Flashcards for NEET Biology are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for Principles of Inheritance and Variation. These flashcards on Principles of Inheritance and Variation are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. This is helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams during last-minute revision. Flashcards For NEET Biology – Principles of Inheritance and Variation, covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Biology. Solve NEET Biology MCQs to check your understanding and outperform in the exam.
Download PDF of NEET Biology Flashcards for Principles of Inheritance and Variation
| Name of the NEET sub-section | Topic | Flashcards helpful for |
| Biology | Principles of Inheritance and Variation | NEET exams |
| Principles of Inheritance and Variation | |
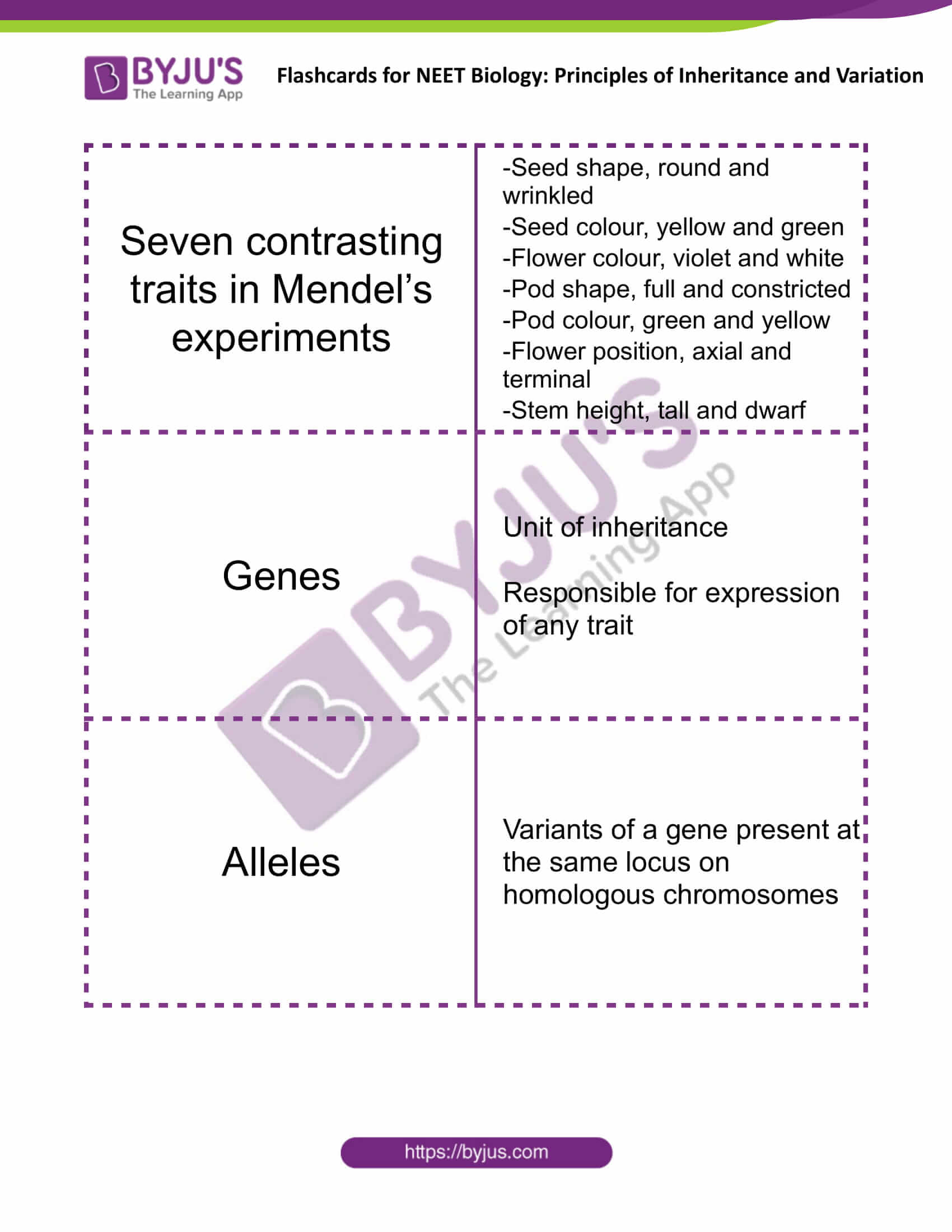
| Seven contrasting traits in Mendel’s experiments | -Seed shape, round and wrinkled
-Seed colour, yellow and green -Flower colour, violet and white -Pod shape, full and constricted -Pod colour, green and yellow -Flower position, axial and terminal -Stem height, tall and dwarf |
| Genes | Unit of inheritance
Responsible for expression of any trait |
| Alleles | Variants of a gene present at the same locus on homologous chromosomes |
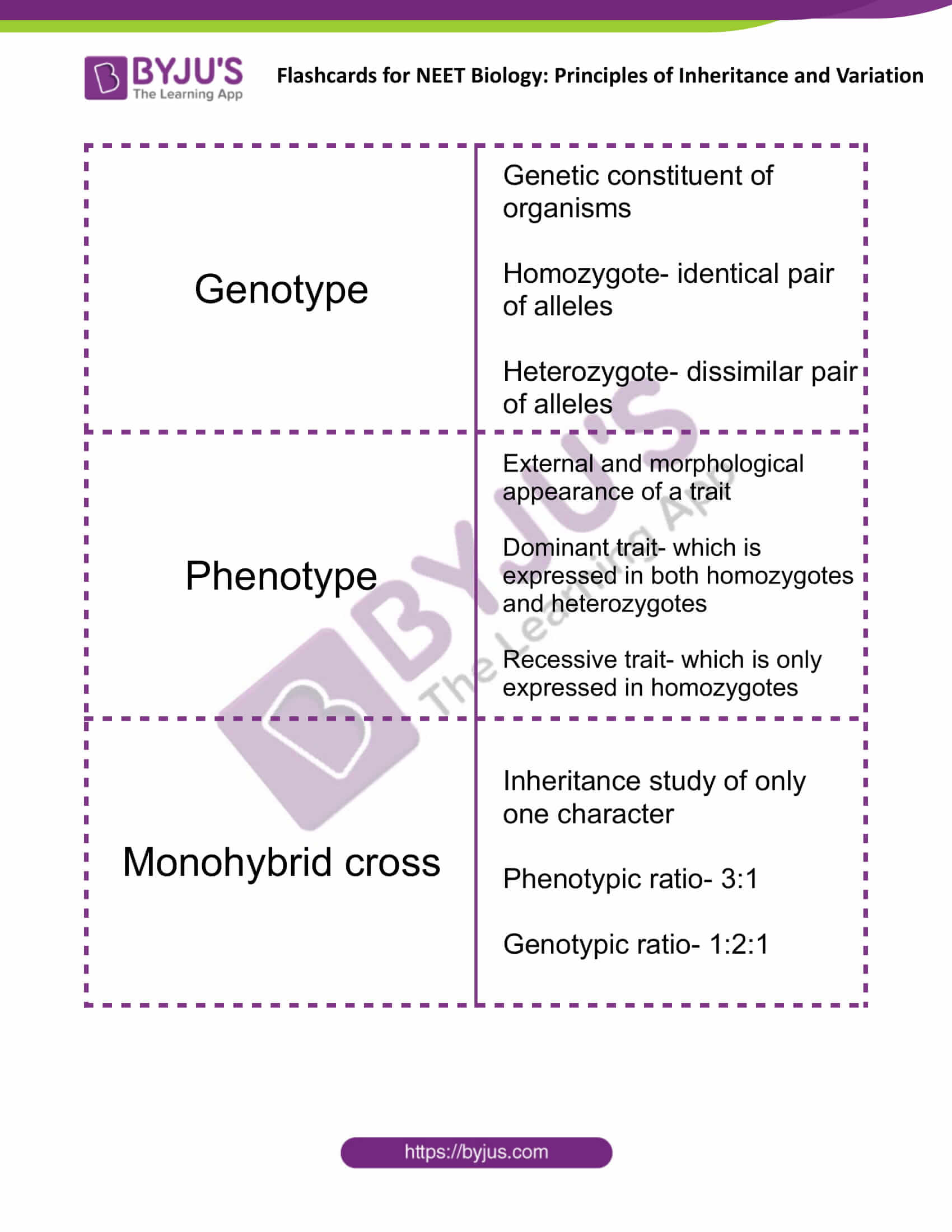
| Genotype | Genetic constituent of organisms
