KCET 2015 Chemistry paper solved by experts at BYJU’S is included on this page. KCET aspirants are advised to go through and practise the questions given in 2015 paper to get familiar with the exam pattern, question types, weightage of marks and also understand the coverage of the important topic. In essence, students will be able to develop better problem-solving skills and also improve the speed of answering the questions.
KCET 2015 - Chemistry
Question 1: The unit cell with crystallographic dimensions, a ≠b ≠c, α =γ= 90 and β≠90 is
- a. Triclinic
- b. Monoclinic
- c. Orthorhombic
- d. Tetragonal
Solution:
Answer: b
The unit cell with crystallographic dimensions a ≠ b ≠c ; α = r = 90 and β≠90 is a monoclinic unit cell. Triclinic unit cell has crystallographic dimensions a ≠ b ≠c; α = β = r = 90°.
Pentagonal unit cell has crystallographic dimensions a ≠ b ≠c ; α= β = r = 90°.
Orthorhombic unit cell has crystallographic dimensions a ≠b ≠c; α = β= r = 90°.
The monoclinic crystal system is one of seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a rectangular prism with a parallelogram as its base. The unit cell will be monoclinic.
Question 2: While charging the lead storage battery.______.
- a. PbSO4 on anode is reduced to Pb
- b. PbSO4 on cathode is reduced to Pb
- c. PbSO4 on cathode is oxidized to Pb
- d. PbSO4 on anode is oxidized to PbO2
Solution:
Answer: a
The charging equation is
2PbSO4 (s) + 2H2O(l) →Pb(s) + Pb O2(s) + 2H+(aq) + 2HSO4 (aq)
Lead storage batteries can be used in automobiles these batteries can be recharged in the charged state each cell contain negative plates of lead (Pb) and positive plates of lead (IV) inside (PbO2) in an electrolyte of approximately 4.2 m-sulphuric acid (H2SO4). The charging process is driven by the forcible removal of electrons from the positive plate and the forcible introduction of them to the negative plate by the charging source.
Question 3: Adenosine is an example of
- a. Nucleotide
- b. Purine base
- c. Pyrimidine base
- d. Nucleoside
Solution:
Answer: d
Adenosine is a nucleoside consisting of adenine and ribose sugar linked glycosidic bond.
A nucleoside consists simply of a nucleoside and five-carbon sugar, whereas a nucleotide is composed of nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. In a nucleoside, the anomeric carbon is linked through a glycoside bond to the N9 of a purine. Examples of nucleosides include. Cytidine, uridine, adenosine, guanidine etc.
Question 4: Orlon has a monomeric unit
- a. Acrolein
- b. Glycol
- c. Vinyl cyanide
- d. Isoprene
Solution:
Answer: c
Orlon is an example of polyacrylonitrile (PAN)

The monomeric unit of orlon is acrylonitrile /vinyl cyanide.
Question 5: The two electrons have the following set of quantum numbers:
P = 3, 2, –2, + 1/2
Q = 3, 0, 0, + 1/2
Which of the following statement is true?
- a. P and Q have the same energy
- b. P has greater energy than Q
- c. P has lesser energy than Q
- d. P and Q represent same electron
Solution:
Answer: b
Orbitals are filled in order of increasing value of (n + l). If 2 orbitals have same value (n + l), then the orbitals with lower value of n will be filled first for p(n + l) = 3 + 2 = 5. For a (n + l) = 3 + 0 = 3. So p has greater energy than q.
Question 6: H2O2 cannot oxidise
- a. PbS
- b. Na2SO3
- c. O3
- d. KI
Solution:
Answer: c
Ozone is a stronger oxidizing agent than H2O2. Ozone is highly unstable hence, it dissociates to form O2 molecule and nascent oxygen which extremely or highly unstable and hence it reacts quickly to oxidize anything in order to attain stability H2O2 can’t oxidize O3.
Question 7: In the given set of reactions, 2-Bromopropane
 the IUPAC name of product ‘Y’ is
the IUPAC name of product ‘Y’ is
- a. N-Methylpropanamine
- b. N-Isopropylmethanamine
- c. Butan-2-amine
- d. N-Methylpropan-2-amine
Solution:
Answer: d

