Flashcards for NEET Biology are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for Neural Control and Coordination. These flashcards on Neural Control and Coordination are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. This is helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams during last-minute revision. Flashcards For NEET Biology – Neural Control and Coordination, covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Biology. Solve NEET Biology MCQs to check your understanding and outperform in the exam.


Download PDF of NEET Biology Flashcards for Neural Control and Coordination
| Name of the NEET sub-section | Topic | Flashcards helpful for |
| Biology | Neural Control and Coordination | NEET exams |
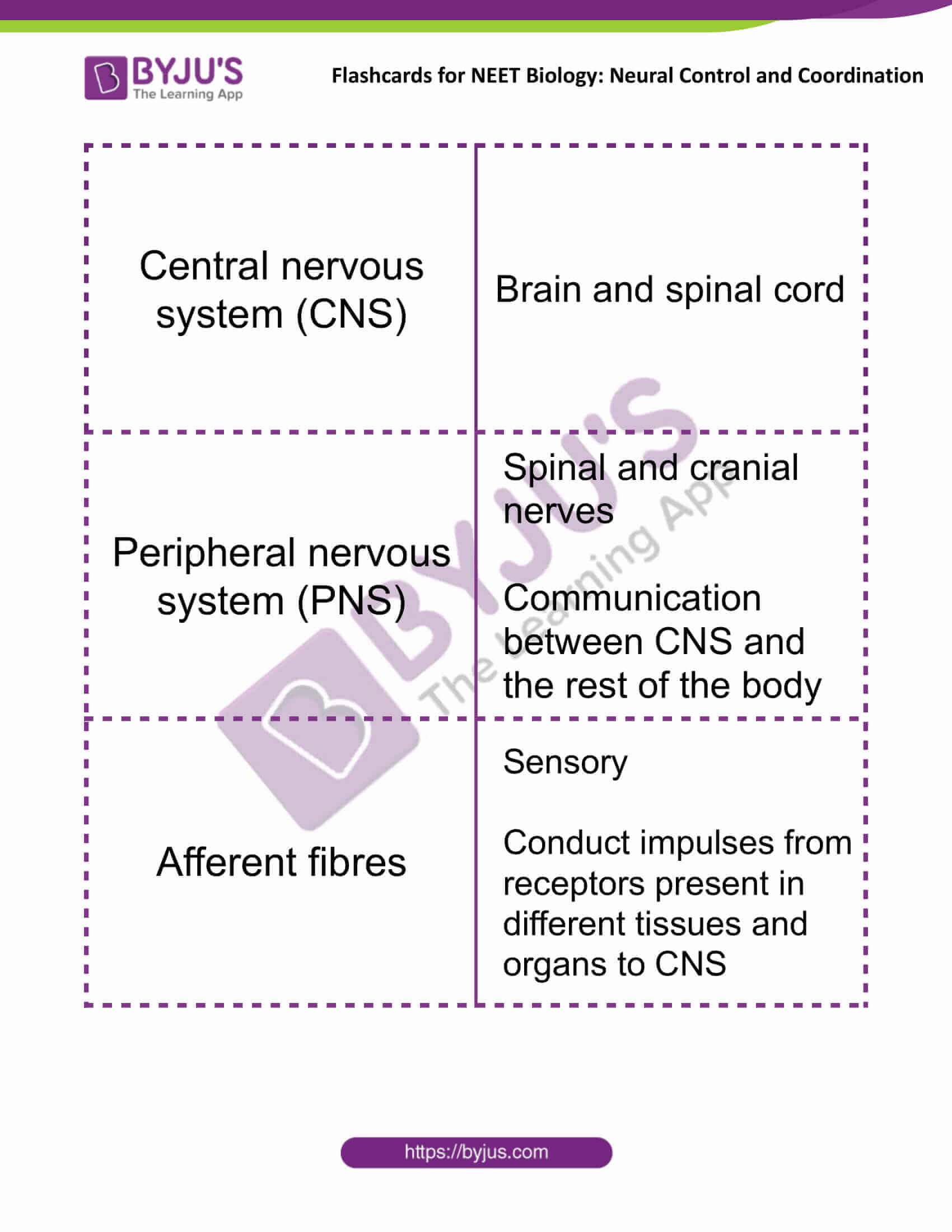
| Central nervous system (CNS) | Brain and spinal cord |
| Peripheral nervous system (PNS) | Spinal and cranial nerves
Communication between CNS and the rest of the body |