Homozygote- identical pair of alleles Heterozygote- dissimilar pair of alleles |
| Phenotype | External and morphological appearance of a trait
Dominant trait- which is expressed in both homozygotes and heterozygotes Recessive trait- which is only expressed in homozygotes |
| Monohybrid cross | Inheritance study of only one character
Phenotypic ratio- 3:1 Genotypic ratio- 1:2:1 |
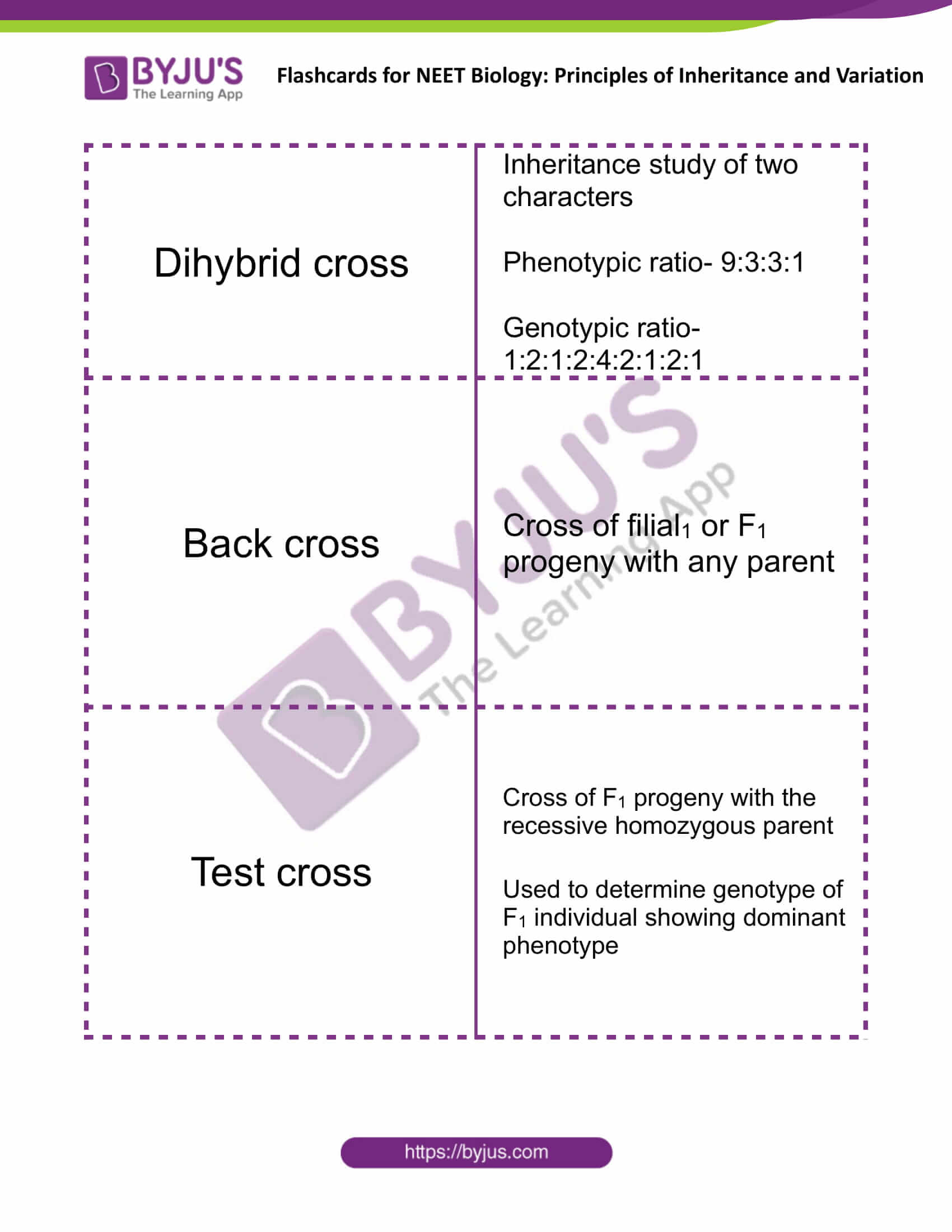
| Dihybrid cross | Inheritance study of two characters
Phenotypic ratio- 9:3:3:1 Genotypic ratio- 1:2:1:2:4:2:1:2:1 |
| Back cross | Cross of filial1 or F1 progeny with any parent |
| Test cross | Cross of F1 progeny with the recessive homozygous parent