Nitrogen is free to donate electron pair forming isocyanides. Isonitrides on reduction with LiAlH4 gives secondary amines.
Question 8: On heating with concentrated NaOH solution in an inert atmosphere of CO2, white phosphorous gives a gas. Which of the following statement is incorrect about the gas?
- a. It is less basic than NH3
- b. It is more basic than NH3
- c. It is highly poisonous and has a smell like rotten fish
- d. It’s solution in water decomposes in the presence of light
Solution:
Answer: b
On heating with concentrated NaOH in an inert environment of CO2 the reaction will be
Pu + 3NaOH + 3H2O → PH3 + 3NaH2PO2
PH3 is formed which is more basic than NH3.
Question 9: Sodium metal crystallizes in B.C.C. lattice with an edge length of 4.29 Å. The radius of the sodium atom is
- a. 2.857 Å
- b. 1.601 Å
- c. 2.145 Å
- d. 1.857 Å
Solution:
Answer: d
In BCC structure the radius of sodium atom is 0.433 a
So, 0.433 × 4.29 Å = 1.86 Å
Question 10: 0.06% (w/v) aqueous solution of urea is isotonic with
- a. 0.06% glucose solution
- b. 0.6% glucose
- c. 0.01 M glucose solution
- d. 0.1 M glucose solution
Solution:
Answer: c
Given : 0.06 % w/v solution of urea
so moles of urea =(0.06/60) = 0.001 mol
Molality of urea solution = (0.001/100) × 1000 = 0.01 m
Therefore, Reaction constant should be same for isotonic
So 0.01 m glucose solution
Question 11: In a first-order reaction, the concentration of the reactant is reduced to 12.5% in one hour. When was it half completed?
a. 3 hr- a. 3 hr
- b. 20 min
- c. 30 min
- d. 15 min
Solution:
Answer: b
Assuming initial concentration is 100 % concentration after three half-lives = 1205.1
Half-life = 60 min/3 = 20 min
Question 12: The electrolyte having maximum flocculation value for AgI/Ag+sol. is
- a. NaCl
- b. Na2S
- c. Na2SO4
- d. Na3PO4
Solution:
Answer: a
The electrolyte having minimum coagulating power will have maximum flocculation value. Hence, NaCl having lowest charge will have minimum coagulation power hence maximum flocculation value.
Question 13: Copper is extracted from Copper pyrites by heating in a Bessemer converter. The method is based on the principle that
- a. Copper has more affinity for oxygen than Sulphur at high temperature
- b. Iron has less affinity for oxygen than Sulphur at high temperature
- c. Copper has less affinity for oxygen than Sulphur at high temperature
- d. Sulphur has less affinity for oxygen at high temperature
Solution:
Answer: a
The reactions involved during the extraction of copper. From copper pyrites are
2Cu2S + 3O2→ 2Cu2O + 2SO2
2Cu2O + Cu2S → 2Cu + SO2
Copper pyrites are heated in blast furnace and the principle used here is that copper has high. Affinity for oxygen than sulphur at high temperature.
Question 14: Which of the following will be able to show geometrical isomerism?
- a. MA3 B – Square planar
- b. MA2 B2 – Tetrahedral
- c. MABCD – Square planar
- d. MABCD – Tetrahedral
Solution:
Answer: c
As it is a known fact that tetrahedral arrangement does not show GI while square planar shows GI. But the condition is that all groups must be different. In MA3B all the arrangements will be the same hence it will not show Gi. Therefore, only MABCD will show GI.
Question 15: The electronic configuration of Gd 2+ is (at. No. of Gd is 64)
- a. [Xe] 4f+8
- b. [Xe] 4f8
- c. [Xe] 4f+7 5d1 6s2
- d. [Xe] 4f+7 5d1
Solution:
Answer: d
‘4’ The electronic configuration of Gd is [Xe] 4f7 sd1 6s2 then the configuration of Gd+2 will be [Xe]4f7 5d1.
Question 16: Here M and Z are

- a. Cu, ZnS
- b. Zn, ZnS
- c. Fe, FeS
- d. AI, AI2S3
Solution:
Answer: b

The reaction of MSO4 with NH4OH gives a white ppt of Zn(OH)2 which when reacted with an excess of NH4OH gives a complex [Zn(NH3)4]2+. When [Zn(NH3)4]2+complex is allowed to react with H2S it will give Zinc sulphide.So m is zinc and z is zinc sulphide.
Question 17: The hydrolysis of optically active 2-bromobutane with aqueous NaOH result in the formation of
- a. (+) butan-2-ol
- b. (–) butan-2-ol
- c. ( ±) butan-1-ol
- d. (± ) butan-2-ol
Solution:
Answer: d
Question 18: The distinguishing test between methanoic acid and ethanoic acid is
- a. Litmus test
- b. Tollen’s test
- c. Esterification test
- d. Sodium bicarbonate test
Solution:
Answer: b
Aldehydes give positive tollen’s test. Methanoic acid is an exception as it has a hydrogen atom as substituent not in any other group attached. So it will give a positive tollen’s test like aldehyde. Ethanoic acid does not give tollen’s test.
Question 19: In H2–O2 fuel cell the reaction occurring at the cathode is

Solution:
Answer: b
For H2O2 cell the reactions of cathode and anode are.
At cathode: O2(g) + 2H2O(l) + 4e–→4OH– (aq)
At anode
2H2(g) + 4OH– (aq) + 4e– → 2H2O(l)
So overall reaction is
2H2(g) +O2(g) + 2H2O (d)
Question 20: Which of the following curve is in accordance with Freundlich adsorption isotherm?

