Table of Content
What is Globalisation?
The term globalisation refers to the integration of the economy of the nation with the world economy. It is a multifaceted aspect. It is a result of the collection of multiple strategies that are directed at transforming the world towards a greater interdependence and integration.
It includes the creation of networks and pursuits transforming social, economical, and geographical barriers. Globalisation tries to build links in such a way that the events in India can be determined by the events happening distances away.
To put it in other words, globalisation is the method of interaction and union among people, corporations, and governments universally.
Also Check: Important Questions for Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation
Effect of Globalisation in India
India is one of the countries that succeeded significantly after the initiation and implementation of globalisation. The growth of foreign investment in the field of corporate, retail, and the scientific sector is enormous in the country.
It also had a tremendous impact on the social, monetary, cultural, and political areas. In recent years, globalisation has increased due to improvements in transportation and information technology. With the improved global synergies, comes the growth of global trade, doctrines, and culture.

Globalisation in the Indian economy
Indian society is changing drastically after urbanisation and globalisation. The economic policies have had a direct influence in forming the basic framework of the economy.
Economic policies established and administered by the government also performed an essential role in planning levels of savings, employment, income, and investments in the society.
Cross country culture is one of the critical impacts of globalisation on Indian society. It has significantly changed several aspects of the country, including cultural, social, political, and economical.
However, economic unification is the main factor that contributes maximum to a country’s economy into an international economy.
Also Read: What are Economic Reforms?
Advantages of Globalisation in India
Increase in employment: With the opportunity of special economic zones (SEZ), there is an increase in the number of new jobs available. Including the export processing zones (EPZ) centre in India is very useful in employing thousands of people.
Another additional factor in India is cheap labour. This feature motivates the big companies in the west to outsource employees from other regions and cause more employment.
Increase in compensation: After globalisation, the level of compensation has increased as compared to the domestic companies due to the skill and knowledge a foreign company offers. This opportunity also emerged as an alteration of the management structure.
High standard of living: With the outbreak of globalisation, the Indian economy and the standard of living of an individual has increased. This change is notified with the purchasing behaviour of a person, especially with those who are associated with foreign companies. Hence, many cities are undergoing a better standard of living along with business development.
| You Might Also Like To Read: |
Impact of Globalisation
Outsourcing: This is one of the principal results of the globalisation method. In outsourcing, a company recruits regular service from the outside sources, often from other nations, that was earlier implemented internally or from within the nation (like computer service, legal advice, security, each presented by individual departments of the corporation, and advertisement).
As a kind of economic venture, outsourcing has increased, in recent times, because of the increase in quick methods of communication, especially the growth of information technology (IT).
Many of the services such as voice-based business processes (commonly known as BPS, BPO, or call centres), accountancy, record keeping, music recording, banking services, book transcription, film editing, clinical advice, or teachers are being outsourced by the companies from the advanced countries to India.
Debate on Globalisation
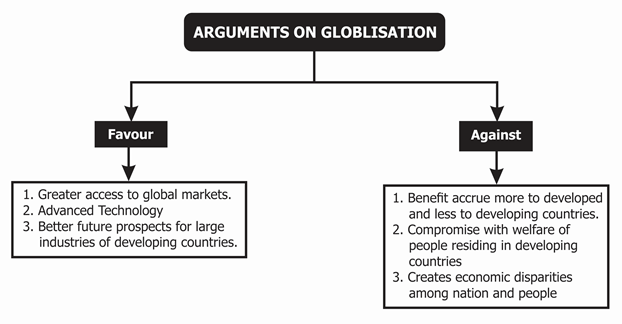
| Also, Explore: |
Solved Questions.
| Q.1- What do you understand by the term ‘globalisation’? |
| (A)Meaning |
|
| (B)Aim |
|
| Q.2- List some arguments in favour and against globalisation. | |
| (A) In favour of globalisation
|
Globalisation resulted in the following:
|
| (B) Against globalisation
|
Globalisation has been criticised by some scholars because according to them:
|
| Important Topics in Economics: |
| Q.1- ______________means integrating the Indian economy with the world economy. |
| a. Liberalisation
b. Privatisation c. Globalisation d. None of the above |
| Q.2-Globalisation is the outcome of__________ and ________. |
| a. Liberalisation
b. Privatisation c. Globalisation d. Both (a) and (b) |
| Q.3- Globalisation aims to create ____________ world. |
| a. Limited
b. Restricted c. Borderless d. None of the above |
For more data on Economics Class 11 Syllabus, commerce notifications and sample papers for Class 11 commerce, stay tuned to BYJU’S.
Frequently Asked Questions on Globalisation
What are the different kinds of globalisation?
The top five types of globalisation are:
1. Financial globalisation.
2. Economic globalisation.
3. Technological globalisation.
4. Political globalisation.
5. Cultural globalisation.
What are examples of Globalisation?
The two examples of globalisation are as follows:
1. Travel: The capacity to travel to other places and experience their cultures.
2. Transportation: The international transportation systems, such as air travel and shipping.
What is the importance of Globalisation?
Globalisation is important to expand the markets and enable a business to make a sensible utilisation of the available resources. It also solves various issues of an individual and the nation, giving them many options to choose from and satisfy their needs. Globalisation boosts exports, discourages import, and uplifts foreign exchange.
What are the main reasons that caused Globalisation?
The main reason that caused globalisation are as follows:
1. Making global travel easier by improving transportation.
2. Advanced technology made communication and sharing of information easier.
3. Minimised tariff barriers and encouraged global trade.
4. Broadening of global media.
What are the positive impacts of Globalisation?
The four positive impacts of globalisation are as follows:
1. Creates efficient markets
2. Increases competition
3. Stabilises security
4. Increases wealth equality across the world
Nice
Very helpful and nice way of explanation
I am so happy with your way of explaination of every topic.
This is very helpful for us. It explains everything so well.
It is very helpful for us and very easy to understand all the things
It is very helpful for us.
amazing notes