Used to determine genotype of F1 individual showing dominant phenotype |
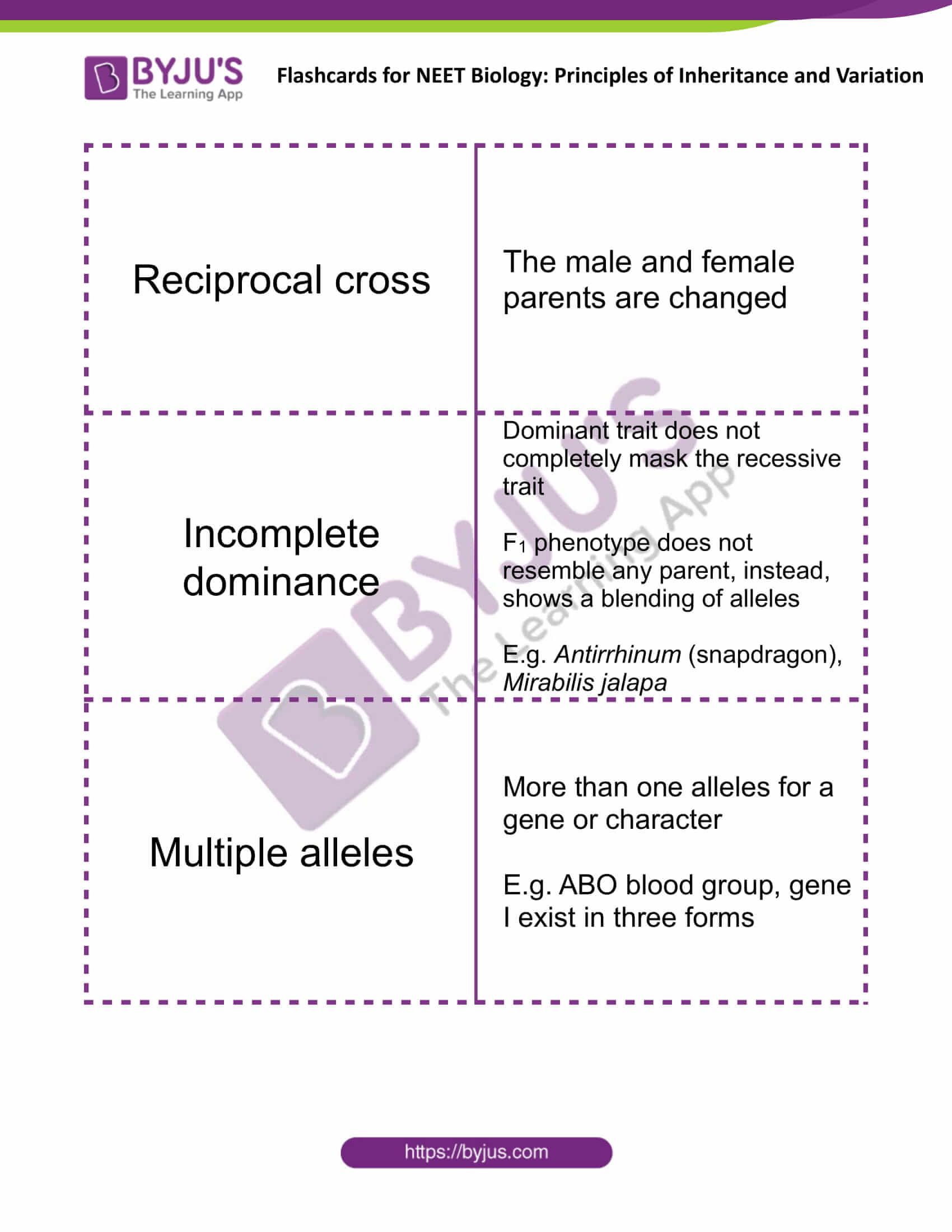
| Reciprocal cross | The male and female parents are changed |
| Incomplete dominance | Dominant trait does not completely mask the recessive trait
F1 phenotype does not resemble any parent, instead, shows a blending of alleles E.g. Antirrhinum (snapdragon), Mirabilis jalapa |
| Multiple alleles | More than one alleles for a gene or character
E.g. ABO blood group, gene I exist in three forms |
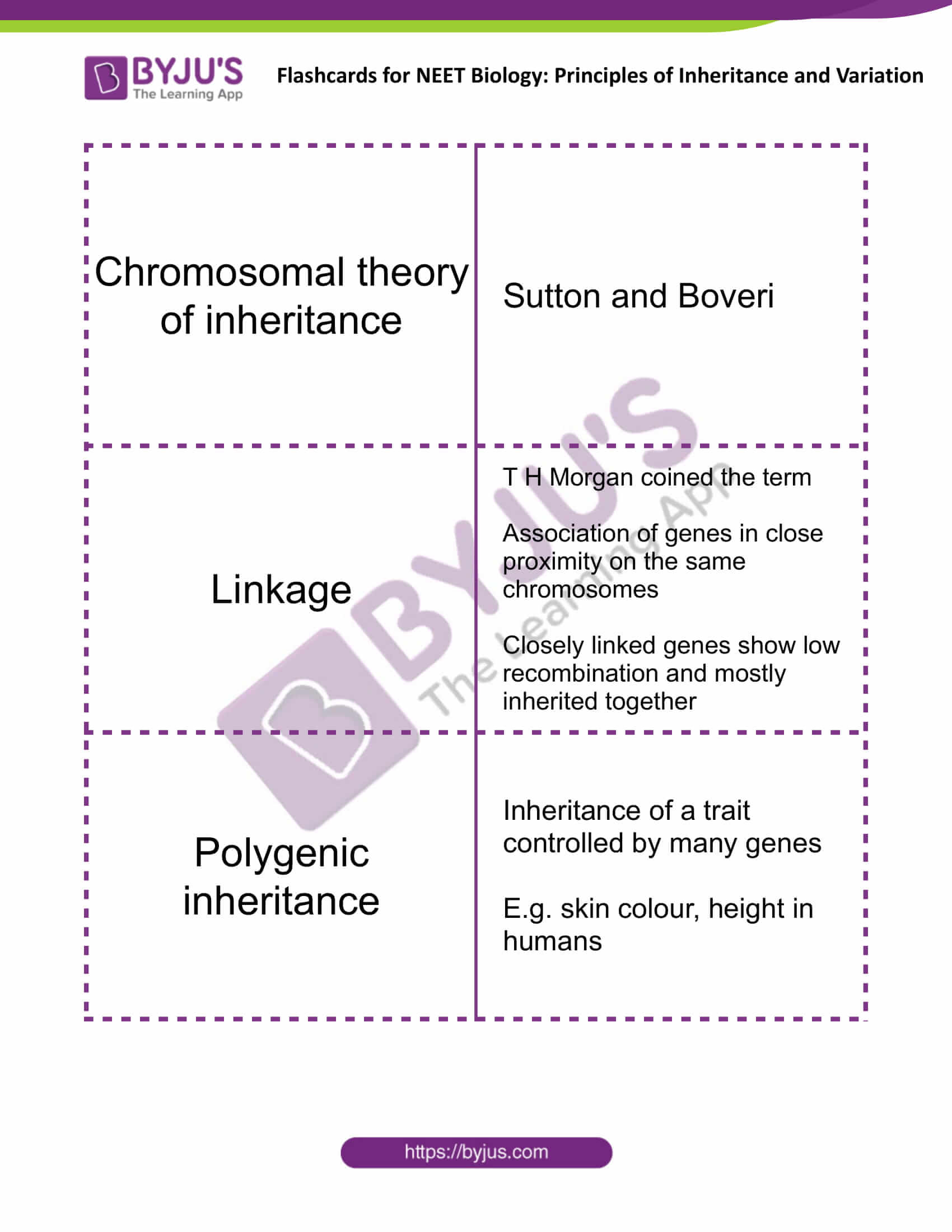
| Chromosomal theory of inheritance | Sutton and Boveri |
| Linkage | T H Morgan coined the term