Solution:
Answer: c
For Freundlich adsorption isotherm

Question 21: How many ions per molecule are produced in the solution when Mohr salt is dissolved in excess of water?
- a. 4
- b. 5
- c. 6
- d. 10
Solution:
Answer: b
When Mohr salt is added in water the dissociation will be as follows.

So, total of 5 ions are obtained.
Question 22: Glycogen is
- a. a polymer of β-D-glucose units
- b. a structural polysaccharide
- c. structurally very much similar to amylopectin
- d. structurally similar to amylopectin but extensively branched
Solution:
Answer: d
Glycogen is multi-branched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi. It is a condensation polymer of α-Glucose, its formula is C6H10O5.
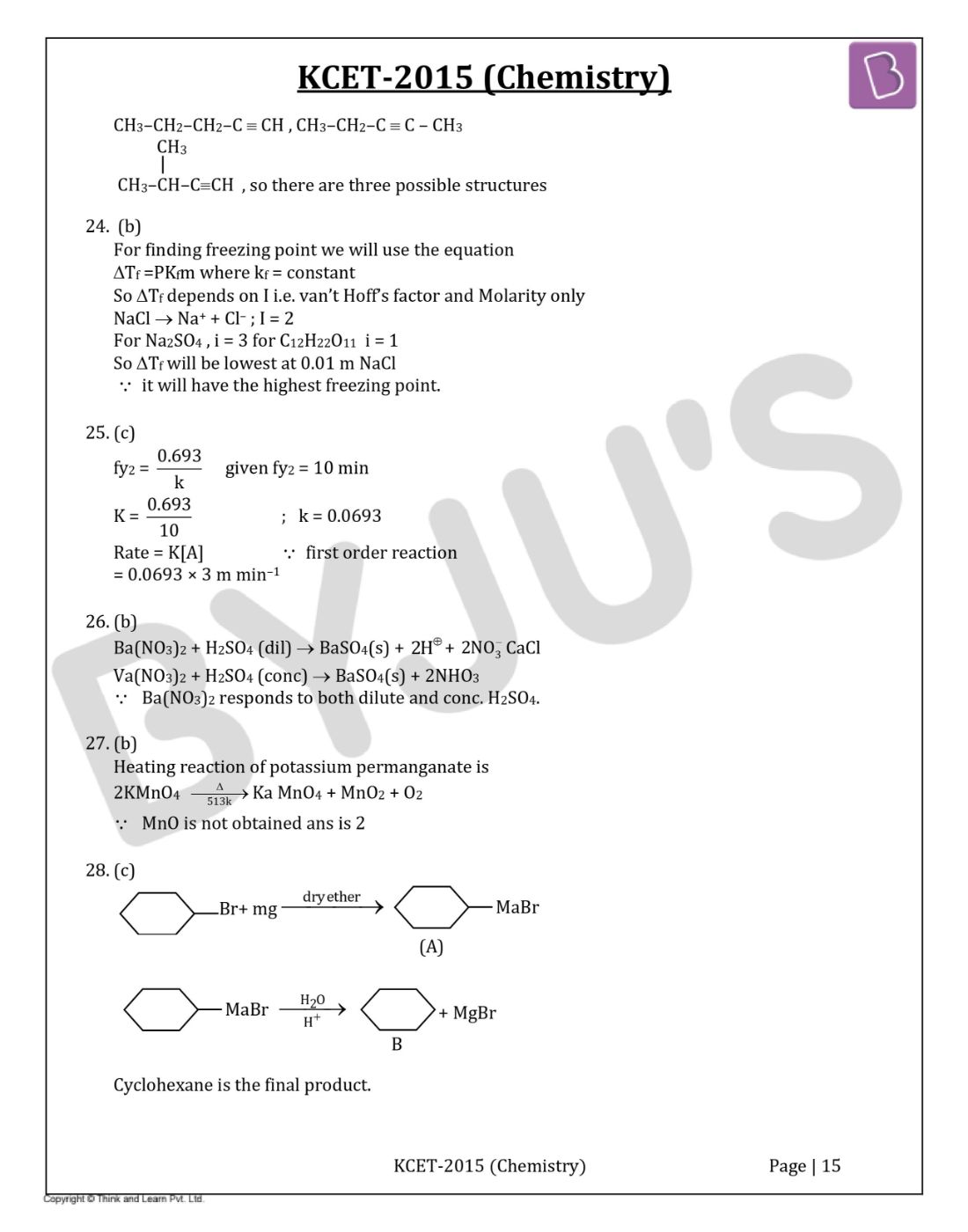
Question 23: Number of possible alkynes with formula C5H8 is
- a. 2
- b. 3
- c. 4
- d. 5
Solution:
Answer: b
The total alkynes possible by formula C5H8are

