Table of Contents:
A. GS1 Related:
B. GS2 Related:
1. Remission power lies with State: SC
2. China tests prototype of fifth-generation fighter jet
C. GS3 Related:
1. India needs lower taxes, higher compliance
2. Agni-V test-fired again from mobile-launcher
D. GS4 Related
E. Important Editorials : A Quick Glance
1. Time to repeal the The Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010
1. 2017 and beyond, let’s get digital
F. Concepts-in-News: Related Concepts to Revise/Learn:
G. BILLS/ACTS/SCHEMES/ORGS IN NEWS
H. Fun with Practice Questions 🙂
I. Archives
.
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Useful News Articles
A. GS1 Related
B. GS2 Related
Category: Polity and Governance
Topic: Union and State Executive
Key Points:
- The Supreme Court has held that the power to grant remission is exclusively that of the State government and not the judiciary,
- The judgment is also in sync with the Tamil Nadu government’s review petition on the question of who has the actual authority — the Centre or the State — in granting remission for seven life convicts in the Rajiv Gandhi assassination case.
- TN government has sought a review of the Constitution Bench verdict, arguing that the State government is the most competent in deciding whether a life term convict deserves to be granted remission.
- The Constitution Bench had earlier held that the Centre and not the State enjoys “primacy” in deciding whether the life convicts in the former PM’s assassination case should be granted remission.
Category: International Relations
Topic: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
Key Points:
- China has tested an improved version of its fifth generation stealth fighter which was previously known as the J-31, the twin engine, radar evading aircraft under development by Shenyang Aircraft Corp.
- The Chinese stealth fighter has strategic significance for India as besides China, Pakistan – which is already producing JF-17 Thunder fighter jet along with Beijing – has already shown a lot of interest in acquiring the stealth fighter.
- The new FC-31 is equipped with state-of-the-art instruments such as electro-optical targeting system and helmet-mounted display and sight system. It seems to have better stealth capabilities, improved electronic equipment and a larger payload capacity.
- China intends to use the FC-31 to capture market share at home and as well as abroad and the company is giving a big push to attract potential foreign buyers with its medium-sized stealth fighter planes.
- China also plans to use the FC-31 to the western monopoly on the fifth-generation fighter jet technology.
C. GS3 Related
Category: Indian Economy
Topic: Taxation
Key Points:
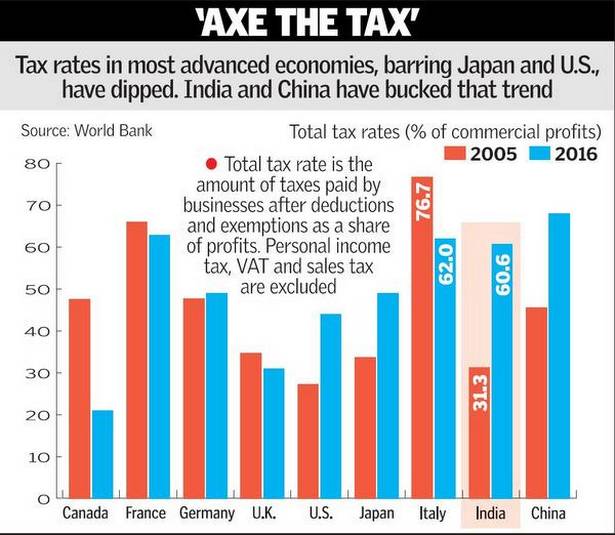
- India needs lower taxation to compete globally and that voluntary compliance of tax by citizens should be encouraged by a citizen friendly administration.
- Payment of legitimate taxes to the government is part of a citizen’s duty, and non-payment of due taxes invites severe consequences.
- In India, “extraordinarily high taxation rates in the past” have encouraged people to evade payment of taxes. A lower level of taxation is required, to provide services that are more competitive in nature.
