June 29th, 2021, PIB:- Download PDF Here
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. Saral Sanchar Portal 2. Provisional Coal Statistics 2020-21 3. Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme 4. Glacial Lake Atlas of Ganga River Basin Released 5. Enforcing Contracts Portal 6. Not-for-Profit Hospital Model in India 7. SERB-FIRE
Context:
Department of Telecommunications (DoT) expanded the Saral Sanchar Portal.
About Saral Sanchar Portal:
- ‘SARAL SANCHAR’ (Simplified Application For Registration and Licenses) is a web-based portal for Issuing various types of licenses and registration certificates.
- It is a part of the various digital initiatives being undertaken by the Dept of Telecommunications, Ministry of Communications, GOI.
- The portal ensures transparency and more efficiency in the process of issuance of licenses and registration certificates.
- Applicants can apply by filling up the prescribed application form online and uploading the documents and application form with digital signature.
- The portal envisages that applicants get prompts and alerts at various stages of application submission so that all necessary requirements are complied with before submitting the application.
- On this portal, application for Access Services, Internet Services and other licenses are being received.
- The following types of licenses/authorizations shall be issued from this portal:
- Unified License
- Unified License-Virtual Network Operator
- WPC Licenses (Wireless Planning and Coordination)
Latest initiative launched on Saral Sanchar Portal:
- The Wireless Planning and Coordination Wing (WPC) of the DoT launched an initiative to facilitate online licensing for use of Spectrum to conduct experiments, demonstrations, etc.
- The scope of the portal has been expanded for the receipt, processing and grant of licenses for spectrum to conduct experiment, demonstration, testing, manufacturing, etc.
- With this addition, nearly all the permissions required from the WPC Wing, which include permissions for equipment type approval, satellite licenses, amateur licenses, allocations by Standing Committee of Radio Frequency Allocation, etc. have become online.
2. Provisional Coal Statistics 2020-21
Context:
Union Minister released the Provisional Coal Statistics 2020-21.
Provisional Coal Statistics 2020-21:
- The statistical publication has been released by the Ministry of Coal.
- It contains provisional information regarding the performance of the Coal and Lignite sector in the last fiscal year 2020-21.
- It provides a valuable and comprehensive ready reference of data to all the concerned stakeholders, policy planners, researchers, national institutes and international institutes and individuals, etc.
- The data is available in the public domain and can be downloaded from the official websites of the Coal Controller’s Organisation (CCO) and the Ministry of Coal.
- It contains pre-audited data, and the final data for 2020-21 would be published in the Coal Directory of India 2020-21.
Coal Controller’s Organisation
- Earlier known as the Coal Commission, this office was established in 1916 and is one of the earliest offices in the coal sector in India.
- The chief objective behind the setting up of the office was to have government control to adequately meet the coal requirement during the First World War.
- Under the various acts that govern the coal sector in the country, the office performs several functions such as laying down the procedure for sampling, inspection, regulation, granting permission for opening/reopening of mines, etc., undertaking research in relation to conservation, development of coal, among others.
- It operates under the Ministry of Coal, GOI.
- It is headed by the Coal Controller.
Additional information:
- The Indian coal deposits are primarily concentrated in the Gondwana sediments located in the Eastern and Central parts of Peninsular India and also in parts of North Eastern Regions viz., Sikkim, Assam and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Indian lignite deposits are in the Tertiary sediments in the Southern & Western parts of the peninsular shield, particularly in Tamil Nadu, Pondicherry, Gujarat, Rajasthan and Jammu & Kashmir. It is also available, in minor quantity, in Kerala & West Bengal.
- In India coal is broadly classified into two types – coking and non-coking.
3. Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme
Context:
PMFME Scheme under Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan completed one year.
Details:
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme launched under the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan to enhance the competitiveness of existing individual micro-enterprises in the unorganized segment of the food processing industry and promote formalization of the sector.
Achievements of the Scheme:
- Under the One District One Product (ODOP) component of the PMFME Scheme, the Ministry of Food Processing Industries approved ODOP for 707 districts for 35 States and UTs, including 137 unique products.
- Under the Capacity Building component of the PMFME Scheme, the National Institute of Food Technology Entrepreneurship and Management (NIFTEM) and the Indian Institute of Food Processing Technology (IIFPT) have been providing training and research support to selected enterprises/groups/clusters in partnership with the State Level Technical Institutions.
- Seed Capital worth Rs. 25.25 Crores have been disbursed to State Rural Livelihood Mission under the scheme.
- 54 Common Incubation Centres were approved in 17 States/UTs.
Read more on the PMFME Scheme in the linked article.
4. Glacial Lake Atlas of Ganga River Basin Released
What’s in the news?
The Ministry of Jal Shakti has released an updated atlas of glacial lakes that are part of the Ganga river basin in the wake of mounting concerns over the impact of climate change on Himalayan glaciers.
Details:
- About 4,707 glacial lakes have been mapped in the Ganga basin.
- In December 2020, a similar exercise had been carried out for the Indus River basin.
- For the present study, glacial lakes with water spread area greater than 0.25 ha were mapped using Resourcesat-2 (RS-2) Linear Imaging Self Scanning Sensor-IV (LISS-IV) satellite data.
- Glacial lakes are identified in nine different types, majorly grouped into four categories based on its process of lake formation, location, and type of damming material.
Area covered in the map:
- The area mapped spans from the origin of the Ganga River to the foothills of the Himalayas covering a catchment area of 2,47,109 sq. km.
- The study portion of the Ganga River basin covers a part of India and transboundary region.