So, there are three possible structures.
Question 24: Which of the following aqueous solution has the highest freezing point?
- a. 0.1 M Sucrose
- b. 0.01 M NaCl
- c. 0.1 M NaCl
- d. 0.01 M Na2SO4
Solution:
Answer: b
For finding freezing point we will use the equation
∆Tf =PKfm where kf = constant
So ∆Tf depends on I i.e. Van’t Hoff’s factor and Molarity only
NaCl → Na++ Cl– ; I = 2
For Na2SO4 ,i = 3 for C12H22O11i = 1
So ∆Tf will be lowest at 0.01 m NaCl
Therefore, it will have the highest freezing point.
Question 25: Half life period of a first-order reaction is 10 min. Starting with initial concentration of 12 M, the rate after 20 min is
- a. 0.0693 M min–1
- b. 0.693 × 3 M min–1
- c. 0.0693 × 3 M min–1
- d. 0.0693 × 4 min–1
Solution:
Answer: c

Question 26:The salt which responds to dilute and concentrated H2SO4 is
- a. CaF2
- b. Ba(NO3)2
- c. Na2SO4
- d. Na3PO4
Solution:
Answer: b

Question 27: On heating potassium permanganate, one of the following compound is not obtained:
- a. O2
- b. MnO
- c. MnO2
- d. K2MnO4
Solution:
Answer: b

Question 28:

Solution:
Answer: c

Cyclohexane is the final product.
Question 29: The formation of cyanohydrins from a ketone is an example of
- a. Nucleophilic substitution
- b. Nucleophilic addition
- c. Electrophilic addition
- d. Electrophilic substitution
Solution:
Answer: b
The reaction involved in the formation of cyanohydrins from a ketone is

By seeing the reaction mechanism we can conclude that is a nucleophile. Hence it is nucleophilic addition reaction.
Question 30: One of the following is an essential amino acid
- a. Tyrosine
- b. Cysteine
- c. Isoleucine
- d. Serine
Solution:
Answer: c
Essential amino acids are amino acids which cannot be synthesized by our body and are taken from external sources. Here isoleucine is an essential amino acid.
Question 31:The aqueous solution of the following salt will have the lowest pH:
- a. NaClO3
- b. NaClO
- c. NaClO2
- d. NaClO4
Solution:
Answer: d
The acidic strength of oxoacids of chlorine increases with increase in chlorine’s oxidation no. So finding oxidation number X of Cl
in HClO2 1 + x – 4 = 0 x = +3
in HClO3 1 + x – 6 = 0 x = + 5
in HClO2 1 + x – 4 = 0 x = +3
in HClO4 1 + x – 8 = 0 x = +7
So acidic strength will be in order
HClO4> HClO3> HClO2>HClO
More the strong acid lower will be the PH so HClO4 is strongest acid thus its salt NaClO4 will have lowest PH.
Question 32: For one of the elements various successive ionization enthalpies (in kJ mol–1) are given below:
|
I.E |
1st |
2nd |
3rd |
4th |
5th |
|
577.5 |
1810 |
2750 |
11,580 |
14,820 |
The element is
- a. Si
- b. P
- c. Al
- d. Mg
Solution:
Answer: c
By seeing data, we can conclude that after ionization energy 3, ionization energies are very high which indicates that element has attained stability after ionization energy 3, so the element will be aluminium (Al)
Question 33: 0.30 g of an organic compound containing C, H and Oxygen on combustion yields 0.44 g CO2 and 0.18 g H2O. If one mol of compound weight 60, then the molecular formula of the compound is
- a.CH2O
- b. C3H8O
- c.C4H6O
- d.C2H4O2
Solution:
Answer: d
Moles of C = moles of CO2
Moles of CO2 = Given mass/molar mass
= 0.44/44 = 0.01 moles
Moles of H = 2α moles of H2O
= 2α(0.18/18) = 0.02 moles
Weight of oxygen = 0.30– wt of carbon- wt of hydrogen
= 0.3 – 0.01× 12–0.02 × 1 = 0.16 am
Moles of O = (0.16/16) = 0.01 moles
Question 34: One of the following amides will not undergo Hoffmann bromamide reaction:
- a. CH3CONH2
- b. CH3CONHCH3
- c. C6H5CONH2
- d. CH3CH2CONH2
Solution:
Answer: b
Hoffman bromamide reaction is shown only by primary amide.
Therefore, among the following CH3CONHCH3 is not primary amide so it will not give Hoffman bromide reaction.
Question 35: Cheilosis and digestive disorders are due to the deficiency of
- a. Thiamine
- b. Ascorbic acid
- c. Riboflavin
- d. Pyridoxine
Solution:
Answer: c
Saliva collecting at the corners of the mouth can cause a build of microorganisms leading to angular cheilitis. It is caused by vitamin B. It is a digestive disorder. Vitamin B is also known as Riboflavin.
Question 36: How many Coulombs of electricity are required for the oxidation of one mole of water to dioxygen?
- a. 9.65 × 104 C
- b. 1.93 × 104 C
- c. 1.93 × 105 C
- d. 19.3 × 105 C
Solution:
Answer: c

