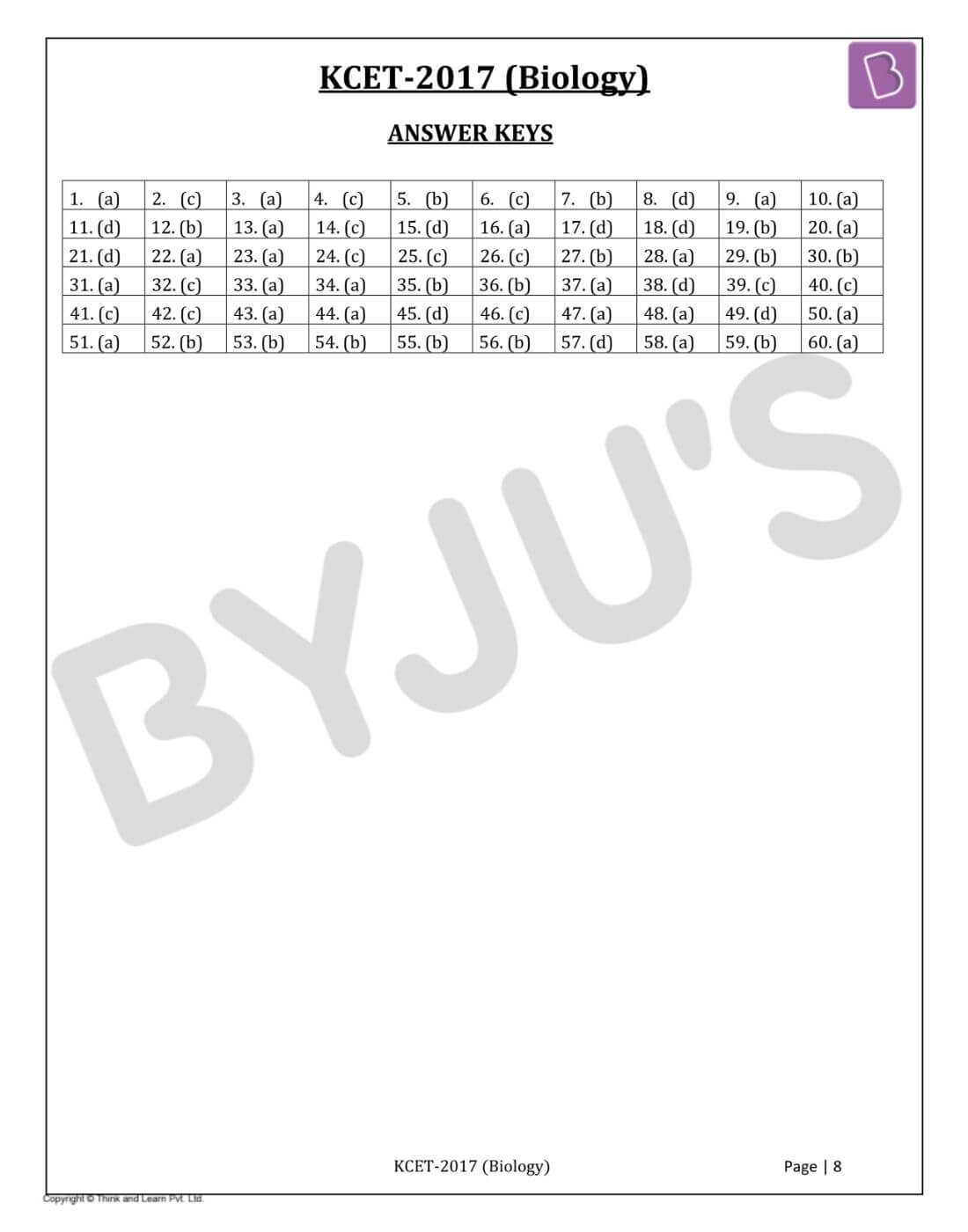
KCET 2017 exam conducted by KEA is one of the most sought out examinations by the students of Karnataka, aspiring to get admission in prestigious institutions. The solutions uploaded at BYJU’S will enable the students to understand the concepts in an easy and the best way. KCET 2017 solved Biology paper is the best resource to gain insight into the marking scheme of the examination. Practising these questions will introduce the students to the blueprint of the question papers. Solving these papers will help the candidates in understanding the important topics, time management and weightage of marks for each topic in the paper.
KCET 2017 - Biology
Question 1: Identify the ‘order’ from the following:
- a. Carnivora
- b. Muscidae
- c. Insecta
- d. Panthera
Solution:
Answer: (a)
• Carnivora is the order of eutherian mammals, which refer to any meat-eating organism. Example- Dogs, Cats, Wolves etc.
• Muscidae is a family of flies found in the superfamily Muscoidea. Example- Housefly, Musca.
• Insects are a class of hexapod invertebrates within the arthropod phylum. Example- Ant, Bugs etc.
• Panthera is a genus within the Felidae family. Example- Tiger, Lion etc.
Question 2: Which of the following options show the characters of mycoplasma?
- a. Smallest living cell without cell wall survive with oxygen
- b. Smallest living cell with cell wall survive with oxygen
- c. Smallest living cell without cell wall survive without oxygen
- d. Smallest living cell with cell wall survive without oxygen
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Mycoplasma is the smallest cell which does not possess a cell wall as an outer covering but has cell membrane as an outer covering. As they do not have cell walls they do not get affected by the antibiotics and cause severe diseases to the plants and animals. They can even survive without oxygen and respire anaerobically.
