TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS1 Related SOCIAL ISSUES 1. ‘No trial in sewer death cases’ B. GS2 Related POLITY 1. Ethics panel debates checks and balances INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS 1. Rohingya handed over to Myanmar HEALTH 1. India ranks fifth in world in pictorial warnings on cigarette packets C. GS3 Related ECONOMY 1. Centre announces 2.5 cut in fuel prices ENVIRONMENT 1. Lions in Gujarat may have been killed by Muted Virus D. GS4 Related E. Editorials ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY 1. Next steps at Gir (The Way Forward to protect the Asiatic Lion) INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS 1. Eyes on India (Japan, South Korea, Taiwan and Australia are forging closer economic ties with India) F. Tidbits 1. Facial Scan in Digi Yatra G. Prelims Fact 1. Konark Sun Temple 2. Taliperu Project H. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions I. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
A. GS1 Related
1. ‘No trial in sewer death cases’
Context
- There was a study released by the Rashtriya Garima Abhiyan (RGA) — an NGO partnering with the Union Ministry of Social Justice for an ongoing manual scavenging census.
- It said a sample study of deaths due to sewer and septic tank cleaning since 1992, shows that First Information Reports (FIR) were filed in only 35% of the cases; none led to a trial or prosecution of any sort.
- Only 31% of affected families received cash compensation, while none received the rehabilitation or alternative jobs to which they are entitled by law.
Details

Concerns voiced
- Promised compensation and permanent jobs for family members were not fulfilled.
- Government building toilets through its Swachh Bharat Abhiyan has not taken into account the question of who will have to clean the septic tanks.
B. GS2 Related
1. Ethics panel debates checks and balances
Context
- In a meeting of the Rajya Sabha’s Parliamentary Committee on Ethics (PCE), members discussed amending Rule 293 of the Rajya Sabha’s procedures, which makes the “declaration of interest” by members a public document.
Details
- The section says that a “register of member’s interest” should be maintained.
- This interest is explained as “personal or specific pecuniary interest (direct or indirect) in a matter being considered by the Council or a Committee”.
- The rules say that a member should not participate in any debate if there is direct conflict of interest, without first declaring it, and that in case of a vote on any issue in the House, the vote of such a member could be challenged.
Discussions that took place
- The members contended said that they while filing their nominations, they declared their assets and liabilities. They had to update any changes in their assets and liabilities every year, too.
- Apart from allowing this information to be in the public domain, it could also be accessed by anyone through the Right to Information Act, they said.
- Some members felt that the availability of information should be made conditional and the present rule should be strengthened.
In reference to RTI
- This Section of Rule 293 is actually contradictory to Right to Information Act because, under this rule, the information can be divulged only through certain conditions — for example, the applicant has to satisfy what the purpose is and that it would not be misused. But under RTI, you can’t have any conditions.
Category: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. Rohingya handed over to Myanmar
Context
- Seven Rohingya Muslim men, arrested in 2012 for illegally entering Assam, were officially handed over to Myanmar authorities at Manipur’s border town Moreh.
Details
- The Rohingya have been usually found to enter India from three townships in Myanmar – Maungdaw, Buthidaung and Rathedaung in Northeastern Rakhine State that borders Bangladesh.

1. India ranks fifth in world in pictorial warnings on cigarette packets
Context
- Canadian cancer society recently released the sixth edition of Cigarette Package Health Warnings: International Status Report in Geneva at WHO framework convention on tobacco control conference, which provides an international overview ranking 206 countries/ jurisdictions based on warning size, and lists those that have finalised requirements for picture warnings.
Canadian Cancer Society
- The Canadian Cancer Society is a national, community-based organisation of volunteers whose mission is the eradication of cancer and the enhancement of the quality of life of people living with cancer.
Details
- 118 countries/jurisdictions worldwide have made picture warnings on cigarettes mandatory, representing a global public health achievement.
- In 2016, 100 countries/jurisdictions had implemented picture warnings.
- Canada was the first country to implement picture warnings in 2001
- In total, 107 countries in the world have made pictorial warnings larger than at least 50 per cent mandatory
- It has ranked 206 countries and territories on the size of their health warnings on cigarette packages, and lists countries and territories that require graphic picture warnings.
India’s ranking
- India has been ranked fifth in the listing of countries that have pictorial health warning on tobacco products, with experts here quick to add that the country is making tremendous progress towards creating public awareness on the health hazards of tobacco abuse.