| Afferent fibres | Sensory
Conduct impulses from receptors present in different tissues and organs to CNS |
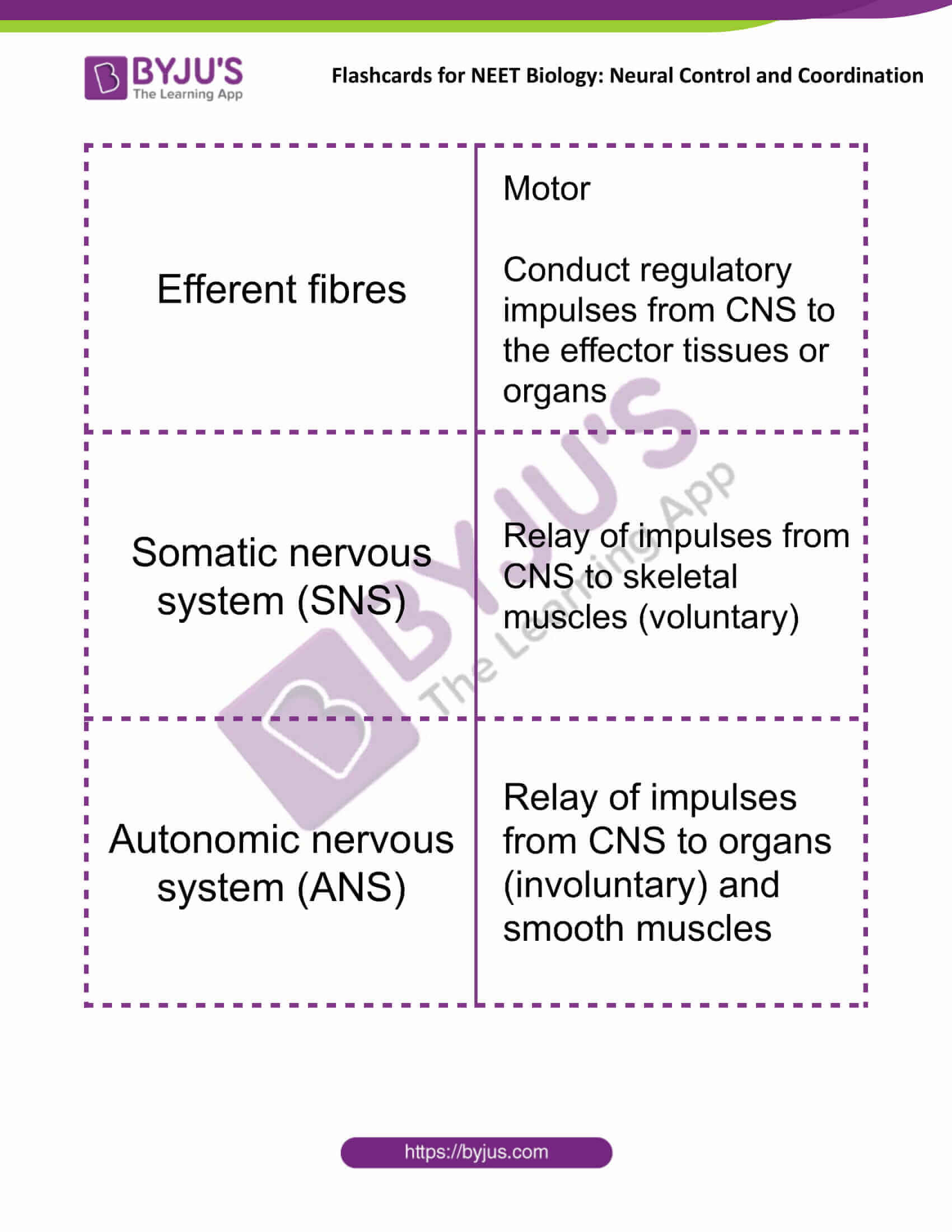
| Efferent fibres | Motor
Conduct regulatory impulses from CNS to the effector tissues or organs |
| Somatic nervous system (SNS) | Relay of impulses from CNS to skeletal muscles (voluntary) |
| Autonomic nervous system (ANS) | Relay of impulses from CNS to organs (involuntary) and smooth muscles |
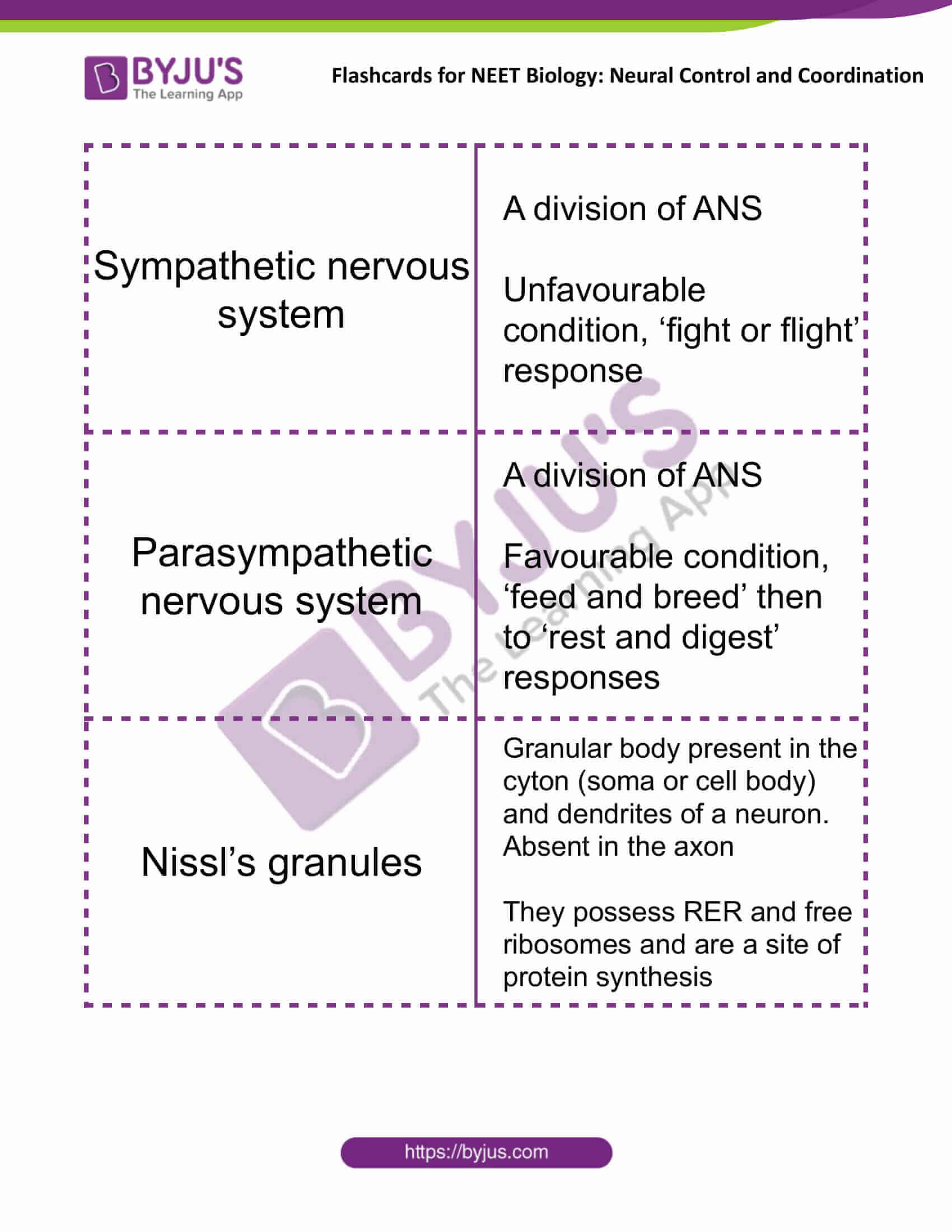
| Sympathetic nervous system | A division of ANS
Unfavourable condition, ‘fight or flight’ response |
| Parasympathetic nervous system | A division of ANS
Favourable condition, ‘feed and breed’ then to ‘rest and digest’ responses |
| Nissl’s granules | Granular body present in the cyton (soma or cell body) and dendrites of a neuron. Absent in the axon
They possess RER and free ribosomes and are a site of protein synthesis |
