TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS1 Related B. GS2 Related GOVERNMENT SCHEMES 1. 7 out of 10 seats sold on flights to smaller cities 2. PM launches cleanliness campaign 3. 37 lakh new mothers receive cash benefits HEALTH 1. Call for policy, action in diabetes prevention, management INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS 1. Bhutan PM’s party ousted in election 2. Does U.S. want India to import more? C. GS3 Related INTERNAL SECURITY 1. Chief Election Commissioner says ‘Democracy under threat from black money, fake news’ SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY 1. PSLV to launch 2 U.K. satellites DEFENCE 1. Submarine plan moves forward after delays ENVIRONMENT & ECOLOGY 1. Researchers dive in to restore coral ecosystems D. GS4 Related E. Editorials F. Tidbits G. Prelims Fact 1. International Coastal Clean-up Day 2. BUFFALO Survey H. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions I. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
A. GS1 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
B. GS2 Related
1. 7 out of 10 seats sold on flights to smaller cities
Context:
- Under the regional connectivity scheme (RCS) or UDAN (Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik) the government had set up a low-cost flying scheme to make air travel affordable and boost domestic traffic to provide for inclusive growth.
- According to data accessed under the RTI, for every 10 seats available under this scheme, as many as seven were grabbed by passengers since its launch last year.
- This indicates the growing demand for flights to smaller cities.
Key Points:
- Under UDAN, which aims to take flying to the masses and enhance air connectivity to Tier-1 and Tier-2 cities, two rounds of bidding have taken place so far.
- Under the scheme eight airlines have started flights on 96 routes out of a total of 428 routes that were awarded to 17 airlines and helicopter operators. But helicopter services are yet to commence.
- Airline operators are required to set aside half of the total aircraft capacity for cheaper fares which are offered at the subsidised rate of ₹2,500 per hour of flight.
- The airlines in return are compensated by the Centre and the respective State government.
- Seat occupancy, also known as passenger load factor, is an indicator of demand on a particular route.
- Analysis of data sought obtained through RTI shows that as many 7.5 lakh seats were made available for sale by eight airline operators, out of which 5.24 lakh seats were sold between the first flight under the scheme in April last year and until August 1st, 2018.
About UDAN:
- UDAN RCS (Regional Connectivity Scheme) was launched in October 2016 to develop the regional aviation market.
- It is a vital component of the National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP), 2016.
- It aims to make flying affordable by providing connectivity to un-served and under-served airports of country through revival of existing airstrips and airports so that persons in regional towns are able to take affordable flights.
- It is applicable on flights covering distance between 200 km and 800 km with no lower limit set for hilly, remote, island and security sensitive regions.
- It seeks to reserve a minimum number of UDAN seats i.e. seats at subsidized rates and also cap fare for short distance flights.
- It has a unique market-based model to develop regional connectivity. It has Viability Gap Funding (VDF) mechanism to meet the VGF requirements under the scheme.
- Airports Authority of India (AAI) under the Ministry of Civil Aviation is the implementing agency of the scheme.
- The scheme has two components. The First componentis to develop new and enhance the existing regional airports to increase the number of operational airports for scheduled civilian flights.
- The Second componentis to add several hundred financially-viable capped-airfare new regional flight routes to connect more than 100 underserved and unserved airports in smaller towns with each other as well as with well served airports in bigger cities by using “Viability Gap Funding” (VGF) where needed
Evaluation of UDAN:
- Infrastructure constraints have checked the pace of implementation of the scheme.
- 40 unserved and 15 underserved airports are not ready yet for operations.
- Some airports owned by State governments and private players have been hesitant in participating as there is little for them to gain with RCS flights exempt from paying landing and parking charges and States required to provide land, security and fire services free of cost.
- However, there may be a silver lining: many routes have seen a steady rise in the number of passengers, though there are still pockets such as those in the northeast which are yet to generate any interest in travellers.
2. PM launches cleanliness campaign
Context:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the “Swachhata Hi Seva” (“cleanliness is service”) campaign.
Key Points:
- The PM said the sanitation coverage in India had increased from 40% to over 90% in the four years of the “Swachh Bharat” (Clean India) project.
- He launched the “cleanliness is service” exercise to promote greater public participation in one of the flagship programmes of the government.
- It will continue till Mahatma Gandhi’s birth anniversary next month.
- The campaign is being coordinated by Union Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation, convening Ministry for the Swachh Bharat Mission.
