The primary, secondary and tertiary sectors represent various business types and the goods they procure and sell in an economic setup. Each sector is interdependent on the other so that the economy as a whole functions properly and efficiently.
The primary sector is where the materials for the secondary sector are gathered. In the secondary sector, the product is then made into consumable item(s) which is then distributed by the tertiary sector.
Economists such as AGB Fisher and Colin Clark were the supporters of these models in the early 20th century.
As this article will highlight the key differences between the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors, candidates writing the IAS Exam this year will find it useful.
Aspirants can find more Difference Between Articles, by visiting the linked page.
Different Economic sectors in India
Before we go into detail about the difference between Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Sector, like every other economy in the world the Indian economy is divided into Primary, Secondary and Tertiary sectors. They are further divided into organized and unorganized sector while in terms of ownership, they are divided into public sector and private sector.
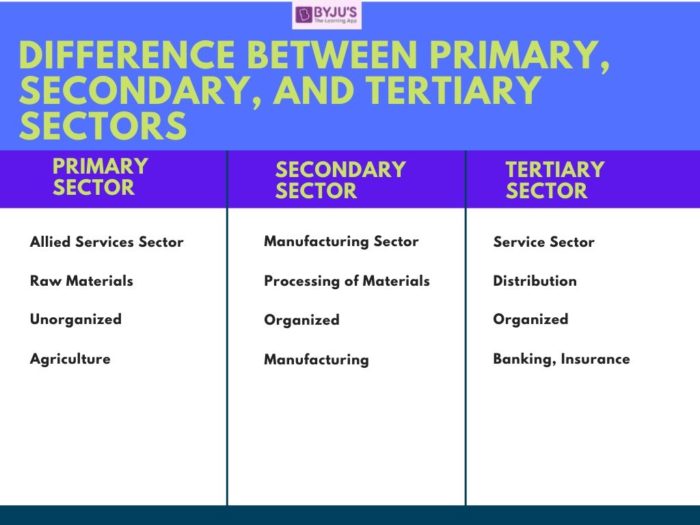
The differences between the three sectors are given in the table below:
Differences between Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Sector
| Primary Sector | Secondary Sector | Tertiary Sector |
| It is known as the agricultural and allied sector services | It is known as the manufacturing sector | It is known as the service sector |
| This sector provides raw materials for goods and services | This sector transforms one good into another by creating more utility from it | The tertiary sector provides useful services for the primary and secondary sectors |
| The primary sector is unorganized and uses traditional techniques | The secondary sector is organized and uses better methods of production | This sector is well organized and uses modern-day logistics techniques to perform its functions |
| Activities in this sector consist of agriculture, forestry and mining | It includes manufacturing units, small scale units, large firms and multinational corporations | Banking, insurance trade and communications come under this sector |
| In most developing nations such as India, this sector is where a large section of the workforce is employed, in comparison to developed nations | The employment rate is in equilibrium as a specialized set of skills is required to find employment in this sector | This sector’s employment share has increased in the ensuing years |
For a thorough preparation in UPSC Indian Economy, the following study materials will be helpful for candidates in their exam preparation:
- Indian Economy Notes for UPSC Exam
- Economy this week
- Syllabus and Strategy for UPSC Economics
- Difference Between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
- Difference Between Economic Survey and Budget
- Difference Between Globalization and Liberalization
Difference between Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Sectors: UPSC Notes – Download PDF Here
FAQ about Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Sectors
Which is the largest sector of India?
Why is secondary sector important for Indian economy?
Candidates can find the general pattern of the UPSC Exams by visiting the UPSC Syllabus page. For more articles and exam-related preparation materials, refer to the links given in the table below:
Related Links

Comments