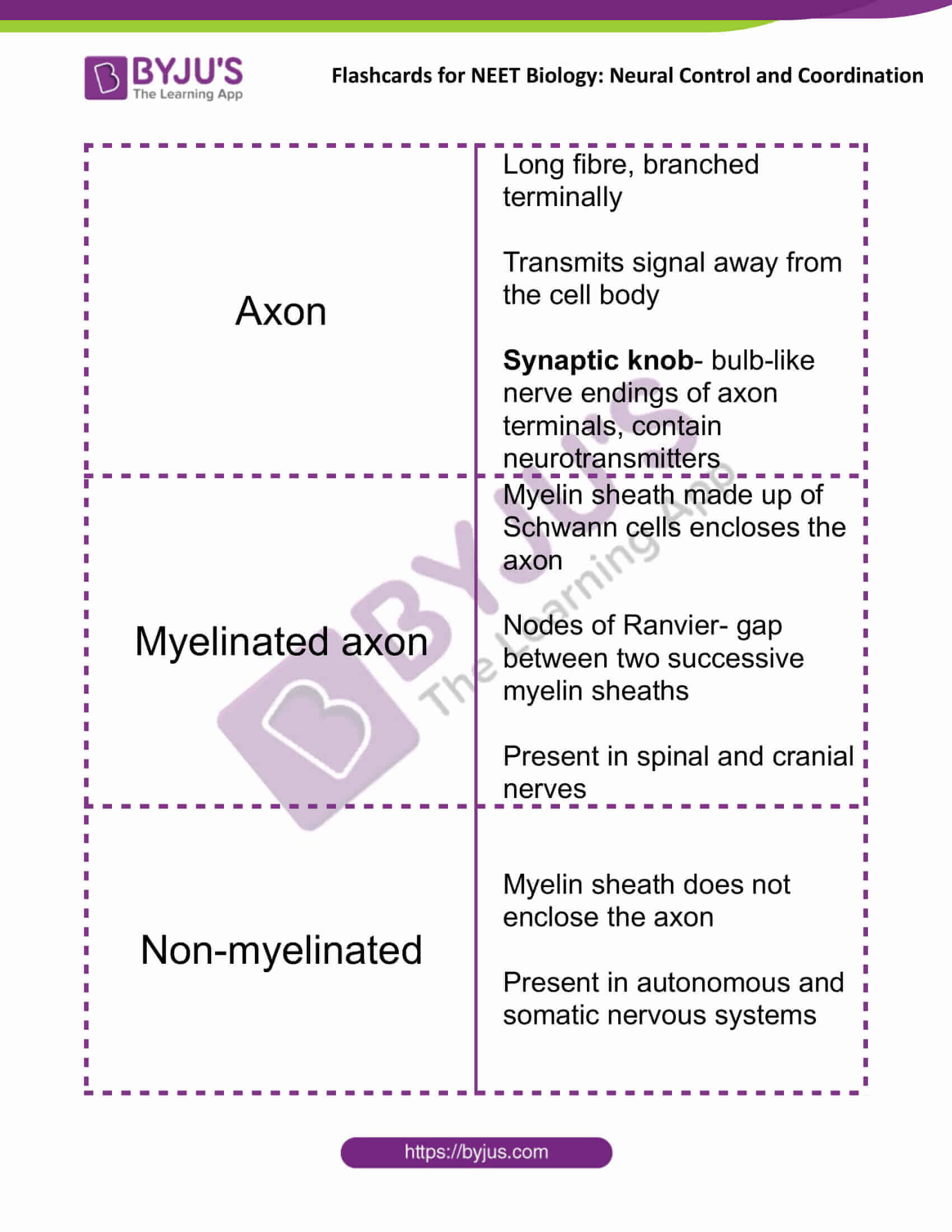
| Axon | Long fibre, branched terminally
Transmits signal away from the cell body Synaptic knob– bulb-like nerve endings of axon terminals, contain neurotransmitters |
| Myelinated axon | Myelin sheath made up of Schwann cells encloses the axon
Nodes of Ranvier- gap between two successive myelin sheaths Present in spinal and cranial nerves |
| Non-myelinated | Myelin sheath does not enclose the axon
Present in autonomous and somatic nervous systems |
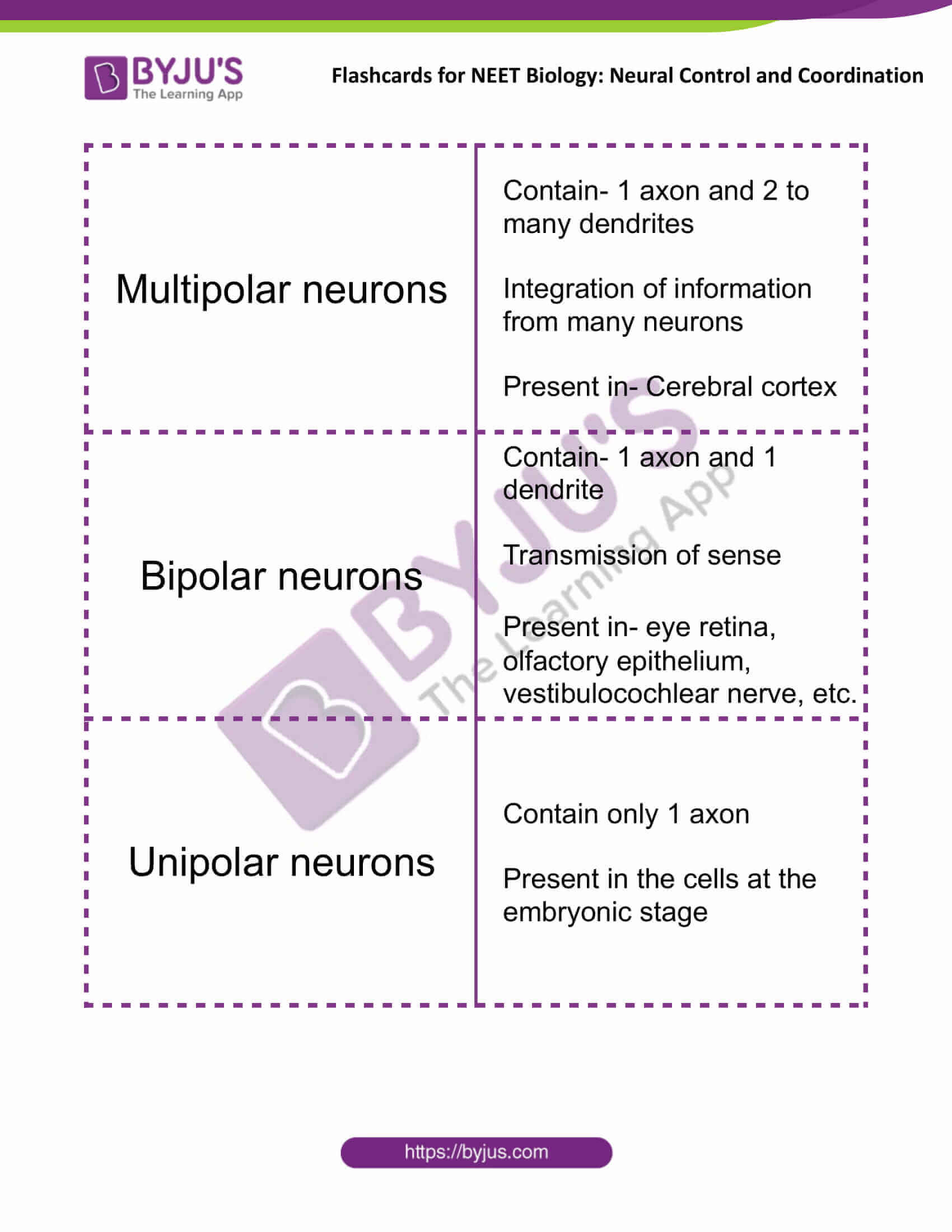
| Multipolar neurons | Contain- 1 axon and 2 to many dendrites
Integration of information from many neurons Present in- Cerebral cortex |
| Bipolar neurons | Contain- 1 axon and 1 dendrite
Transmission of sense Present in- eye retina, olfactory epithelium, vestibulocochlear nerve, etc. |
| Unipolar neurons | Contain only 1 axon
Present in the cells at the embryonic stage |
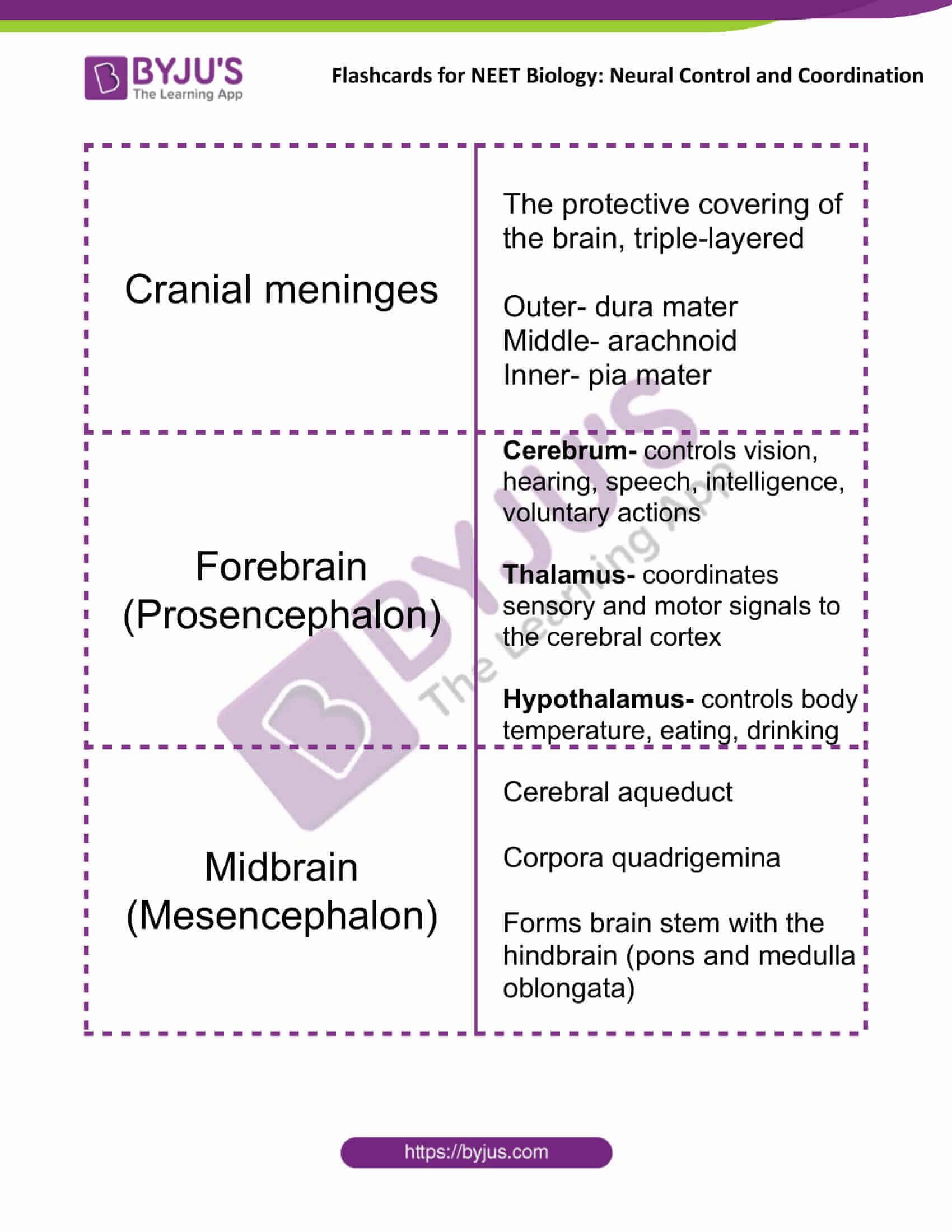