- Its objective is to mobilise people and reinforce Jan Aandolan (mass movement) for sanitation to contribute to Mahatma Gandhi’s dream of a Clean India.
- It will see large scale mobilisation of people from all walks of life to undertake shramdaan (voluntary work for cleanliness and construction of toilets and to make their environments open defecation free. There will be targeted cleaning of public and tourist places.
- The main agenda of the campaign will be to reach out to the poor and marginalised and provide them with sustainable sanitation services.
3. 37 lakh new mothers receive cash benefits
Context:
- Under the Centre’s maternity benefits programme nearly 37 lakh women have received cash incentives since the launch of Matru Vandana Saptah last year.
Key Points:
-
The Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY) offers pregnant women and lactating mothers’ ₹5,000 as assistance for the first birth in the family. The programme’s aim is to reduce malnutrition.
-
A sum of ₹1,000 is also given to women after institutional delivery under the Janani Suraksha Yojana.
-
The scheme has an estimated 51.6 lakh beneficiaries a year.
-
As many as 48.11 lakh women have been enrolled in the Matru Vandana Saptah and the Centre has disbursed an amount of ₹1,168.63 crores to various States.
-
It is implemented by the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
About Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY):
- It is a Maternity Benefit Programme that is implemented in all the districts of the country in accordance with the provision of the National Food Security Act, 2013.
- Under – nutrition continues to adversely affect majority of women in India. In India, every third woman is undernourished and every second woman is anaemic.
- An undernourished mother almost inevitably gives birth to a low birth weight baby. When poor nutrition starts in – utero, it extends throughout the life cycle since the changes are largely irreversible.
- Owing to economic and social distress many women continue to work to earn a living for their family right up to the last days of their pregnancy. Furthermore, they resume working soon after childbirth, even though their bodies might not permit it, thus preventing their bodies from fully recovering on one hand, and also impeding their ability to exclusively breastfeed their young infant in the first six months.
Objectives of PMMVY –
-
Providing partial compensation for the wage loss in terms of cash incentives so that the woman can take adequate res t before and after delivery of the first living child.
-
The cash incentive provided would lead to improved health seeking behaviour amongst the Pregnant Women and Lactating Mothers (PW& LM).
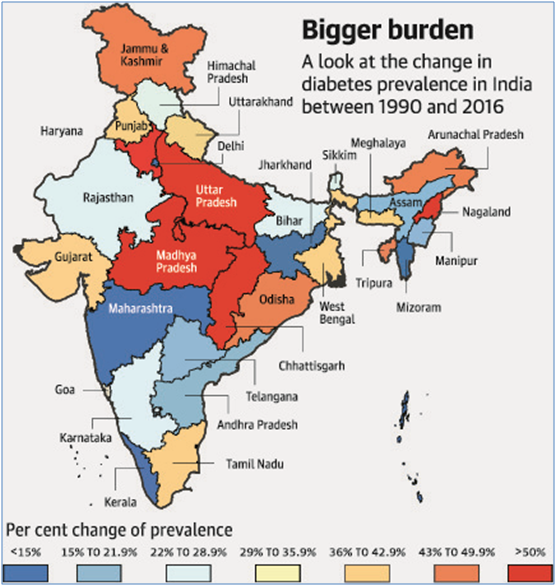
1. Call for policy, action in diabetes prevention, management
Context:
- The Global Burden of Disease Study 2016 which was released recently points out that the prevalence of diabetes has increased more rapidly in the less-developed States of the country.
- The report contains alarming statistics for India. According to it the total number of people with diabetes grew from 26 million in 1990 to 65 million in 2016. The prevalence of diabetes in India was 5.5 % in 1990, but it has increased to 7.7 % in 2016.
Key Points:
- The report says uncontrolled diabetes and its associated complications are likely to take a heavy toll in the coming decades on India’s healthcare system.
- In order to ensure more effective prevention and management of diabetes, the report highlights the need for policy and health system action which is commensurate with the disease burden in each State.
- It calls for effective policy implementation by terming the increase in diabetes prevalence “a potentially-explosive public health situation”,.
- When combined with appropriate allocation of financial and human resources, and a robust disease monitoring system, this would help in prevention, treatment and reduction of diabetes deaths and, in turn, curb the growing disease burden.
- The highest prevalence is seen in the states of Tamil Nadu and Kerala, followed by Delhi, Punjab, Goa, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh and Tripura.
- The increase in loss of health from diabetes since 1990 is the highest among all major non communicable diseases.