- Indian packaging has the warning on 85% of both sides.
- India, meanwhile, is the only SAARC country to have a Quit-Line number on tobacco products and the fourth in Asia after Thailand, Malaysia and Singapore.
Quit-Line number
- The pack warning will help to warn people, especially the illiterate and children, about the harms of tobacco consumption. The Quit-Line number will help those who want to quit
- The current pictorial warnings on both sides of all packets of cigarettes, bidis and all forms of chewing tobacco products in India came into effect in April 2016 on the direction of the Rajasthan High Court and, subsequently, the Supreme Court of India.
Other Countries
- East Timor is ranked first with 85% of the front and 100% of the back of the packaging being used for pictorial warnings.
- Nepal follows with 90% coverage on both sides.
- New Zealand is at fourth with 87.5 per cent
- India, Hong Kong and Thailand hold fifth place jointly with 85 per cent cigarette warnings
Significance
- Pictorial health warnings on tobacco products are the most cost-effective tool for educating people on the health risks of tobacco use.
- In a country like India, where people use several languages and dialects, the pictorial warning transcends the language and in many cases also the illiteracy barrier.
- The 85% pictorial warnings on all cigarettes, bidis and chewing tobacco packages manufactured and sold in India have resulted in 92% of adults (surveyed under GATS 2016-2017) believing that smoking caused serious illness and 96% saying use of smokeless tobacco causes serious illness.
C. GS3 Related
1. Centre announces 2.5 cut in fuel prices
Context
- Union Finance Minister Arun Jaitley announced that the center has decided to implement a cumulative cut by 5 a litre on fuel prices, with the Centre absorbing 1.5 of this and the oil marketing companies (OMCs) by 1.
- BJP-ruled States including Gujarat, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Chattisgarh, Jharkhand, Assam and Tripura announced a cut in VAT of up to 2.5 per litre to affect a 5 per litre reduction in pump rates.
Details
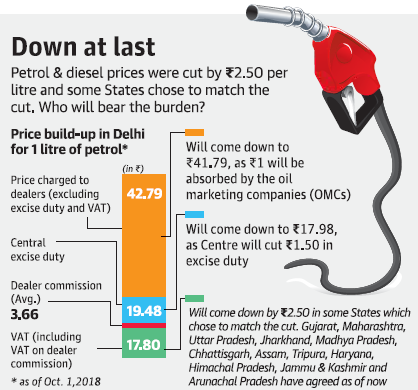
Marginal impact on fiscal deficit
- Jaitley said this would have only a marginal impact on the fiscal deficit — less than 0.05% of the fiscal deficit — since the excise duty cut would be balanced out by higher direct tax collections.
Significance
- As a consumer-friendly measure it will ease the burden on the common man
- The cut is also probably a signal to the RBI ahead of its monetary policy announcement on the Centre’s commitment to keep inflation in check.
1. Lions in Gujarat may have been killed by Muted Virus
Context
- Gujarat officials are grappling with the death of 21 lions, wildlife experts say that more than the numbers it’s the fear of a mutation in a virus as the likely cause of deaths
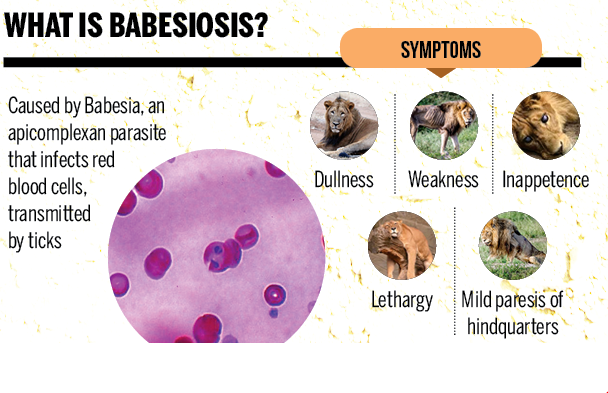
- The lions succumbed to the deadly infection of canine distemper virus (CDV) and tick-borne babesiosis.
- The Gir sanctuary in Gujarat is the last habitat of the Asiatic lion of which 500-600 survive.
Stats
According to a 2015 census, Gir is home to 523 lions, including 109 male, 201 female, 73 sub-adults and 140 cubs.