| Cranial meninges | The protective covering of the brain, triple-layered
Outer- dura mater Middle- arachnoid Inner- pia mater |
| Forebrain (Prosencephalon) | Cerebrum- controls vision, hearing, speech, intelligence, voluntary actions
Thalamus- coordinates sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex Hypothalamus- controls body temperature, eating, drinking |
| Midbrain (Mesencephalon) | Cerebral aqueduct
Corpora quadrigemina Forms brain stem with the hindbrain (pons and medulla oblongata) |
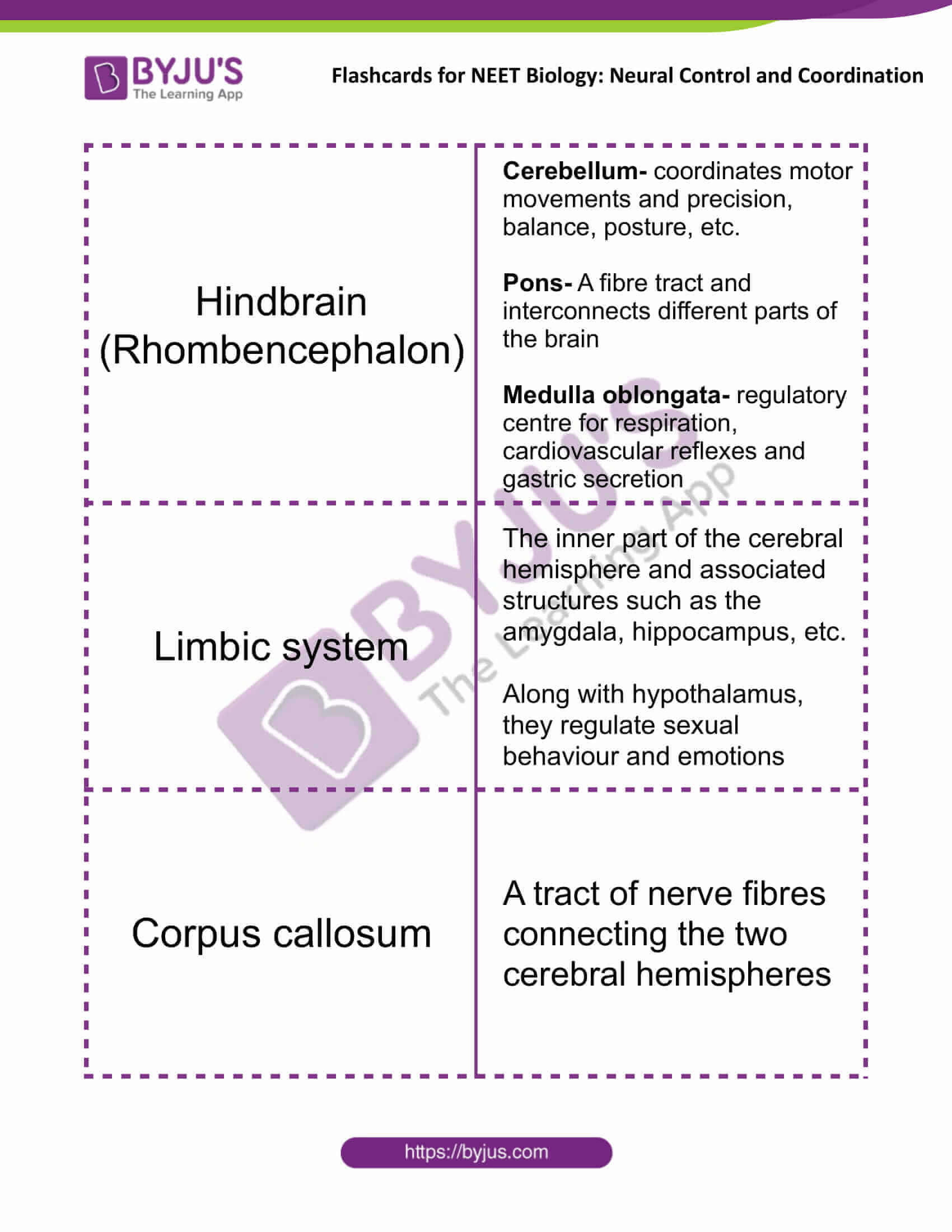
| Hindbrain (Rhombencephalon) | Cerebellum- coordinates motor movements and precision, balance, posture, etc.
Pons- A fibre tract and interconnects different parts of the brain Medulla oblongata- regulatory centre for respiration, cardiovascular reflexes and gastric secretion |
| Limbic system | The inner part of the cerebral hemisphere and associated structures such as the amygdala, hippocampus, etc.