- Diabetes contributed to 3% of all deaths in India, with an increase in death rates due to diabetes from 1990 to 2016.
- This highlights the low likelihood of meeting national and global targets for reducing deaths due to diabetes by 2025 and 2030, respectively.
- Among the risk factors contributing to diabetes in India in 2016, high BMI had the highest impact, while the other factors were dietary risks, tobacco use, occupational exposure to second hand smoke, low physical activity, and alcohol use.
- The prevalence of being overweight in persons aged 20 years or older had increased from 9% in 1990 to 20.4% in 2016.
Way Forward:
- Promoting a healthy and active lifestyle and interventions to prevent obesity, providing public facilities to increase physical activity, and taxing junk foods, would go a long way in reducing the numbers. The way forward would be creating awareness about diabetes.
Category: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. Bhutan PM’s party ousted in election
Key Points:
- In the first round of elections in Bhutan, the incumbent Prime Minister Tshering Tobgay’s People’s Democratic Party (PDP) has been ousted and will not contest in the second and final round to be held next month.
- Instead, the Druk Nyamrup Tshogpa (DNT) headed by Dr. Lotay Tshering, and the Druk Phuensum Tshogpa (DPT) will face off on October 18th. The DNT won the highest number of votes.
Background:
- Tshering Tobgay’s term had seen very cordial relations between India and Bhutan, including during the last year’s tense Doklam standoff with China.
- He had re-established the historic and friendly ties between the two after a few brief controversies with the previous Bhutanese government over its increasing bonhomie with China.
- India will be closely watching the outcome of the next rounds as the Himalayan country holds great strategic significance for India’s foreign policy and national security interests.
2. Does U.S. want India to import more?
Context:
- US President Trump has unleashed a trade war against many countries based on his electoral promise of ‘America First’.
- As a result, the US government has imposed higher duties on imports to spur local manufacture and increase jobs in the U.S.
- The same spirit is also behind the move to pressure India to import at least $10 billion a year more from the U.S. over the next three years.
India – US trade volume:
- According to the U.S. Census Bureau, India imported $25.7 billion from the U.S. in 2017 while it exported $48.6 billion to the largest economy in the world.
- The U.S.’s latest demand from India is to cut its trade deficit by close to half, through increased purchases of civilian aircraft and natural gas.
How does it affect India?
- Such a policy of the US could be disastrous for India — not only will India’s exports to the U.S. suffer, but it would have wasted precious dollar resources in signing up for imports under pressure.
- Even if the U.S. continued to grow, an increase in imports by India, merely to address the trade gap, would have a telling effect on the exchange rate.
- Indian government officials have estimated an extra $26 billion expenditure due to rising oil prices.
- Oil importers buy dollars to pay for their imports. That has contributed significantly to the falling rupee, which has lost as much as 14% this year, making it the worst performing currency in Asia.
- Spending an extra $10 billion a year on imports from the U.S. would mean further pressure on the rupee.
- A falling rupee makes life difficult for other Indian importers. This would have a domino effect on the rest of the economy.
- Rising prices could dampen consumer demand, resulting in poorer profit margins for industry.
C. GS3 Related
1. Chief Election Commissioner says ‘Democracy under threat from black money, fake news’
Key Points:
- While addressing a symposium, the CEC has said that with the rise of fake news, data theft, data harvesting, profiling, targeted communication etc., democracy in the world is facing a very potent threat.
- The CEC said that the media should adopt some international practices, including regular columns that highlight the fake news stories of the week.
- He also spoke about ‘state funding of elections’ and observed that it was not an option at present, as the current law was inadequate to counter black money used in elections.
- He emphasised the need to update technology to harmonise the electoral roll and avoid duplicity and the need for an automated technology that can simultaneously update the electoral roll as births and deaths take place.
- According to a former CEC present on the occasion, the ‘Democracy Index’, which is produced by the United Kingdom-based Economic Intelligence Unit, had highlighted the same issues with regard to India that the Election Commission had been highlighting — criminalisation of politics and money power.
About Democracy Index:
- The Democracy Index is an index compiled by the UK-based company the Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) that intends to measure the state of democracy in 167 countries.
- The index was first produced in 2006 and is based on 60 indicators grouped in five different categories measuring pluralism, civil liberties and political culture.
- It categorises countries as one of four regime types: full democracies, flawed democracies, hybrid regimes and authoritarian regimes.
- India has been placed under the category of flawed democracies.
Category: SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
1. PSLV to launch 2 U.K. satellites
Context:
- ISRO will launch two earth observation satellites of U.K on the 16th of September.