Canine Distemper Virus (CDV)
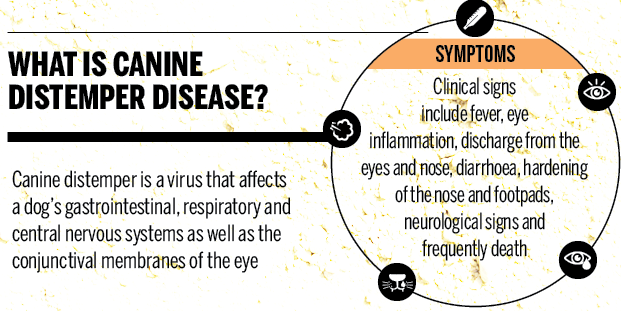
Babesiosis
Warnings Ignored
Action Plan
- Vaccinate dogs in the vicinity against CDV, like in Serengeti where close to 30000 dogs were vaccinated
- Tick control measures among domesticated bovine animals goats and sheep in Gir’s vicinity
- The lions may have caught the CDV from other carnivores like hyenas or leopards
- As a precautionary measure, Gir authorities have captured and isolated 31 lions from areas adjacent to the one in which the deaths have occurred.
Earlier Instances
Gir has long lived in the shadow of potential epidemics.
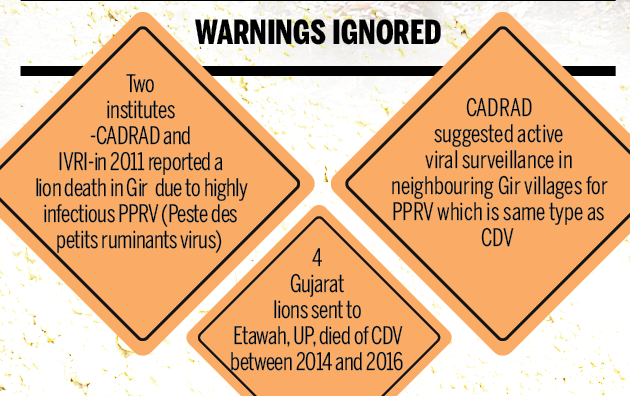
- In 2012, studying frozen tissue samples taken from the carcass of a lion that died in 2007, IVRI researches flagged the presence of the Peste Des Petits Ruminants virus (PPRV).
- PPRV or ‘Goat Plague’ is highly contagious, and can be deadlier than even CDV that wiped out a third of Africa’s lions in the mid-1990s.
- But it infects only domestic livestock — small ruminants like goats and sheep.
- It is part of a family of morbilliviruses that causes canine distemper in many carnivore species, measles in humans, and rinderpest in cattle. There is no record of PPRV making carnivores sick.
D. GS4 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
E. Editorials
Category: ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
1. Next steps at Gir (The Way Forward to protect the Asiatic Lion)
Note to the Students:
This topic has been in the news for some time now. Here we have taken the liberty to give a detailed background on this topic, touching upon press releases in The Hindu that have featured the same topic over the past few days. Students are advised to consider this as an important issue for the exam.
Background:
- There has been an alarming development where many Asiatic lions have died in the Gir forest.
- 23 lions since September 12, 2018 have died.
- The Gujarat government, had initially insisted that the lions had died due to infighting for territorial domination.
- Currently, the government has sprung into action and launched not only rescue efforts but also called experts from outside, including London, and imported a vaccine from the United States.
- At the moment, more than 500 lions have already been screened to detect viral infections in the Gir forests and revenue areas. This has been done so because as Asiatic lions are spread in as many as eight districts in the Saurashtra region.
- It is important to note that the Gir forests, are the only abode of Asiatic lions in the world.
- The lions are famously known as Gujarat’s pride.
- Apart from the 23 lions that have died since September 12, 2018, as many as 36 are battling for their lives.
- A deadly outbreak of the Canine Distemper Virus (CDV) and tick-borne Babesiosis is killing these lions.


Analysis:
- It is important to note that in the year 2013, the Supreme Court had issued an order that lions from Gujarat be relocated to the Kuno sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh as a check against the threat of epidemic.
- Further, even wild animals are subject to State politics. Gujarat has been unwilling to part with its lions, calling them “its pride” in an affidavit.
- On October 3, 2018, the Supreme Court of India, noting that the death of so many lions was a serious matter, asked the Central government to look into it.