Question 3: Which class of Algae reproduces asexually by non-motile spores and sexually by non-motile gametes?
- a. Rhodophyceae
- b. Phaeophyceae
- c. Chlorophyceae
- d. Cyanophyceae
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The algae which belong to the group Rhodophyceae can reproduce sexually as well as asexually. In asexual reproduction, the non-motile spores are produced which form the new cell body. The sexual reproduction is the fusion of the non-motile gametes to form the embryo which develops to form the new algal body. In phaeophyceae reproduction takes place both asexually and sexually. Asexual reproduction takes place by zoospores. Sexual reproduction takes place by both isogamy and anisogamy. In Chlorophyceae, sexual reproduction occurs by isogamy, anisogamy or oogamy. The blue green algae (Cyanophyceae) reproduce by both vegetative and asexual means. They vegetative reproduction performs through fission.
Question 4: Which of the following plants produce zygomorphic flowers?
- a. Hibiscus
- b. Canna
- c. Gulmohar
- d. Mustard
Solution:
Answer: (c)
• Zygomorphic flowers have the symmetry in which the flowers can be divided into halves only through the division in one plane.
• A flower when cut in two equal halves through any vertical plane passing through the axis then its symmetry remains undisturbed. Such a flower is called an actinomorphic flower.
• The flowers of the plant Gulmohar are zygomorphic in nature.
• Canna, mustard, and hibiscus plants have flowers which are actinomorphic.
Question 5: The secondary wall material Suberin is deposited on the walls of
- a. Pericycle of stem and endodermis of root
- b. Phellem of stem and endodermis of root
- c. Epidermis of stem and endodermis of root
- d. Phellogen and phelloderm
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Suberin is a fatty material which is deposited on the certain cells of the plants. The material is deposited on the phellem cells in the stem and the endodermal cells of the root. On the endodermis, the suberin deposition results in the formation of the Casparian strips which prevents the flow of water.
Question 6: The type of epithelium found in the fallopian tube which functions to move particles or mucous in specific direction is:
- a. Squamous epithelium
- b. Cuboidal epithelium
- c. Ciliated epithelium
- d. Columnar epithelium
Solution:
Answer: (c)
The internal lining of the tube like structures possesses the ciliated epithelium. The cells bear shorter hair-like projections called cilia which beat and allow the movement of the particles. Their function is to move particles or mucus in a specific direction over the epithelium organs like bronchioles and fallopian tubules.
Question 7: Which one of the following is not included under the endomembrane system?
- a. Endoplasmic reticulum
- b. Mitochondria
- c. Lysosome
- d. Vacuole
Solution:
Answer: (b)
The endomembrane system is composed of the membranous structures in the cell. The common structures which are included are the lysosome, vesicles, vacuoles, cell membrane, endoplasmic reticulum, nuclear membrane, etc. Mitochondria, peroxisomes and chloroplast are not included under the endomembrane system.
Question 8: In the following diagrammatic representation of a standard ECG the ‘T’ represents

- a. Depolarisation of Atria
- b. Depolarisation of Ventricles
- c. Repolarisation of Atria
- d. Repolarisation of Ventricles
Solution:
Answer: (d)

• Each peak in the ECG is identified with a letter from P to T that corresponds to a specific electrical activity of the heart.
• The P- wave represents the electrical excitation (or depolarization) of the atria, which leads to the contraction of both the atria.
• The QRS complex represents the depolarization of the ventricles which initiates the ventricular contraction. The contraction starts shortly after Q and marks the beginning of the systole.
The T-wave represents the return of the ventricles from excited to normal state (repolarisation). The end of the T- wave marks the end of systole.
Question 9: Which of the following is not a characteristic of facilitated transport?
- a. Uphill transport
- b. Highly selective
- c. Requires special membrane proteins
- d. Transport saturates
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Facilitated transport is the selective transport of the ions or the molecules through special membrane proteins called as channel proteins. The transport depends on the concentration gradient or the saturation limit. The movement is in accordance with the concentration gradient and hence a downhill transport. Transport proteins provide high selectivity and transport only certain molecules. The uphill transport is an example of the active transport in which there is transport opposite to the concentration gradient.
Question 10: Identify the elements whose deficiency causes both necrosis and chlorosis
- a. Mg, K
- b. Mo, Ca
- c. Fe, Mn
- d. Cu, Co
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The plant requires the elements for the growth and developmental processes. The deficiency of the element causes adverse effects on the growth of the plant. The deficiency of the elements Mg and K result in necrosis and chlorosis. Necrosis is the death of the living tissue and chlorosis is the decolorization of the pigment of the leaves.