Key Points:
- Breaking a five-month-long lull for the Indian Space Research Organisation PSLV-C42 will mark the first fully commercial trip of the year.
- After ISRO put the replacement navigation satellite, IRNSS-1I to space aboard the PSLV-C41 rocket on April 12th, it has not carried out any launch.
- Later ISRO had recalled its GSAT-11 from the South American launch port of Kourou the space agency has said that the long gap was not related with the satellite recall but for the sake of readiness of the two customer satellites.
- The PSLV is being launched in its core-alone format, minus the external boosters.
- The two satellites together weigh nearly 889 kg; this is the optimum payload that a core-alone PSLV can launch.
- PSLV-C42 is scheduled for launch from the first launch pad of the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota.
- It will place the two satellites – NovaSAR and S1-4, to a sun-synchronous (‘pole-to-pole’) orbit 583 km from Earth.
- The satellites belong to Surrey Satellite Technologies Ltd. of UK, which had signed a commercial launch contract with Antrix Corporation.
Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV):
- It is a medium-lift launch vehicle that has become the most reliable workhorse for ISRO.
- It was developed to allow India to launch its Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) satellites into sun-synchronous orbits.
- PSLV can also launch small size satellites into geostationary transfer orbit (GTO).
- The PSLV has four stages using solid and liquid propulsion systems alternately.
- The first stage is one of the largest solid rocket boosters in the world.
- The second stage employs the Vikas engine and carries liquid propellant.
- The third stage uses solid propellant and while the fourth stage is powered by twin engines carrying liquid propellants.
- There are currently two operational versions of the PSLV — the core-alone (PSLV-CA) without any strap-on motors, and the (PSLV-XL) version, with six extended length (XL) strap-on motors.
- Some notable payloads launched by PSLV include India’s first lunar probe Chandrayaan-1, India’s first interplanetary mission, Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan) and India’s first space observatory, Astrosat.
- PSLV has gained credence as a small satellite launcher due its numerous multi-satellite deployment campaigns with auxiliary payloads usually ride sharing along an Indian primary payload.
- Most notable among these was the launch of PSLV C37 on 15 February 2017 successfully deploying 104 satellites in sun-synchronous orbit, tripling the previous record held by Russia for most number of satellites sent to space on a single launch.
Antrix Corporation:
- Antrix Corporation Limitedis the commercial arm of ISRO.
- Its objective is to promote the ISRO’s products, services and technologies.
- It was incorporated as a private limited company owned by the Indian government on 28 September 1992.
- The company is a Public Sector Undertaking (PSU), wholly owned by the Government of India. It is administered by the Department of Space.
1. Submarine plan moves forward after delays
- After being delayed due to policy clarity, the Indian Navy’s ambitious deal for procuring six advanced conventional submarines under Project-75I and processed through the Strategic Partnership (SP) model is moving forward.
- The project is estimated to cost over ₹60,000 crore and the Ministry of Defence (MoD) has initiated the process to finalise specific guidelines.
Key Points:
- The desired objectives under Project-75I include the creation of industrial eco-system, the range and scope of technology transfer, indigenisation of content, indigenisation of the pressure hull steel, research and development and skilling roadmaps.
- Responding to the Navy’s Request for Information four foreign OEMs have expressed interest.
- The contenders are Naval Group of France, Rosoboron export Rubin Design Bureau of Russia, ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems of Germany and Saab group of Sweden.
- Only two Indian companies – Larsen and Toubro and Reliance Defence, have shipyards and hence eligible to participate in the tender.
- The only Indian shipyard with experience of manufacturing submarines is the Mazagon Dock Ltd, which is a defence public sector undertaking and, is also expected to be considered.
Project – 75I:
- Project 75I-class submarine is a follow-on of the Project 75 Kalvari-class submarine for the Indian navy.
- Under this project, the Indian Navy intends to acquire 6 diesel-electric submarines, which will also feature advanced Air-independent propulsion (AIP) systems to enable them to stay submerged for longer duration and substantially increase their operational range.
- The project got clearance from Defence Acquisition Council in 2014.
- All six submarines are expected to be constructed in Indian shipyards in accordance with the Make in India initiative of the government.
- The Project 75I-class submarines will have a vertical launch system (VLS) to enable them to carry multiple Brahmos supersonic cruise missiles, making the submarines fully capable of anti-surface and anti-ship warfare missions.