Question 37:100 cm3 of 1 M CH3COOH was mixed with 100 cm3 of 2 M CH3OH to form an ester. The change in the initial rate if each solution is diluted with an equal volume of water would be
- a. 2 times
- b. 4 times
- c. 0.5 times
- d. 0.25 times
Solution:
Answer: d

Question 38: Which of the following colloids cannot be easily coagulated?
- a. Lyophobic colloids
- b. Multimolecular colloids
- c. Macromolecular colloids
- d. Irreversible colloids
Solution:
Answer: c
Macro molecular colloids are a type of Lyophobic colloids. Lyophobic colloids are stable and do not easily coagulate. So, the answer is a macromolecular colloid.
Question 39:. The complex ion having a minimum magnitude of ∆0(CFSE) is
- a. [Cr(CN)6]3–
- b. [Co(NH3)6]3+
- c. [Co(Cl)6]3–
- d. [Cr(H2O)6]3+
Solution:
Answer: c
When complex contains web ligand than CFSE has a lower value.
Therefore, CFSE decreases in order
[CO(NH3)6]3+> [Cr (CN)6]3– ≅ [Cr(CH2O)6]3+> [COCl6]3–
Order of field strength is Cl– < H2O < NH3< CN–
CFSE = (–0.4x + 0.6y) so
x= number of electrons in eg
y = number of electrons in eg
so = 4 × (0.4) + 2 × 0.6
= –0.4 ∆0
For Cr 3+ cl3 low spin [Cr (CN)6]3– , [Cr (H2O)6]3+
∆0 = 3 × (–0.4) = 1.2∆0
∆0 = 6 × (–0.4) + 0 × 0.6 = – 2.4∆0
Therefore, for [CoCl6] compare magnitude of ∆0 CFSE is minimum.
Question 40: The arrangement of following compounds:
i. bromomethane
ii. bromoform
iii. chloromethane
iv. dibromomethane
In the increasing order of their boiling point is
- a. iii <i<iv < ii
- b. iv < iii <i< ii
- c. ii < iii <i< iv
- d. i< ii < iii < iv
Solution:
Answer: a
B.P increases with increase in molar mass
CH3Cl < CH3 Br < CH2 Br2< CHBr3
iii<i< iv < ii
Question 41: Iodoform can be prepared from all, except
- a. propan-2-ol
- b. butan-2-one
- c. propan-1-ol
- d. acetophenone
Solution:
Answer: c

The above reaction is Iodoform test. This test is used to detect the compounds having.
RCOCH3 or RCH (OH) CH3 structure.
Therefore, Propan-1-ol does not contain the required group So, it does not give iodoform test
Question 42: Identify ‘Q’ in the following sequence of reactions:

