Dengue and Malaria have two commonalities between them: They are spread by mosquitoes and they are both responsible for scores of fatalities around the world each year.
Apart from these, the two mosquito-borne diseases are different from each other due to a wide array of factors.
Dengue fever is a tropical disease caused by the dengue virus.
Malaria is a fatal blood disease caused by a protozoan parasite. It results in intermittent and remittent fever.
Keeping the context of the IAS Exam in mind, this article will highlight further differences between Dengue and Malaria.
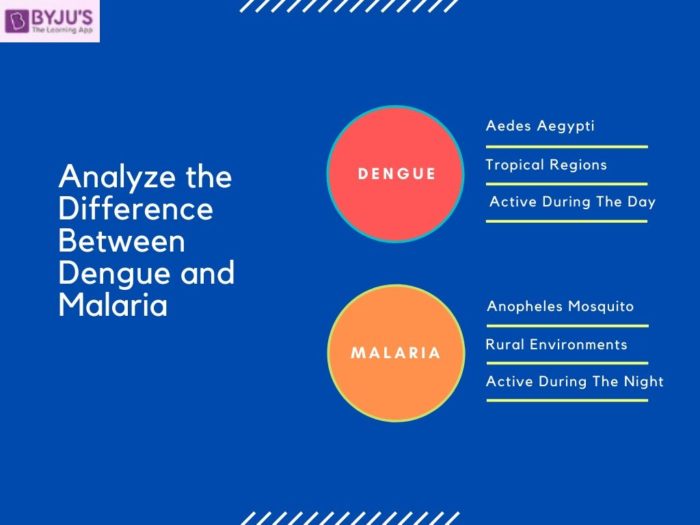
Differences between Dengue and Malaria
| Dengue |
Malaria |
| Dengue is transmitted by an infected Aedes aegypti mosquito bite. It can also spread if another uninfected mosquito bites the infected person and then spreads it to other people. Aedes aegypti mosquito bite during the day time | Malaria is transmitted through the bite of a female anopheles mosquito. Only the bite from this species of mosquito can spread the fever in contrast to dengue. The anopheles mosquito is active during the night time |
| Dengue is more widespread in tropical and subtropical regions. It is endemic in predominantly urban locations of Africa, the Americas, South East-Asia and Eastern Mediterranean | Malaria has affected many regions in Asia, Latin America and in some limited areas of Europe and the Middle East. Cases of Malaria are more to be found in rural environments |
| The incubation period for dengue ranges from three to fourteen days after being bitten by the infected mosquito | The onset of malarial fever is ten to fifteen days after being bitten by the mosquito |
| The bite from the Aedes aegypti mosquito is the only known mode of transmission of the dengue disease. | The following are the modes of transmission for malaria:
|
The following are the symptoms of dengue:
|
The following are the symptoms of malaria:
|
| There are no vaccines available for dengue, hence avoiding mosquito bites and adequately taking fluids is recommended | Although no vaccines are available there are many anti-malarial medicines available. They are:
|
| When dengue fever progresses to dengue hemorrhagic fever, it can become a life-threatening complication. It can lead to pneumonia and swelling of the heart. | Life-threatening complications of malaria include:
|
| Dengue is diagnosed through an antigen test and anti-body test | Malaria is diagnosed by microscopic tests of the visuals of the virus |
Both dengue and malaria are covered under the Science and Technology segment of the UPSC Exams. Aspirants can find links to study this segment below:
- Science and Technology Notes for UPSC
- Decoding Science and Technology for UPSC
- General Science Preparation Strategy for UPSC
- Science and Technology QUestion in UPSC Mains GS-3
Difference Between Dengue and Malaria – Download PDF Here
Frequently Asked Questions about Dengue and Malaria
What is common between malaria and dengue?
How infectious is Malaria?
To know more about the general pattern of the UPSC exams, candidates can visit the UPSC Syllabus 2020 page. More UPSC preparation-related articles are given in the table below:
Related Links
Comments