Association of genes in close proximity on the same chromosomes Closely linked genes show low recombination and mostly inherited together |
| Polygenic inheritance | Inheritance of a trait controlled by many genes
E.g. skin colour, height in humans |
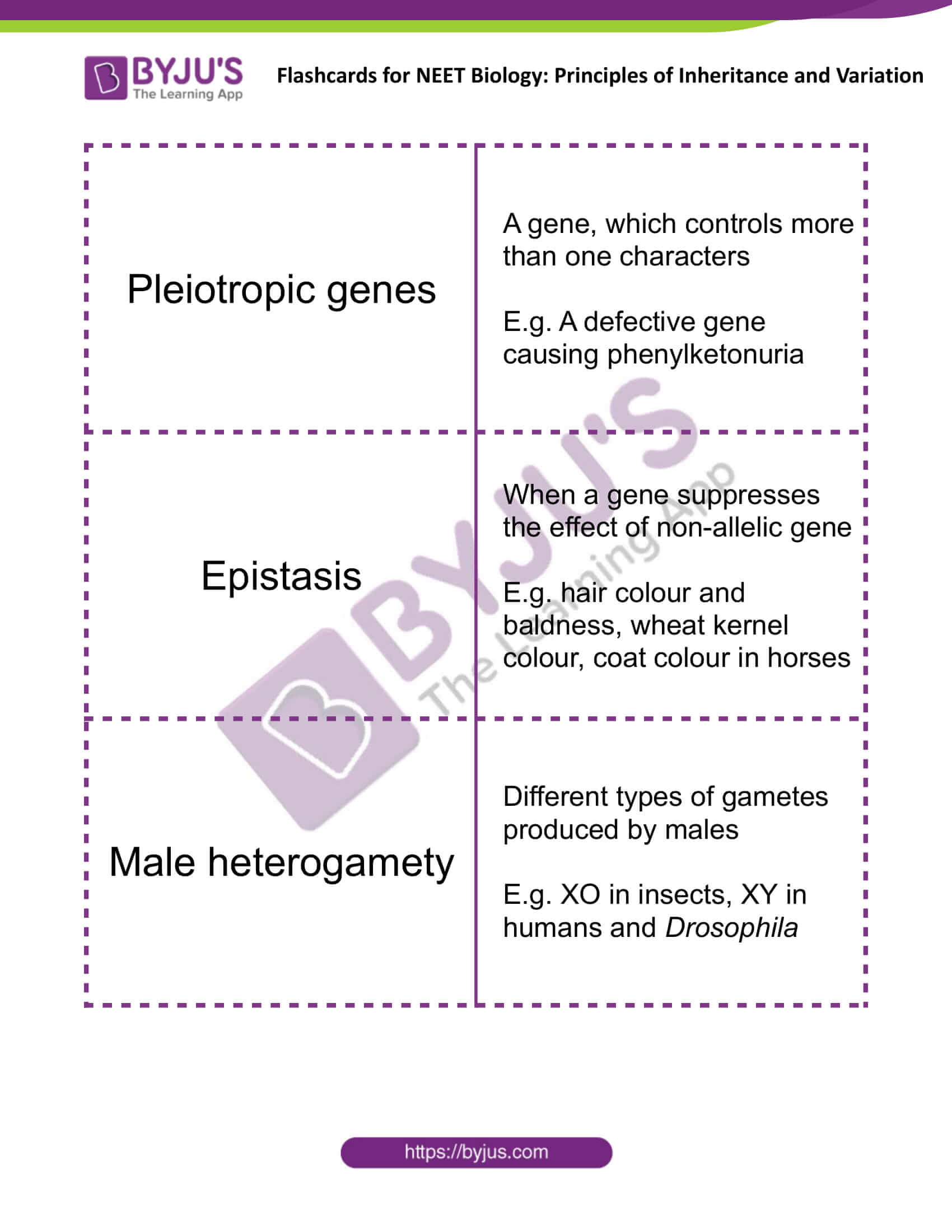
| Pleiotropic genes | A gene, which controls more than one characters
E.g. A defective gene causing phenylketonuria |
| Epistasis | When a gene suppresses the effect of non-allelic gene
E.g. hair colour and baldness, wheat kernel colour, coat colour in horses |
| Male heterogamety | Different types of gametes produced by males
E.g. XO in insects, XY in humans and Drosophila |
