CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 3 Metals And Non-Metals
In a periodic table, all elements found on the planet have been appropriately ordered based on their increasing atomic numbers. There are a total of 118 elements known to us, 92 of which are derived naturally, and the remaining 26 are created artificially in the laboratory. Based on their physical and chemical properties, these elements can be divided into three groups: Metalloids, Metals, and Non-Metals.
For more information on Metals and Non-Metals, watch the below video

Physical Properties
Physical Properties of Metals
● Hard and have a high tensile strength – Carbon is the only non-metal with very high tensile strength.
● Solid at room temperature – One non-metal, bromine, is a liquid at room temperature. The other non-metals are solids at room temperature, including carbon and sulfur.
● Sonorous – Metals produce a typical ringing sound when hit by something.
● Good conductors of heat and electricity – Graphite is a good conductor of heat and electricity.
● Malleable, i.e., can be beaten into thin sheets
● Ductile, i.e., can be drawn into thin wires
● High melting and boiling points (except Caesium (Cs) and Gallium (Ga)) – Graphite, a form of carbon (a non-metal), has a high boiling point and exists in a solid state at room temperature.
● Dense (except alkali metals). Osmium – highest density, and lithium – least density
● Lustrous – Metals have the quality of reflecting light from their surface and can be polished, e.g., gold, silver and copper. Iodine and carbon are non-metals which are lustrous. Note that carbon is lustrous only in certain forms like diamond and graphite.
● Silver-grey in colour (except gold and copper) – Metals usually have a silver or grey colour.
Non-Metals
Nonmetals are those elements which do not exhibit the properties of metals.
Physical Properties of Non-metals
- Occur as solids, liquids and gases at room temperature
- Brittle
- Non-malleable
- Non-ductile
- Non-sonorous
- Bad conductors of heat and electricity
Exceptions in Physical Properties
- Alkali metals (Na, K, Li) can be cut using a knife.
- Mercury is a liquid metal.
- Lead and mercury are poor conductors of heat.
- Mercury expands significantly for the slightest change in temperature.
- Gallium and caesium have very low melting points.
- Iodine is non-metal, but it has lustre.
- Graphite conducts electricity.
- Diamond conducts heat and has a very high melting point.
Examples of Non-metals
- Hydrogen – Gas
- Nitrogen – Gas
- Oxygen – Gas
- Fluorine – Gas
- Chlorine – Gas
- Bromine – Liquid
- Iodine – Solid
- Carbon – Solid
- Sulphur – Solid
- Phosphorous – Solid
- Silicon – Solid
For more information on the Physical Properties of Metals and Non-Metals, watch the below video

To know more about the Properties of Metals and Non-Metals, visit here.
Chemical Properties
Chemical Properties of Metals
● Alkali metals (Li, Na, K, etc.) react vigorously with water and oxygen or air.
● Mg reacts with hot water.
● Al, Fe and Zn react with steam.
● Cu, Ag, Pt, and Au do not react with water or dilute acids.
Reaction of Metals with Oxygen (Burnt in Air)
A metal oxide is formed when metals are burned in the air and react with oxygen in the air. Metal oxides are a type of basic material found in nature. They change the colour of red litmus to blue. To avoid reactions with oxygen, moisture, and carbon dioxide in the air, sodium and potassium metals are kept in kerosene oil.
Metal + Oxygen→ Metal oxide (basic)
● Na and K are kept immersed in kerosene oil as they react vigorously with air and catch fire.
4K(s)+O2(g)→2K2O(s) (vigorous reaction)
● Mg, Al, Zn, and Pb react slowly with air and form a protective layer that prevents corrosion.
2Mg(s)+O2(g)→2MgO(s) (Mg burns with white dazzling light)
4Al(s)+3O2(g)→2Al2O3(s)
● Silver, platinum and gold don’t burn or react with air.
Basic Oxides of Metals
Metal oxides are crystalline solids that contain a metal cation and an oxide anion. They typically react with water to form bases or with acids to form salts. MO + H2O → M(OH)2 (where M = group 2 metal). Thus, these compounds are often called basic oxides.
Some metallic oxides get dissolved in water and form alkalis. Their aqueous solution turns red litmus blue.
Na2O(s)+H2O(l)→2NaOH(aq)
K2O(s)+H2O(l)→2KOH(aq)
Amphoteric Oxides of Metals
Amphoteric oxides are metal oxides which react with both acids as well as bases to form salt and water.
