TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS1 Related B. GS2 Related INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS 1. Deep Ocean Mission (DOM) GOVERNANCE 1. FASTag C. GS3 Related ECONOMY 1. DigiYatra 2. Drugmakers to look beyond its largest market the U.S DEFENCE 1. National Advanced Surface to Air Missile System (NASAMS) D. GS4 Related E. Editorials POLITY AND GOVERNANCE 1. Layers of protection: on changes in anti-corruption law F. Tidbits 1. Arakan Rohingya Salvation Army (ARSA) says it will not pose threat to India 2. Govt. panel to study stressed power sector H. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions I. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
A. GS1 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
B. GS2 Related
Category: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. Deep Ocean Mission (DOM)
- It is an initiative of Ministry of Earth Sciences
- It will help in improving India’s position in ocean research field.
- The mission proposes to explore the deep ocean similar to the space exploration started by ISRO
Key Deliverables
- It is working to deliver offshore desalination plant that will work with tidal energy, and developing a submersible vehicle that can go to a depth of at least 6,000 metres with three people on board.
- So, the focus will be on technologies for deep-sea mining, underwater vehicles, underwater robotics and ocean climate change advisory services
India’s Exclusive Rights to Explore Polymetallic Nodules
- India has been allotted a site of 1,50,000 square kilometres in the Central Indian Ocean Basin (CIOB) by the UN International Sea Bed Authority for exploitation of polymetallic nodules (PMN).
- These are rocks scattered on the seabed containing iron, manganese, nickel and cobalt.
International Seabed Authority (ISA)
- ISA is a UN body set up to regulate the exploration and exploitation of marine non-living resources of oceans in international waters. It has responsibility for the regulation of seabed mining beyond the limits of national jurisdiction. It was established in 1994.
- India actively contributes to the work of International Seabed Authority.
1. FASTag
- It’s a reloadable tag that automatically deducts toll charges and allows a vehicle to pass through a toll gate without stopping for the payment.
- It uses radio frequency identification (RFID) technology to make cashless payments through a prepaid account linked to it.
- The tag is fixed to the windscreen of a vehicle and an RFID antenna in the canopy of the toll gate scans the QR code and the tag identification number, following which the boom barrier lifts to allow a vehicle to pass through.
- The tag, which is valid for five years, comes in seven different colours — violet, orange, yellow, green, pink, blue, black. Each colour is assigned to a particular category of vehicles.
How does it work?
- The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has tied up with 20 banks to allow people to recharge their cards as well as for owners of old vehicles to purchase a FASTag.
- The tags can also be procured from kiosks set up at toll plazas. The cost of the device varies from one bank to another but on an average a buyer pays ₹600 for the device out of which ₹200 can be used for transactions at toll booth while the balance goes towards the cost of the device and the bank’s fee.
- The NHAI also has a mobile application for FASTag that allows users to buy and recharge these tags as well as seek information on toll rates on different routes. It also allows them to give their feedback.
- Once the vehicle passes through a toll booth, the user receives an SMS alert regarding the charge debited to his or her account.
Benefits for the users
- Users are refunded 5% of the total toll paid by them in a given month.
- Users can also pass through the plaza without having to stop their vehicle to make the payment.
- Cab operators and transporters say that the technology also allows them to track the movement of their vehicles as they receive SMS alerts.
Concerns
- Many plazas don’t have a dedicated lane for RFID tags, which means that one still has to wait in a queue along with other vehicles which need to stop to make cash transaction.
- At many places, RFID readers don’t work.
C. GS3 Related
1. DigiYatra
- It is an initiative of Ministry of Civil Aviation
- The ‘DigiYatra’ is an industry-led initiative coordinated by the Ministry in line with the Prime Minister Modi’s Digital India’s vision to transform the nation into a digitally empowered society.
- It aims to bring together entire industry to develop a digital ecosystem that will deliver Indian customers a seamless, consistent and paperless service experience at every touch point of their journey.
- The basic objective is to reduce queues at airports and bring efficiency to the boarding process
- All aviation stakeholders – airlines, airport operators, security and immigration agencies, cab operators, retail establishment and others are working to devise digital standards which can enable seamless exchange of data and information.
