TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS1 Related B. GS2 Related International Affairs/Bilateral Relations 1. N. Korea: Japan draws in India 2. ‘Fly’ on train from Mumbai by 2022 3. Five challenges in the Ahmedabad-Mumbai bullet train project 4. Japan calls for ‘Free and Open Indo-Pacific Strategy’ 5. Asia Africa Growth Corridor aims for people-centric growth strategy C. GS3 Related Economy 1. India at 103 rank on Global Human Capital Index, lowest among BRICS nations D. GS4 Related E. Prelims Fact F. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions G. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
A. GS1 Related
Nothing here for Today!!!
B. GS2 Related
Category: INTERNATIONAL AFFAIRS/BILATERAL RELATIONS
1. N. Korea: Japan draws in India
Context:
Japan’s Prime Minister visit to India
In News:
Strategic Convergence:
- India and Japan asked North Korea to shut down its nuclear and missile programmes.
- India and Japan, both hinted at Pakistan’s past involvement with North Korean nuclear and missile programmes and sought accountability of “all parties” who helped Pyongyang acquire nuclear technology.
Cross-border terrorism:
- Japan promised to help India deal with cross-border terrorism: support can be provided both indirectly in international platforms or directly to deal with organisations like Lashkar-e-Taiba, Jaish-e-Mohammed and the Islamic State
- A joint statement issued after the summit sought the implementation of Resolution 1267 of the UN Security Council to counter cross-border terrorism.
Japan’s focus on Northeast States:
- Japan, at present, has two infrastructure projects in Meghalaya and Mizoram and more projects are likely to be added to the list after feasibility studies.
Expanded Maritime cooperation:
- Maritime cooperation between the Japan Maritime Self Defence Force (JMSDF) and the Indian Navy had expanded to include ‘anti-submarine aspects’.
- India and Japan, both agreed to support small islands in the region as part of their common strategy.
Joint Exercise:
- Expansion of joint exercises in areas of humanitarian assistance and disaster relief (HA/DR), peacekeeping operations and counter-terrorism, which will also include joint field exercises between the Japanese and Indian land forces next year.
2. ‘Fly’ on train from Mumbai by 2022
In news:
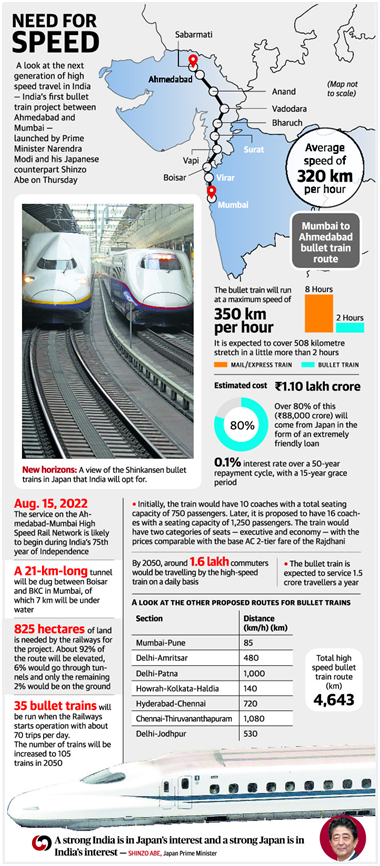
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi and his Japanese counterpart Shinzo Abe laid the foundation stone in Ahmedabad for the country’s first Rs. 1,10,000 crore, 508 km high-speed rail project between Mumbai and Ahmedabad.
- The ambitious project is being implemented with nearly 90% financial support and technology from Japan.
- Key Fact: To be built on elevated corridor with a seven-km undersea tunnel in Mumbai, the project will be based on the famed Japanese Shinkansen high-speed railway system with a record of zero casualties in its 50 years of operation.
- Dead line for completion: August 15, 2022, the day when India marks 75 years of Independence.
- The project will be executed through a special purpose vehicle, the National High Speed Rail Corporation Ltd.