| Female heterogamety | Different types of gametes produced by females
E.g. ZW in birds |
| Parthenogenesis | Development of an individual from an unfertilised egg
E.g. male drones of honey bees contain haploid chromosomes |
| Mutation | Change in the DNA sequence due to deletion, insertion or substitution
Point mutation- change in single base pair in DNA, e.g. sickle cell anaemia Frame-shift mutation- due to deletion or insertion of base pairs |
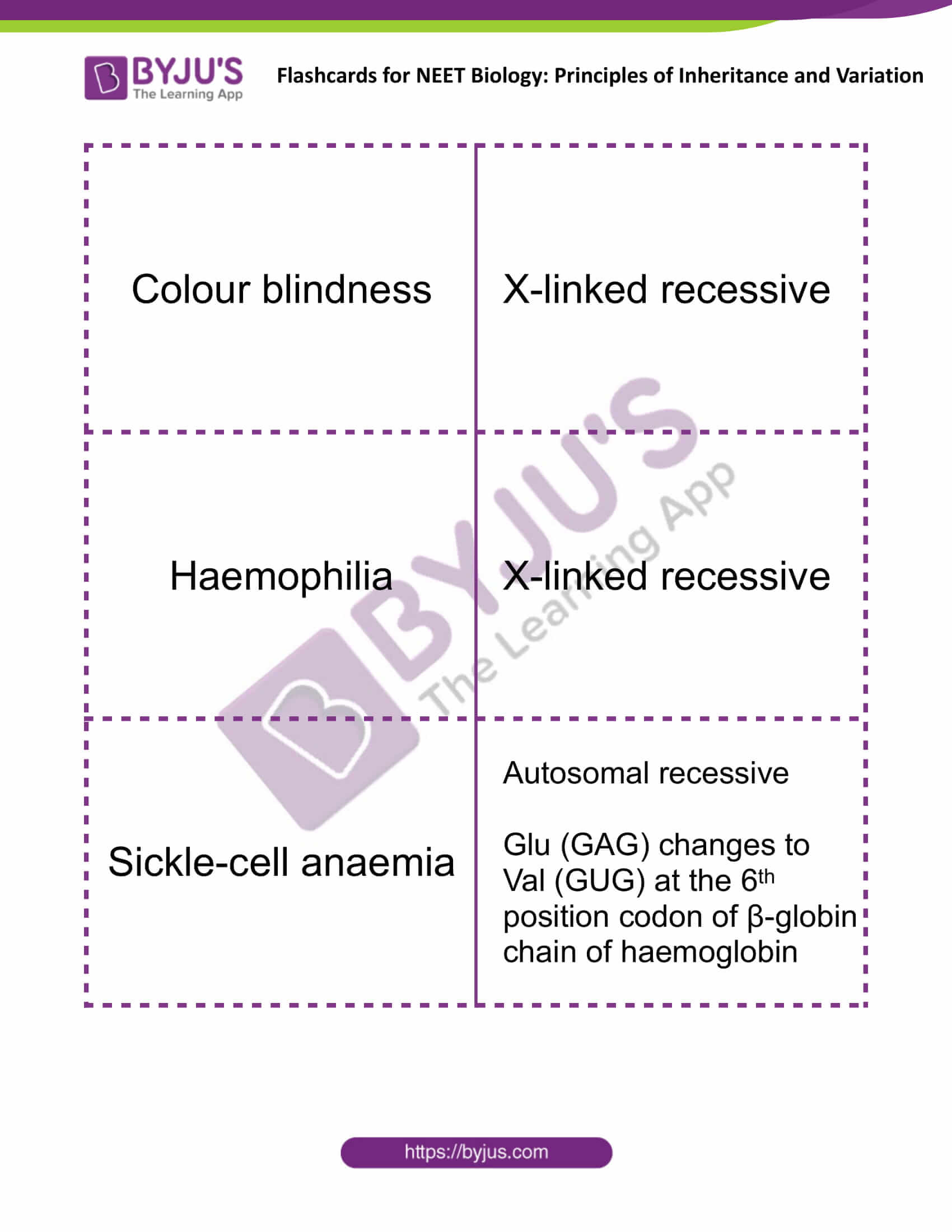
| Colour blindness | X-linked recessive |
| Haemophilia | X-linked recessive |
| Sickle-cell anaemia | Autosomal recessive
Glu (GAG) changes to Val (GUG) at the 6th position codon of β-globin chain of haemoglobin |