Four Key Pillars
- Connected Passengers, Connected Airports, Connected Flying and Connected Systems
Features
- Submit grievances, share experiences and provide feedback
- Get a prompt when their luggage reaches the baggage claim belt
- Receive relevant information pertaining to various facilities, protocols, airline timings, queue lengths at airports etc
- Walk-through security scanners swiftly owing to advanced biometric security solutions
- Plan their trips efficiently by identifying price trends and estimate future airfares at the time of ticket booking
Implementation
- The facility will use digital technology to enhance air passenger experience all the way from ticket booking to airport entry check, security check and aircraft boarding.
- For this, a passenger needs to enrol in to DigiYatra program through AirSewa app and a DigiYatra verified passenger will get hassle free entry at airport through E-Gates.
- The ID verification will be done by the BCAS-approved Government ID. At the entry gate a single token for the passenger will be created.
Privacy concern addressed
- This facility is in conformity with privacy guidelines of the Supreme Court
- When an individual enters the airport, their images will be captured and then they will be able to go through the full lifecycle of travel in a seamless manner
- Once an individual establishes identity they will be able to pass through the entire lifecycle of the travel and this facility is optional.
- If somebody does not want to disclose identity, there will be separate provision for them.
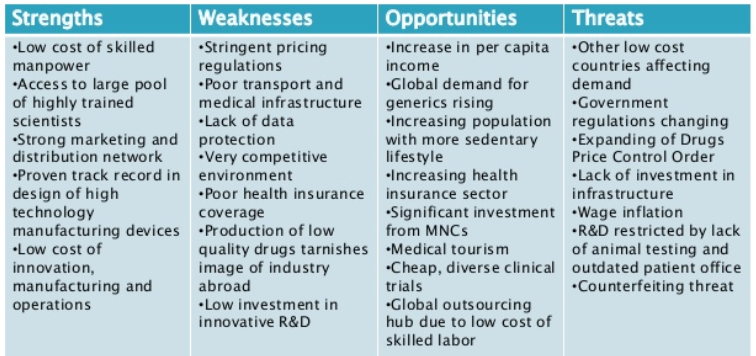
2. Drugmakers to look beyond its largest market the U.S
Context
- Strict regulations, tough policy approach under President Trump and pricing pressures are forcing Indian firms to look beyond U.S.
Details
- North America, primarily the U.S., accounted for more than 30% of India’s pharma exports in FY18. But, market has recorded a contraction in India’s drug export basket with time.
- This is due to long-standing regulatory issues to increased pricing pressure and a tougher policy approach on the part of the Trump administration.
- So, with no signs of abating any time soon, a shift in focus seems more of a necessity than a choice.
SWOT analysis of Pharma sector
1. National Advanced Surface to Air Missile System (NASAMS)
Context
- India is in talks with the U.S. to procure an advanced air defence system to defend the National Capital Region (NCR) from aerial attacks.
Details
- The NASAMS was developed by Raytheon in partnership with KONGSBERG Defence and Aerospace of Norway.
- The system can be deployed to identify, engage and destroy aircraft, helicopters, cruise missiles and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), as well as protect high-value assets and mass population centres against air-to-surface threats.
- NASAMS-II is an upgraded version of the NASAMS and features new 3D mobile surveillance radars and 12 missile launchers for quicker reaction.
- Owned by seven countries, it has been integrated into the US National Capital Region’s air defense system since 2005. Apart from the US, it is also in service in Norway, Finland, Spain and the Netherlands.
D. GS4 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
E. Editorials
Category: POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. Layers of protection: on changes in anti-corruption law
Focus of the article
- Protecting honest public servants is important; so are anti-corruption efforts
Context
- The amendments to the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988, adopted recently by both Houses of Parliament
Background of the topic
- Moves to make changes in this law, aimed at combating corruption in government, were initiated during the UPA’s second term in office and largely centred on the misuse of one provision — Section 13 (1) d.
- Former Prime Minister Manmohan Singh had criticised this section, under which public servants are culpable for securing a pecuniary advantage for another “without any public interest”, for ignoring a foundational principle of criminal law: mens rea (the intention or knowledge of wrongdoing that constitutes part of a crime, as opposed to the action or conduct of the accused).
- This resulted in many honest officials being prosecuted even when they gained nothing and merely exercised their power or discretion in favour of someone.
Highlights of the Bill
- The Prevention of Corruption (Amendment) Bill, 2013 amends the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988.
- The Act covers the offence of giving a bribe to a public servant under abetment. The Bill makes specific provisions related to giving a bribe to a public servant, and giving a bribe by a commercial organisation.
- The Bill redefines criminal misconduct to only cover misappropriation of property and possession of disproportionate assets.