Solution:
Answer: c

Question 43: Cryolite is
- a. Na3AlF6 and is used in the electrolysis of alumina for decreasing electrical conductivity
- b. Na3AlF6 and is used in the electrolysis of alumina for lowering the melting point of alumina only
- c. Na3AlF6 and is used in the electrolysis of alumina for lowering the melting point and increasing the conductivity of alumina
- d. Na3AlF6 and is used in the electrolytic refining of alumina
Solution:
Answer: c
Na3Alf6 is the formula of crinoline. It is used in the electrolysis of alumina
Since it lowers down the fusion temperature from 2050° C to 950°C
Therefore, Na3Alf6 is used in the electrolysis of amnion for lowering.
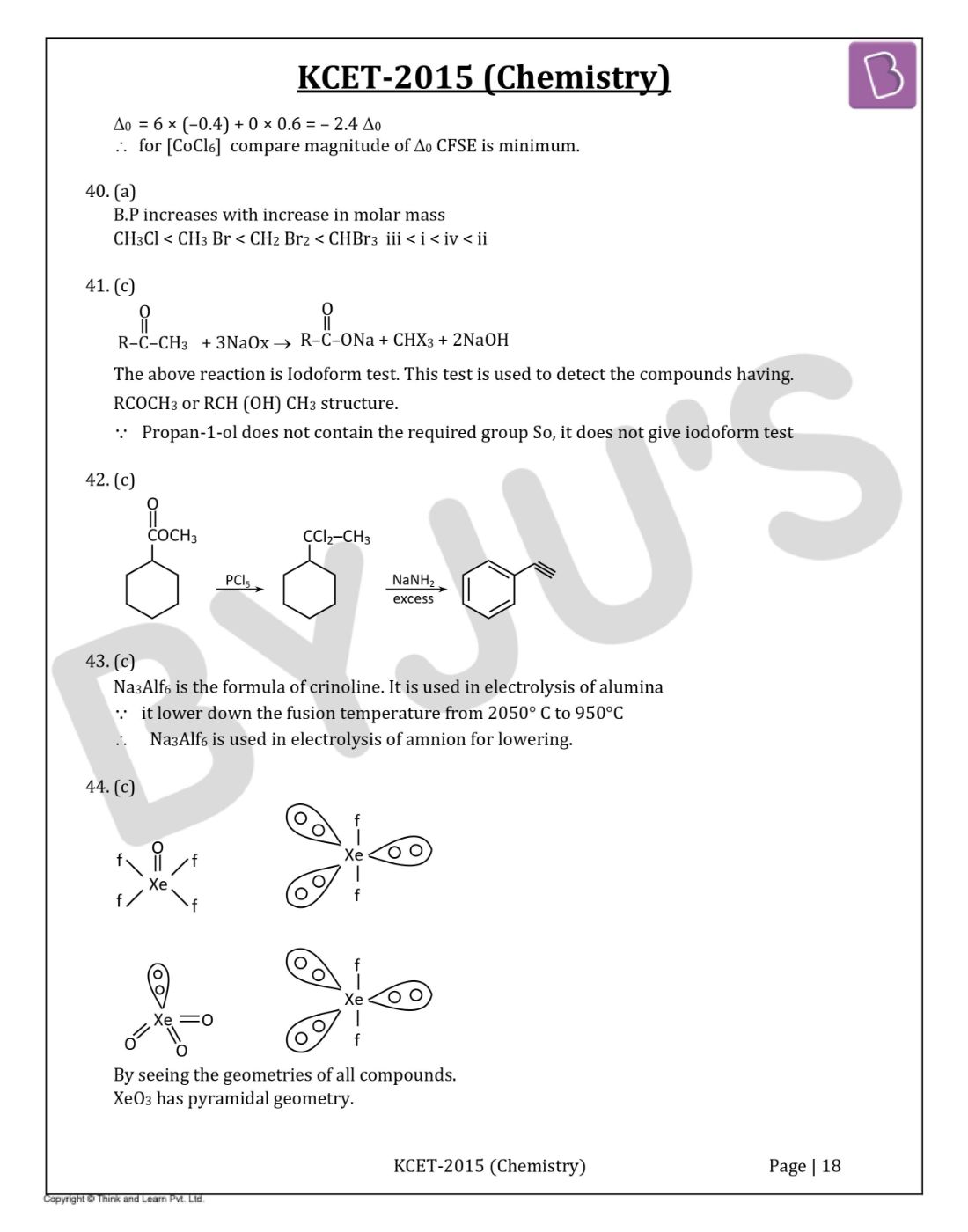
Question 44: Which of the following compound of Xenon has pyramidal geometry?
- a. XeOF4
- b. XeF2
- c. XeO3
- d. XeF4
Solution:
Answer: c

