The JEE Main 2024 Mathematics syllabus is released by the National Testing Agency. On this page, you can check the complete JEE Main 2024 syllabus for Mathematics that is published by NTA. Students are advised to download the PDF of the JEE Main 2024 Mathematics syllabus for reference.
The National Testing Agency (NTA) is in charge of overlooking the JEE Main examination and all the related things, such as releasing admit cards, announcing the results, and more. The syllabus mostly remains unchanged despite other changes, especially in the exam pattern. In any case, students can go through the JEE Main Maths syllabus, which will help them formulate a proper strategy for studying in an organised manner for IIT JEE 2024.
Each and every concept included in JEE Main syllabus for Maths is important, and the questions could be expected from anywhere. Understanding JEE Main maths syllabus will help the engineering aspirants to develop a clear understanding of what concepts are to be prepared or avoided for better results in JEE Main. For Mathematics, the most important thing that students need to have is rigorous practice. The more problems students practise, the better they will be at solving questions with accuracy and speed. Apart from this, the students can also check the detailed subject-wise list of all the topics included in JEE Main Physics and Chemistry syllabi from below-given links.
Download JEE Main Syllabus
Students can download the PDF of the whole JEE Main 2024 syllabus for Maths below.
Download JEE Main Maths Syllabus PDF
JEE candidates can also view the detailed list of all the concepts mentioned below.
JEE Main Maths Syllabus Topics
| Unit 1: Sets, Relations, and Functions |
|
| Unit 2: Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations |
|
| Unit 3: Matrices and Determinants |
|
| Unit 4: Permutations and Combinations |
|
| Unit 5: Mathematical Induction |
| The principle of mathematical induction and its simple applications. |
| Unit 6: Binomial Theorem and its Simple Applications |
|
| Unit 7: Sequence and Series |
|
| Unit 8: Limit, Continuity and Differentiability |
|
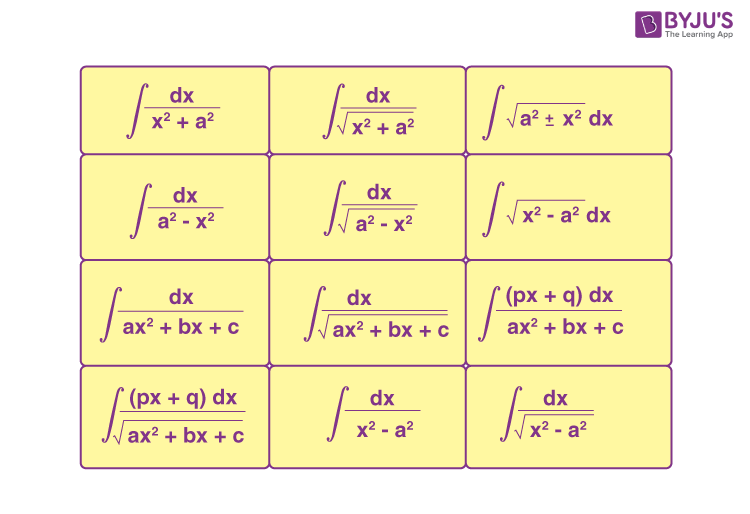
| Unit 9: Integral Calculus |
|
| Unit 10: Differential Equations |
|
| Unit 11: Coordinate Geometry |
|
| Unit 12: 3D Geometry |
|
| Unit 13: Vector Algebra |
|
| Unit 14: Statistics and Probability |
|
| Unit 15: Trigonometry |
|
| Unit 16: Mathematical Reasoning |
|
The JEE Main Maths syllabus mainly comprises all the topics included in Class XI and Class XII Maths syllabi. Students are advised to prepare a list of all the important Maths concepts in JEE Main syllabus and practise rigorously to ensure a meritorious position in the exam.
Also, read:
- JEE Test Series
- JEE Main 2022 Question Papers
- JEE Main Answer Key
- JEE Advanced 2024 Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Notes
- Best books for IIT JEE Maths
Sure Shot Topics for Mathematics – JEE Main

Tips to Revise Maths JEE Main Syllabus in 3 Months

100 Most Important Maths JEE Main Questions – Part 1

100 Most Important Maths JEE Main Questions – Part 2

5 Common Mistakes to Avoid in JEE Maths Exam

Frequently Asked Questions
Who publishes the JEE Main 2024 syllabus?
The National Testing Authority publishes the JEE Main 2024 syllabus.
Are there any changes in the JEE Main 2024 Mathematics syllabus?
The NTA has released the JEE Main 2024 Mathematics syllabus, and there are no changes in the syllabus.
When will the authorities release the JEE Main syllabus 2024?
The NTA released the syllabus and the official JEE Main 2024 notification.
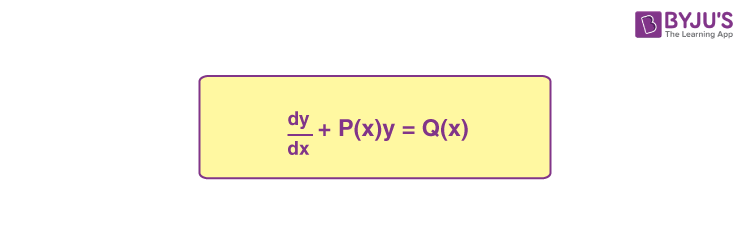
Comments