- The Bill modifies the definitions and penalties for offences related to taking a bribe, being a habitual offender and abetting an offence.
- Powers and procedures for the attachment and forfeiture of property of public servants accused of corruption have been introduced in the Bill.
- The Act requires prior sanction to prosecute serving public officials. The Bill extends this protection to former officials.
Impact of the amendment
- Insofar as it had a chilling effect on governance and deterred bold decision-making, the amended form may have a liberating effect on honest officials.
- It is more concise and restricts criminal misconduct to two offences: misappropriating or converting to one’s own use property entrusted to a public servant or is in his control, and amassing unexplained wealth.
- There was concern initially with the wording, “intentionally enriches himself illicitly during the period of his office”, as it raised a doubt whether the ‘intention’ to amass wealth would also have to be proved. Now an explanation has been added that a person “shall be presumed to have intentionally enriched himself” if he cannot account for his assets through known sources of income.
- By making citizens liable for offering a bribe to a public servant, the anti-corruption law has been brought in line with the UN Convention Against Corruption.
Criticism
- The penal provision can empower people by allowing them to cite it to refuse to pay a bribe. At the same time, what happens when the police or any other agency refuses to register a complaint? People may be left in the lurch with no redress. Further, it may render them vulnerable to threats from unscrupulous public servants who collect money to speed up public services but do not deliver.
- The most unacceptable change is the introduction of a prior approval norm to start an investigation. When a prior sanction requirement exists in law for prosecution, it is incomprehensible that the legislature should create another layer of protection in the initial stage of a probe.
Way Forward
Public servants need to be protected against unfair prosecution, but a genuine drive against corruption needs a package of legislative measures. These should contain penal provisions, create an ombudsman in the form of a Lokpal or Lokayukta, as well as assure citizens of time-bound services and whistle-blower protection. Laws to fulfill these objectives are either not operational or are yet to materialise. Protecting honest public servants is important; so are anti-corruption efforts.
F. Tidbits
1. Arakan Rohingya Salvation Army (ARSA) says it will not pose threat to India
Context
- The Armed group ARSA in Myanmar says it poses no threat to India and expressed “heartfelt appreciation” for Indian support to the Rohingya refugees.
Details
- The group’s struggle is to ensure the rights of the Rohingya refugees and that it is not connected to the Islamic State (IS) or Pakistan’s intelligence agencies.
Background
- The statement was issued following reports in an Indian daily that the group had targeted the Assam Rifles recently near the India-Myanmar border and that it aims to build training camps in the Myanmar territories close to Indian frontiers.
- ARSA denied the attack and termed the news report as “blatant manipulation”.
2. Govt. panel to study stressed power sector
Context
- The government announced its intention to set up a high-level empowered committee under the Cabinet Secretary to resolve the stress in the thermal power sector.
Details
- To resolve the stress and revive assets, the government has decided to set up a high-level empowered committee headed by Cabinet Secretary with representatives from the Ministry of Railways, Ministry of Finance, Ministry of Power, Ministry of Coal, and the lenders having major exposure to the power sector
- The committee is to look into the various issues in the thermal power sector with a view to resolve them and take steps to maximise the efficiency of investment, including changes in the fuel allocation policy, regulatory framework, mechanisms to facilitate sale of power, payment security mechanisms, the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), asset restructuring company (ARC) regulations
G. Prelims Fact
Nothing here for today!!!
H. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
Question 1. Sanjay Dubri National Park is in the state of
- Rajasthan
- Odisha
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
See
Question 2. Theyyam festival is hosted in
- Tamilnadu
- Kerala
- Karnataka
- Andhra Pradesh
See
Question 3. Consider the following with reference to E-Government Development Index (EGDI):
- It is published by World Economic Forum.
- It is published yearly. It speaks about e governance initiatives taken by Govt and Private companies in a country.
The correct code is:
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither of them
See
Question 4. Consider the following statements about Tiger:
- Its IUCN status is critically endangered
- India has the highest number of tigers
- In India, Karnataka leads in state ranking
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
- Only 3
- Only 1
- Only 2 and 3
- Only 1 and 3
See
I. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
- Public sector should involve as much as Private sector in manufacturing of medicines. Explain.
-
Knowledge is power, but access to knowledge is another kind of power. Explain in reference to E governance. Also, comment how India improved its ranking in e participation Index.
- India is a land of tolerance and melting pot of cultural values. Illustrate with examples.
Also, check previous Daily News Analysis
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Current Affairs Webinar’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series
Comments