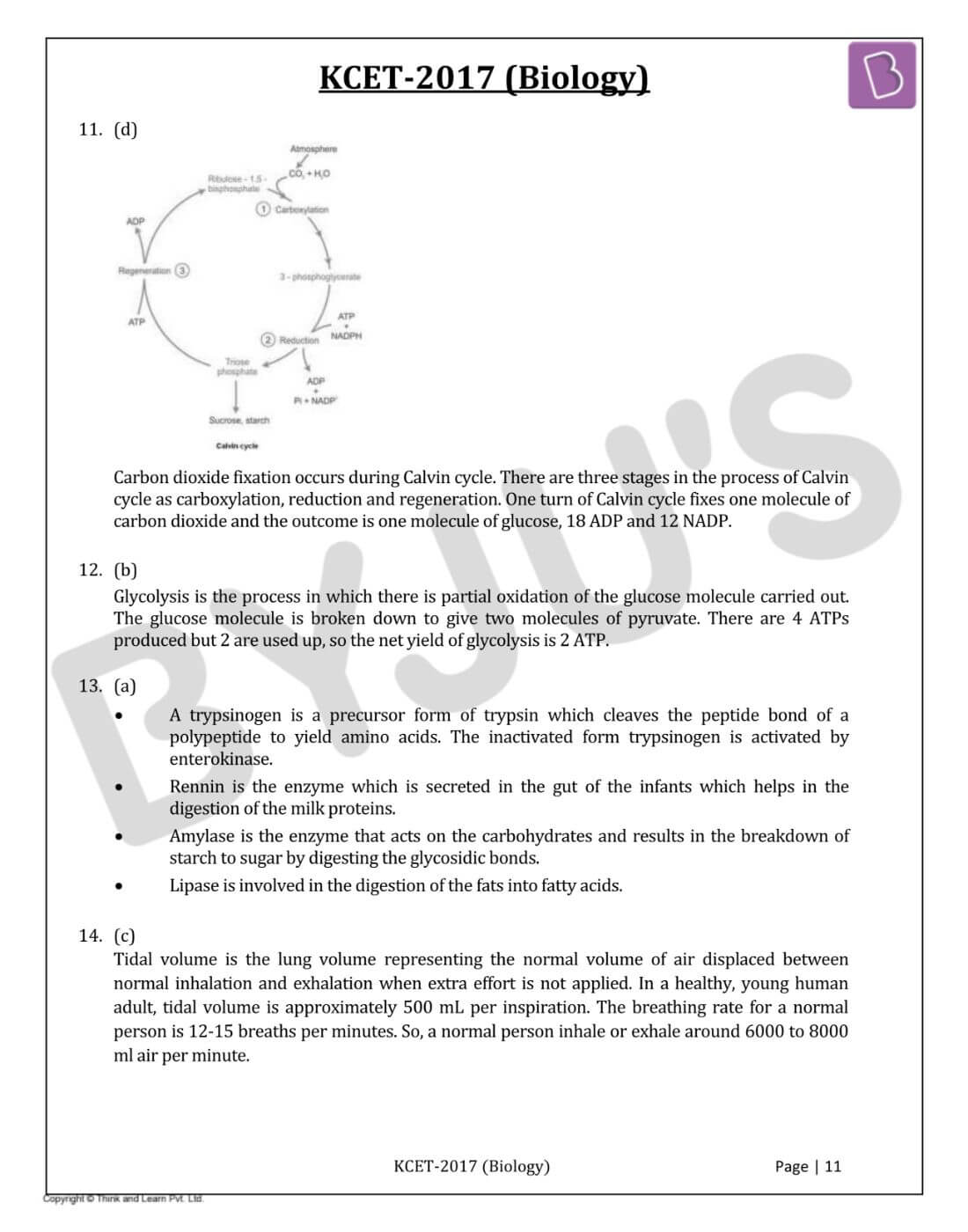
Question 11: The outcome of Calvin cycle include:
- a. 6 CO2, 18 ATP, 12 NADPH
- b. One glucose, 18 ATP, 12 NADPH
- c. 6 CO2, 18 ATP, 12 NADPH
- d. One glucose, 18 ADP, 12 NADP
Solution:
Answer: (d)

Carbon dioxide fixation occurs during Calvin cycle. There are three stages in the process of Calvin cycle as carboxylation, reduction and regeneration. One turn of the Calvin cycle fixes one molecule of carbon dioxide and the outcome is one molecule of glucose, 18 ADP and 12 NADP.
Question 12: The number of ATP molecules utilised for the breakdown of one molecule of glucose during glycolysis is:
- a. 4
- b. 2
- c. 6
- d. 8
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Glycolysis is the process in which there is partial oxidation of the glucose molecule carried out. The glucose molecule is broken down to give two molecules of pyruvate. There are 4 ATPs produced but 2 are used up, so the net yield of glycolysis is 2 ATP.
Question 13: Match the enzymes of Column-I with the functions of Column-II. Choose the correct option:
|
Column-I |
Column-II |
|
1. Enterokinase |
p. digests milk proteins |
|
2. Rennin |
q. digests carbohydrates |
|
3. Amylase |
r. activates try |
|
4. Lipase |
s. acts on nucleic acids |
|
t. breakdown fats |
- a. 1-r, 2-p, 3-q, 4-t
- b. 1-r, 2-p, 3-t, 4-q
- c. 1-s, 2-p, 3-t, 4-q
- d. 1-s, 2-q, 3-p, 4-t
Solution:
Answer: (a)
• A trypsinogen is a precursor form of trypsin which cleaves the peptide bond of a polypeptide to yield amino acids. The inactivated form trypsinogen is activated by enterokinase.
• Rennin is the enzyme which is secreted in the gut of the infants which helps in the digestion of the milk proteins.
• Amylase is the enzyme that acts on the carbohydrates and results in the breakdown of starch to sugar by digesting the glycosidic bonds.
• Lipase is involved in the digestion of the fats into fatty acids.