- The government foresees an India where voluntary tax compliance increases. Tax authorities are generally judged by the quality of what they write or decide. The quantum of fairness followed by authorities will define the quality of interpretation of tax laws by the authorities. The voluntary compliance by citizens via payment of due taxes need must be reciprocated by authorities through a citizen-friendly administration.
Category: Science & Technology
Topic : Defence
Key Points:
- The test-launch of India’s most formidable ballistic missile, Agni-V, from the Abdul Kalam Island, off the Odisha coast, was a remarkable success, and clearly signaled that India’s nuclear deterrence capability has indeed come of age.
- This is the 4th consecutive success for Agni-V, which can deliver a nuclear payload weighing about 1.5 tonnes over a distance of 5,000 km and beyond.
- It was the 2nd time that Agni-V was fired from a canister mounted on a TATRA truck parked on the Island. A gas generator located at the bottom of the canister kicked out the long-range, 3-stage, surface-to-surface ballistic missile that weighs around 50 tonnes, is 17 mts long and is 2-mts in diameter.
- A missile launched from a canister mounted on a road-mobile launcher gives it a great degree of operational flexibility. This means it can be launched literally from a road in a city, after stopping the traffic, giving it a very quick reaction time. The missile can be made vertical in 3 minutes and the actual launch takes a few more minutes. After lift-off, the truck can speed away.
- During the launch, the 2 stages jettisoned and the missile accelerated as it plunged back towards the earth. All re-entry systems worked perfectly. The heat-shield made up of carbon-carbon composites and encasing the dummy warhead, withstood a temperature of about 4,000 degrees Celsius. The on-board computer guided the missile towards its impact point in the southern Indian Ocean. After a 20-minute flight, it fell near the Australian waters.
- The set of five Agni’s form the bulwark of India’s nuclear deterrence and second strike capability. While Agni-I has a range of 700 km, Agni-II 2,000 km, and Agni-III 3,000 km, Agni-IV can take out targets 4,000 km away.

D. GS4 Related
E. Important Editorials: A Quick Glance
Category: Polity and Governance
Topic: Bills, NGO’s
Key Points:
- The Union Home Ministry recently rejected the license renewal applications, under the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010 of 25 NGO’s.
- Most of the affected organizations are rights-based advocacy groups, with some involved in human rights field.
- The government has defended its actions by claiming that these NGOs had violated the norms of FCRA by engaging in activities detrimental to public interest. But its decision has invited criticism from different quarters.
- Civil society members have condemned the move and accused the government with “abuse of legal procedures”. The National Human Rights Commission has issued a notice to MHA
- The original FCRA was enacted in 1976 by the Indira Gandhi-led government during the Emergency phase. It prohibits electoral candidates, political parties, judges, MPs and even cartoonists from accepting contributions from foreign sources. Its intent was clearly to clamp down on political dissent.
- The justification given for the law was to prevent foreign interference in domestic politics. It was the Cold War era, when both the Soviets and the Americans meddled in the internal politics of post-colonial nations to further their strategic interests. Amidst suspicions of the ubiquitous ‘foreign hand’ in stoking domestic turmoil, the FCRA was aimed at preventing political parties from receiving funding from foreign sources.
- But India embraced foreign funding by opening up its economy in 1991. The Indian state had no issues in accepting contributions from foreign sources such as the World Bank or the IMF. With the state itself wooing foreign investment, Indian businesses and political parties too, helped themselves to foreign funds.
- There are 3 major changes that make the new Act more stringent than the old one. Firstly, FCRA registration under the earlier law was permanent, but now under the new one, it expires after 5 years, and has to be renewed afresh. This instantly hands the government with a whip to bring errant NGOs to its heels.
- Second, the new law puts a restriction (50%) on the proportion of foreign funds that could be used for administrative purposes, thus allowing the government to control how a civil society organisation (CSO) spends its funds.