- India’s Bharat Heavy Electricals Ltd and Japan’s Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd will tie up for manufacturing the rolling stock for bullet train project.
- A training centre in Vadodara is being set up to train over 4,000 employees who will be responsible for execution, operation and maintenance of the bullet train.
- The project will cover 12 stations — Mumbai, Thane, Virar, Boisar, Vapi, Bilimora, Surat, Bharuch, Vadodara, Anand, Ahmedabad and Sabarmati — and once operational, the train is expected to service 1.5 crore travellers a year.
3. Five challenges in the Ahmedabad-Mumbai bullet train project
Context:
- Construction of the first bullet train between Ahmedabad and Mumbai is happening on 14 September at a function attended by Narendra Modi and Shinzo Abe
- It is a major leap in infrastructure development in India, this project signifies the friendship and collaboration between India and Japan
Specialties:
- The 534-km Rs1 trillion high-speed rail project will operate trains with average speeds of 200-250kmph
- It will be a game-changer in terms of inter-urban connectivity and establish India as a market for such technologies
- Japan is providing a loan that would cover 80% of the estimated project cost at 5% interest, with a 15-year moratorium followed by a 35-year payback period.
Challenges
Route design which would include questions like:
- Detailed alignment choice, especially when it is over ground, keeping in view land acquisition challenges versus providing access to the population along the corridor.
- Generate urban growth around the station, and even shift the centre of gravity of the urban area.
- Number of stations: Demand for more stations would increase the catchment and reduce the average speed due to higher number of stops. One option is to have different service categories like fast (stopping at all stations) and super-fast (only at major cities).
Evacuation facilitation:
- Efficient bus services as well as accessible parking lots for private vehicles should be provided.
- At major stations, where passengers could move to other trains, th transfer must be seamless.
Land acquisition:
- This will be a critical issue, especially where the alignment would veer off from existing railway lands.
- It would be best addressed by the line ging over ground, where the actual acquisition would be limited
Human resource development:
- It would be important to train a large number of Indian engineers and managers for design, construction and operations at standards that would be essential for high speed rail, including for stringent safety standards
Future expansion:
- It would be useful to have a perspective on how the expansion of this line would happen.
4. Japan calls for ‘Free and Open Indo-Pacific Strategy’
Context:
- Prime Minister Shinzo Abe’s visit to India.
- Announcement of Free and Open Indo-Pacific Strategy.
In news:
- During the visit Shinzo Abe highlighted the country’s intensifying focus on the Indo-Pacific region and Tokyo’s evolving foreign policy.
- Japan’s new concept- “Free and Open Indo-Pacific Strategy”:
- Aims to prepare Japan to deal with the fast changing global and regional order and threats from China and North Korea.
- Strategy aims to create a “free and open” Asia-Pacific region which connects parts of eastern Africa, south Asia and southeast Asia with the western Pacific Ocean region and Japan.
- The ‘Free and Open Indo-Pacific Strategy’ rests on “two oceans” — Indian and Pacific — and “two continents” — Africa and Asia.
- Connectivity between Asia and Africa through a free and open Indo-Pacific, is expected to support stability and prosperity of the region.
- Inference: by connecting “two oceans” and “two continents”, Japan is quietly challenging China’s aggressive plans in the South China Sea that pose a threat to the energy lane that sustains Japanese economy.