By seeing the geometries of all compounds.
XeO3 has pyramidal geometry.
Question 45: After adding a non-volatile solute freezing point of water decreases to –0.186°C. Calculate ∆Tb if Kf = 1.86 K kg mol–1 and Kb = 0.521 K kg mol–1
- a. 0.521
- b. 0.0521
- c. 1.86
- d. 0.0186
Solution:
Answer: b
∆Tf = kgm ; m = ∆Tf / Kf
∆0m = (0.126/1.86) = 0.1
∆Tb = Kbm = 0.521 × 0.1 = 0.0521
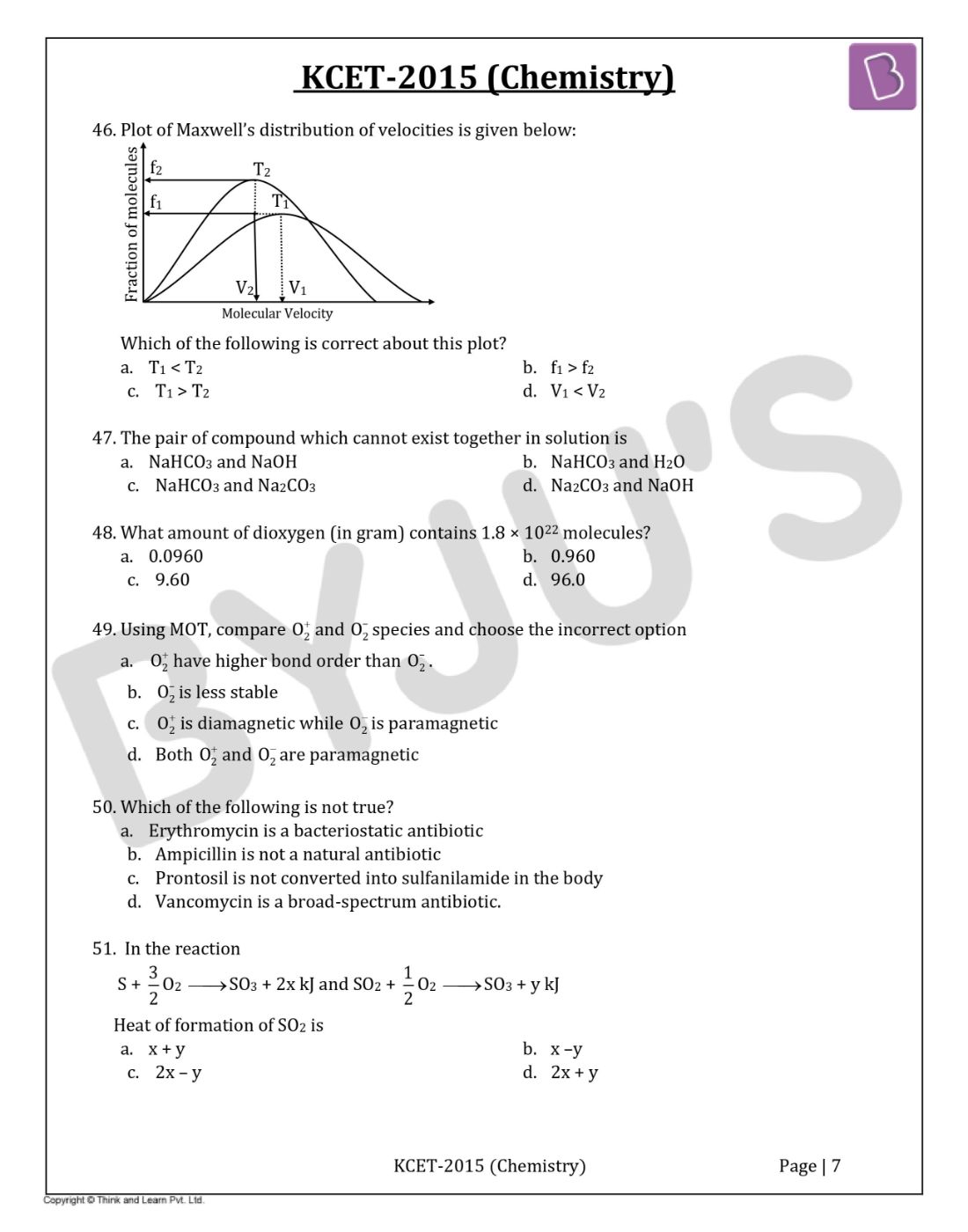
Question 46: Plot of Maxwell’s distribution of velocities is given below:

- a. T1< T2
- b. f1> f2
- c. T1> T2
- d. V1< V2
Solution:
Answer: c
By seeing the plot we can conclude that on increasing the temperature, the molecular velocity increases.
V1> V2 then T1> T2
Question 47: The pair of compounds which cannot exist together in solution is
- a. NaHCO3 and NaOH
- b. NaHCO3 and H2O
- c. NaHCO3 and Na2CO3
- d. Na2CO3 and NaOH
Solution:
Answer: a
NaHCO3 is slightly acidic and NaOH is a strong base so when they both are dissolved together then they will react and the reaction is as follows
Therefore, NaHCO3 and NaOH cannot exist together.
Question 48: What amount of dioxygen (in gram) contains 1.8 × 1022molecules?
- a. 0.0960
- b. 0.960
- c. 9.60
- d. 96.0
Solution:
Answer: b
32 g of O2 have Na molecules
So 1.8× 1022 molecules of O2 will have
\(\frac{32X1.8X10^{22}}{6.022X10^{23}} = 0.955\)= 0.960
Question 49: Using MOT, compare and species and choose the incorrect option
- a. \(O_{2}^{+}\)have a higher bond order than
- b. \(O_{2}^{-}\)is less stable
- c. \(O_{2}^{+}\)is diamagnetic while is paramagnetic
- d. Both \(O_{2}^{+}\)and\(O_{2}^{-}\)are paramagnetic
Solution:
Answer: c
For finding B.O of O+2 the configuration of O+2 is
σ1s2 σ *1s2 σ 2s2 σ *2s2 σ 2Pz2(παpα2 = παpy2)
(π*2 px1=π*2Py )
Total electrons in O+2 ions is 15
Bond order = (Nb –Na)/2
Nb = No. Of electrons in BMO
Na = No. Of electrons in ABMO
BO = (10-5/2)
BO = 0.25
Electronic configuration for O-2 is
σ s2 σ *1s2 σ 2s2 σ *2s2 σ 2Pz2 σ(παpx2 = παpy2)
(π*α px2=π*αPy1)
BO = (10-7)/2 = 0.15
Ion with higher bond order will be stable. Nature of is paramagnetic and is diamagnetic.
Question 50: Which of the following is not true?
- a. Erythromycin is a bacteriostatic antibiotic
- b. Ampicillin is not a natural antibiotic
- c. Prontosil is not converted into sulfanilamide in the body
- d. Vancomycin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Solution:
Answer: c
Prontosil is an antibacterial drug.
When it is taken then it will convert to sulfanilamide in the body.
Question 51: In the reaction

