CNA 16 Dec 2021:- Download PDF Here
TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS 1 Related B. GS 2 Related C. GS 3 Related AGRICULTURE 1. The push for Zero Budget Natural Farming DEFENCE AND INTERNAL SECURITY 1. The growth of India’s defence exports ECONOMY 1. Cabinet approves ₹76,000 crore push for semiconductor makers D. GS 4 Related E. Editorials POST-INDEPENDENCE HISTORY 1. A thorn in Pakistan-Bangladesh relations POLITY AND GOVERNANCE 1. A false Conflation between duties and rights ECONOMY 1. Mixed Signals F. Prelims Facts 1. Durga Puja gets intangible cultural heritage tag 2. Where is the caste data? G. Tidbits 1. U.S. tests laser weapon in West Asia 2. Rising oil imports H. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions I. UPSC Mains Practice Questions

A. GS 1 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
B. GS 2 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
C. GS 3 Related
1. The push for Zero Budget Natural Farming
Topic: Issues related to Direct and Indirect Farm Subsidies/Farming techniques
Prelims: ZBNF- Techniques; Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana.
Mains: Pros and cons of ZBNF.
Background:
- In a recent speech the Prime Minister called for mass adoption of Zero budget natural farming (ZBNF). The Prime Minister is also set to highlight ZBNF’s benefits and provide more details on the strategies to implement it at the national summit on agro and food processing to be held in Anand, Gujarat.
- The Centre has sanctioned support for converting four lakh additional hectares of crop land in eight States to using ZBNF techniques under the Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana.
- These developments are indicative of the fact that ZBNF seems to be on top of the Government’s agricultural agenda.
Zero budget natural farming:
- Zero-budget natural farming is a technique of farming that aims to bring down input costs by making farmers rely on natural inputs, shifting away from agricultural chemicals, such as pesticides and fertilisers. ZBNF is a method of chemical-free agriculture drawing from traditional Indian practices.
- It was originally promoted by agriculturist Subhash Palekar.
- ZBNF recommends the “four wheels”: Bijamrit, Jivamrit, Mulching and Waaphasa and three methods of insect and pest management: Agniastra, Brahmastra and Neemastra (all different preparations using cow urine, cow dung, tobacco, fruits, green chilli, garlic and neem).
- Bijamrit is the microbial coating of seeds with formulations of cow urine and cow dung.
- Jivamrit is used for the enhancement of soil microbes using an inoculum of cow dung, cow urine, pulse flour, soil and jaggery. This is a fermented microbial culture that adds nutrients to the soil and acts as a catalytic agent to promote the activity of microorganisms and earthworms in the soil.
- Mulching is the covering of soil with crops or crop residues.
- Waaphasa is the building up of soil humus to increase soil aeration.
- The ZBNF method also promotes soil aeration, minimal watering, intercropping, bunds and discourages intensive irrigation and deep ploughing.
Significance of ZBNF:
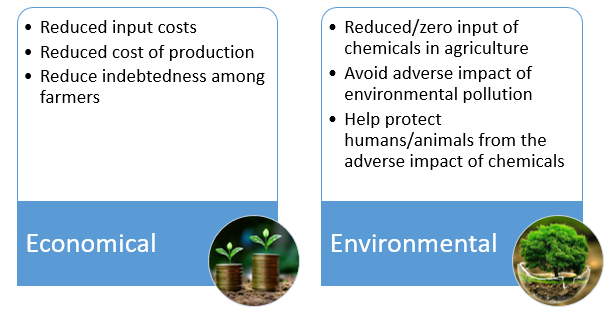
Category: DEFENCE AND INTERNAL SECURITY
1. The growth of India’s defence exports
Topic: Security Challenges & their Management
Prelims: Draft Defence Production & Export Promotion Policy 2020.
Mains: Status of defence exports from India; Significance and initiatives being taken.
