The group 17 of the modern periodic table consists of:
-
Fluorine
-
Chlorine
-
Bromine
-
Iodine
-
Astatine
These elements are known as the halogens. The word Halogen is a Greek word which means salt producer. These elements are called salt producers because chlorine, bromine, and iodine are highly electronegative in nature and form anions that constitute the anionic part of salts found in the seawater. The last element of the group, astatine is radioactive in nature. All these elements belong to the p block of the modern periodic table. After the alkali group, the halogen family constitutes the most homogenous group in the modern periodic table.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Halogens
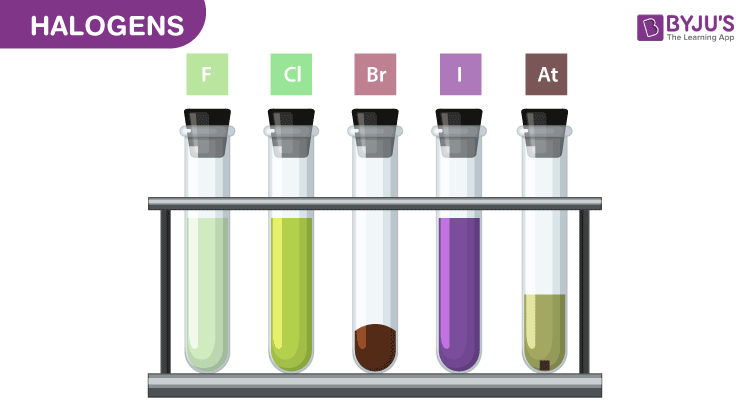
Halogens show very smooth variations in their physical properties. Fluorine and chlorine are in the gaseous state, bromine in liquid and iodine in the solid state. The melting and boiling point of halogens increases with increase in the atomic number of the element. All the members of the halogen family are coloured. This happens due to the absorption of the radiation in the visible region which results in the excitation of the electrons in the outer shell to higher energy levels. They absorb different quanta of radiation, hence display different colours. We have fluorine which is yellow, chlorine is greenish yellow, bromine is red and iodine is violet. Fluorine and chlorine react with water. Bromine and iodine are sparingly soluble in water but are highly soluble in other organic solvents such as chloroform and carbon disulphide.
The halogens generally exhibit -1 oxidation state but chlorine, bromine, and iodine also exhibit +1, +3, +5 and +7 states. The higher oxidation state of halogens is obtained only when they are in combination with highly electronegative atoms of fluorine and oxygen. The halogens are highly reactive in nature. They often react with metals and non-metals to form halides. The reactivity of halogen family decreases as we move down the group. Halogens readily accept electrons as they are short of one electron to form an octet. Hence, they have strong oxidizing nature. Fluorine is the strongest oxidizing agent in the halogen family and it oxidizes other halide ions in the solution.
| Period | Element | Symbol | Atomic Number | Electronic Configuration |
| 2 | Fluorine | Fl | 9 | [He] 2s2 2p5 |
| 3 | Chlorine | Cl | 17 | [Ne] 3s2 3p5 |
| 4 | Bromine | Br | 35 | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p5 |
| 5 | Iodine | I | 53 | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p5 |
| 6 | Astatine | At | 85 | [Xe]4f14 5d10 6s2 6p5 |
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Why halogens are coloured?
Why are halogens strong oxidising agents?
What elements are called halogens?
Which halogen is radioactive?
Which halogen is a liquid at room temperature?
Give an example of an interhalogen compound.
IF7 is an example of an interhalogen compound.
Click to learn about the oxidation state of Group 17 elements and their properties. Download BYJU’S the learning app to experience whole new technique to understand Chemistry.

Comments