Along with hypothalamus, they regulate sexual behaviour and emotions |
| Corpus callosum | A tract of nerve fibres connecting the two cerebral hemispheres |
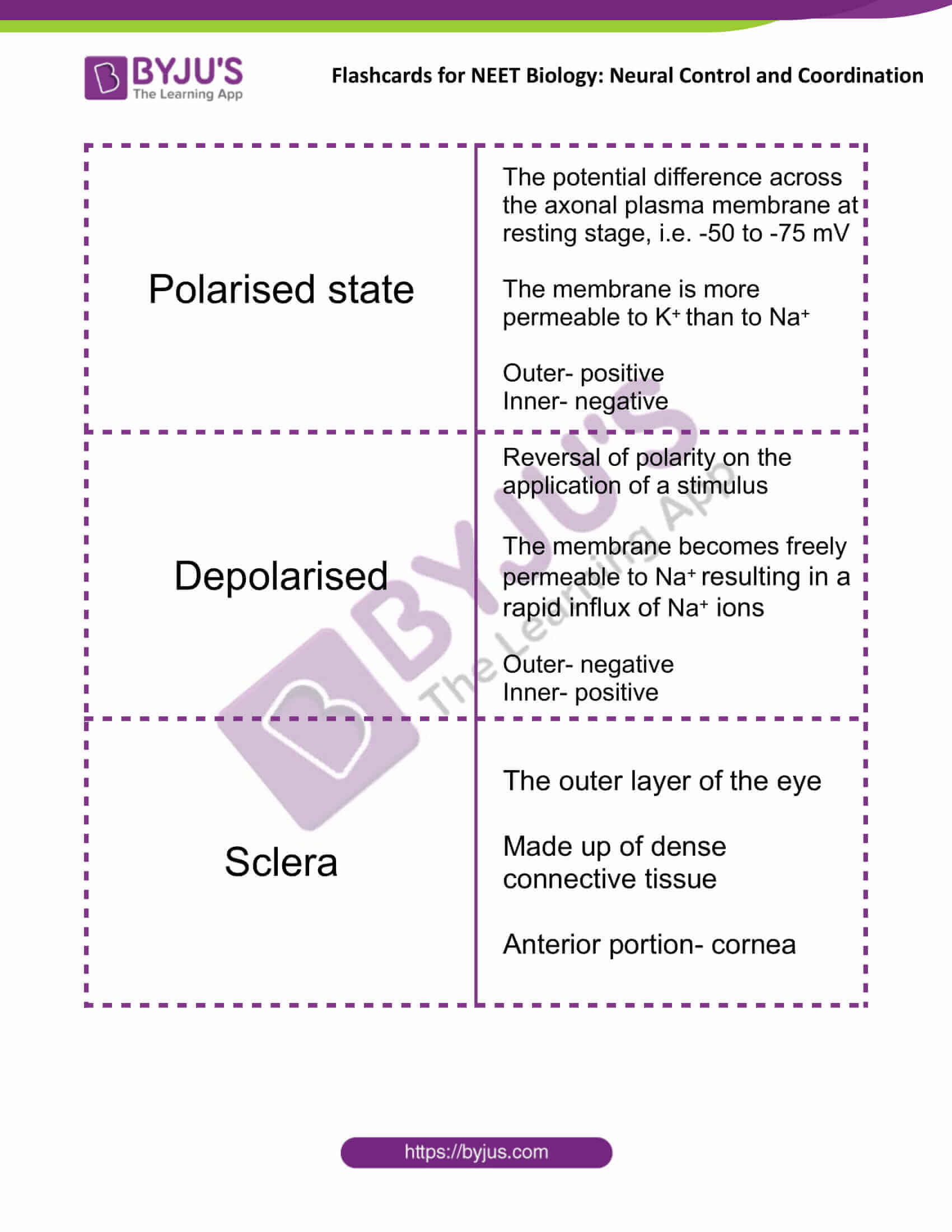
| Polarised state | The potential difference across the axonal plasma membrane at the resting stage, i.e. -50 to -75 mV
The membrane is more permeable to K+ than to Na+ Outer- positive Inner- negative |
| Depolarised | Reversal of polarity on the application of a stimulus
The membrane becomes freely permeable to Na+ resulting in a rapid influx of Na+ ions Outer- negative Inner- positive |
| Sclera | The outer layer of the eye
Made up of dense connective tissue Anterior portion- cornea |
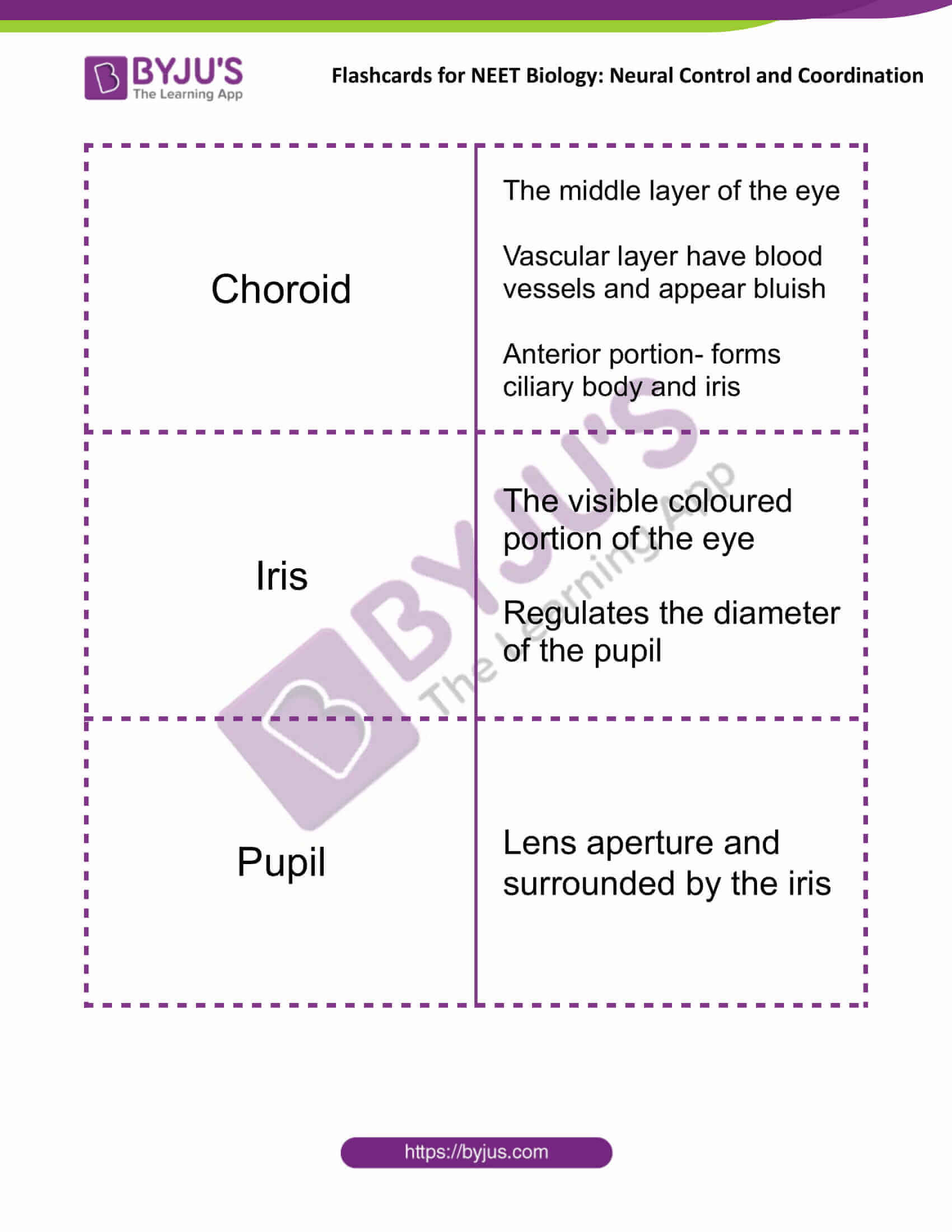
| Choroid | The middle layer of the eye
Vascular layer have blood vessels and appear bluish Anterior portion- forms ciliary body and iris |
| Iris | The visible coloured portion of the eye
