TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS1 Related B. GS2 Related POLITY 1. Why don’t you trust PM, Law Minister asks judiciary INTERNATIONAL AFFAIRS/BILATERAL RELATIONS 1. Rajnath leaves for Russia, to sign 2 pacts HEALTH ISSUES 1. WHO releases guidelines on child sex abuse C. GS3 Related ECONOMY 1. Time for consolidation of reforms initiated in 42 months: Niti Aayog 2. What do amendments to IBC mean to promoters? ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND ECOLOGY 1. Surge in oxygen levels led to explosion of life: study 2. Coral transplant raises Barrier Reef survival hopes INTERNAL SECURITY AND DEFENSE RELATED DEVELOPMENTS 1. IAF banks on LCA, new fighter to bolster fleet D. GS4 Related E. Prelims Fact F. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions G. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
A. GS1 Related
Nothing here for Today!!!
B. GS2 Related
1. Why don’t you trust PM, Law Minister asks judiciary
Context:
- The National Judicial Appointments Commission (NJAC) judgment, revived the Supreme Courts collegiums system of appointment of judges.
In news:
- Union Law Minister Ravi Shankar Prasad said that at the core of the verdict is the judiciary’s distrust in the capability of the Law Minister and the Prime Minister to appoint a “fair judge.”
Background information:
- Under the now struck down Article 124A of the Constitution, the Law Minister was an ex officio member of the NJAC and the Prime Minister was part of the three-member panel which nominated the two eminent persons to the NJAC, which was meant to give the political class an equal say in judicial appointments to the Supreme Court and the High Courts.
In the Collegium system, the Chief Justice of India (CJI) and a panel comprising four senior-most judges of the Supreme Court recommend appointments and transfers of judges. The collegium system evolved after three landmark judgments of the Supreme Court, popularly known as the ‘three judges cases’ that comprised the first, second and the third judges cases.
The first judges case was the SP Gupta case. It was decided on December 30, 1981 that the President, with sensible reasons, could reject judges’ names recommended by the CJI. This shifted more power on the executive from the judiciary in the appointments process.
In the second judges’ case, a nine-judge bench of the Supreme Court overturned the verdict of the first judges case by creating a Collegium system. The majority verdict delivered by Justice J.S. Verma in the Supreme Court Advocates on Record Association Vs Union of India case on October 6, 1993, stated that the CJI should be entrusted with the primary role of appointments of judges. However, the three judges ruling in this case could not reach a consensus on the exact role of the CJI in the process, leading to a lot of confusion in the appointment and transfer of judges for years.
The final judgement in the series, the third judges case (October 28, 1998) made things clearer after the President’s request to the Supreme Court for a clarity. In this case, the Supreme Court came up with nine guidelines that the Collegium system should follow to function effectively. This case established the supremacy of the judiciary in the appointment and transfer of judges.
WHAT IS NJAC?
NJAC or the National Judicial Appointments Commission is a constitutional body proposed to replace the existing Collegium system of appointing judges. The NJAC proposed a transparent and broad-based process of selection of judges of the Supreme Court and High Courts. The judges of the Supreme Court and High Courts were to be selected by the NJAC commission, whose members were drawn from the judiciary, legislature and civil society.
The NJAC was established by amending the Constitution (99th Amendment) Act, 2014, passed by the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha in August 2014. Alongside, the Parliament also passed the National Judicial Appointments Commission Act, 2014, to regulate the functions of NJAC. The State legislatures of 16 states ratified both the Bills and the President gave his assent on December 31, 2014. The NJAC Act and the Constitutional Amendment Act came into force from April 13, 2015.
Constitution of the NJAC
The NJAC will consist of six people: the Chief Justice of India (CJI), two senior-most judges of the Supreme Court, the Law Minister, and two ‘eminent persons’. These eminent persons would be nominated for a three-year term by a committee consisting of the CJI, the Prime Minister, and the Leader of the Opposition in the Lok Sabha. One eminent person had to be nominated from among the Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, OBCs, minorities or women. These eminent persons were not eligible for re-nomination.
Category: INTERNATIONAL AFFAIRS/BILATERAL RELATIONS
1. Rajnath leaves for Russia, to sign 2 pacts
Context:
- Home Minister Rajnath Singh three-day visit to Moscow.
In news:
- India and Russia will sign two key pacts for cooperation in tackling all forms of terrorism, and smuggling of narcotics.
- The pact will reinforce the bilateral relationship between the two nations through the exchange and sharing of information, expertise, and help in curbing terrorism and enhancing security in the region.
- The proposed pact, which will replace the agreement of October 1993, is a step towards consolidating the benefits accrued in the field of security and seeks to jointly fight new and evolving risks and threats.