- The third and the most important distinction is that while the 1976 law was largely aimed at political parties, the new law shifts the focus to “organizations of a political nature”. The FCRA Rules, 2011 has enabled the government to target inconvenient NGOs, especially those working on governance accountability.
- The UN Special Rapporteur on the Rights to Freedom of Peaceful Assembly and of Association undertook a legal analysis of the FCRA, 2010 and it has stated in its report that the FCRA provisions and rules “are not in conformity with international law, principles and standards”. Right to freedom of association is part of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (article 20), a violation of this right clearly constitutes a human rights violation.
- NGO funding has to be regulated. One cannot deny the fact that corrupt NGOs exist, or that unscrupulous NGOs that access foreign funds may serve as conduits for money laundering purposes. But there are much better ways to address these concerns than an act that institutes an ‘Inspector Raj’ for the NGO domain.
- It is high time to repeal the FCRA and revive the idea of an autonomous, self-regulatory body for CSOs.
Business Line
Category: Science & Technology
Topic: Artificial Intelligence
Key Points:
- The rise of AI: Artificial intelligence (AI) isn’t coming — it’s already here. 2016 saw many consumer-facing autonomous services hit a tipping point — self-driving cars, AI-powered chatbots, etc. AI is all set to move from consumer-focused used cases to the real enterprise world in 2017 and hit us hard. Over the next few years, every aspect of our commercial world will be affected by the new machines.
- AI will be the number one driver of business change in 2017 and beyond. AI-led automation will accelerate the pace of modernisation in middle- and back-office operations, thereby truly digitising the fundamental operational blocks. Big data is an enabler for AI because it provides the necessary capacity for learning algorithms to consume data and use it to make strategic decisions.
- Internet of Things (IoT) in Asia Pacific is set to explode to 8.6 billion devices by 2020, growing from a current annual market of $250 billion to $583 billion in 2020.
- The IoT is still evolving when it comes to standardisation, and presents data privacy and security risks. More connected devices mean exponential growth in the amount of personal and sensitive data generated. A single security breach on one device could infect an entire network, considering that multiple devices are interconnected on a home or business network.
- Cyber-attacks are estimated to cost businesses as much as $400 billion annually — larger than the GDP of roughly 160 of the 196 countries in the world. Alarm bells are already ringing with recent reports of cyber-attacks launched through connected refrigerators and malicious e-mails sent via household appliances. IT departments and CIOs/CISOs who have not kept up with security standards in the region will fall behind in ways that will be nearly impossible to make up in the dynamic digital security landscape. The IoT security role within IT departments will be a reality soon, if it isn’t already
PIB:
Category: Polity and Governance
Topic: Government Initiatives
Key Points:
Following are the main highlights of the activities of the Department of Food & Public Distribution during the year 2016:
- National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013:
The National Food Security Act (NFSA) was enacted in 2013 and was being implemented in only 11 States/UTs in May, 2014. During 2016, special attention was given for its implementation wherein remaining States/UTs were constantly pursued through meetings, conferences, video conferences (VCs), correspondence, visits etc. to expedite implementation of the Act. As a result, 13 more States/UTs joined NFSA during the year and the Act is now being implemented in all the States/UTs and covers about 80 crore persons under the Act.
For the first time under the NFSA, Rs.2200 crore has been released to State Governments as Central assistance to meet the expenditure incurred on intra-State movement of food grains and fair price shop dealers’ margins. Under erstwhile TPDS, State Governments were required to either meet this expenditure on their own or pass it on to beneficiaries.
- Major Reforms in TPDS:
Sustained efforts have resulted in significant reforms in TPDS making it more transparent and leak proof and better targeting of food subsidy. Cash Transfer for food grains under Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) scheme has been implemented in 3 UTs.
- Improving Food grain Management:
- FCI has developed a software for Online Procurement Management System (OPMS) which is being used for procurement
- Under Riverine movement of foodgrains, FCI moved 2267 MT foodgrains to Tripura via Bangladesh during August, 2016 to September, 2016 from Kolkata.
