Aim Of The Experiment
To study the different slides and identifying them with various characteristics. The various specimens are:
- Amoeba
- Hydra
- Liver fluke
- Ascaris lumbricoidis
- Leech
- Earthworm
- Prawn
- Silkworm
- Snail
- Starfish
- Shark
- Rohu
- Frog
- Lizard
- Pigeon
- Rabbit
Materials Required
- Freshly prepared animal specimens
- Pencil
- Record file
- Eraser
- Sharpener
- Rules
- Practical guide/A laboratory guide
Amoeba Proteus
Classification
| Kingdom | Phylum | Class | Order | Genus | Species |
| Protista | Protozoa | Sarcodine | Amoebida | Amoeba | Proteus |
Discussion
- It is a microscopic, unicellular entity with a diameter of 0.2-0.5mm, appearing greyish in colour.
- The amoeba is usually found in ditches, ponds, lakes or rivers that contain adequate decomposed organic matter.
- When observed under a microscope, amoeba seems to be like a jelly that has an irregular shape containing a little mass of hyaline protoplasm. This protoplasm can be classified into a notable inner endoplasm and outer octoplasm.
Characteristic Features
- Irregular shape
- Unicellular
- Exhibit pseudopodia – They are blunt and finger-like projections that are used in locomotion and phagocytosis
- They exhibit contractile vacuole
Hydra

Classification
| Kingdom | Phylum | Class | Order | Genus | Species |
| Animalia | Cnidaria | Hydrozoa | Hydrozoida | Hydra | Vulgaris |
Discussion
- They are solitary and freshwater forms that are found attached to rocks, stones and weeds
- The body resembles a cylindrical and an elongated tube wherein the posterior end is attached to the substratum by a basal disc and the anterior end is free
- The body wall of hydra is made up of two cell layers referred to as diploblastic
- The epidermis consists of cnidocytes or stinging cells that serve as defensive and offensive organs
Characteristic Features
- Possess a soft body and are diploblastic
- The free end exhibits an inverted funnel-like structure known as hypostome which is the mouth
- The mouth is girdled with a circlet of around 5 to 10 long and hollow structures known as tentacles. These tentacles help in capturing prey as these structures contain cnidoblasts which assist in the killing of the prey.
- The gastrovascular cavity is present which opens to the mouth
Liver Fluke (Fasciola herpatica) present, which
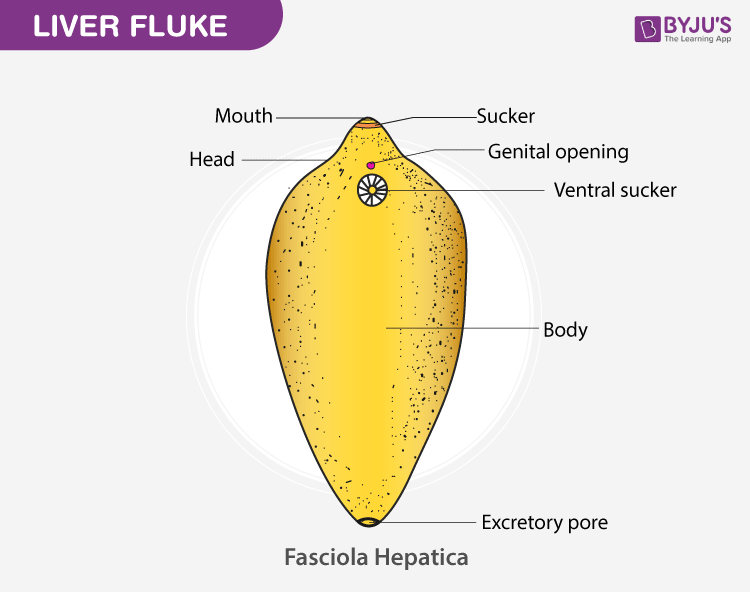
Classification
| Kingdom | Phylum | Class | Order | Genus | Species |
| Animalia | Platyhelminthes | Trematoda | Echinostoma | Fasciola | Hepatica |
Discussion
- Usually found in internal organs such as bile ducts of goats, sheep, and cattle as it is an endoparasite. It is sometimes also found in a few vertebrates but not in humans.
- They are known to cause liver rot – a disease of the liver
- It resembles a triangular shape that is flat and leaf-like parasite approximately 25mm long. It possesses a ventral an oval sucker known as the acetabulum which adheres to the bile duct.
- The body of the liver fluke is covered with cuticle with spinules.
Characteristic Features
- Leaf-like body resembling a triangular shape
- The body of the liver fluke is covered with cuticles
- Exhibits two suckers
Roundworm (Ascaris lumbricoides)
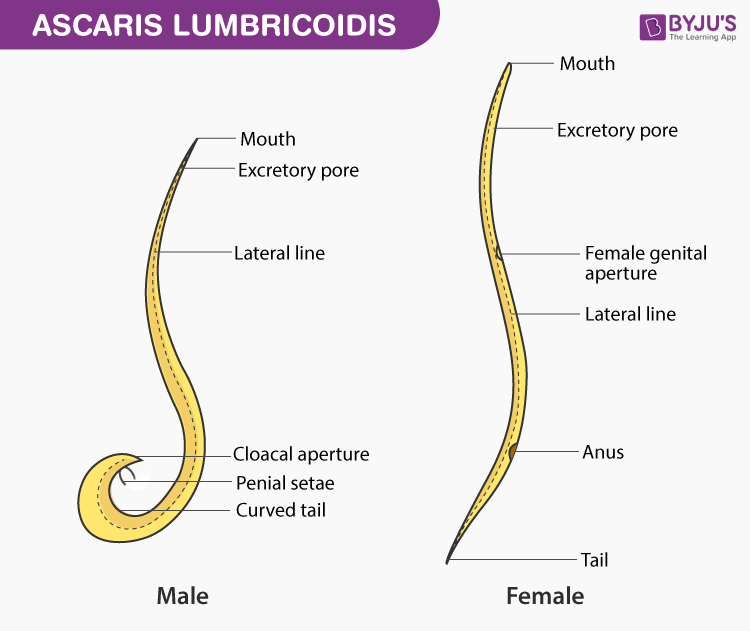
Classification
| Kingdom | Phylum | Class | Order | Genus | Species |
| Animalia | Nemanthelminthes | Nematoda | Ascaroidea | Ascaris | Lumbrecoides |
Features
- It is an endoparasite found in the intestine of man.
- It can cause weakness, anaemia, laziness and adverse abdominal discomfort
- The body is long, cylindrical and unsegmented with pointed edges.
- The body is covered by a soft and thin cuticle that is marked with fine striations.
- The body shows four longitudinal ridges throughout the body
- The anterior end of the body possesses a mouth.
- On the ventral surface, the excretory pore is located just a little behind the mouth.
- They are unisexual, exhibiting a well-defined sexual dimorphism.
Leech (Hirudinaria granulosa)