Question 14: The volume of air inspired or expired by a healthy man per minute is:
- a. 1000 ml − 1100 ml
- b. 2500 ml − 3000 ml
- c. 6000 ml − 8000 ml
- d. 400 ml − 500 ml
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Tidal volume is the lung volume representing the normal volume of air displaced between normal inhalation and exhalation when extra effort is not applied. In a healthy, young human adult, tidal volume is approximately 500 mL per inspiration. The breathing rate for a normal person is 12-15 breaths per minute. So, a normal person inhales or exhales around 6000 to 8000 ml air per minute.
Question 15: The blood cell that secretes histamine, serotonin and heparin is:
- a. Neutrophil
- b. T-lymphocyte
- c. Killer cell
- d. Basophil
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Basophils are a type of white blood cell, which contains granulated cytoplasm. They are the largest type of granulocyte. They are responsible for inflammatory reactions during an immune response, as well as in the formation of acute and chronic allergic diseases, including anaphylaxis, asthma, atopic dermatitis, and hay fever. The granules in the cytoplasm contain the molecules histamine, heparin and serotonin which are released during the allergic reactions. Heparin is the anticoagulant, histamine is an allergic agent and serotonin affects the motor activities.
Question 16: The hormones involved in maintaining calcium balance in the human body are:
- a. PTH and TCT
- b. PTH and LTH
- c. TCT and FSH
- d. MSH and ACTH
Solution:
Answer: (a)
There are two hormones which are secreted in the human body involved in the calcium metabolism. The parathormone (PTH) is secreted by the cells of the parathyroid glands and are involved in increasing the level of blood calcium. The hormone thyrocalcitonin (TCT) is secreted by the C cells of the thyroid gland is responsible for increasing the uptake of calcium by the cells.
Question 17: Amoeba is immortal because:
- a. it is multicellular
- b. it is microscopic
- c. it reproduces by sexual method only
- d. parental body is distributed among the offsprings during binary fission
Solution:
Answer: (d)
The protozoans like the Amoeba are considered as immortal because they divide by binary fission. During this type of asexual reproduction, there is distribution of the parent body into two daughter cells. The parental identity gets lost in the case of binary fission.
Question 18: Which of the following is not a pre-fertilization event in higher organisms?
- a. Gametogenesis
- b. Gamete transfer
- c. Meiosis
- d. Cleavage
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Meiosis in gamete mother cells forms the gametes during the process of gametogenesis. This is followed by transfer of male gametes to the female reproductive tract to facilitate fertilization. Fertilization forms zygote which then undergoes cleavage to form morula. So, gametogenesis, gamete transfer and meiosis are the events that occur before fertilization but cleavage occurs after fertilization.
Question 19: If a tetraploid plant contains 48 chromosomes in its nucellus, then number of chromosomes in the egg cell and in a synergid respectively:
- a. 48 and 48
- b. 24 and 24
- c. 24 and 48
- d. 48 and 24
Solution:
Answer: (b)
The plant is tetraploid (4n) and there are 48 chromosomes in the nucleus. The egg cell and the synergid are produced by meiotic division and are haploid in nature. So, 48 / 2 = 24 chromosomes in the egg and synergid.
Question 20: Pollen grains are generally spherical, measuring about:
- a. 25-50 micrometers
- b. 25-50 millimeters
- c. 25-50 nanometers
- d. 25-50 centimeters
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The pollen grain is the male gametophyte which contains the male gametes. The pollen grain is spherical and measures about 25-50 micrometers. It is surrounded by two layers as exine which forms the outer layer and intine which forms the inner layer. The generative cell divides to form the two male gametes.
Question 21: Which of the following characters is not required for autogamy?
- a. Flowers require synchrony in pollen release and stigma maturation
- b. Anthers and stigma should lie close to each other
- c. Flowers should be bisexual
- d. Required pollination agents
Solution:
Answer: (d)
In autogamy, the flowers are bisexual and anther and stigma are close to each other. The flowers are synchronized in the release of the pollen and the maturation of the stigma to allow successful autogamy. Pollinating agents are not required for the autogamy which is self-fertilization but they are involved in the transfer of the pollen grain by cross pollination.
Question 22: Which one of the following characters favours the process of normal spermatogenesis in human male?
- a. Descent of testes into scrotum
- b. Testes remain in the abdominal cavity
- c. Infection by mumps virus during childhood
- d. Increased scrotal temperature
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The sperms are produced in the testes in which the process of spermatogenesis takes place. The temperature of the scrotum is 2-3o C less as compared to the body temperature which is necessary for the maintenance of the optimum temperature for spermatogenesis. So, it is necessary that the testes must descend down into the scrotum.
Question 23: Accessory ducts of reproductive system of human female include:
- a. Oviduct, uterus & vagina
- b. Oviduct, ovaries & ovarian ligaments
- c. Oviduct, ovaries & mammary glands
- d. Ovaries, uterus & vagina
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The female reproductive system is composed of the reproductive organs and accessory ducts and glands. The oviduct, uterus, and vagina are the accessory ducts which are involved in the process of reproduction. The oviduct is the site for fertilization of the egg and the sperm. The uterus is the site for implantation and the vagina acts as the birth canal.
Question 24: In human females, the number of primary follicles left in each ovary at puberty is:
- a. 3000 − 30,000
- b. 30,000 − 60,000
- c. 60,000 − 80,000
- d. 1,50,000 − 1,60,000
Solution:
Answer: (c)
There are about a million follicles which divide to form the primary follicles in the ovary of the foetus. Many primary follicles degenerate and at puberty, there are only 60,000-80,000 primary follicles present which is formed by the mitotic division of the germ cells.