Regulates the diameter of the pupil |
| Pupil | Lens aperture and surrounded by the iris |
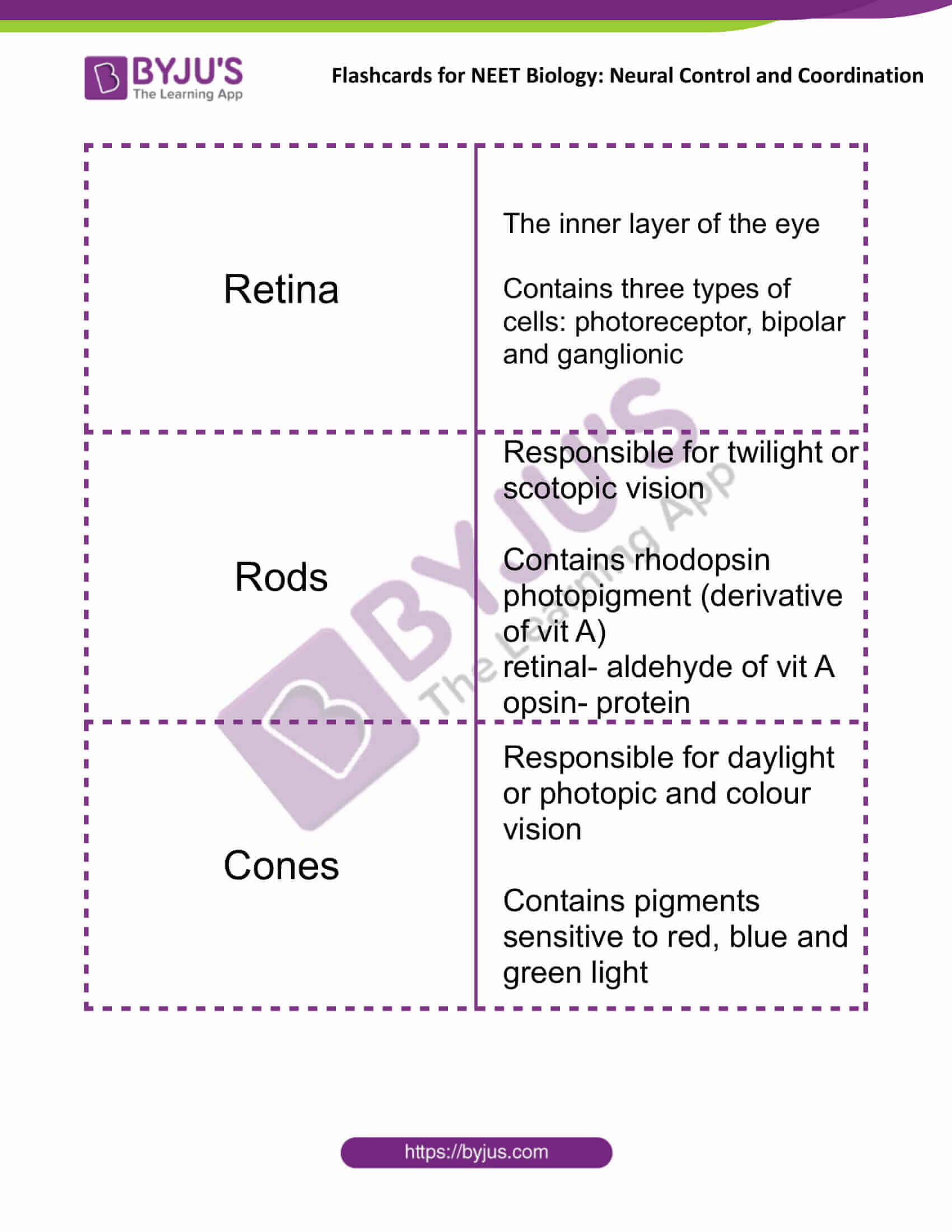
| Retina | The inner layer of the eye
Contains three types of cells: photoreceptor, bipolar and ganglionic |
| Rods | Responsible for twilight or scotopic vision
Contains rhodopsin photopigment (derivative of vit A) retinal- aldehyde of vit A opsin- protein |
| Cones | Responsible for daylight or photopic and colour vision
Contains pigments sensitive to red, blue and green light |
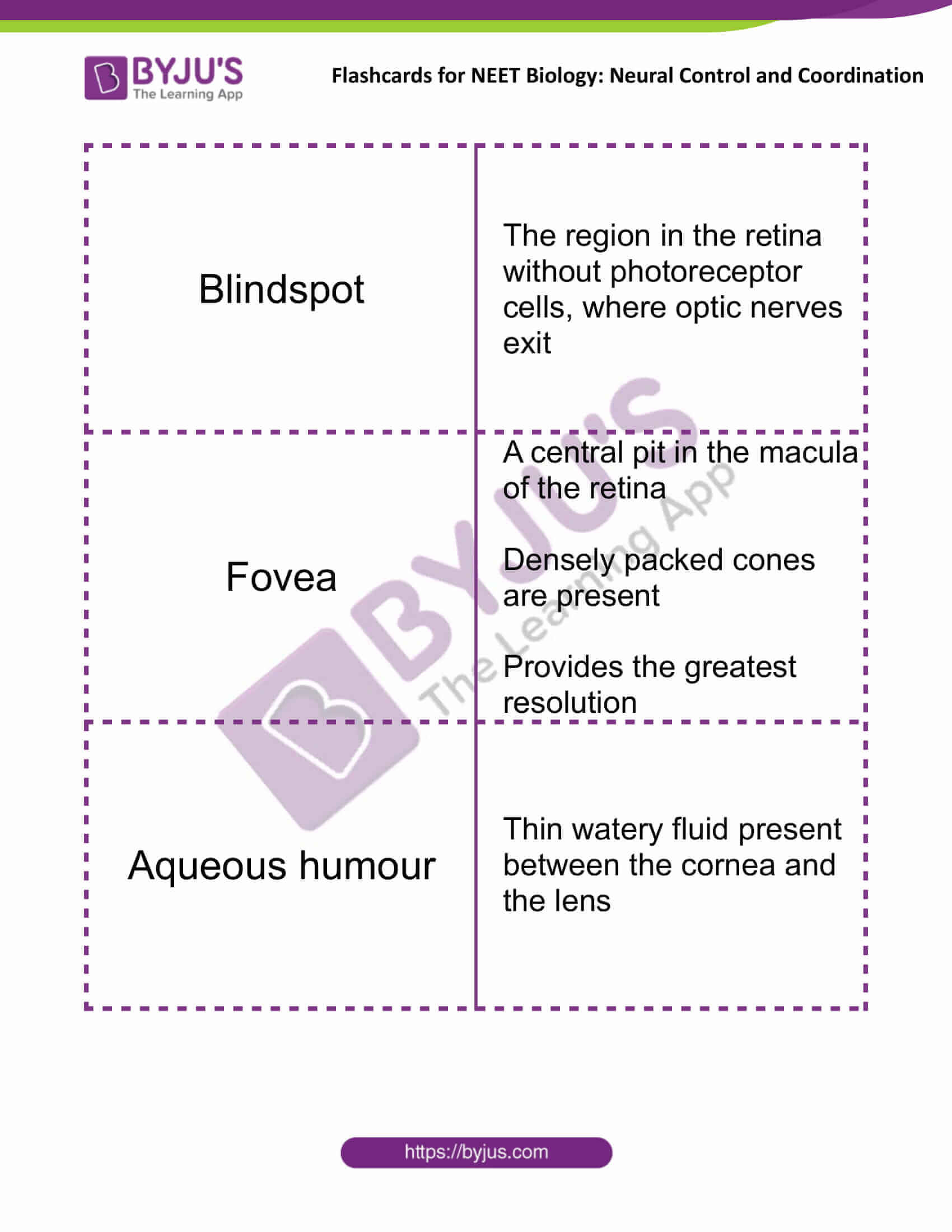
| Blindspot | The region in the retina without photoreceptor cells, where optic nerves exit |
| Fovea | A central pit in the macula of the retina
Densely packed cones are present Provides the greatest resolution |
| Aqueous humour | Thin watery fluid present between the cornea and the lens |
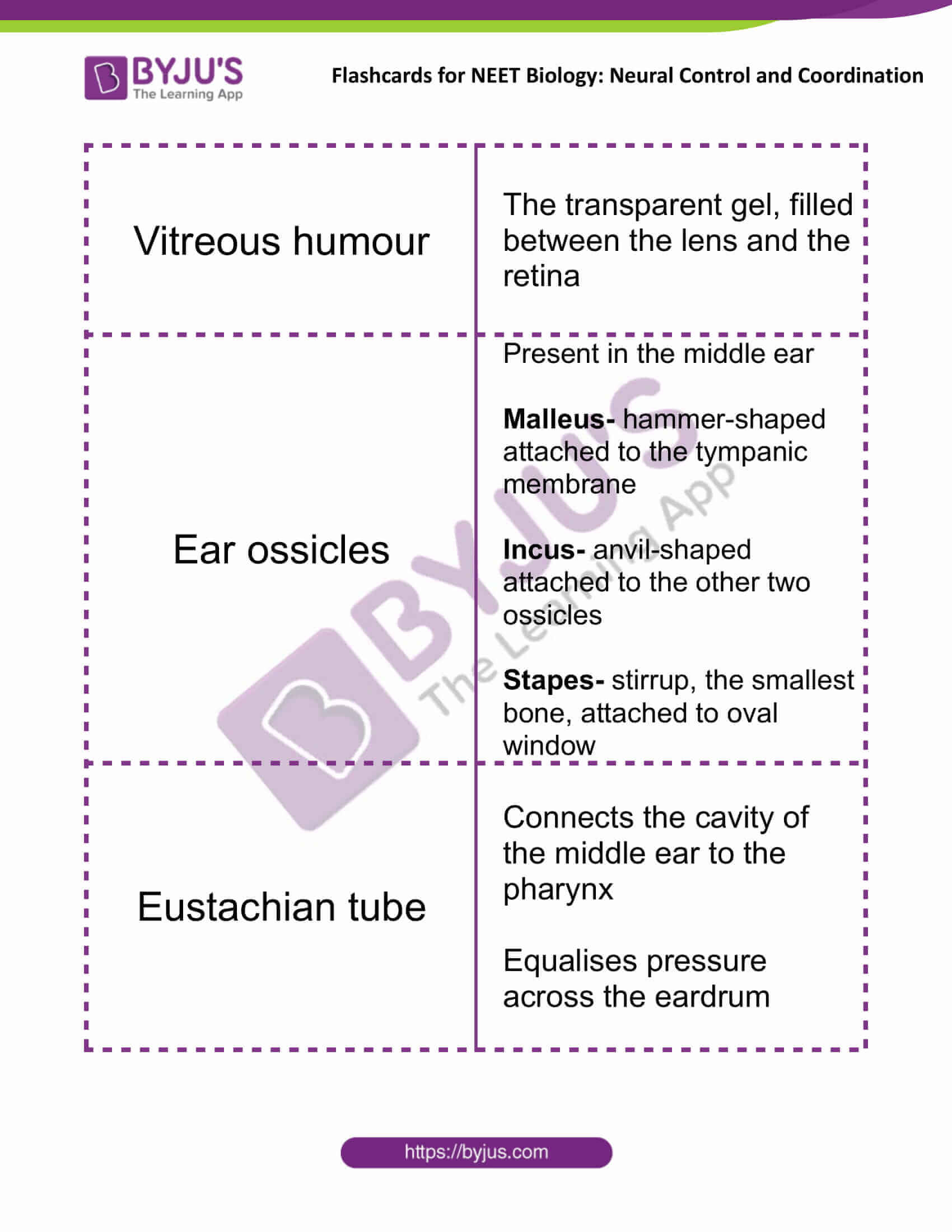
