Table of Contents:
A. ECONOMY
2. Local steel may become a must for $59-bn. infra spend
3. Government has conveyed concerns on H-1B visa to the US
B.SOCIAL ISSUES
2. India first in bribery rate, says global NGO
3. Supreme Court opens surrogacy window for singles
C.ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
1. Law to regulate use of air conditioners
2. Need to make people aware about the negative impact of Arsenic
D. TERMS OF THE DAY
E. Fun with Practice Questions 🙂
F. Archives
************************************************************************************************************
.
************************************************************************************************************
Useful News Articles for UPSC Current Affairs
A. ECONOMY
Objective:
It allows entrepreneurs and skilled professionals greater freedom to work across the Commonwealth.
Key Points:
- Under the APEC scheme, which includes 19 fully participating countries, including Australia, Hong Kong, Russia and Singapore, business travellers are able to apply for five-year-long, short-term, multiple-entry permits to other member states, freeing them from the need to apply for visas every time they travel.
- The lack of formal mechanisms to promote trade and investment has been a challenge but the fundamentals and ‘Commonwealth Factor’ remain strong and the trade ministers meeting is a positive step towards unlocking the potential.
- Another focus area would be on the ease of doing business and the implementation of the WTO facilitation agreement, which came into force on February 22.
- A united Commonwealth which takes advantage of commonwealth countries’ historic ties can be extremely beneficial.
- India may soon mandate the use of local steel in government infrastructure projects worth billions of dollars, sources said, pitching it as a WTO-compliant protectionist measure aimed at further cutting cheap imports, mainly from China.
- The government expects the move to boost sales of local companies such as JSW Steel and Tata Steel, and eventually attract global steelmakers such as Arcelor Mittal and POSCO to invest in the country.
- India, the world’s third-largest steel consumer, has budgeted a record $59 billion for 2017-18 for steel-intensive infrastructure projects such as ports, roads, railways and power.
- The preference in procurement will enhance demand and thus production. Definitely it is ‘Make in Steel’ and thus ‘Make in India.
What WTO Rules says:
- The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade of the World Trade Organisation, allows an exception to “procurement by governmental agencies of products purchased for governmental purposes and not with a view to commercial resale or with a view to use in the production of goods for commercial sale.
Conclusion
- The protectionist move would shrink foreign companies’ sales in the world’s fastest growing steel market.
- Indian IT companies are servicing more than 75% of Fortune 500 companies.
- The government has conveyed its concerns at a ‘very senior level’ in the US administration on the move to curb H-1B visa processing.
- Under the current system, companies submitting applications for H-1B visas for potential employees can pay an additional sum for expedited service, which is known as premium processing.
- The temporary suspension could last up to six months, according to the US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). The H-1B visas are widely used by Indian IT companies.
- The Indian companies have created four-lakh jobs, not only in America but other parts of the world, Prasad said adding that the Indian IT companies and IT professionals are giving lot of opening to American companies in India too.
- The US said last week that it will temporarily suspend premium processing of H-1B visas from April 3, eliminating the option of shorter waiting period for the programme that helps highly skilled foreigners work at American firms.
- Premium processing costs an additional $1,225 and ensures a response from the USCIS within 15 days or the fee is refunded. Processing of standard H-1B applications takes between three and six months.
B. SOCIAL ISSUES
BACKGROUND
- Women in India are being forced out of the workforce.
- India and Pakistan have the lowest rates of women labor force participation in Asia, says International Labor Organization (ILO).
- Nepal, Vietnam, Laos and Cambodia that have the highest, while richer nations like Singapore, Malaysia and Indonesia falling in between.
- Moreover, labor force participation in India seems to be declining.
- The National Sample Survey found that while in 1999-2000, 25.9% of all women worked; by 2011-12 this proportion had dropped to 21.9%.
- Of the 185 nations that are part of the ILO database, since the 1990s, 114 countries have recorded an increase in the proportion of women in the workforce, and only 41 recorded declines, with India leading the pack.
Access Based on Equality and its Consequences
- Optimistic point of view: with rising incomes, women have the opportunity to escape harsh labor in farms and on construction sites, and focus on their families.
- pessimistic and realistic explanation: with declining farm sizes, increasing mechanization, and consequently waning labor demands in agriculture, women are being forced out of the workforce.
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) has brought more rural women into wage labor.
- Increased availability of wage work also enhances women control over household decision-making.
Drawbacks
- A solution needs to be created for inconsistency in MNREGA. First, in view of shrinking farm work, we need to create opportunities for women to move from agricultural to non-agricultural manual work. Second, we must foster a work environment that allows more women, especially urban and educated women, to take up salaried jobs. Thirdly, villages where roads can be constructed, both men and women were more likely to undertake non-agricultural work but this effect was greater for women.
- Prevalence of a rigid work environment in India and the dearth of family-friendly work institutions create hurdles to women access to white-collar jobs.