- A quantity of 20,000 metric tonnes of par-boiled rice has been exported to Egyptian Government on Government to Government basis out of Central Pool Stock. The export was done in the interest of diplomatic gain for India.
- Improving Storage:
A road map for creation of 100 Lakh MT storage capacity in the form of Steel Silos by FCI and other agencies including State Governments on PPP mode for wheat and rice has been approved.
- Reforms in Sugar Sector:
- Sustained surplus production over domestic consumption in the past 5 sugar seasons had led to subdued sugar prices, which had stressed the liquidity position of the industry throughout the country leading to build up cane price arrears.
- To mitigate the situation, Government has taken the following measures:
- Extended financial assistance of Rs.4305 crore directly credited to farmers account on behalf of sugar mills through banks. About 32 lakh farmers have been benefited.
- Facilitated supply of ethanol under EBP programme by fixing remunerative price and waiving off excise duty on supply of ethanol during sugar season 2015-16.
- A comprehensive performance based production subsidy has been extended to farmers against their cane dues contingent on mills undertaking export and supplying of ethanol.
- Ethanol Blending Programme (EBP) has achieved historical success as supplies of ethanol during the current year have reached record level of more than 110 crore litres which has never been achieved earlier.
- Policy Changes:
Fortification of Staple Food
To address acute malnutrition in the population, a strategy of Fortification in Food has been adopted. As a consequence of inputs and proactive initiatives taken by DFPD in consultation with all Stakeholders, FSSAI has operationalized the standards for fortification of Wheat Flour, and Oil w.e.f. 16th October, 2016. Technology & cost for rice fortification are under review.
Wheat-Rice Policy
Government of India formulated a wheat-rice policy in June 2016 with an objective that the States, which annually procure more wheat or rice than their present annual entitlement/demand for wheat and rice respectively, will be allocated the preferred food grains as per their requirement in the normal NFSA allocation i.e. AAY and Priority category. The allocation in the tide over category will be at the discretion of the Department and subject to availability of food grains in the Central Pool and impact on food subsidy.
F. Concepts-in-News: Related Concepts to Revise/Learn:
- Agni V
- Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010
- Remission
G. BILLS/ACTS/SCHEMES/ORGS IN NEWS
Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010
National Food Security Act
H. Fun with Practice Questions 🙂
Question 1: Which of the following committees dealt with Public Distribution Security - PDS reforms?
b) Shantha Kumar committee
c) Ratan Watal committee
d) Santhanam committee
Question 2: ‘Internet of things’ (IoT) appears in news. It is related to?
b) Virtual Private Network
c) Cloud Computing
d) Artifical Intelligence
Question 3: Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the ‘Agni-V’ missile?
-
(i) It is developed by DRDO
(ii) It is an inter-continental missile with an operational range of 5000-7000 kms
(iii) It uses both solid and liquid propellants
a) (i) only
b) (i) and (ii) only
c) (ii) and (iii) only
d) All 3 are correctly matched
Question 4: Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Pardoning powers of the President of India?
- The President shall have the power to grant pardons, reprieves, respites or remissions of punishment or to suspend, remit or commute the sentence of any person convicted of any offence.
- The President shall have the power to suspend, remit or commute a sentence of death.
a) (1) only
b) (2) only
c) Both (1) & (2)
d) Neither (1) nor (2)
Question 5: Which of the following statements are true?
-
(i) India ratified the Convention on Supplementary Compensation for Nuclear Damage (CSC)
(ii) India has passed its own domestic nuclear liability law, the Civil Law for Nuclear Damage (CLND) Act in 2010
a) (i) only
b) (ii) only
c) Both (i) and (ii)
d) Neither (i) nor (ii)
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Online Current Affairs Crash Course’.
Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
I. Archives:
You can check out some more recent News Analysis sections to build even more context
Practice More: Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series

Comments