Defence exports from India:
- India’s defence exports have increased over 5 times between 2016-17 and 2020-21. The defence exports are valued at around ₹8,434.84 cr in 2020-21.
- The Government has set an ambitious target to achieve exports of about ₹35,000 crore ($5 billion) in aerospace and defence goods and services by 2025.
- India has been exporting to over 40 nations and is emerging as a global defence exporter. India figures in the Top 25 defence exporters.
- Indian Ocean Region nations have emerged as a major destination for Indian defence exports.
- According to the latest report of the Swedish think tank Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), three Indian companies figure among the top 100 defence companies in the 2020 rankings — Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), Ordnance Factory Board and Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL).
- India has the capacity to supply different types of missile systems, LCA/helicopters, multi-purpose light transport aircraft, warships and patrol vessels, artillery gun systems, tanks, radars, military vehicles, electronic warfare systems and other weapons systems.
Factors contributing to defence export growth:
- The changing geopolitical scenario has got many smaller nations worried about their security and are looking to strengthen their defence capabilities. This provides a market for Indian defence products.
- India has developed the required technical capabilities to be able to produce defence goods at low-cost and high-quality.
Defence imports:
- There has been an overall drop in India’s arms imports between 2011-15 and 2016-20, according to a 2020 SIPRI report. However India continues to remain among the top importers.
Steps taken to boost defence production:
- Simplified defence industrial licensing
- Issuance of two “positive indigenisation lists” that cannot be imported and can only be procured from domestic industry.
- A percentage of the capital outlay of the defence budget has been reserved for procurement from domestic industry.
Steps taken to boost defence exports:
- Relaxation of export controls and grant of no-objection certificates
- Incentives under the foreign trade policy
- Facilitation of Lines of Credit for countries to import Indian defence product
- Defence attaches in Indian missions have been empowered to promote defence exports
- Draft Defence Production & Export Promotion Policy 2020.
1. Cabinet approves ₹76,000 crore push for semiconductor makers
Topic: Indian Economy & Issues Relating to Planning, Mobilization of Resources, Growth, Development & Employment
Prelims: PLI scheme for semiconductor and display systems- provisions
Mains: Significance of the scheme.
Context:
- The Union Cabinet has approved a Production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme for semiconductor and display board production
Details:
- The scheme has been provided with a budget of around ₹76,000 crore scheme to boost semiconductor and display manufacturing in the country.
- The programme aims to provide a globally competitive incentive package to companies in the sector.
- The scheme would provide fiscal support of up to 50% of the project cost for setting up semiconductor and display fabrication units.
- The government will work towards setting up high-tech clusters with the required infrastructure in place.
- Also a specialised and independent ‘India Semiconductor Mission’ will be set up under the leadership of global experts in semiconductor and display industry. It will act as the nodal agency for efficient and smooth implementation of the schemes on semiconductors and display ecosystem.
Significance:
- The scheme will provide an impetus to domestic electronic design and production capabilities.
- Electronics manufacturing in the country had increased to $75 billion over the past seven years and is expected to reach $300 billion in the next six years.
- The programme will help make India a global hub of electronic system design and manufacturing. The scheme is expected to attract investment of ₹1.67 lakh crore and lead to production worth ₹9.5 lakh crore.
- The programme will also help create highly skilled employment opportunities in India. The entire programme would lead to 35,000 high-quality direct jobs and indirect employment for 1 lakh persons. This would provide an opportunity to harness the demographic dividend of the country.
- The programme would propel innovation and build domestic capacities to ensure the digital sovereignty of India.
- Domestic production will help uphold trust in digital devices. This has gained utmost importance in the current geopolitical scenario where the security of critical information infrastructure holds immense strategic importance.
D. GS 4 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
E. Editorials
Category: POST-INDEPENDENCE HISTORY
1. A thorn in Pakistan-Bangladesh relations
- This article discusses the 1971 war of Independence of Bangladesh. For information on this topic refer to the following articles:
Category: POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. A false Conflation between duties and rights
Topic: Features of Indian Constitution
Prelims: Increased emphasis on duties vis-a-vis rights of citizens.