- Long distances between the home and the workplace increase both commuting time and work burdens, leaving workers with even less time for family duties
- Skewed work-family equation for women in India is the demand for investing in children’s education over professional achievement.
- Considering the contrast between the reasons for fertility decline in the West, where it was fueled by the desire for self-fulfillment among both men and women, and in India, where small families have emanated from the desire to promote future achievements of children by focusing on their education rather than on better employment prospects for the parents.
Sharing the burden
- Before the influx of global firms in India, work structures in Indian companies and even the government were highly inflexible.
- Indian firms have chosen to follow the American model with demands for extended work hours as well as attendance on Saturdays and Sundays. This creates a time bind for both men and women where something must give.
- Work-family balance requires increased participation by men in household chores and caring for children. Now it is the self-motivation required as the American model of work facilitates the quality time.
Government Reports
- The Economic Survey 2016-17 expressed concern that the demographic dividend is already receding.
- Reducing the opportunity for the Indian economy to catch up with its East Asian counterparts.
- The consequences of reducing obstacles to women full economic participation far exceed the demographic advantages of having a larger pool of young workers.
- Thus talk of the gender dividend rather than the demographic dividend is the need of the hour.
- Survey conducted among 16 Asia-Pacific nations by Transparency International between July 2015 and January 2017.
- India had the highest bribery rate (69%), Vietnam follows with 65%, Thailand 41% and Pakistan 40%. China reported a much lower 26%.
- Japan had the lowest incidence of bribery at 0.2 per cent. South Korea and Australia recorded 3% each, Hong Kong 2% and Taiwan 6%.
- Bribes for various public services range from services in public schools and hospitals and for getting IDs, voter cards and permits and accessing utilities to the police.
- 31% to 45% said they paid bribes for court services as well.
- “More than one in four people paid bribe, when accessing basic services like medicine, education or water,” the survey said.
- Over a third said that their legislative representatives, officials and local councilors were highly corrupt (from 35 to 37 per cent).
Present Scenario
- Draft Surrogacy (Regulation) Bill 2016, allows only infertile, legally-wedded Indian couples to avail this option.
Current considerations
- Supreme Court Bench led by Justice RanjanGogoi allowed a representation to be made before the parliamentary committee to consider including a “specific provision” in the Bill so as to facilitate single persons also to embrace parenthood through surrogacy.
- The new Bill is to constitute a National Surrogacy Board, State Surrogacy Board and appointment of authorities for regulation of practice and process of surrogacy.
Objective of the Bill
- The law is meant to end commercial surrogacy or, as the Supreme Court had once in 2009, termed “fertility tourism” in the country.
Ethical Issues Involved
- Commercial surrogacy and the treatment of babies as a “commodity” is the biggest fear prevailing.
- Abandonment of the infants (Unplanned couplets, girl child) as seen earlier with respect to Australian couple.
- Issues with respect to citizenship of the child.
Cautious Steps to be taken
- There should be a separate register maintained for surrogate children.
- Sensitized staff should conduct inspections on the ground to prevent exploitation.
Way forward
- The draft Bill should also consider the categories other than married Indian couples, like single women or men, gay or lesbian couples and such others.
- The Bill does not allow married couple, who have children, adopted or surrogate or biological, to have children via surrogacy. Such consideration can strengthen the genetic pool.
C. ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
What’s in news?
- The Union Environment Ministry is coming up with a law that will require-commercial spaces, airports, offices-to ensure that air conditioners function at pre-set temperatures.
Why in news?
- At several places, air conditioners are set to extremely low temperatures-irrespective of whether the weather required it to be so- and thereby consuming an excess of electricity.
Advantages
- Saving electricity, which in a way lead to saving environment since electricity generated using thermal station requires mining of coal.
- Helps in attaining global standards of curtailing HCFC’s (Hydrochlorofluorocabon) use.
Practice elsewhere
- In Japan, there are regulations that require air-conditioners be set at a specific temperature depending on the season.
- Regulations’ which allows employees to wear casuals instead of formal business-wear.
Facts review
- India is under progress to phase out hydrochlorofluorocarbons which are widely used in refrigerants and air conditioners and has agreed to stop the use of HCFCs by 2030
- India is one of the largest consumers of HCFC’s after china.
What’s in news?
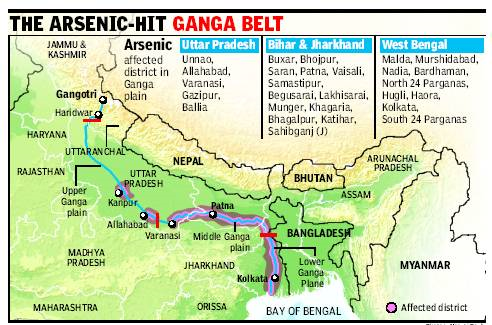
- Union Minister of Water Resource Development and Ganga Rejuvenation, has underlined the need to make people aware about the negative impact of Arsenic in Ganga basin area.