- Project 75I submarines will also be armed with torpedoes and will feature advanced stealth capabilities such as a greater ability to suppress noise and acoustic signatures.
Category: ENVIRONMENT & ECOLOGY
1. Researchers dive in to restore coral ecosystems
- Coral reefs, which are also called the ‘rainforests of the oceans’, represent one of the most diverse ecosystems on earth, and they play a very significant role in maintaining marine biodiversity. But there wellbeing is gravely threatened by coral bleaching which is caused by climate change and water pollution.
- A team from National Centre for Coastal Research, Chennai, plans to work on coral monitoring and restoration in the Gulf of Mannar region.
Key Points:
- The team plans to assess the location and coverage of corals through remote sensing, and then study how the sediment affects the coral reef.
- The team will also set up an acquatech park which will help the local people rear marine ornamental fish towards a sustainable livelihood.
- The group has prior experience in studying corals across the country. They have successfully transplanted and nurtured corals in the Lakshadweep region. Now they are set to work in the Gulf of Mannar.
Coral bleaching:
- An increase in sea surface temperatures leads to coral bleaching and the breaking of the symbiotic relationship that corals have with the unicellular algae dinoflagellates.
- All corals are not equally sensitive. The most vulnerable are the branching corals, for example, Acropora species, and the least susceptible are the massive ones, for example Favia species.
- Coral reefs in India are only seen in some localities around the Gulf of Mannar, Gulf of Kutch, Lakshadweep islands and Andaman and Nicobar Islands. In many of these places, bleaching of corals and related cnideria species such as giant clam and tentacle sea anemone have been observed
- However, constructive interventions exist for this problem. The methods include reducing harvest of herbivorous fish and minimising anthropogenic causes of bleaching.
- The National Centre for Coastal Research, which comes under the Ministry of Earth Sciences, conducted a mapping of corals for Gulf of Kutch, Gulf of Mannar, Lakshadweep and Andaman and Nicobar islands over a period of five years, from 2000 to 2005. Their results were startling, as they found less than 40% of the coral reefs in India were still alive.
- From 2005 to present, the team, with support from Department of Science and Technology, has surveyed the area around Agatti and Kavaratti islands in the Lakshadweep, and in an area approximately one acre, transplanted branching corals, massive corals and foliac corals.
- Over the last decade, this region has seen restoration of live corals in these areas.
D. GS4 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
E. Editorials
Nothing here for today!!!
F. Tidbits
Nothing here for today!!!
G. Prelims Fact
1. International Coastal Clean-up Day
- ICC was started by the Ocean Conservancy in 1986 to engage volunteers in collecting marine debris such as garbage, plastic etc.
- It is celebrated annually on the third Saturday in September.
- It relies on community participation.
- It is one of the missions coordinated by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) to explore the origins of the earliest galaxies.
- The Beyond Ultra-deep Frontier Fields And Legacy Observations (BUFFALO) survey will observe six massive galaxy clusters and their surroundings and allow astronomers to determine how rapidly galaxies formed in the first 800 million years after the Big Bang — paving the way for observations with upcoming observatories such as the James Webb Space Telescope.
- Its extended fields of view will also allow better 3-dimensional mapping of the mass distribution (of both ordinary and dark matter) within each galaxy cluster.
H. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
Question 1. Which of the following is responsible for coral bleaching in the oceans?
- Chlorine
- Hydrochloric Acid
- Carbonic Acid
- None of the above
See
Question 2. Which of the following is related to trade disputes between India and USA?
- Compulsory Licensing
- CAATSA
- LEMOA
- COMCASA
See
Question 3. Which of the following is not an objective under UDAN?
- To provide for affordable, low-cost domestic air travel.
- To revive existing airstrips and airports.
- To enhance air connectivity to Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities.
- To provide for inclusive growth through better connectivity.
See
Question 4. Which of the following statement is true?
- PSLV is a 3-stage solid fuelled rocket.
- India’s Mars mission was launched by a GSLV rocket.
- GSLV rocket has no strap-on motors.
- GSLV engine makes use of cryogenic technology.
See
I. Practice Questions for UPSC Mains Exam
-
The civil aviation sector in India is in dire need of reforms. Evaluate.
-
Depreciation of the rupee is tied to the economic and foreign policy decisions of the US. Elaborate.
-
Explain how climate change can trigger bleaching of corals. What role do corals play in the marine ecosystem? Discuss the ongoing environmental crisis in the Great Barrier Reef.
Also, check previous Daily News Analysis
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Current Affairs Webinar’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series
Comments