For example – Al2O3, ZnO, PbO, SnO
Al2O3(s)+6HCl(aq)→2AlCl3(aq)+3H2O(l)
Al2O3(s)+2NaOH(aq)→2NaAlO2(aq)+H2O(l)
ZnO(s)+2HCl(aq)→ZnCl2(aq)+H2O(l)
ZnO(s)+2NaOH(aq)→Na2ZnO2(aq)+H2O(l)
For more information on Chemical Properties of Metals and Non-Metals, watch the below video

To know more about the Chemical Properties of Metals, visit here.
Reactivity Series
The reactivity series of metals, also known as the activity series, refers to the arrangement of metals in the descending order of their reactivities.
The below table illustrates the reactivity of metals from high order to low order.
| Symbol | Element |
| K | Potassium ( Highly Active Metal) |
| Ba | Barium |
| Ca | Calcium |
| Na | Sodium |
| Mg | Magnesium |
| Al | Aluminium |
| Zn | Zinc |
| Fe | Iron |
| Ni | Nickel |
| Sn | Tin |
| Pb | Lead |
| H | Hydrogen |
| Cu | Copper |
| Hg | Mercury |
| Ag | Silver |
| Au | Gold |
| Pt | Platinum |
To know more about Reactivity Series, visit here.
Roasting
Converts sulphide ores into oxides on heating strongly in the presence of excess air.
It also removes volatile impurities.
2ZnS(s)+3O2(g)+Heat→2ZnO(s)+2SO2(g)
Calcination
Converts carbonate and hydrated ores into oxides on heating strongly in the presence of limited air. It also removes volatile impurities.
ZnCO3(s)+heat→ZnO(s)+CO2(g)
CaCO3(s)+heat→CaO(s)+CO2(g)
Al2O3.2H2O(s)+heat→2Al2O3(s)+2H2O(l)
2Fe2O3.3H2O(s)+heat→2Fe2O3(s)+3H2O(l)
Reaction of Metals with Water or Steam
Aluminium, iron, and zinc are metals that do not react with either cold or hot water. However, when they come into contact with steam, they produce metal oxide and hydrogen. Lead, copper, silver, and gold are metals that do not react with water.
Metal+Water→Metalhydroxide or Metaloxide+Hydrogen
2Na+2H2O(cold)→2NaOH+H2+heat
Ca+2H2O(cold)→Ca(OH)2+H2
Mg+2H2O(hot)→Mg(OH)2+H2
2Al+3H2O(steam)→Al2O3+3H2
Zn+H2O(steam)→ZnO+H2
3Fe+4H2O(steam)→Fe3O4+4H2
Reaction of Metals with Acid
Metal+diluteacid→Salt+Hydrogengas
2Na(s)+2HCl(dilute)→2NaCl(aq)+H2(g)
2K(s)+H2SO4(dilute)→K2SO4(aq)+H2(g)
Only Mg and Mn, react with very dilute nitric acid to liberate hydrogen gas.
Mg(s)+2HNO3(dilute)→Mg(NO3)2(aq)+H2(g)
Mn(s)+2HNO3(dilute)→Mn(NO3)2(aq)+H2(g)
Displacement Reaction
A more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound or solution.
How Do Metals React with the Solution of Other Metal Salts
A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from its salt solution in a displacement reaction. Metal displacement reaction is a common name for this reaction. The reactivity of certain regularly used metals has been ordered in decreasing order. This is referred to as the reactivity or activity series.
Metal A+Salt of metal B → Salt of metal A + Metal B
Fe(s)+CuSO4(aq)→FeSO4(aq)+Cu(s)
Cu(s)+2AgNO3(aq)→Cu(NO3)(aq)+2Ag(s)
- It’s a component of thermite welding. Aluminium displaces iron from its oxide in this process.
- It is used in the production of steel. In which iron is displaced from its oxide by carbon.
- It is mostly utilised in metal extraction.
Reaction of Metals with Bases
The base has a bitter taste and a slippery texture. A base dissolved in water is called an alkali. When chemically reacting with acids, such compounds produce salts. Bases are known to turn blue on red litmus paper.