Heat of formation of SO2 is
- a. x + y
- b. x –y
- c. 2x – y
- d. 2x + y
Solution:
Answer: Bonus
Question 52: Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their acidic strength:
i. m-nitrophenol
ii. m-cresol
iii. phenol
iv. m-chlorophenol
- a. iii < ii < I < iv
- b. ii < iv < iii <i
- c. ii < iii < iv <i
- d. ii < iii < I < iv
Solution:
Answer: c
The compound will be more acidic when it is stable after donating a proton i.e. when the conjugate base is more stable then the compound will be more acidic.
The groups such as CH3 shows-I effect and decreases the acidic strength when attached to the group.
So by analysing structures.

So increasing order of acidic strength will be ii < iii < iv <i
Question 53: In the sequence of following reactions:

The starting compound ‘P’ is
- a. o-nitro toluene
- b. m-nitro toluene c. o-bromo toluene
- d. p-nitro toluene
Solution:
Answer: d

Question 54: Acetic acid is treated with Ca(OH)2 and the product so obtained is subjected to dry distillation. The final product is
- a. ethanal
- b. propanal
- c. propanone
- d. ethanol
Solution:
Answer: c

Question 55: The correct statement is
- a. BF3 is the strongest Lewis acid among the other boron halides
- b. Bl3 is the weakest Lewis acid among the boron halides
- c. There is maximum pπ–pπ back bonding in BF3
- d. There is minimum pπ–pπ back bonding in BF3
Solution:
Answer: c
The maximum pπ– pπ back bonding exists in
Bf3 because as the size of the halogen atom increases down the group, the overlapping of the vacant 2p-orbital of boron cannot take place easily and efficiently
p-orbital will be of high energy levels.
Question 56: Which of the following compound possesses the “C – H” bond with the lowest bond dissociation energy?
- a. Toluene
- b. Benzene
- c. n-pentane
- d.2, 2-dimethyl propane
Solution:
Answer: a
Toluene exhibits lowest bond dissociation energy because of involvement of C–H in hyperconjugation.
Question 57: In presence of HCl, H2S results in the precipitation of Group-2 elements but not Group-4 elements during qualitative analysis. It is due to
- a. higher concentration of S2–
- b. higher concentration of H+
- c. lower concentration of S2–
- d. lower concentration of H+
Solution:
Answer: c
H2S is a weak electrolyte.
Therefore, it ionizes slightly but HCl is a strong electrolyte.
So it can be easily ionized.
\(H_{2}S\rightleftharpoons 2H^{+}+S^{-2}\)HCl →H++ Cl–
If DOD of H2S is low then the concentration of S–2 will also be low.
sulphides with low solubility will be easily precipitated.
Question 58: One of the following conversion results in the change of hybridization and geometry:

Solution:
Answer: c
In the conversion of Bf3 to Bf4- the hybridisation changes. Bf3 has sp2 hybridisation and Bf4- has sp2 hybridization
Therefore, the answer is 3 i.e. Bf3 to Bf4-
Question 59: Water softening by Clark’s process uses
- a. CaHCO3
- b. NaHCO3
- c. Na2CO3
- d. Ca (OH)2
Solution:
Answer: d
Clark’s process is a type of water treatment used for water softening. Here calcium hydroxide is used to remove hardness i.e. calcium and magnesium ions.
The bicarbonate which is present in water undergoes reaction with lime to produce carbonates of calcium and magnesium.
Clark’s process uses Ca(OH)2.
Question 60: An alkali metal hydride (NaH) reacts with diborane in ‘A’ to give a tetrahedral compound ‘B’ which is extensively used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis. The compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ respectively are
- a. C2H6 and C2H5Na
- b. CH3COCH3 and B3N3H6
- c. C6H6 and NaBH4
- d. (C2H5)2O and NaBH4
Solution:
Answer: d

But since the hint is given that the reagent is extensively used so it will be NaBH4 and solvent is diethyl ether.