| Vitreous humour | The transparent gel, filled between the lens and the retina |
| Ear ossicles | Present in the middle ear
Malleus- hammer-shaped attached to the tympanic membrane Incus- anvil-shaped attached to the other two ossicles Stapes- stirrup, the smallest bone, attached to the oval window |
| Eustachian tube | Connects the cavity of the middle ear to the pharynx
Equalises pressure across the eardrum |
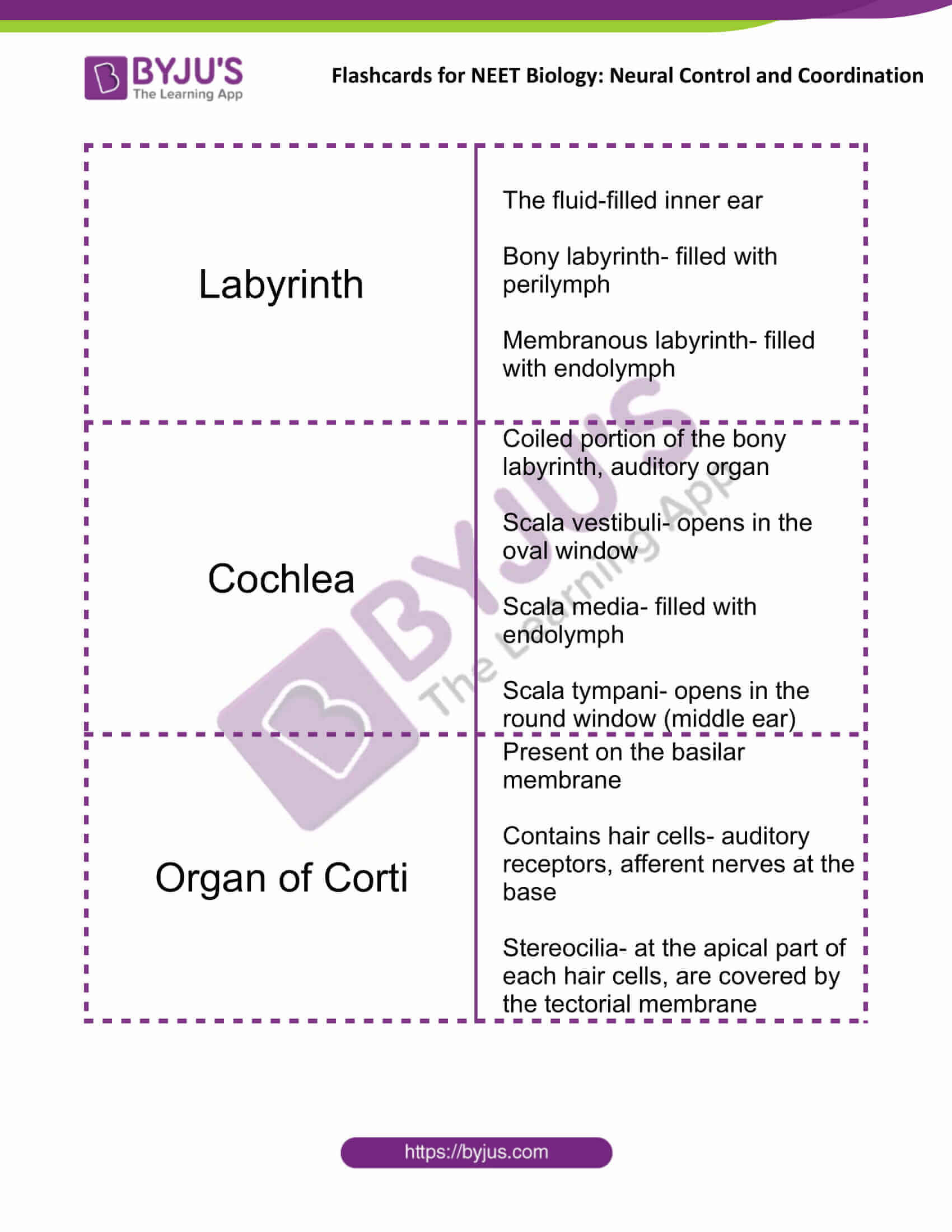
| Labyrinth | The fluid-filled inner ear
Bony labyrinth- filled with perilymph Membranous labyrinth- filled with endolymph |
| Cochlea | Coiled portion of the bony labyrinth, auditory organ
Scala vestibuli- opens in the oval window Scala media- filled with endolymph Scala tympani- opens in the round window (middle ear) |
| Organ of Corti | Present on the basilar membrane