Classification
| Kingdom | Phylum | Class | Order | Genus | Species |
| Animalia | Annelida | Hirudinaria | Gnathobdellida | Hirudinaria | Granulosa |
Also Refer: Annelida
Features
- It is found in freshwater ponds and sluggish streams.
- Commonly known as Indian cattle leech, it is a temporary ectoparasite that feeds on cattle and blood.
- The body is elongated, dorsoventrally flattened and metamerically segmented. The body has 33 segments.
- Exhibits powerful organ attachments and locomotion.
- There are five pairs of small eyes situated dorsally in the first five segments.
- The anus is present at the base of the posterior sucker dorsally.
- The anterior end has an anterior sucker which is cup-shaped, turned downwards and ventral, wherein the mouth is centrally located. The posterior end has a posterior sucker, which is circular and is highly muscular. It is formed as a result of the fusion of the last 7 segments.
- Leech is bisexual.
Earthworm (Pheretima Posthuma)

Classification
| Kingdom | Phylum | Class | Order | Genus | Species |
| Animalia | Annelida | Oligochaeta | Terricelae | Pheretima | Posthuma |
Features
- Commonly found in moist soil.
- The body is long, triploblastic, cylindrical, eucoelomate and metamerically segmented.
- The mouth is at the anterior end and anus at the posterior end.
- The clitellum (a circular band of glandular tissue) is located at the 14th, 15th, and 16th segments
- Earthworms are hermaphrodites.
- Presence of a single female genital aperture mid-ventrally in the 14th segment.
- Presence of a pair of male genital apertures ventrolaterally in the 18th segment.
- A pair of genital papillae are located ventrolaterally in the 17th and the 19th segment
- The anus is present in the last segment.
- Setae are the locomotory structures that are located on all segments except the first and the last.
Prawn (Palaemon)