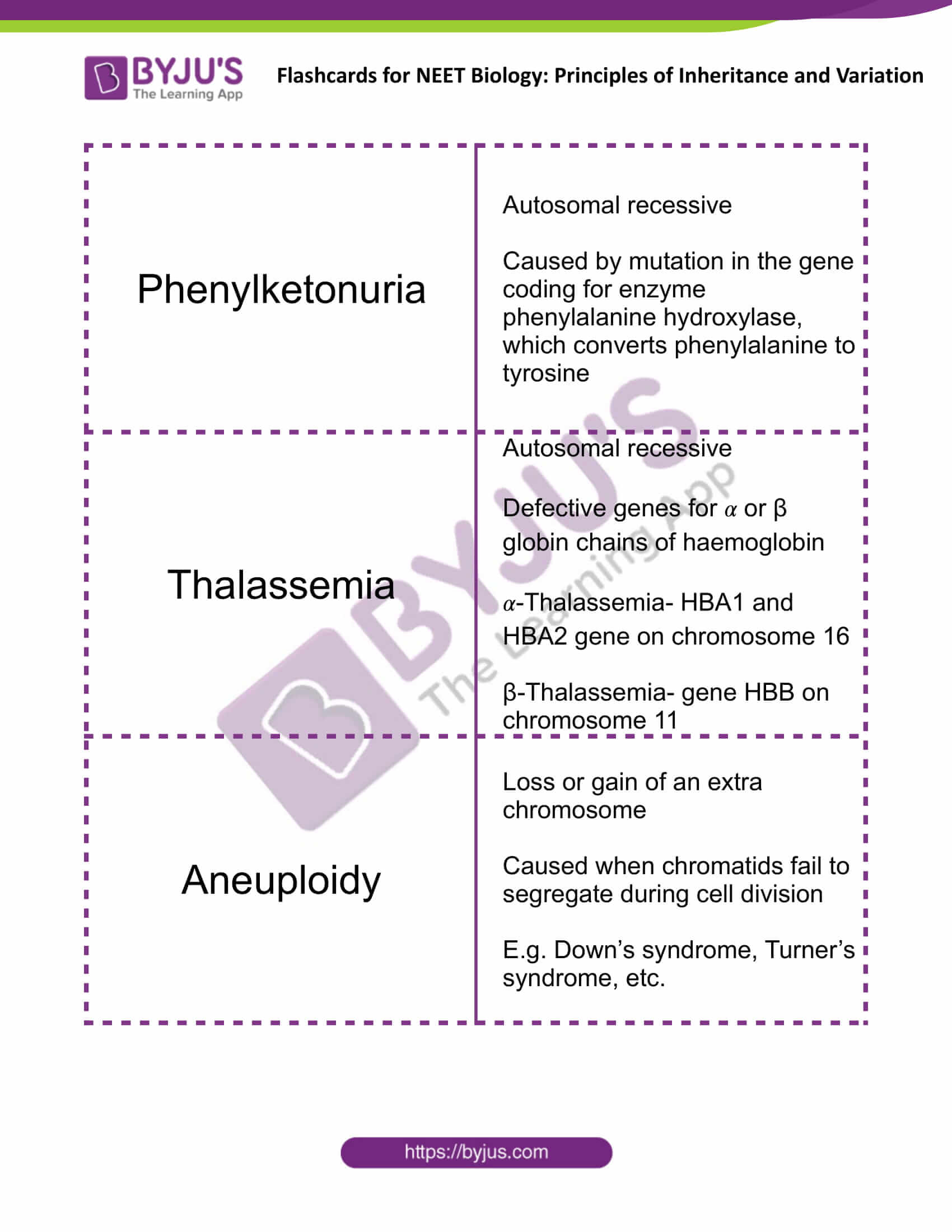
| Phenylketonuria | Autosomal recessive
Caused by mutation in the gene coding for enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, which converts phenylalanine to tyrosine |
| Thalassemia | Autosomal recessive
Defective genes for 𝛼 or β globin chains of haemoglobin 𝛼-Thalassemia- HBA1 and HBA2 gene on chromosome 16 β-Thalassemia- gene HBB on chromosome 11 |
| Aneuploidy | Loss or gain of an extra chromosome
Caused when chromatids fail to segregate during cell division E.g. Down’s syndrome, Turner’s syndrome, etc. |
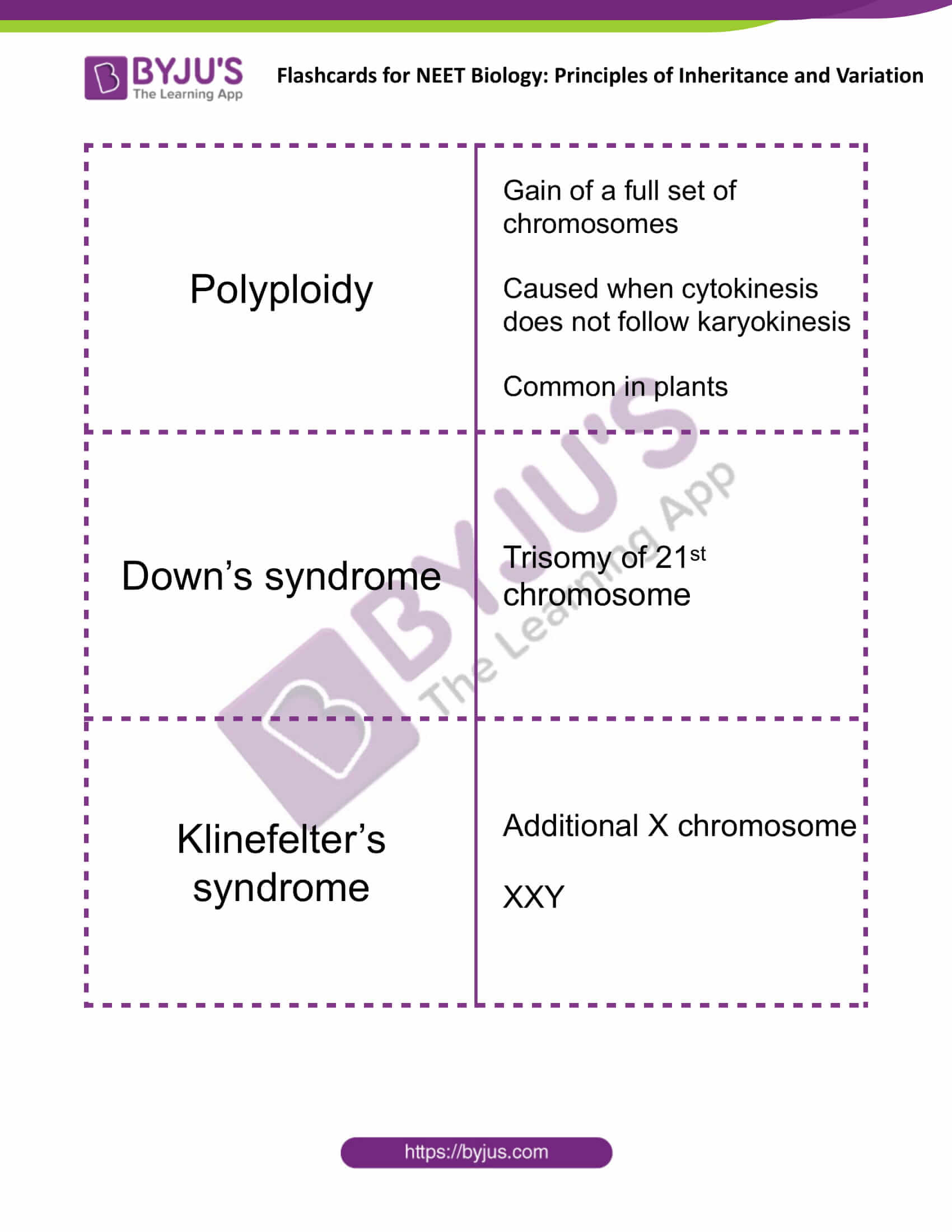
| Polyploidy | Gain of a full set of chromosomes
Caused when cytokinesis does not follow karyokinesis Common in plants |
| Down’s syndrome | Trisomy of 21st chromosome |
| Klinefelter’s syndrome | Additional X chromosome
XXY |
| Turner’s syndrome | Monosomy, one of the sex chromosomes is missing
XO |
| True breeding plant | Stable trait inheritance for several generations on self-fertilisation
Homozygous for traits Produces similar offsprings on self-fertilisation |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Biology, only at BYJU’S.
Recommended Video:
Probabilities in Genetics Class 11 & 12 Biology | NEET Botany Preparation | NEET 2022 Exam
Also Check:
NEET Flashcards: Cell The Unit Of Life
NEET Flashcards: Cell Cycle And Cell Division


Comments