Base+metal → salt+hydrogen
2NaOH(aq)+Zn(s) → Na2ZnO2(aq)+H2(g)
2NaOH(aq)+2Al(s)+2H2O(l) → 2NaAlO2(aq)+2H2(g)
Extraction of Metals and Non-Metals
Applications of Displacement Reaction
Uses of displacement reaction
- Extraction of metals
- Manufacturing of steel
- Thermite reaction: Al(s)+Fe2O3(s) → Al2O3+Fe(molten)
The thermite reaction is used in the welding of railway tracks, cracked machine parts, etc.
Occurrence of Metals
Most elements, especially metals, occur in nature in a combined state with other elements. All these compounds of metals are known as minerals. But out of them, only a few are viable sources of that metal. Such sources are called ores.
Au, Pt – exists in the native or free state.
Extraction of Metals
The process of extracting metal ores buried deep underground is called Mining. The metal ores are found in the earth’s crust in varying abundance. The extraction of metals from ores is what allows us to use the minerals in the ground! The ores are very different from the finished metals that we see in buildings and bridges. Ores consist of the desired metal compound and the impurities and earthly substances called Gangue.
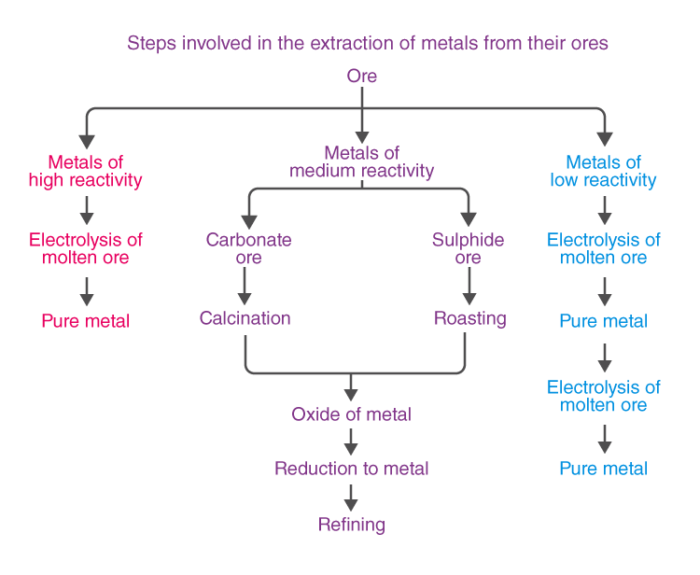
Metals of high reactivity – Na, K, Mg, Al.
Metals of medium reactivity – Fe, Zn, Pb, Sn.
Metals of low reactivity – Cu, Ag, Hg
To know more about the Extraction of Metals, visit here.
Enrichment of Ores
It means the removal of impurities or gangue from ore through various physical and chemical processes. The technique used for a particular ore depends on the difference in the properties of the ore and the gangue.
In chemistry, a gangue is an undesirable substance or impurity that surrounds the mineral in an ore deposit, such as sand, rock, or any other material. When it comes to mining, this mineral is very frequent.
Extracting Metals Low in Reactivity Series
By self-reduction- when the sulphide ores of less electropositive metals like Hg, Pb, Cu etc., are heated in air, a part of the ore gets converted to oxide, which then reacts with the remaining sulphide ore to give the crude metal and sulphur dioxide. In this process, no external reducing agent is used.
1. 2HgS(Cinnabar)+3O2(g)+heat→2HgO(crude metal)+2SO2(g)
2HgO(s)+heat→2Hg(l)+O2(g)
2. Cu2S(Copper pyrite)+3O2(g)+heat→2Cu2O(s)+2SO2(g)
2Cu2O(s)+Cu2S(s)+heat→6Cu(crude metal)+SO2(g)
3. 2PbS(Galena)+3O2(g)+heat→2PbO(s)+2SO2(g)
PbS(s)+2PbO(s)→2Pb(crudemetal)+SO2(g)
Extracting Metals in the Middle of Reactivity Series
Calcination is a process in which ore is heated in the absence of air, or air might be supplied in limited quantity. Roasting involves heating ore lower than its melting point in the presence of air or oxygen. Calcination involves the thermal decomposition of carbonate ores.
Smelting – it involves heating the roasted or calcined ore (metal oxide) to a high temperature with a suitable reducing agent. The crude metal is obtained in its molten state.
Fe2O3+3C(coke)→2Fe+3CO2
Aluminothermic reaction – also known as the Goldschmidt reaction, is a highly exothermic reaction in which metal oxides, usually of Fe and Cr, are heated to a high temperature with aluminium.