Question 25: Implantation is influenced by
- a. FSH
- b. LH
- c. Progesterone
- d. Relaxin
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Progesterone is secreted by the corpus luteum. It prepares the uterus for the implantation of fertilized eggs and controls the development of the foetus in the uterus. The hormone is responsible for the increase in the cell lining of the uterus leading to implantation and maintenance of pregnancy.
Question 26: In India the action plans for family planning were initiated in the year:
- a. 1972
- b. 1947
- c. 1951
- d. 1950
Solution:
Answer: (c)
India was amongst the first countries in the world to initiate action plans and programs at a national level to attain total reproductive health as a social goal. These programs called family planning were initiated in 1951 and were periodically assessed over the past decades.
Question 27: The inner cell mass of blastocyst becomes:
- a. extraembryonic membranes
- b. differentiated into embryo proper
- c. chorionic villi
- d. Placenta
Solution:
Answer: (b)
The blastocyst is composed of the outer cell layer called the trophoblast and the inner cell mass. The inner cell mass will form all the tissues of the embryo and differentiate into embryo proper. The trophoblast will form the placental structures.
Question 28: Example for autosomal hyper aneuploidy is:
- a. Down’s syndrome
- b. Klinefelter’s syndrome
- c. Turner’s syndrome
- d. Haemophilia
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Aneuploidy means an organism does not have the normal number of chromosomes. Down's syndrome is mainly caused due to an extra copy of chromosome 21 which is hyper aneuploidy of the autosomal chromosome.
The extra copy is formed due to nondisjunction of chromosomes during meiosis.
Question 29: In dihybrid cross, when F1 plants (RrYy) are self hybridised, the ratio of segregation of yellow and green in F2 is:
- a. 1:2:1
- b. 3:1
- c. 9:3:3:1
- d. 1:1:1:1
Solution:
Answer: (b)
In dihybrid cross, when pea plant with round shaped seeds with yellow colour seed (RRYY) is crossed with pea plant showing wrinkled shape with green cotyledons (rryy), the F1 generation will have round shaped seeds with yellow colour seed (RrYy) progeny. When F1 plants (RrYy) are self hybridised, 12 yellow and 4 green seeds are produced. Therefore, the ratio of segregation of yellow and green in F2 is 3:1.
Question 30: Replacement of which one of the following nucleotides in the HbA gene causes sickle cell anaemia?
- a. A to T
- b. T to A
- c. U to A
- d. C to G
Solution:
Answer: (b)
This is an autosome linked recessive trait that can be transmitted from parents to the offspring when both the partners are carriers for the gene. The mutation causing sickle cell anaemia is a single nucleotide substitution (A to T) in the codon for amino acid 6. The change converts a glutamic acid codon (GAG) to a valine codon (GTG). The form of hemoglobin in persons with sickle-celled anaemia is referred to as HbS.
Question 31: The type of sex determination in honey bee is:
- a. Haplo-diploidy
- b. Haploidy
- c. Diploidy
- d. ZZ-ZW
Solution:
Answer: (a)
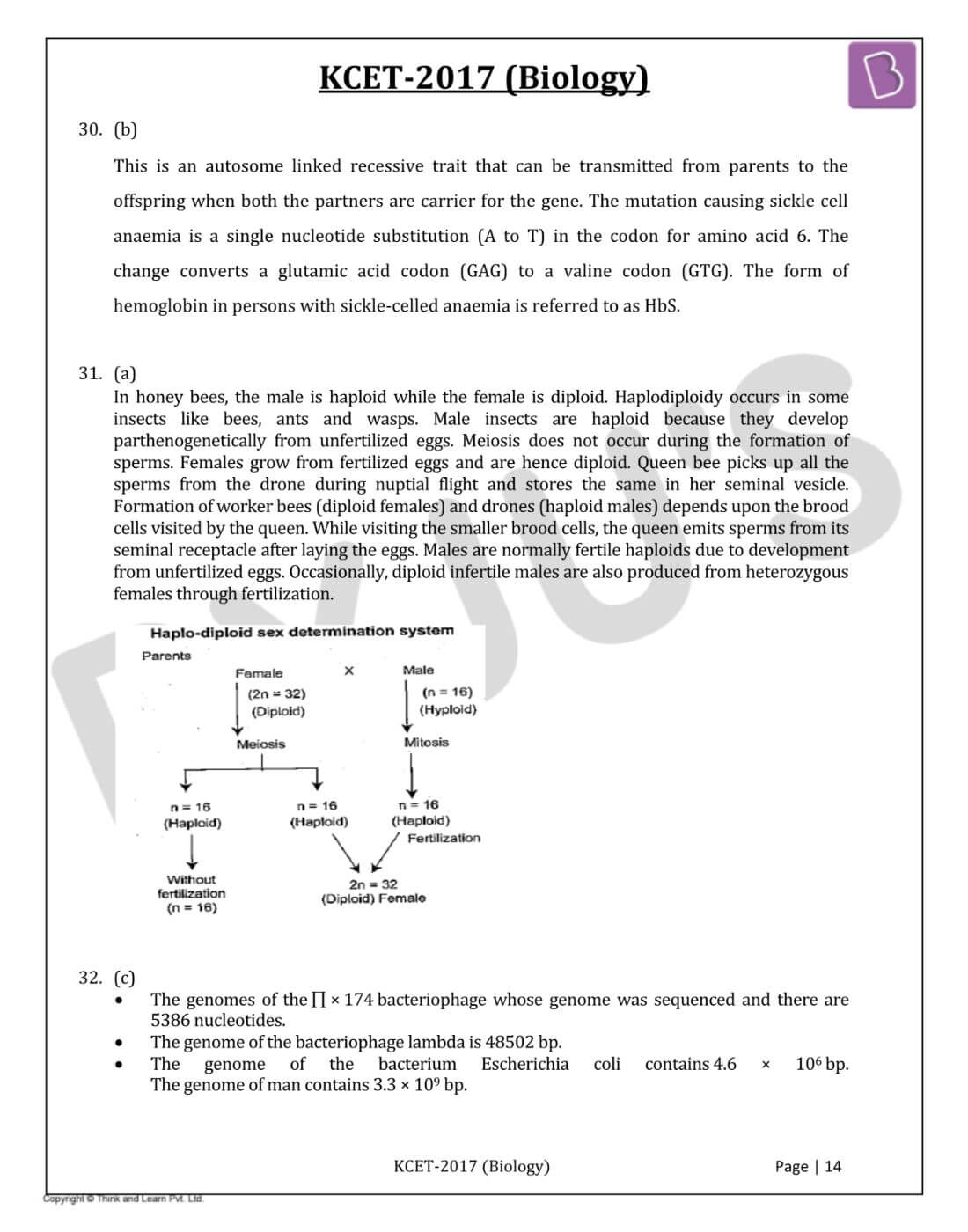
In honey bees, the male is haploid while the female is diploid. Haplodiploidy occurs in some insects like bees, ants and wasps. Male insects are haploid because they develop parthenogenetically from unfertilized eggs. Meiosis does not occur during the formation of sperms. Females grow from fertilized eggs and are hence diploid. Queen bee picks up all the sperms from the drone during nuptial flight and stores the same in her seminal vesicle. Formation of worker bees (diploid females) and drones (haploid males) depends upon the brood cells visited by the queen. While visiting the smaller brood cells, the queen emits sperms from its seminal receptacle after laying the eggs. Males are normally fertile haploids due to development from unfertilized eggs. Occasionally, diploid infertile males are also produced from heterozygous females through fertilization.