- High value of arsenic in groundwater is geogenic in nature, but as a large population is dependent on groundwater resources for drinking purposes in Ganga basin and is under the risk of health hazards, it becomes emergent to go for mitigation measures as well as alternate sources of water so that locals can be protected from negative impact of arsenic in groundwater.
- Awareness of public on water quality especially about poisonous arsenic contamination need to be done and making available alternate source of water with efforts of central and state governments as well as organizations and NGOs working in the field of groundwater.
Facts review
- Arsenic in ground water is a geogenic contaminant i.e. caused by natural geologic processes.
- Arsenic-containing groundwater in Ganga River basin is hosted by the sediments deposited by the rivers during the late Quaternary or Holocene age (<12 thousand years).
- Incidence of high arsenic in groundwater reported from various parts of the country, particularly in the Ganga- plains is a serious threat to the health of human being. Over the last three decades, numerous measures have been initiated which includes alternate arrangement for supply of arsenic free water to the affected populace and providing arsenic removal plants.
- Arsenic occurrences in ground water in these areas are highly sporadic in nature and all the sources in these areas are not necessarily contaminated.
Mitigation measure
- Technological options to combat arsenic menace, in groundwater, to ensure supply of arsenic free water, in the affected areas can be in-situ remediation of arsenic from aquifer system, ex-situ remediation of arsenic from tapped groundwater by arsenic removal technologies.
- Use of surface water source as an alternative to the contaminated groundwater source, tapping alternate safe aquifers for supply of arsenic free groundwater or combination of above techniques.
- Out of the above options, arsenic removal technologies and ex-situ treatment technique are being practiced widely to provide potable water to the people in the arsenic affected areas after treatment of contaminated groundwater. Their large scale use in West Bengal, based on different operating principles, with various degrees of success and failure, has been reported.
D. TERMS OF THE DAY
- Alternaria is a genus of ascomycete fungi.
- Alternaria species are known as major plant pathogens.
- They are also common allergens in humans, growing indoors and causing hay fever or hypersensitivity reactions that sometimes lead to asthma.
- At least 20% of agricultural spoilage is caused by Alternaria species; most severe losses may reach up to 80% of yield, though. Many human health disorders can be caused by these fungi, which grow on skin and mucous membranes, including on the eyeballs and within the respiratory tract.
- Botrytis cinerea is a necrotrophic fungus that affects many plant species, although its most notable hosts may be wine grapes. In viticulture, it is commonly known as botrytis bunch rot; In horticulture, it is usually called grey mould or gray mold.
E. Fun with Practice Questions 🙂
Question 1: Which among the following is a greenhouse gas?
- Water Vapor
- Carbon Dioxide
- Ozone
- Hydroflourocarbons
Choose the correct answer
a) 1,2 and 3.
b) 1 and 2
c) 1 and 3
d) All are correct.
Question 2: Consider the following statement with respect to Hydro fluorocarbon (HFC’s)
- HFC’s pose no harm to Ozone.
- HFC’s global warming potential is very high compared to that of Chlorofluorocabons and Hydro fluorocarbon.
Choose the correct answer
a) Both A and B are correct.
b) Only B
c) Neither A nor B
d) Only A
Question 3: Which among the following gas falls under the six basket of Green House gas that is mentioned in Kyoto Protocol?
a) Carbon Dioxide, Methane, Nitrous oxide, Sulphur hexafluoride, Hydroflurocarbon, Perflurocarbons.
b) Carbon Dioxide, Methane, Nitrous oxide, Sulfur hexafluoride, Hydro chloroflurocarbon, Perflurocarbons.
c) Carbon Dioxide, Methane, Nitrous oxide, Sulfur hexafluoride, Chlorofluorocarbons, Perflurocarbons.
d) None of the above.
Question 4: Drinking Arsenic contaminated ground water leads to?
1. Skin Cancer and Skin lesions
2. Lungs cancer
3. Kidney cancer
4. Brain tumor
Choose the correct answer
a) 1 and 3
b) 1 and 4
c) 1,2 and 3
d) All are correct
Question 5: Kigali amendment is up-gradation of
a) Kyoto Protocol
b) Montreal Protocol
c) Rwanda Agreement
d) Bali Agreement
Question 6: Consider the following statements with respect to Pre-Conception and Pre-Natal Diagnostic Techniques Act, 1994
1. The main purpose of enacting the act is to ban the use of sex selection techniques after conception and prevent the misuse of prenatal diagnostic technique for sex selective abortion.
2. Parliament of India enacted to stop female foeticides and arrest the declining sex ratio in India.
Identify the incorrect statements
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) None of the above
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Online Current Affairs Crash Course’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
I. Archives:
You can check out some more recent News Analysis sections to build even more context
Practice More: Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series

Comments