Fe2O3+2Al→Al2O3+2Fe+heat
Cr2O3+2Al→Al2O3+2Cr+heat
Extraction of Metals Towards the Top of the Reactivity Series
Electrolytic reduction:
1. Down’s process: Molten NaCl is electrolysed in a special apparatus.
At the cathode (reduction):
Na+(molten)+e−→Na(s)
Metal is deposited.
At the anode (oxidation):
2Cl−(molten)→Cl2(g)+2e–
Chlorine gas is liberated.
2. Hall’s process: A mixture of molten alumina and a fluoride solvent, usually cryolite (Na3AlF6), is electrolysed.
At the cathode (reduction):
2Al3++6e–→ 2Al(s)
Metal is deposited.
At the anode (oxidation):
6O2– → 3O2(g)+12e–
Oxygen gas is liberated.
The metals at the top of the reactivity series are highly reactive. They cannot be obtained from their compounds by heating with carbon, because these metals have more affinity for oxygen than carbon. Hence, for the extraction of such metals electrolytic reduction method is used.
Refining of Metals
Refining of metals – removing impurities or gangue from crude metal. It is the last step in metallurgy and is based on the difference between the properties of metal and gangue.
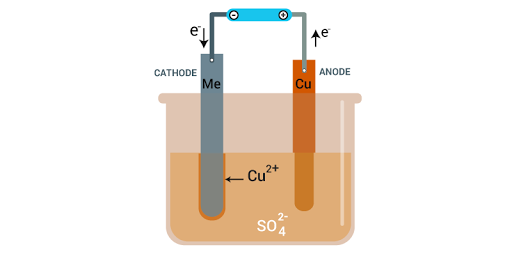
Electrolytic Refining
Metals like copper, zinc, nickel, silver, tin, gold etc., are refined electrolytically.
Anode: impure or crude metal
Cathode: a thin strip of pure metal
Electrolyte: aqueous solution of metal salt
From anode (oxidation): metal ions are released into the solution
At cathode (reduction): the equivalent amount of metal from the solution is deposited
Impurities deposit at the bottom of the anode.
To know more about Electrolytic Refining, visit here.
The Why Questions
Electronic Configuration
Group 1 elements – Alkali metals
| Element | Electronic Configuration |
| Lithium(Li) | 2,1 |
| Sodium(Na) | 2,8,1 |
| Potassium(K) | 2,8,8,1 |
| Rubidium(Rb) | 2,8,18,8,1 |
Group 2 elements – Alkaline earth metals
| Element | Electronic Configuration |
| Beryllium(Be) | 2,2 |
| Magnesium(Mg) | 2,8,2 |
| Calcium(Ca) | 2,8,8,2 |
| Stronium(Sr) | 2,8,18,8,2 |
How Do Metals and Non-Metals React?
Metals lose valence electron(s) and form cations.
Non-metals gain those electrons in their valence shell and form anions.
The cation and the anion are attracted to each other by strong electrostatic force, thus forming an ionic bond.
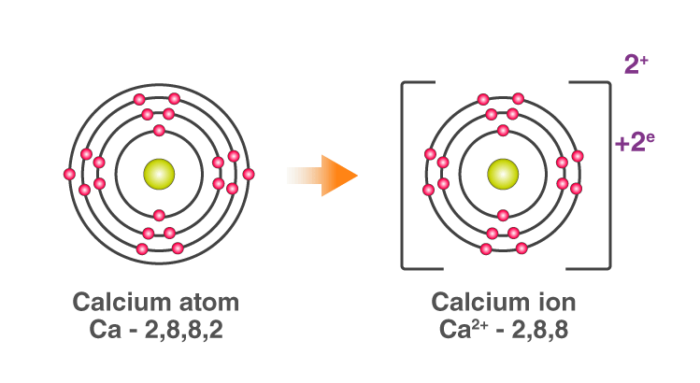
For example: In calcium chloride, the ionic bond is formed by opposite-charged calcium and chloride ions.
The calcium atom loses 2 electrons and attains the electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas (Ar). By doing so, it gains a net charge of +2.