1. WHO releases guidelines on child sex abuse
Key Points:
- In a first, the World Health Organisation has formulated clinical guidelines on responding to children and adolescents who have been sexually abused.
- The guidelines put forward recommendations for the frontline health care providers — general practitioners, gynaecologists, paediatricians, nurses and others — who may directly receive a victim of sexual abuse or may identify sexual abuse during the course of diagnosis and treatment.
Opinion by Indian doctors about the new guidelines:
- While Indian doctors have welcomed the new guidelines, they feel that there is more than just guidelines required in the country.
- Ground training of all first line respondents is missing.
- The victims and their families face the worse in terms of investigation and its outcome. It is not adequate to pass on the burden on the healthcare sector. The government needs to adopt a policy that will streamline all the other aspects as well.
Disclosure by child
- The new WHO guidelines focuses on the recommendations and good practice suggestions in terms of disclosure made by the child, obtaining medical history, conducting physical examinations and forensic investigations, documenting findings, offering preventive treatment for HIV post exposure, pregnancy prevention, and other sexually transmitted diseases, psychological and mental health interventions among others.
- The guidelines highlight that child sexual abuse has a short-term as well as long-term mental health impact like lifetime diagnosis of post-traumatic stress, anxiety, depression, externalising symptoms, eating disorders, problems with relationships, sleep disorders and suicidal and self-harm ideation and behaviours.
- Health consequences of the abuse include the risk of pregnancy, gynaecological disorders such as chronic non-cyclical pelvic pain, menstrual irregularities, painful periods, genital infections and sexually transmitted infections, including HIV.
Re-traumatisation
- One of the most commonly seen mistakes in handling child sexual abuse cases is re-traumatising the child as well as his parents with questions. Such mistakes can be avoided if those dealing with such cases are well trained.
C. GS3 Related
1. Time for consolidation of reforms initiated in 42 months: Niti Aayog
In news:
- Niti Aayog Vice Chairman Rajiv Kumar said the time has come for consolidation of reforms, including GST, bankruptcy code and benami law, initiated by the Modi government in the last 42 months to ensure that the steps deliver the “desired fruits”.
- The new initiatives in the next 18 months, should focus on health and education sectors as these two are going to be critical for human resource development.
Export sector:
- Continued weakness of the exports sector has been a major concern, which is not taking off as expected.
2. What do amendments to IBC mean to promoters?
What is bankruptcy? What is the IBC’s intent?
- A company is bankrupt if it is unable to repay debts to its creditors (banks, suppliers etc). The inability to repay debts by some Indian firms has resulted in a huge pile of non-performing assets for the banking system.
- The Indian government had introduced the IBC as a method to tackle the issue. Under the Code, a resolution has to be found for the indebted company within 270 days. Otherwise, a liquidator is appointed. The company can also opt for voluntary liquidation by a special resolution in a general meeting.
What are the key elements of the amendment?
- The amendment has inserted two new sections in the insolvency code — Section 29A, which provides for persons ineligible to be a Resolution Applicant; and Section 235A, which provides for punishment for contravention of the provisions where no specific penalty or punishment is provided.
Section 29A says those ineligible to be a Resolution Applicant include:
- Wilful defaulters (ie, those associated with non-performing assets, or are habitually non-compliant and, therefore, are likely to be a risk to successful resolution of insolvency of a company);
- Those whose accounts are classified as Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) for one year or more and are unable to settle overdue amounts including interest and charges relating to the account before submission of the Resolution Plan;
- Those who have executed an enforceable guarantee in favour of a creditor, in respect of a corporate debtor undergoing a Corporate Insolvency Resolution Process or Liquidation Process under the Code and others connected to the above, such as promoters or those in management control of the Resolution Applicant, or those who will be promoters or in management control of corporate debtor during the implementation of the Plan, the holding company, subsidiary company, associate company or related party of the above persons.
Category: ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND ECOLOGY
1. Surge in oxygen levels led to explosion of life: study
Highlights of a new study:
- A boost in levels of oxygen may have caused a three-fold increase in biodiversity during between 445 and 485 million years ago.
- The explosion of diversity, recognised as the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event, brought about the rise of various marine life, tremendous change across species families and types, as well as changes to the Earth, starting at the bottom of the ocean floors.
- This oxygenation is supported by two approaches that are mostly independent from each other, using different sets of geochemical records and predicting the same amount of oxygenation occurred at roughly the same time as diversification.
- It should be stressed that this was probably not the only reason why diversification occurred then. It is likely that other changes — such as ocean cooling, increased nutrient supply to the oceans and predation pressures – worked together to allow animal life to diversify for millions of years.
Chemical signatures
- Using geochemical proxies, high-resolution data and chemical signatures preserved in carbonate rocks formed from seawater, researchers were able to identify an oxygen increase during the Middle and Late Ordovician periods.