Benefits of the Atlas:
- Provides a comprehensive and systematic glacial lake database for Ganga River basin with size > 0.25 ha.
- Can be used as reference data for carrying out change analysis, both with respect to historical and future time periods in the context of climate change impact studies.
- Provides an authentic database for regular or periodic monitoring of changes in spatial extent (expansion/shrinkage), and formation of new lakes.
- Can be used in conjunction with glacier information for their retreat and climate impact studies.
- Can be useful in identifying potential critical glacial lakes and consequent GLOF
- The information can be used for disaster mitigation planning and related programmes.
Context:
Justice Department launched the “Enforcing Contracts Portal”.
About the portal:
- The website (https://doj.gov.in/eodb/) is envisioned to be a comprehensive source of information pertaining to the legislative and policy reforms being undertaken on the “Enforcing Contracts” parameters.
- It includes the latest data related to the functioning and disposal of commercial cases in the Dedicated Commercial Courts of Mumbai, Delhi, Bengaluru and Kolkata.
- The portal also hosts online reporting by all high courts regarding the mediation and arbitration centres annexed to the Commercial Courts in order to monitor and promote institutional mediation and arbitration by way of Pre-institutional Mediation and Settlement (PIMS) of commercial cases.
Background:
- The Doing Business Report is a flagship publication of the World Bank Group that benchmarks business regulations in 191 economies.
- The report measures regulations that enhance as well as constrain business activity.
- Within this, the Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) index is a ranking system which is an indication of an economy’s position relative to that of other economies across 11 areas of business regulation.
- Read more on the Ease of Doing Business Index in the link.
- The “Enforcing Contracts” indicator is one such essential area that measures time and cost to resolve a standardized commercial dispute as well as a series of good practices in the judiciary.
- The nodal department for monitoring reforms to strengthen the “Enforcing Contracts” regime for Ease of Doing Business in India is the Department of Justice, Ministry of Law and Justice in coordination with e-Committee, Supreme Court of India and the High Courts of Delhi, Bombay, Calcutta and Karnataka.
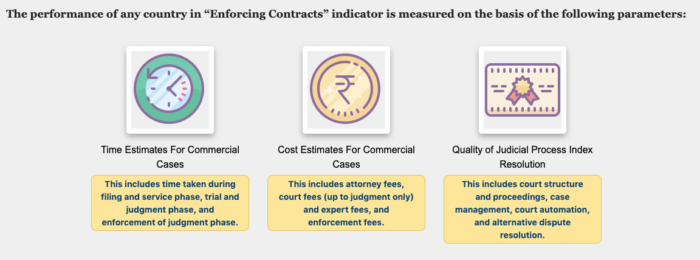
Image source: https://doj.gov.in/eodb/
6. Not-for-Profit Hospital Model in India
Context:
NITI Aayog released Report on Not-for-Profit Hospital Model in India.
Details:
- In a step towards closing the information gap on such institutions and facilitating robust policymaking in this area, the NITI Aayog released the report on not-for-hospital model.
- The study provides insights into the operation model of not-for-profit hospitals. It presents research-based findings on such hospitals—categorized under ownership and premise of service—and makes subsequent comparisons with private hospitals and health schemes of the Union government.
- The not-for-profit hospital sector provides not only curative but also preventive healthcare.
- It links healthcare with social reform, community engagement, and education.
- It uses government resources and grants to provide cost-effective healthcare to people without being concerned about profits.
- The study discusses in detail the cost-containment strategies implemented by not-for-profit hospitals. It seeks to understand the challenges that burden the operations of these institutions and hinder their growth.
- Some of the proposed interventions in the report are:
- Developing criteria to identify these hospitals
- Ranking them through a performance index
- Promoting top hospitals for practising philanthropy
- Using the expertise of these hospitals in managing human resources with limited finance in remote areas
7. SERB-FIRE
What is SERB-FIRE?
- SERB-FIRE is a program of the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) for funding industry relevant research engagement.
- SERB has signed a Letter of Intent (LoI) with a group of industries to institute the SERB-FIRE program to stimulate industry-relevant research in India.
- SERB-FIRE is under the Industry Relevant R&D (IRRD) scheme of SERB.
- It aims to utilize the expertise available in academic institutions and national laboratories to solve industry-specific problems for the larger benefit of society.
- With this initiative, the Indian research community will be able to pursue industry-relevant research opportunities in the areas of deep technologies that are novel, transformative, and can have a ground-breaking impact on a national scale.
- This is a first-of-its-kind initiative to advance deep tech-based research in India by SERB in partnership with Intel India.
- SERB-FIRE is a novel initiative to bring together industry and academia on a common platform to exchange ground-breaking ideas and co-promote innovative research.
- The focus of the program is on futuristic science and technology thematic areas.
Benefits:
- It is expected to increase research opportunities in the space of Artificial Intelligence (AI)/Machine Learning (ML), platform systems, circuits & architecture, Internet of Things (IoT), materials & devices, security, and so on from edge to cloud.
- The FIRE program is a joint government and industry initiative with a co-funding mechanism to promote innovative technology solutions and strengthen academic research through collaboration with key research and development (R&D) organizations in India.
- Having been conceived in collaboration with Intel India, it is also being extended to other industry members, which would increase its impact and reach.
Read previous PIB here.
June 29th, 2021, PIB:- Download PDF Here
| Related Links | |||
| UPSC Mains Exam | Government Exams | ||
| Bharat Stage Emission Standards |
Dr BR Ambedkar |
||
| Electoral Bonds |
Digital India |
||

Comments