Question 32: Match the number of nucleotides of the genome of Column-I with the organisms of Column-II. Choose the correct option given below:
|
Column-I |
Column-II |
|
1. 5386 nucleotides |
p. E. Coli |
|
2. 48502 bp |
q. man |
|
3. 4.6 * 106 bp |
r. Drosophila |
|
4. 3.3* 109 bp |
s. s. φ × 174 bacteriophage |
|
t. bacteriophage – lambda |
- a. 1-s, 2-q, 3-p, 4-t
- b. 1-s, 2-p, 3-q, 4-r
- c. 1-s, 2-t, 3-p, 4-q
- d. 1 − r, 2 − t, 3 − s, 4 − p
Solution:
Answer: (c)
• The genomes of the Π × 174 bacteriophage whose genome was sequenced and there are 5386 nucleotides.
• The genome of the bacteriophage lambda is 48502 bp.
• The genome of the bacterium Escherichia coli contains 4.6 × 106 bp. The genome of man contains 3.3 × 109 bp.
Question 33: The average length of hnRNA in humans is,
- a. 3000 bases
- b. 2.4 million bases
- c. 1500 bases
- d. 500 bases
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The average length of the hnRNA in humans is about 3000 bases. The hnRNA is spliced and posttranscriptional modifications are carried out in order to synthesize the mature mRNA which measures about 1800-2000 bases.
Question 34: If E. coli is allowed to grow for 40 minutes in a medium containing N15, then the number of N14 / N14 containing DNA would be:
- a. zero
- b. 20
- c. 10
- d. 2
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The experiment performed by Messelson and Stahl proved that the replication pattern of the DNA is semi-conservative. The DNA helix is composed of two strands.
During replication, the strands separate and the new strands are formed on the original template strands. One of the strands remains the older and one new strand is synthesized and the process is known as semi-conservative. Since, the cells are grown in medium containing N15 so there will be no strand with N14 / N14 i.e. E. coli is allowed to grow for 40 minutes in a medium containing N15 then the number of N14 / N14 containing DNA would be zero.
Question 35: Polymerisation of DNA nucleotides during the synthesis of lagging strand occurs in:
- a. 3' → 5' direction
- b. 5' → 3' direction
- c. Any direction
- d. promoter to terminator direction
Solution:
Answer: (b)
DNA replication is the process in which the DNA is replicated and two copies are synthesized. The two strands of the DNA helix separate and the new strands are formed on the original strands, known as the template strands. The strand which is synthesized in 3'-5' direction is the leading strand and the strand which is synthesized in the opposite 5' - 3' direction is the lagging strand which contains the Okazaki fragments.
Question 36: In lac-operon concept of gene expression, allolactose acts as,
- a. repressor
- b. inducer
- c. co-repressor
- d. co-enzyme
Solution:
Answer: (b)
The lac operon is the inducible cluster of genes in the prokaryotes involved in the lactose metabolism. When the cell is placed in a Lactose rich medium, Lactose is transported through the membrane with the help of permease into the cell which is then converted to allolactose that binds to the repressor protein, and prevents it from binding to the operator, thereby inducing the expression of the Lac operon.
Question 37: The anticodon found on the t-RNA for tryptophan amino acid is.