A Detailed Look into the 2013 Order:
- Specific observation made by the Supreme Court:
“Asiatic lion, it has been noticed, has been restricted to only one single habitat, i.e. the Gir National Forest and its surrounding areas and an outbreak of possible epidemic or natural calamity might wipe off the entire species. A smaller population with limited genetic strength are more vulnerable to diseases and other catastrophes in comparison to large and widespread population.”
- Further, the Supreme Court of India also noted as to how 30% of the lion population in Tanzania’s Serengeti was killed due to an outbreak of canine distemper.
- Canine Distemper is a viral disease that affects animals.
- Gujarat’s response to this order by the Supreme Court was that lions are now spread over the Greater Gir region and this reduces the threat.
- The Gujarat government also added that when ill, the lions are routinely picked up, medically treated, and then released.
Wildlife Conservation Vs. Treating Wild Animals
- It is important to note that there exists a conflict between the idea of wildlife conservation and that of treating wild animals. This is so because, wildlife conservation concerns itself with maintaining ecological processes and reducing threats to endangered species. It does not entail treating wild animals for disease (in the way domestic animals are) as this can go against the processes of natural selection.
- Further, although treating wild animals appears to be a caring thing to do, it is not conducive to the ‘natural’ process of life and death, and ultimately compromises on immunity.
- Some experts believe that the lines of what comprises wildlife conservation are getting blurred. For example, wildlife conservation in the age of man, is very different- sometimes protected areas resemble zoos.
- Having said this, even the most flexible of wildlife conservationists would agree that intensive artificial medical treatment of wild animals does not augur well for long-term sustainability.
- It is felt that the role of wildlife managers should be to reduce unnatural threats, and not to unnaturally prolong life. Although Gujarat has done a good job of conserving its lions, it should also turn its attention to reducing the drivers of disease.
The Way Forward:
- Without a doubt, after the lion deaths, it is believed that Gujarat should work towards colonising new habitats outside the Gir landscape within the State of Gujarat.
- Having said this, there are spatial limitations in the industrialised State of Gujarat.
- An option that one can consider is the Barda wildlife sanctuary.
- In conclusion, a geographically separate population of Asiatic lions needs to be created.
Category: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. Eyes on India (Japan, South Korea, Taiwan and Australia are forging closer economic ties with India)
Editorial Analysis:
-
Recently, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan and Australia have unveiled strategies to forge closer economic ties with India.
- Experts believe that Asia is currently in a state of flux.
The Current State of Affairs:
- Currently, China’s Belt and Road Initiative is reshaping the region’s geography, with roads and railways traversing Eurasia and new ports dotting the Indian Ocean basin.
- As a matter of fact, China’s militarisation of the South China Sea continues, despite negotiations towards a code of conduct.
- Japan has been involved in resuscitating the Trans-Pacific Partnership and concluding a trade agreement with the European Union. In doing so, Japan has found itself in an unexpected leadership position.
- In fact, Japan is now contemplating constitutional revisions that would enable it to play a more overt military role.
It is important to note that Article 9 of the Japanese Constitution, outlaws war as a means to settle international disputes involving the state. The Constitution came into effect on May 3, 1947, following World War II.
- It must also be noted that Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and Australia have all unveiled strategies to diversify their economic interdependence, away from mainland China and towards Southeast Asia and India. Thus, the center of gravity is shifting towards Southeast Asia and India.
Reasons for the shift in Policy:
- The ongoing trade and tariff war between the U.S. and China is one reason.
- Further, a longer-term concern is Beijing’s use of its economic muscle for political purposes.
- In fact, there are many instances which come to light in this regard. They range from a) suspending rare earth metal exports to Japan in 2010 or b) punishing a major South Korean corporation for Seoul’s decision to install a missile defence system in 2017.
Further, China’s limited market growth potential and questions of access and reciprocity are additional considerations.
Certain Specific Policies:
- Japan’s Free and Open Indo-Pacific strategy is meant to diversify investments to more promising markets in Southeast Asia, India, and Africa.
- On top of this. South Korean President Moon Jae-in has unveiled a New Southern Policy.
- During his India visit, Mr. Moon said that while the policy is focussed on Southeast Asia, it also “makes India Korea’s key partner for cooperation”.
- Similarly, Taiwan, which is a G20-sized economy whose political status is disputed, has announced a New Southbound Policy with significant accompanying investments in India by Taiwanese electronics manufacturers.