Contains hair cells- auditory receptors, afferent nerves at the base Stereocilia- at the apical part of each hair cells, are covered by the tectorial membrane |
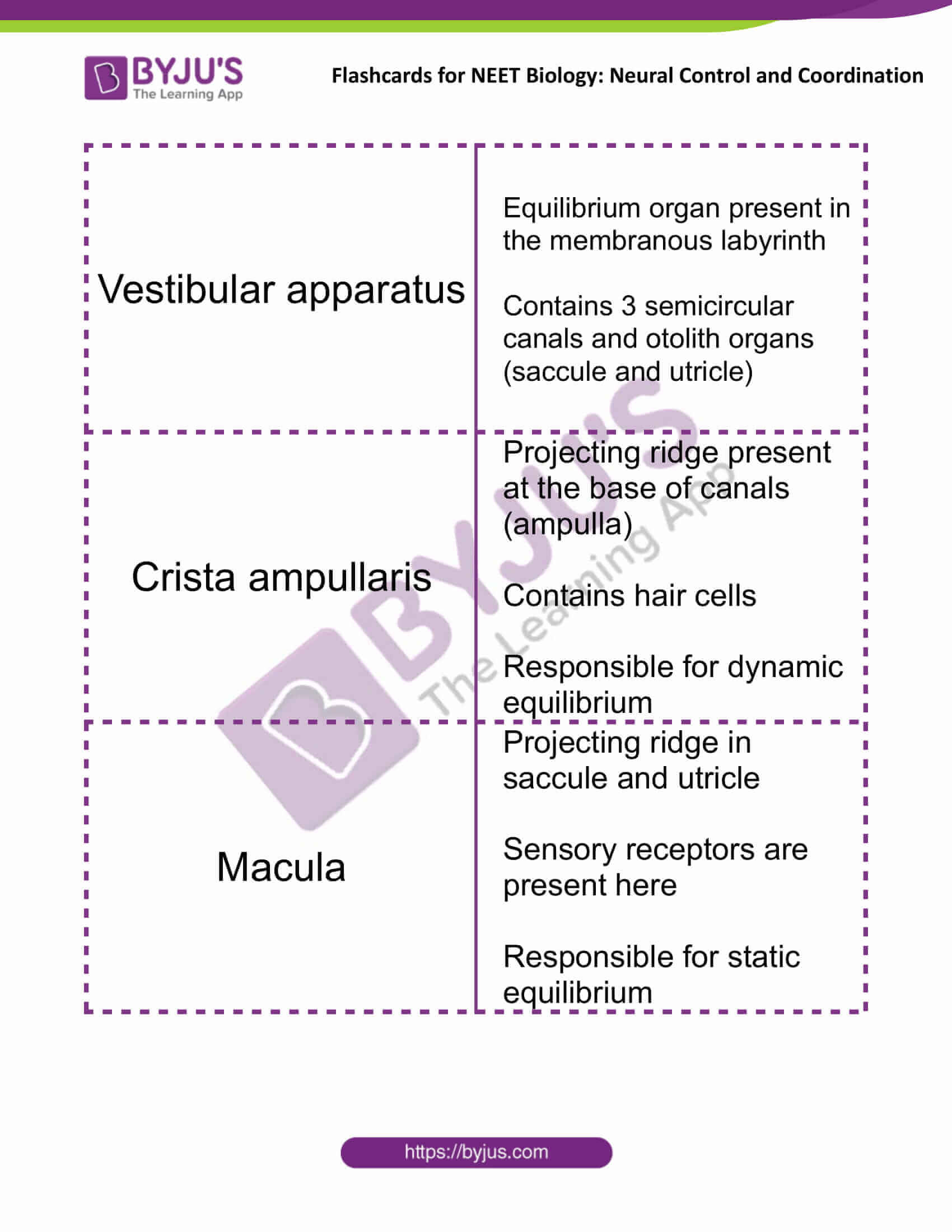
| Vestibular apparatus | Equilibrium organ present in the membranous labyrinth
Contains 3 semicircular canals and otolith organs (saccule and utricle) |
| Crista ampullaris | Projecting ridge present at the base of canals (ampulla)
Contains hair cells Responsible for dynamic equilibrium |
| Macula | Projecting ridge in saccule and utricle
Sensory receptors are present here Responsible for static equilibrium |
| Otoliths | Statoconium or statolith
Calcium carbonate crystals in saccule and utricle Play role in spatial orientation |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Biology, only at BYJU’S.
Also Check:
NEET Flashcards: Digestion And Absorption
NEET Flashcards: Breathing And Exchange Of Gases
NEET Flashcards: Body Fluids And Circulation

Comments