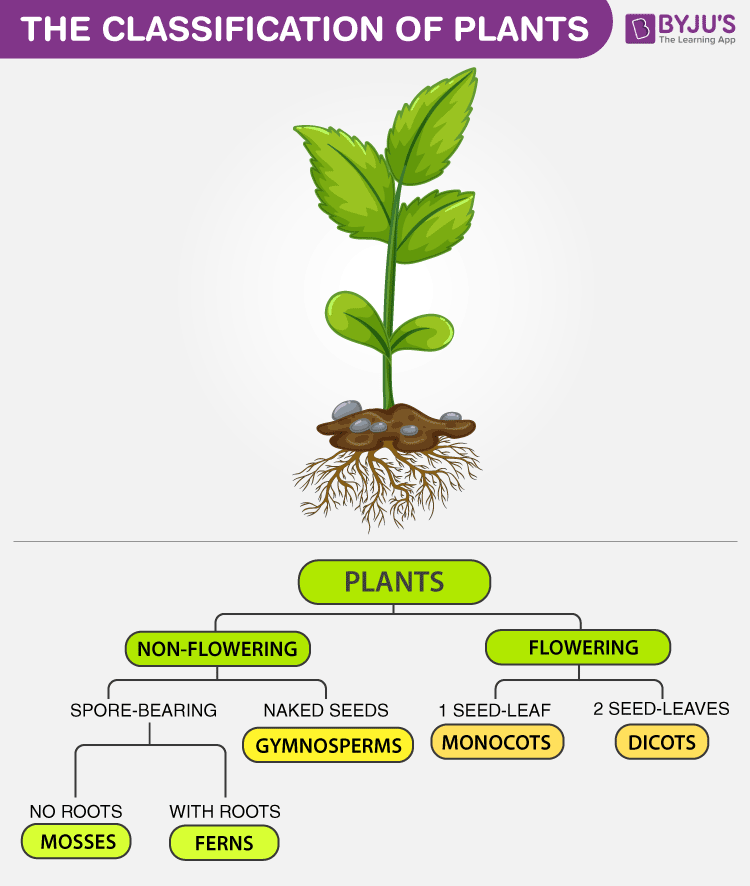
Classification Of Plants
However, from a biological perspective, plants can be classified as:
Classification based on Life Cycle
Plant species can be classified based on their life cycle.
Annuals
These are plants that complete their life cycle during a single season. They are normally herbaceous. Examples like corn, rice, wheat, and pulses are annuals plant.
Biennials
These are plants that require two years to complete their life cycle. They are normally herbaceous. For example, carrot, cabbage, onions, and beetroot are biennials plant.
Perennials
These are plants that have a long lifespan – typically more than two years. They are characteristically woody or herbaceous. Rose, lavender, dianthus, and lilies are prominent examples of perennials.
Taxonomic Classification Of Plants
Taxonomy is a system for classifying plants based on their genetic and evolutionary relationship. Plant Taxonomy is a branch of science that continues to change as new species are being found almost every day.
Plants are classified into a separate kingdom called the Kingdom Plantae. This current system of classification of plants is based on the evolutionary relationship amid other plants.
Coniferophyta (Gymnosperms)
It is a group of plants which is primarily evergreen and are native to the temperate zone. There are about 700 species discovered to date. They are vascular, non-flowering plants which produce seeds without the production of flower and fruits. Some common examples of gymnosperm include pines, cycads, cedars, etc.
Anthophyta (Angiosperms)
They can grow into big trees as well as small shrubs, bushes and herbs. The angiosperms are distributed all over the world (>250,000 species). Most of the plants that we see around us are grouped under this division.
Angiosperms are characterised by the seeds that are fully enclosed in fruits. They are subdivided into- Monocotyledonous and Dicotyledonous. Some common examples of angiosperms include mango trees, roses, jasmine, marry gold, etc.
Monocotyledons
Monocotyledonous plants are commonly referred to as monocot plants. They are flowering plants with seed containing one cotyledon. The venation pattern of their leaves is parallel-veined. Some common examples of monocot plants are rice, corn, sugarcane, tulips, onion, etc. There are around 50,000 species of monocotyledonous plants discovered to date.
Dicotyledons
Dicotyledonous plants are commonly referred to as dicot plants. They are flowering plants, mostly grown as herbs, shrubs, and trees with the seed containing two cotyledons. The venation pattern of their leaves radiates from a central main vein. Some common examples are figs, eucalyptus, potato, tomato, hibiscus, etc. There are around 200,000 species of dicotyledonous or dicots plants.
Also Explore: Difference Between Monocotyledon and Dicotyledon.
Importance of Plant Classification
The main purpose of classifying plants is to ensure that the right plants are correctly named, grouped and identified.
Plants are classified based on these 3 characteristics:
- The evergreen plants are plants that retain leaves at all times (all year round).
- Woody plants can also be grouped as deciduous or evergreen.
- Deciduous plants are seasonal plants which shed its leaves at the end of the growing season, either during the winter season in the temperate climate or during the dry season in the tropical climate.
Explore more: Angiosperms and Gymnosperms
To learn more about the plant types and classification of plants, explore BYJU’S Biology.

Frequently Asked Questions on The Classification Of Plants
What are vascular plants?
The vascular plants are a large group of terrestrial plants, which have specialized tissues for conducting water and nutrients to different parts of plants. All plants including the members of the Phylum Pteridophyta, Gymnosperms, and Angiosperms are classified as vascular plants.
What are Gymnosperms?
Gymnosperms refer to those plants which have naked seeds. Overall, there are about 600-650 different types of gymnosperm plants.
What are the examples of Angiosperms?
Mustard plants, oak trees, pea plant and lilies are the best examples of Angiosperms.
List out the classification of plants based on their life cycle?
Based on their life cycle, plants are further classified into:
Annuals
Biennials
Perennials.
What are the examples of Monocotyledonous?
Monocotyledonous plants are also referred to as the monocot plants. There are around 40 to 50,000 species of monocotyledonous plants. Examples of monocot plants are corn, onion, sugarcane, tulips, rice, etc.
What are the examples of Flowering and Non-flowering Plants?
Rose, Tulips, Jasmine, Marigold are examples of flowering plants. Cedars, Redwoods, Pines are examples of non-flowering plants.

Thanks for helping me goodbye 😃😃😃😃😃😃😃
good word i enjoyed to cover my work
I find it helpful. Thanks
Nice classification.
Thank you for giving real information
Thank you so much! For notes☺️☺️
It has been very helpful thanks
It is a good resource l would recommend this piece to anyone in the world
It helped me a lot in my internals project and also gave me a lot of facts. Thank you so much
god bless you for helping us.
thank u.
Thanks a lot