- Even the Australian government has commissioned an ambitious India Economic Strategy.
- The India Economic Strategy has the goal of making India its third-largest investment destination and export destination by 2035.
- Generally speaking, although while policies are not driven by short-term necessities, political concerns are increasingly informing economic preferences.
In conclusion, experts believe that the stars are aligning in Asia for the acceleration of India’s economic growth. Further, investors, increasingly backed by their governments, are increasingly focussed on the Indian market.
F. Tidbits
Context
- A facial scan will soon enable air travellers to skip long queues and zip through various check points at airports in the country. The Centre is set to introduce the “Digi Yatra” facility.
- The facility, which is voluntary, would require passengers to initially register themselves at a web portal by providing an identity proof
Procedure
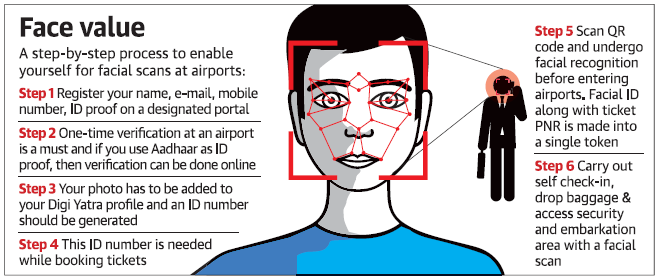
G. Prelims Fact
- Konark Sun Temple is a 13th-century sun temple at Konark on the coastline of Odisha.
- The name Konark derives from the combination of the Sanskrit words Kona (corner or angle) and Arka (the sun).
- The temple is attributed to king Narasimhadeva I of the Eastern Ganga Dynasty
- Dedicated to the Hindu god Surya, what remains of the temple complex has the appearance of a 100-foot (30 m) high chariot with immense wheels and horses, all carved from stone.
- Also called the Surya Devalaya, it is a classic illustration of the Odisha style of Hindu temple architecture.
- This temple was called the “Black Pagoda” in European sailor accounts as early as 1676 because its great tower appeared black.
- Similarly, the Jagannath Temple in Puri was called the “White Pagoda”. Both temples served as important landmarks for sailors in the Bay of Bengal.
- Declared a UNESCO world heritage site in 1984, it remains a major pilgrimage site for Hindus, who gather here every year for the Chandrabhaga Mela around the month of February.
- Taliperu Reservoir is a medium irrigation project constructed across the Taliperu River, a tributary of Godavari River located at Cherla Village and Mandal, Khammam District, Telangana.
- The river has been harnessed for agricultural purposes through extensive canal systems developed in that region.
H. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
Question 1. Which of the following statement/s is/are correct?
-
Judges of the Supreme court are appointed by the President.
-
Judges of the Supreme court can be removed on the ground of proven misbehavior only.
-
Schedule 3 deals with the Oath or affirmation to be subscribed by the judges.
Options:
- i) and ii) only
- i) and iii) only
- i) only
- All of the above
See
Question 2. Consider the following:
-
Promotion of International peace and security is covered under DPSPs.
-
Protection and improvement of the environment is the duty of both, citizens and the state.
-
Prohibition of consumption of alcohol is a duty of the state, as provided under the DPSPs.
Which of the above statement/s is/are correct?
- i) only
- i) and ii) only
- All of the above
- None of the above
See
Question 3. Consider the following:
- Fundamental duties can be enforced by writs.
- These duties extend to foreign nationals staying in India.
Choose the correct option:
- Only i) is correct
- Only ii) is correct
- Both are correct
- Both are incorrect
See
Question 4. Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
- Bandipur – Tiger
- Kaziranga – One Horned Rhino
- Gir – Gharial
Options:
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- None of the Above
See
I. Practice Questions for UPSC Mains Exam
- The process of defence acquisition has come under scrutiny recently. Examine the challenges that prevail in acquiring critical defence equipment. What are the steps one can take to overcome some of these challenges.
- India has a vibrant and active diaspora spread across the world. Examine the role that the Indian diaspora can play as far as furthering international cooperation between India and other nations.
- Recently, many Asiatic lions in Gujarat’s Gir sanctuary have lost their lives. Examine the steps that can be taken to remedy the situation.
Also, check previous Daily News Analysis
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Current Affairs Webinar’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series
Comments