Mains: Provisions of the constitution and their inter-relation.
Context:
Recently, On Constitution Day, Minister of Law and Justice, Kiren Rijiju, emphasized that to make India great we need to create a balance between rights and duties.
This view is in consonance with Gandhiji’s famous quote-
“Real rights are a result of the performance of duty”
Generally speaking, most rights come with duties. For example- when Rights against discrimination are promised to citizens there is a simultaneous imposition of duty on the government to ensure equality.
However there is a general fear that the government wants to make rights conditional on the performance of extraneous or irrelevant duties.
Constitutional Provisions with respect to rights and duties:
Part III of the Indian Constitution contains provisions related to fundamental rights. These fundamental rights have limitations but these rights were given sacrosanct importance in ensuring human dignity.
During the National Emergency of 1975, the then Prime Minister Indira Gandhi on the recommendation of the Sawran Singh Committee added Part IV-A i.e fundamental duties.
Article 51A encouraged citizens to perform several duties: among others, to uphold and protect the sovereignty, unity, and integrity of India; to defend the country and render national service when called upon to do so; to protect and improve the natural environment; to safeguard public property.
Problem with such an approach:
- Different people have different conceptions of duties that citizens must abide by.
- The Constituent Assembly did not see duty as an important part of their vision.
- Fundamental duties in Part IV are vague, ambiguous, and difficult to be understood by the common man.
- The list of duties is not exhaustive as it does not cover other important duties like casting votes, paying taxes, family planning, and so on. In fact, the duty to pay taxes was recommended by the Swaran Singh Committee.
- Such an approach can infringe on the Right to freedom of speech and expression.
- Making the rights subject to certain extrinsic duties can be seen as repugnant to a republic’s vision.
Conclusion:
Making rights subject to certain extrinsic duties can be seen as repugnant to the republic’s vision. The discourse needs to focus instead on the exact nature of duties that create rights.
Category: ECONOMY
Topic: International Trade
Mains: Effects of Liberalization on the economy and Changes in industrial policy.
Context:
- India has been giving ambiguous cues regarding its stand on economic globalization.
- On one hand, Foreign Minister rebuked Globalisation supporters for not acknowledging geopolitical motivations behind the open market. On the other hand, ministers and dignitaries are busy convincing investors for Atmanirbhar Bharat.
Problems with Protectionism:
- In face of rising anti-china sentiment, there is an opportunity for India to be its substitute, especially in manufacturing.
- The earlier period of protectionism during the 1960s-70s lead to a lot of inefficiencies in production and also restricted access to products. It also leads to a low-productivity cycle by supporting low-productivity businesses.
- Lack of capital for new initiatives can be tackled with foreign investment.
- Protectionism stifles access to technology.
Argument in favour of protectionism:
- Non-existence of fair global trade order.
- Relying on other countries may compromise Sovereignty of the country.
- Pandemic has highlighted the limitations of the global supply chain.
- Countries like China use trade as a weapon by blocking supplies.
Way forward:
- Since India is benefiting from rising exports and is also looking for free-trade agreements with partners like UAE, Canada, the EU, there is no benefit in denying or rebuffing globalization. Rather India should take whatever opportunity it can find viz-a-viz globalization.
F. Prelims Facts
1. Durga Puja gets intangible cultural heritage tag
- Durga Puja in Kolkata, has made it to the UNESCO’s Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
- Census is a subject under the Union List.
G. Tidbits
1. U.S. tests laser weapon in West Asia
- The U.S. Navy has successfully tested its Laser Weapon System Demonstrator in the Gulf of Aden
- The system could be used to counter bomb-laden drone boats
- The Gulf of Aden is the body of water separating East Africa from the Arabian Peninsula.