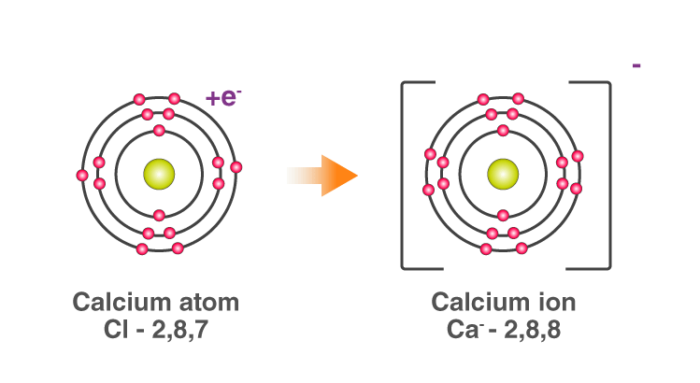
The two Chlorine atoms take one electron each, thus gaining a charge of -1 (each) and attain the electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas (Ar).
Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are neutral compounds that are made up of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. Binary ionic compounds (ionic compounds containing only two types of elements) are named by first writing the name of the cation, then the name of the anion.
The electrostatic attractions between the opposite-charged ions hold the compound together.
Example: MgCl2, CaO, MgO, NaCl etc.
Properties of Ionic Compound
Ionic compounds
- Are usually crystalline solids (made of ions).
- Have high melting and boiling points.
- Conduct electricity when in aqueous solution and when melted.
- Are mostly soluble in water and polar solvents.
To know more about Ionic Compounds, visit here.
Physical Nature
Ionic solids usually exist in regular, well-defined crystal structures.
Electric Conduction of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds conduct electricity in the molten or aqueous state when ions become free and act as charge carriers.
In solid form, ions are strongly held by electrostatic forces of attraction and are not free to move; hence do not conduct electricity.
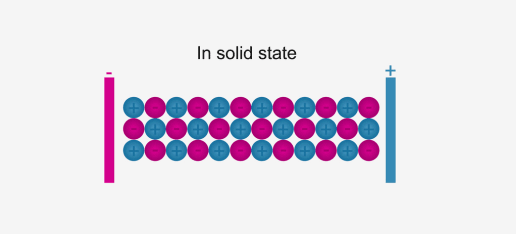
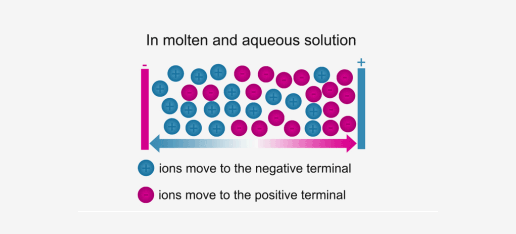
For example, ionic compounds such as NaCl do not conduct electricity when solid, but when dissolved in water or in a molten state, they will conduct electricity.
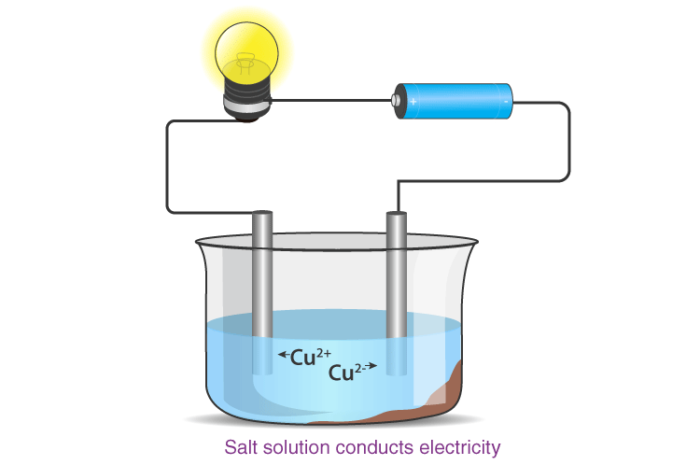
Melting and Boiling Points of Ionic Compounds
In ionic compounds, the strong electrostatic forces between ions require a high amount of energy to break. Thus, the melting point and boiling point of an ionic compound are usually very high.