- They found a nearly 80% increase in oxygen levels where oxygen constituted about 14% of the atmosphere during the Darriwilian Stage (Middle Ordovician 460-465 million years ago) and increased to as high as 24% of the atmosphere by the mid-Katian (Late Ordovician 450-455 million years ago).
Key Inference: the oxygenation of the atmosphere and shallow ocean took millions of years, and only when shallow seas became progressively oxygenated were the major pulses of diversification able to take place.
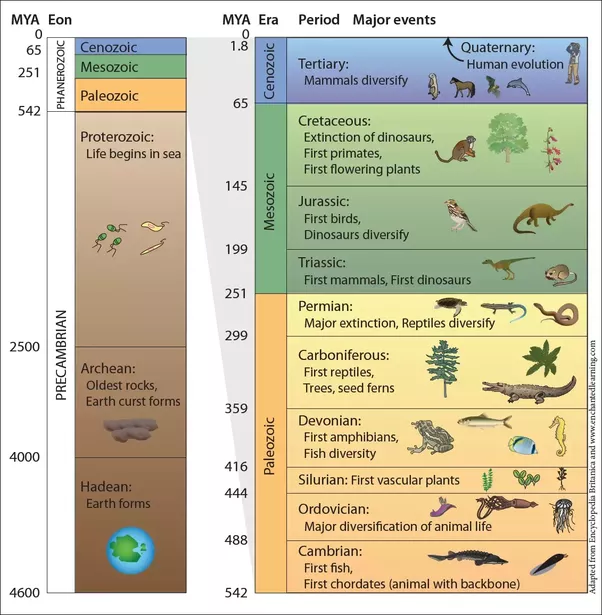
- Geological Time Scale: The geologic time scale (GTS) is a system of chronological dating that relates geological strata (stratigraphy) to time, and is used by geologists, paleontologists, and other Earth scientists to describe the timing and relationships of events that have occurred during Earth’s history.
- The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.2 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period 485.4 million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period 443.8 Mya
2. Coral transplant raises Barrier Reef survival hopes
Context:
- The Great Barrier Reef is reeling from an unprecedented second-straight year of coral bleaching because of warming sea temperatures linked to climate change.
- The larval-restoration approach
In news:
- Coral bred in one part of the Great Barrier Reef was successfully transplanted into another area, Australian scientists said, in a project they hope could restore damaged ecosystems around the world.
- In a trial at the reef’s Heron Island off Australia’s east coast, the researchers collected large amount of coral spawn and eggs late last year, grew them into larvae and then transplanted them into areas of damaged reef.
- When they returned eight months later, they found juvenile coral that had survived and grown, aided by underwater mesh tanks.
Contrasting approach
- The larval-restoration approach contrasts with the current “coral gardening” method of breaking up healthy coral and sticking healthy branches on reefs in the hope they will regrow, or growing coral in nurseries before transplantation.
Category: INTERNAL SECURITY AND DEFENSE RELATED DEVELOPMENTS
1. IAF banks on LCA, new fighter to bolster fleet
In news:
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) is looking at the indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas and the soon-to-be-procured single-engine fighter jet to arrest a dramatic fall in its squadron strength as the deal for 36 Rafale jets lands in the middle of political maelstrom.
- The IAF has a sanctioned strength of 42 squadrons and a projected requirement of 45 to face the anticipated threat of a two-front war.
- As on date the IAF has 33 squadrons and by the end of next month it will be down to 31 squadrons.
Strategic Partnership model:
- Lockheed F-16 and Saab Gripen have tied up with Tata and Adani, respectively, to build the jets locally with technology transfer.
D. GS4 Related
Nothing here for Today!!!
E. PRELIMS FACT
Nothing here for Today!!!
F. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
Question 1. Among the following who are the Agaria Community?
- A traditional toddy tappers community of Andhra Pradesh.
- A traditional fishing community of Maharashtra.
- A traditional silk-weaving community of Karnataka.
- A traditional salt-pan workers community of Gujarat.
See
Question 2. In which State is the Buddhist site Tabo Monastery located?
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Himachal Pradesh
- Sikkim
- Uttarakhand
See
See
See
See
Select the correct answer using the codes below. See
G. UPSC Mains Practice Questions Explain various types of revolutions, took place in Agriculture after Independence in India. How these revolutions have helped in poverty alleviation and food security in India? (2017) “Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Current Affairs Webinar’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.” Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series Question 3. In which one of the following States has India’s largest private sector sea
port been commissioned recently?
Question 4. An increase in the Bank Rate generally indicates that the
Question 5. If Panchayats are dissolved, elections are to be held within
Question 6. The National Mission on Cultural Mapping of India intends to
GS Paper I
GS Paper III
Also, check previous Daily News Analysis
Comments