- a. ACC
- b. UGG
- c. UCC
- d. CUU
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Each tRNA contains a set of three nucleotides called an anticodon. The anticodon of a given tRNA can bind to one or a few specific mRNA codons. The codon on the mRNA which codes for amino acid tryptophan is 5'-UGG-3'. The anticodon on the tRNA will be 3'-ACC-5' which will code for the amino acid tryptophan.
Question 38: Which one of the following is the identifiable character of Neanderthal man?
- a. brain capacity 650 cc-800 cc
- b. developed pre-historic cave art
- c. lived before 2 million years ago
- d. buried their dead.
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Neanderthal man is the early species of modern man and was known as Homo sapiens neanderthalensis. The lower jaw was strong with strong jaw muscles and did not have a chin. The cranial capacity of this species was 1450 cc. They buried the dead persons and performed the rituals after the death of the similar ones.
Question 39: Identify the plants that are dominant during the Jurassic period.
- a. Angiosperms and Bryophytes
- b. Sphenopsida and Ginkgos
- c. Ferns, Conifers and Cycads
- d. Monocotyledons and Arborescent lycopods
Solution:
Answer: (c)
The Jurassic period started 213 million years ago and lasted until 240 million years ago. The Jurassic period is the period of the large mammals like dinosaurs. This was the period in which the plants like the ferns, conifers, and cycades dominated.
Question 40: In humans, common cold is caused by:
- a. Retrovirus
- b. Baculovirus
- c. Rhinovirus
- d. Rhabdovirus
Solution:
Answer: (c)
The rhinovirus is the most common viral infectious agent in humans and is the predominant cause of the common cold. Rhinovirus infection proliferates in temperatures of 33–35 °C, the temperatures found in the nose.
Question 41: Which of the following vector-borne diseases caused by Aedes mosquitoes?
- a. Ascariasis and Filariasis
- b. Malaria and Sleeping sickness
- c. Dengue and Chikungunya
- d. Kala azar and Filariasis
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Dengue and chikungunya are viral diseases which are caused by humans. The diseases are transmitted by the bite of the Aedes mosquito and carrying of the blood from the infected person to the healthy person. Only the female mosquitoes are involved in the transmission of the disease.
Question 42: Morphine is obtained from the:
- a. Inflorescence of Cannabis
- b. Leaves of Erythroxylum
- c. Latex of Poppy plant
- d. Root of Atropa
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Heroine commonly called smack is chemically diacetylmorphine which is a white, odourless, bitter crystalline compound. This is obtained by acetylation of morphine which is extracted from the latex of poppy plant papaver somniferum. Generally, taken by snorting and injection, heroine is depressant and slows down body functions.
Question 43: Inbreeding depression occurs due to continuous
- a. Intra − breeding
- b. Inter − breeding
- c. Inter-generic breeding
- d. Interspecific breeding
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Intrabreeding is the process in which the organisms of the same species do breed with each other. This causes inbreeding depression in which the progeny becomes weaker due to the continuous breeding of the animals within the same species. Inbreeding depression can be reduced by cross-breeding.
Question 44: Identify the correct combination of crop-variety and insect pests
- a. Okra − Pusa sawani − Shoot and Fruit borer
- b. Flat bean − Pusa Gaurav − Fruit borer
- c. Brassica − Pusa A-4 − Aphids
- d. Brassica − Pusa sem-3 − Jassids
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Pusa gaurav variety of brassica is resistant to aphids. Pusa Sem 2 and Pusa Sem 3 of flat beans are resistant to jassids, aphids and fruit borer. Pusa Sawani and Pusa A-4 varieties of okra are resistant to shoot and fruit borer.
Question 45: Which of the following crops is developed by mutation breeding, that is resistant to yellow mosaic virus and powdery mildew?
- a. Cow-pea
- b. Okra
- c. Chilli
- d. Mung bean
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Breeding techniques helped in the development of new resistant varieties of the plants. The mutation techniques help in the production of the mung bean varieties which are resistant to the yellow vein mosaic virus and the powdery mildew. The generation of these varieties helped in increasing the yield.
Question 46: Which one of the following has been commercialised as a blood-cholesterol lowering agent?
- a. Streptokinase
- b. Cyclosporin-A
- c. Statins
- d. α -Trypsin-A
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Statins are the molecules that act as inhibitors of certain enzymes. The statins help to lower the level of cholesterol in the blood by acting as inhibitors of the enzymes which are involved in the formation of cholesterol. This prevents the formation of cholesterol and the level of cholesterol in the blood is reduced. The common example of the organism which is used for the production of statin is Monascus purpureus.
Question 47: As the organic matter increases in a water body, the BOD:
- a. increases
- b. decreases
- c. remains unchanged
- d. not a parameter
Solution:
Answer: (a)
BOD is the amount of oxygen required by microbes to break down the organic matter present in a certain volume of a sample of water. In polluted water, BOD is high as it contains a large number of organisms. High BOD values in the water of a river mean that the water is highly polluted.
Question 48: Restriction endonucleases are isolated from some bacteria. Their role in bacteria is:
- a. defence against virus
- b. synthesis of proteins
- c. act as genetic material
- d. help in reproduction
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The restriction enzymes are the enzymes which cleave the DNA at specific recognition sites. These enzymes are isolated from the bacteria which produce the enzymes to cleave the viral genome and provide protection against the viral infection.
Question 49: From which bacterium the REN-Sal-I is isolated?