Solubility of Ionic Compounds
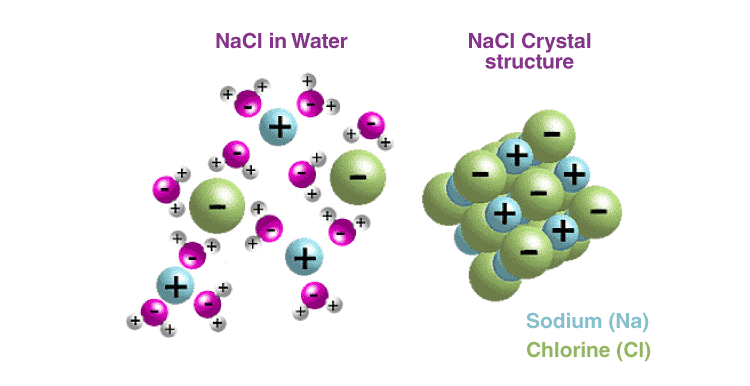
Most ionic compounds are soluble in water due to the separation of ions by water. This occurs due to the polar nature of water.
For example, NaCl is a 3-D salt crystal composed of Na+ and Cl− ions bound together through electrostatic forces of attraction. When a crystal of NaCl comes into contact with water, the partially positive-charged ends of water molecules interact with the Cl− ions, while the negatively charged end of the water molecules interacts with the Na+ ions. This ion-dipole interaction between ions and water molecules assists in the breaking of the strong electrostatic forces of attraction within the crystal and, ultimately, in the solubility of the crystal.
Corrosion
Alloys
Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of a metal with other metals or nonmetals. Alloy formation enhances the desirable properties of the material, such as hardness, tensile strength and resistance to corrosion.
Examples of a few alloys:
Brass: copper and zinc
Bronze: copper and tin
Solder: lead and tin
Amalgam: mercury and other metal
To know more about Alloys, visit here.
Corrosion
Gradual deterioration of a material, usually a metal, by the action of moisture, air or chemicals in the surrounding environment.
Rusting:
4Fe(s)+3O2(from air)+xH2O(moisture)→2Fe2O3. xH2O(rust)
Corrosion of copper:
Cu(s)+H2O(moisture)+CO2(from air)→CuCO3.Cu(OH)2(green)
Corrosion of silver:
Ag(s)+H2S(from air)→Ag2S(black)+H2(g)
For more information on Corrosion of Metals, watch the below video

To know more about Corrosion, visit here.
Students can refer to the short notes and MCQ questions along with separate solution pdf of this chapter for quick revision from the links below:
- Metals and Non-Metals Short Notes
- Metals and Non-Metals MCQ Practice Questions
- Metals and Non-Metals MCQ Practice Solutions
Prevention of Corrosion
Prevention:
1. Coating with paints or oil or grease: The application of paint or oil or grease on metal surfaces keep out air and moisture.
2. Alloying: Alloyed metal is more resistant to corrosion. Example: stainless steel.
3. Galvanization: This is a process of coating molten zinc on iron articles. Zinc forms a protective layer and prevents corrosion.
4. Electroplating: It is a method of coating one metal with another by the use of an electric current. This method not only lends protection but also enhances the metallic appearance.
Examples: silver plating, and nickel plating.
5. Sacrificial protection: Magnesium is more reactive than iron. When it is coated on articles made of iron or steel, it acts as the cathode undergoes a reaction (sacrifice) instead of iron and protects the articles.
Read More:
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 – Metals and Non-metals
- Carbon and its Compounds Class 10 Chapter 4 Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Solutions for Chapter 3 – Metals and Non-metals
- Metals and Non-Metals
- Maths Notes For Class 10
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Notes
Frequently Asked Questions on Metals and Non-Metals
A student performs an experiment in which he dipped a copper coil into the silver nitrate solution. What will be observed from this experiment?
A grey-coloured layer of silver appears on the surface of the copper coil.
A student performs an experiment of burning magnesium ribbon in the air. A chemical reaction takes place, and as a result, a white powder X forms along with a bright white light. The aqueous solution of changes the colour of litmus paper to?
Oxides of metals like magnesium are basic in nature. Therefore, the aqueous solution will change the red litmus to blue.
The atomic number of two elements, A and B, are 12 and 8, respectively. What type of compound is formed when they combine?
The compound formed is AB which is ionic in nature. As we know, an ionic compound is a chemical compound in which ions are held together by electrostatic force. The electronic configuration of two elements, A and B, are 2, 8, 2 and 2, 6, respectively. From their electronic configuration, we see that A (magnesium) is a metal and B (oxygen) is a non-metal; thereby, A loses its valence electrons and forms a cation, while B accepts those electrons and forms an anion. These oppositely charged ions are drawn closer due to electrostatic forces, and an ionic compound (MgO) is formed.
Comments