5. Asia Africa Growth Corridor aims for people-centric growth strategy
Context:
- Asia Africa Growth Corridor (AAGC)
- Emergence of Idea: during the joint declaration issued by Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Prime Minister Shinzo Abe in November 2016
Asia Africa Growth Corridor:
- The AAGC envisages a people-centric sustainable growth strategy
- The AAGC is an economic cooperation agreement between the governments of India and Japan
- It engages various stakeholders- governments, firms, think tanks and civil society
- It would be raised on the four pillars of
- Development and cooperation projects,
- Quality infrastructure and institutional connectivity,
- Enhancing capacities and skills, and
- People-to-people partnership
- The strengths of AAGC will be aligned with the development priorities of different countries and sub-regions of Asia and Africa
- AAGC-led growth in Africa and Asia will be responsive to the collective commitment to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Trade Facilitation:
- In a study conducted by the European Commission, it is found that the time taken for export and import activities is among the highest in Africa (excluding the northern region)
- Moreover, the documents required to export and import are also on the higher side in Africa
- According to OECD trade facilitation indicators, Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa are below the best practices
- However, achieving the desired level of trade facilitation is a challenging task for Africa and Asia because of lack of technical know-how and skills
India’s role:
- India has already made efforts through various initiatives to develop capabilities in other countries in Asia and Africa in the past
- Although many of them are not fully developed due to paucity of resources
- But we can re-energize such projects/initiatives through AAGC funding that could lead to promotion of imports and exports
- India must evolve appropriate strategy to meet import and export requirements of partner countries in the medium term
Reasons for low level growth in Africa:
- The low level of private investment in Africa is withholding high growth
- Owing to risky projects on long gestation projects, there has been lukewarm response from investors
- Possible Solution: Private investors may be attracted by using limited state funding using the European Investment Fund (EIF) Model
- The EIF consists of subsidizing investment, loss protection, capital relief, reduced interest rate, low collateral requirements, lease and guarantee
Way forward:
- Working closely with the international community, the Asia Africa Growth Corridor will be instrumental in realizing a free and open Indo-Pacific region
- As a unique process, AAGC takes a multi-stakeholder as well as participatory approach towards development
C. GS3 Related
1. India at 103 rank on Global Human Capital Index, lowest among BRICS nations
Global Human Capital Index
- India has been placed at a low 103 rank, the lowest among BRICS economies, on the World Economic Forum’s (WEF’s) Global Human Capital Index
- India is ranked lower than its BRICS peers
- Among the South Asian countries also, India was ranked lower than Sri Lanka and Nepal
- The index has been topped by Norway
Criterion adopted for Ranking
- The list takes into account “the knowledge and skills people possess that enable them to create value in the global economic system” to measure the ‘human capital’ rank of a country
Other Rankings by the WEF’s survey
- India also ranks “among the lowest in the world” when it comes to the employment gender gap
- But has fared well when it comes to development of skills needed for the future with a rank of 65 out of total 130 countries
- India ranks 118 for labour force participation among the key 35-54 year old demographic, it shows too many Indians are engaged in informal or subsistence employment
D. GS4 Related
Nothing here for Today!!!
E. PRELIMS FACT
Nothing here for Today!!!
F. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
Question 1. NNP at factor cost is
- GNP at market price – depreciation
- NNP at market price – Indirect taxes
- NNP at market prices+ subsidies
- NNP at market price- indirect taxes+ subsidies.
See
Question 2. Which of the following is the top level organizational structure of WTO?
- General Council
- Ministerial Conference
- Dispute settlement body
- Goods council
See
Question 3. Which if these is NOT one of the major styles or schools of ancient Indian art?
- Amravati
- Mathura
- Gandhara
- Sarnath
See
Question 4. Identify the correct statement with reference to K9 Vajra
- It is a Submarine
- It is an artillery gun
- It is a naval ship
- None of the above
See
Question 5. Section 139AA inserted in the Income Tax Act, which was in news recently
deals with?
- Provision of Aadhaar being mandatory for getting a PAN.
- Provision of Aadhaar being mandatory for getting a GST number.
- Provision of Aadhaar being mandatory for getting IT rebates.
- None of the above
See
G. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
GS Paper I
- In many ways, Lord Dalhousie was the founder of modern India”. Elaborate
GS Paper II
- “Asia Africa Growth Corridor will help in developing institutional mechanisms and models for connecting people, think tanks and businesses” Discuss.
- “While it is of great value that India has Japan’s support for building the Ahmedabad-Mumbai bullet train, there are multiple challenges that need to be overcome.” Dicsuss.
Also, check previous Daily News Analysis
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Current Affairs Webinar’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series
Comments