- The Gulf of Aden sits along the southern coast of war-torn Yemen, which has been at war since Iranian-backed Houthi rebels seized its capital, Sanaa, in 2014. The Houthis have deployed drone boats into these waters, which can be piloted remotely and sent up to a target before detonating.
- There has been a substantial increase in India’s oil imports in November from a year earlier.
- Iraq remained the top oil supplier to India, followed by Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. Kuwait is the fourth-biggest supplier.
H. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions
Q1. The famous Sri Ramna Kali temple is in which of the following nations?
- Pakistan
- Nepal
- Bangladesh
- Cambodia
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: c
Explanation:
- Sri Ramna Kali temple is situated in Bangaldesh.
- This temple was destroyed by the Pakistani forces during the 1971 war. In a symbolic gesture, the Indian President will inaugurate the refurbished temple.
Q2. Consider the following traditions and choose the ones which have been recognized by UNESCO as part of India’s intangible cultural heritage:
- Yoga
- Kumbh Mela
- Tradition of Vedic chanting
- Nowruz
- Durga Puja
Choose the correct statements:
- 1,2 & 5 only
- 2, 4 & 5 only
- 1 & 3 only
- All of the above
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: d
- The following have been recognized as part of India’s intangible cultural heritage by UNESCO:
- Kutiyattam
- Vedic chanting
- Ramlila
- Ramman
- Chhau dance
- Kalbelia dance
- Mudiyettu
- Durga puja in Kolkata
- Buddhist chanting in Ladakh
- Sankirtana
- Traditional craft of thateras
- Nawrouz
- Kumbh mela
Q3. Rustom II, developed by the DRDO is
- A hypersonic missile system
- An unmanned aerial vehicle or Drone
- A tank suitable for high altitude warfare
- A sonar system for identifying underwater mineral nodules
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: b
Explanation:
- Rustom II is an unmanned aerial vehicle or Drone.
- It is a Medium Altitude Long Endurance unmanned air vehicle (UAV) being developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation for the three services, Indian Army, Indian Navy and the Indian Air Force of the Indian Armed Forces.
Q4. Which of these schemes is/are correctly matched with the States where they are operating?
Scheme State
- SAHAY Chhattisgarh
- KALIA Odisha
- Saras Suraksha Kavach Rajasthan
Choose the correct code:
- 1 & 2 only
- 2 & 3 only
- 1 & 3 only
- All of the above
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: b
Explanation:
- SAHAY scheme of the state of Jharkhand focuses on the development of sports.
- KALIA scheme is a package for farmer’s welfare. KALIA stands for “Krushak Assistance for Livelihood and Income Augmentation”. This scheme has been launched by Odisha Government to accelerate Agricultural Prosperity and reduce poverty in the State.
- Saras Suraksha Kavachis a scheme of the state of Rajasthan. It provides dairy farmers an insurance cover.
Q5. Which one of the following suggested that the Governor should be an eminent person from outside the State and should be a detached figure without intense political links or should not have taken part in politics in the recent past? (UPSC 2019)
- First Administrative Reforms Commission (1966)
- Rajamannar Committee (1969)
- Sarkaria Commission (1983)
- National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (2000)
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: c
Explanation:
- Sarkaria Commission was set up in 1983 by the central government of India. The Sarkaria Commission’s charter was to examine the central-state relationship on various portfolios and suggest changes within the framework of Constitution of India.
- One of the major suggestions of the commission was that the Governor should be an eminent person from outside the State and should be a detached figure without intense political links or should not have taken part in politics in the recent past.
I. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
- Should our fundamental rights be linked with fundamental duties? Critically discuss. (250 words; 15 marks)[GS-2, Polity]
- What is Zero Budget Natural Farming? What are the pros and cons of this method? (250 words; 15 marks)[GS-3, Economy]
Read the previous CNA here.
CNA 16 Dec 2021:- Download PDF Here

Comments