Classification
| Kingdom | Phylum | Class | Order | Genus | Species |
| Animalia | Arthropoda | Crustaceae | Decapoda | Palaemon | Malcolmsonii |
Also Refer: Arthropoda
Features
- It is a freshwater entity that is found in ponds, lakes and rivers.
- The body is laterally compressed and protected by a chitinous exoskeleton. The body exhibits an anterior cephalothorax and a posterior abdomen
- The cephalothorax is formed by the fusion of 5 segments that constitute the head and the thorax is composed of 8 segments.
- The carapace is an exoskeleton shield that protects the cephalothorax. Anteriorly, it is produced into a serrated median process known as the rostrum.
- Pair of stalked eyes at the base of the rostrum.
- There is one pair of appendage at each segment of the cephalothorax. 5 pairs in the head region, 8 pairs of the thoracic region. The last 5 pairs are for walking known as pereopods.
- The abdomen has 6 segments followed by a telson which is a conical flat piece.
- A pair of abdominal segments at the ventral side known as pleopods or swimmers are present.
- Uropods are the last pair of abdominal appendages.
See Read: Difference Between Endoskeleton And Exoskeleton
Silkworm (Bombyx Mori)

Classification
| Kingdom | Phylum | Class | Order | Genus | Species |
| Animalia | Arthropoda | Insecta | Lepidoptera | Bombyx | Mori |
Features
- An adult silk moth has a creamy white colour and is about 3 inches in length having two wings.
- The body can be distinguished into the head, thorax, and abdomen and is covered with tiny scales.
- The larvae undergo a metamorphosis for four months post which they stop feeding. Through its spinnerets, they secrete a slimy fluid. This liquid, when it comes in contact with air turns into silk thread and stays coiled and wrapped around its body to form the pupa.
- Larva from the cocoon.
- Two pairs of wings are present along with three pairs of legs.
Apple Snail (Pila Globosa)

Classification
| Kingdom | Phylum | Class | Order | Genus | Species |
| Animalia | Mollusca | Gastropoda | Prosobranchiata | Pila | Globosa |
Features
- It has a slim and soft body that is enveloped in a coiled calcareous shell.
- The shell opening is sealed by an operculum – thick plated.
- The body can be distinguished into the head, foot, visceral mass and mantle.
- There is a slight sexual dimorphism with separation of the sexes.
- The shell is coiled and univalved.
- The foot is broad and muscular.
- The head is distinct from tentacles and eyes.
StarFish (Asterias)

Classification
| Kingdom | Phylum | Class | Order | Genus | Species |
| Animalia | Echinodermata | Asterioda | Forcipulata | Asterias | Rubers |
Features
- It is a marine form found in the rocky and sandy parts of the sea
- A star-shaped body consisting of a central disc with 5 radiating arms. Broad at the base and taper towards the extremities
- The body can be distinguished into an oral surface directed downwards and aboral surface directed upwards
- On the oral surface at the centre of the disc, a pentagonal mouth is present. 5 narrow ambulacral grooves emerge from the 5 corners of the mouth, which extend along the middle of the oral surface of 5 arms up to their margins
- Each of this groove has 2 double rows of tube feet helping in locomotion
- The aboral surface has many spines and the anus is located at the centre of the disc on the same surface
- The madreporite is a perforated calcareous plate located between the bases of two arms on the aboral surface
Shark (Scolidon Sorrakowah)
Classification
| Kingdom | Phylum | Subphylum | Class | Genus |
| Animalia | Chordata | Vertebrata | Chondrichthyes | Scoliodon sp. |
Features
- It is widely distributed in marine waters. It is precious and attacks the preys with powerful jaws.
- The body is long, laterally compressed and spindle-shaped that tapers at both ends.
- It can be distinguished into the head, trunk, and tail.
- The ventral surface is pale in colour while the lateral and dorsal body surface is dark grey.
- The skin is covered by an exoskeleton of dermal scales, placoid scales. The head is dorsoventrally flattened, which is produced to form a snout.
- The head has a large pair of circular eyes at the sides, the mouth is wise crescentic present ventrally. A pair of nostrils is present in the front.
- 5 pairs of naked gill slits are present behind the eyes.
- The trunk has two types of fins – lateral fins and median fins.
- Between the bases of the pelvic fins, a cloacal aperture is present
- Male sharks have a pair of claspers.
Carp (Labeo Rohita or Rohu)
Classification
| Kingdom | Phylum | Subphylum | Class | Genus | Species |
| Animalia | Chordata | Vertebrata | Osteichthyes | Labeo | Rohita |
Features
- It is a freshwater bony fish that is found in rivers and ponds. It is a source of food
- The body is compressed, fusiform and matures up to 1m in length. The body is distinguished into the head, trunk, and tail and is covered by a large overlapping cycloid scales
- Head is depressed to form a blunt snout and has a subterminal fringe lipped mouth with no teeth, a pair of eyes and nostrils
- Four pairs of gill slits on the lateral side of the body behind the eyes. The gill slits are covered by an operculum. The lateral line is clear and distinct.
- The trunk comprises of a pair of pectoral fins, a pair of pelvic fins, a dorsal fin a ventral or anal fin and a homocercal caudal fin.
Frog(Rana Tigrina)
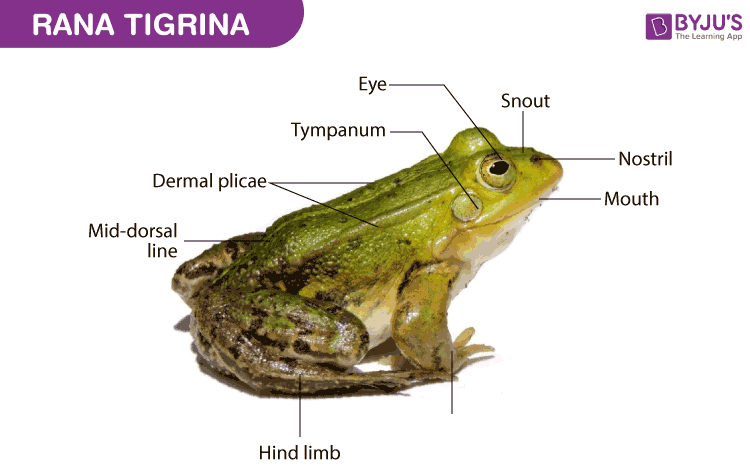
Classification
| Kingdom | Phylum | Subphylum | Class | Order | Genus | Species |
| Animalia | Chordata | Vertebrata | Amphibia | Anura | Rana | Tigrina |
Features
- It is terrestrial and nocturnal.
- The body is distinguished into the head and the trunk.
- The skin is warty and dry.
- The head has a pair of eyes, nostrils, tympanum, parotid glands and a mouth.
- The mouth is large with no teeth.
- The tympanum is well developed and the eyes are large.
- Behind the tympanum, the parotid glands are present, which secretes a poisonous fluid that has an irritating effect.
- The trunk has a pair of hind limbs, forelimbs, and at the posterior end there is a cloaca.
- Shorter forelimbs wherein each one has 3 webless fingers and a thumbpad.
- The hind-limbs are longer wherein each one has 3 toes with a highly reduced web.
See Also: Difference Between Frog And Toad
Lizard (Hemidactylus)