- a. Escherichia coli
- b. Streptococcus aureus
- c. Haemophilus influenzae
- d. Streptomyces albus
Solution:
Answer: (d)
The restriction enzymes are isolated from the bacterial sources and are named according to the name of the bacterial species. The enzyme Sal I is isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces albus. This is the first enzyme which is isolated from the bacterium.
Question 50: A transformed bacteria with human genes, fails to produce desired protein. The reason could be:
- a. Human genes may have intron which bacteria cannot process.
- b. Amino acid codons for humans and bacteria differ.
- c. Human protein is formed but degraded by bacteria.
- d. The bacterial promoter gene cannot induce transcription of human gene
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Human genes have introns, the intervening non-coding sequences which are removed by post transcriptional modification of hnRNA. Bacterial genes do not have introns and bacteria lack the intron splicing machinery. The transformed bacteria with human gene, fails to produce desired protein due to inability of splicing the introns to produce the matured mRNA from the hnRNA.
Question 51: Read the statements 1 and 2. Choose the correct option:
Statement 1: RNAi take place in all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms as a method of cellular defence.
Statement 2: RNA interference is a pre-translational process.
- a. Statement-1 incorrect, statement-2 correct.
- b. Statement-1 correct, statement-2 incorrect.
- c. Both statements are correct.
- d. Both statements are incorrect.
Solution:
Answer: (a)
RNAi method involves the use of the single-stranded complementary RNA segment to silence the gene of the parasite. This is the common method for defense in the eukaryotic organisms. This is a pre-translational process in which the ssRNA binds to the mRNA and forms the hybrid structure which cannot be read by the polymerase.
Question 52: The human protein α -1 antitrypsin is obtained from:
- a. transformed bacteria
- b. transgenic animal
- c. transgenic plant
- d. a plant from Western Ghats
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Transgenic sheep are genetically modified animals, so that her milk produces a human protein called alpha antitrypsin, a potential treatment for the disease cystic fibrosis.
Question 53: Psammophytes are growing in/on
- a. Rock
- b. Deserts
- c. Water
- d. Shades
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Psammophyte are the plants that grow in sands, primarily in deserts. These plants are marked by a number of adaptations, this property enabling them to exist on wind-blown sands. Psammophytic trees and shrubs form strong adventitious roots on those parts of their trunks buried in the sand.
Question 54: A plant shows the following modifications:
(i) Leaves covered with dense hairs
(ii) Leaf surface shiny or glabrous
(iii) Leaf blade remains rolled during day
The adaptation of the plant is to:
- a. conserve water
- b. prevent excessive heat
- c. check transpiration
- d. absorb water
Solution:
Answer: (b)
The modification (morphological/anatomical) of plant to prevent excessive heat is: • Leaves covered with dense hairs.
• Leaf surface is shiny or glabrous.
• Leaf blade lamina rolled during the day.
Question 55: Mac Arthur’s vision of 5 closely related species of warblers living on the same tree were able to avoid competition and co-exist by behavioural difference. This is an example for:
- a. Competitive release
- b. Resource partitioning
- c. Competitive exclusion principle
- d. Adaptive radiation
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Resource partitioning is the phenomenon when there are many species living in the same region but have adapted to different resources. This causes a reduction in the fight for the same resource. When there are five closely related species of the warblers on the same tree without any competition, this type of behavioral difference is due to resource partitioning.
Question 56: Climax community is a state of:
- a. non − equilibrium
- b. near equilibrium
- c. pioneer species
- d. changing community
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Climax community is an ecological community in which the species composition remains stable and exists in balance with each other and their environment. It is an ecological community that has reached the final stage of ecological succession. It is a state of near equilibrium in which the population remains relatively unchanged until destroyed by an event such as fire or human interference.
Question 57: The process of decomposition delays when,
- a. the detritus is made up of sugars and nitrogen compounds
- b. aeration is sufficient
- c. warm and moist environment exists
- d. detritus is rich in lignin and chitin
Solution:
Answer: (d)
The process of decomposition involves the breaking of the complex inorganic compounds into smaller organic nutrients. The detritus rich in the lignin and chitin are decomposed slowly. The reason is that the lignin and chitin are hard polymeric substances which are not easily destroyed by the action of the enzymes secreted by the bacteria.
Question 58: The variety of indigenous cows is an example for:
- a. Genetic diversity
- b. Species diversity
- c. Ecological diversity
- d. Microbial diversity
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The difference in the genetic composition of the organism within a species is known as the genetic diversity. The variety of the indigenous cows belongs to the same species but have certain different characters. This is the reason they are an example of genetic diversity.
Question 59: So far 1.5 million species are identified, in which the number of fungi species identified is more than the combined total of:
- a. Algae, lichens, mosses and ferns
- b. Fishes, amphibians, reptiles and mammals
- c. Molluscans and crustaceans
- d. Molluscans, fishes and amphibians
Solution:
Answer: (b)
The estimated number of species of the fungi is about 2 to 4 million. This is the global estimated richness of the fungal species. This number is more than the combined total of the species of the fishes, amphibians, reptiles and mammals.
Question 60: The safe method of disposal of e-waste is:
- a. incineration
- b. burning in open field
- c. thrown into water
- d. dumping in forest
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The e-waste refers to the electronic waste which is increasing in the amount every day. There are sources of metals and plastic in the electronic waste and so, it is necessary to dispose off the waste properly. The safe method considered for the disposal of this form of waste is incineration in which the waste is burned at very high temperature in a furnace.