Classification
| Kingdom | Phylum | Subphylum | Order | Genus |
| Animalia | Chordata | Reptilia | Lacertilia | Hemidactylus sp. |
Features
- It is typically brown in colour and is 8-14cm in length.
- The body can be distinguished into the head that is thick and flattered, the neck is short, the trunk is large with a tapering tail.
- The head has a pair of eyes having movable eyelids, ear openings and nostrils.
- The skin is covered with tiny scales and is dry.
- The tail has annular pores of scales. These scales can be broken.
- They have four limbs, each having five clawed digits.
Pigeon (Columba Livia)

Classification
| Kingdom | Phylum | Subphylum | Class | Genus | Species |
| Animalia | Chordata | Vertebrata | Aves | Columba | Livia |
Features
- It is adapted for an aerial or volant mode of life and is a common domesticated bird.
- The body is boat-shaped and can be distinguished into the head, trunk and tail.
- The entire body surface except the feet is covered by feathers. The feet are covered by epidermal scutes
- The head has a pair of eyes, a pair of slit-like nostrils and a short beak.
- Eyes are large, rounded with movable eyelids and a nictitating membrane that is well developed.
- The forelimbs are modified into wings to take a flight.
- The hind limbs are pushed forward for bipedal locomotion. The digits end in claws.
- They have pneumatic bones. Teeth are absent and the skull is monocondylar.
Rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus)

Classification
| Kingdom | Phylum | Subphylum | Class | Order | Genus | Species |
| Animalia | Chordata | Vertebrata | Mammalia | Lagomorpha | Oryctolagus | Cuniculus |
Features
- The body can be distinguished into a head, trunk, neck and a small bushy tail.
- The entire body is covered with hair of black or brown colour
- The presence of two largely movable pinned behind the eyes. The colour of the eyes is pink.
- The mouth appears to have fleshy and soft lower and upper lips
- Sexual dimorphism is observed. Sexes are distinct and separate
- They possess the characteristic mammary glands, which end in nipples, located in the abdominal region.
For more Biological concepts, experiments and other related topics, visit us at BYJU’S Biology
Further Reading
| Metamorphism – Lifecycle Of Frogs And Insects |
| Classification of Animal Kingdom |
| Animal Kingdom- Animalia, Subphylum |
| Bird Skeletal System |
| Gait Of Animals |



Comments