KCET 2017 Paper with Solutions Chemistry is a perfect resource which helps the candidates in understanding different methods of solving a particular problem. Candidates can download the previous years’ question papers of KCET to figure out the frequently occurring questions in the main exams. Practising the KCET previous year papers will guide the students to attempt each question with the best possible approach and arrive at the solution as soon as possible to save time. Solving these papers with solutions will make the students understand the concepts and coverage for the upcoming exam.
KCET 2017 - Chemistry
Question 1: If 3.01 × 1020 molecules are removed from 98 mg of H2SO4, then the number of moles of H2SO4 left are
- a. 0.1 × 10–3 mol
- b. 0.5 × 10–3 mol
- c. 1.66 × 10–3 mol
- d. 9.95 × 10–2 mol
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Number of moles of H2SO4 left = N / Na
Now, finding N
For 98 gm of H2SO4 the molecules are 6.02 × 1020
H2SO4 left = 6.02 × 1020 – 3.01 × 1020 = 3.01 × 1020
Number of moles of H2SO4 left = N / NA
= 3.01 × 1020 / 6.02 × 1023
= 0.5 × 10–3 mol
Question 2: The correct set of quantum number for the unpaired electrons of the chlorine atom is
- a. 2, 0, 0, + 1 / 2
- b. 2, 1, – 1 , + 1 / 2
- c. 3, 1 , 1, ± 1 / 2
- d. 3, 0, 0, ± 1 / 2
Solution:
Answer: (c)
For finding out unpaired electron of chlorine atom we have to find electronic configuration Cl = 1S2 2S2 2P6 3S2 3P5
n = 3, l = 1, m = 1, s = ± 1 / 2
Question 3: The electronegativities of C, N Si and P are in the order of
- a. P < Si < C < N
- b. Si < P < N < C
- c. Si < P < C < N
- d. P < Si < N < C
Solution:
Answer: (c)
As we move down the group, the electronegativity increases Si < P < C < N.
Question 4: Which of the following structures of a molecule is expected to have three bond pairs and one lone pair of electrons?
- a. Tetrahedral
- b. Trigonal Planar
- c. Pyramidal
- d. Octahedral
Solution:
Answer: (c)
It is given that there is a total of three bond pairs and one lone pair.
∴ Total electron pair is 4 which shows sp3 hybridization.
∵ It is given that one lone pair is also present than geometry will be pyramidal.
Question 5: Which of the following is the correct electron dot structure of N2O molecule?

Solution:
Answer: (b, c)
The structure of

The positive charge is on the N atom due to its less electronegativity than oxygen. The structure in option C is also a stable configuration since octets of nitrogen and oxygen are fulfilled and no charge separation is there.
Question 6: The pressure of real gases is less than that of ideal gas because of
- a. Intermolecular attraction
- b. Finite-size of particles
- c. Increase in the number of collisions
- d. Increase in the kinetic energy of the molecules
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The intermolecular attraction between the particles of a real gas is much less hence the pressure of real gas is less than that of an ideal gas. Their energy is less ∵ they do not collide with each other at an impact. The pressure of real gases is less than that of ideal gas because of intermolecular attraction.
Question 7: A reaction has both ΔH and ΔS –ve. The rate of reaction
- a. increases with increase in temperature
- b. increases with decrease in temperature
- c. remain unaffected by the change in temperature
- d. cannot be predicted for change in temperature
Solution:
Answer: (b)
We know, ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
Given ΔH and ΔS are negative.
Therefore the expression will be
ΔG = –ΔH + TΔS
–ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
By seeing the above equation for negative ΔG the value of ΔS must be less than ΔH.
ΔH > TΔS
So, the reaction will be exothermic. If the reaction is exothermic then, it’s rate will increase with a decrease in temperature.
Question 8: The equilibrium constant for the reaction N2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2NO(g) is 4 × 10–4 at 2000 K. In presence of a catalyst the equilibrium is attained ten times faster. Therefore the equilibrium constant in presence of a catalyst of 2000 K is
- a. 40 × 10–4
- b. 4 × 10–2
- c. 4 × 10–3
- d. 4 × 10–4
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Equilibrium constant does not depend on the catalyst.
So, the value of constant is the same that is 4 × 10–4.
Question 9: The reaction quotient ‘Qc’ is useful in predicting the direction of the reaction. Which of the following is incorrect?
- a. If Qc > Kc, the reverse reaction is favoured
- b. If Qc < Kc, the forward reaction is favoured
- c. If Qc = Kc, no reaction occur
- d. If Qc > Kc, the forward reaction is favoured
Solution:
Answer: (d)
If the reaction is in reverse direction then the reaction quotient is greater than equilibrium constant Qc > Kc.
If the reaction is in equilibrium then reaction quotient is equal to equilibrium constant Qc > Kc.
If Qc > Kc. The reaction is forward.
Question 10: 3ClO–(aq) → ClO– + 2Cl– is an example of
- a. Oxidation reaction
- b. Reduction reaction
- c. Disproportionation reaction
- d. Decomposition reaction
Solution:
Answer: (b)
3ClO–(aq) → ClO– + 2Cl–
The oxidation state of chlorine changes from +1 to – 1.
This reaction is an example of a reduction reaction.
Question 11: In the manufacture of hydrogen from water gas (CO + H2), which of the following is the correct statement?
- a. CO is oxidized to CO2 with steam in the presence of a catalyst followed by absorption of CO2 in alkali.
- b. CO and H2 are separated based on the difference in their densities.
- c. Hydrogen is isolated by diffusion
- d. H2 is removed by occlusion with pd.
Solution:
Answer: (a)

The reaction shown above is the reaction of the manufacturing of hydrogen from water gas. Here, CO is oxidized to CO2 with steam in the presence of a catalyst. Then the absorption of CO2 in alkali takes place.
So the answer is CO is oxidized to CO2.
Question 12: Plaster of Paris is represented as
- a. CaSO4 · (1 / 2) H2O
- b. CaSO4 · H2O
- c. CaSO4 · 2H2O
- d. CaSO4
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The formula for plaster of paris is CaSO4 · (1 / 2) H2O.
Question 13: Addition of mineral acid to an aqueous solution of Borax, the following compound is formed
- a. Boron hydride
- b. Orthoboric acid
- c. Meta boric acid
- d. Pyroboric acid
Solution:
Answer: (b)
The reaction involved in the addition of mineral acid to the aqueous solution of borax is

So, orthoboric acid is formed as a product.
Question 14: Identify the correct statement in the following:
- a. n-butane and isobutane are functional isomers
- b. Dimethyl ether and ethanol are chain isomers
- c. Propan-l-ol and propan-2-ol are position isomers
- d. Ethanoic acid and methyl methanoate are position isomers
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Position isomers are those in which both compounds have a different position of a substituent but have the same parent chain and functional group.

∴ Propan-l-ol and propan-2-ol are position isomers.
Question 15: In which of the following, haemolytic bond fission takes place?
- a. Alkaline hydrolysis of ethyl chloride
- b. Addition of HBr to double bond
- c. Free radical chlorination of methane
- d. Nitration of Benzene
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Homolytic bond fission takes place when the bonded molecules are of same or almost equal electronegativity or where bonding pairs of electrons move independently.
So, in free radical chlorination of methane homolytic fission takes place.
The mechanism is shown below.

So the answer is “free radical chlorination of Methane”.
Question 16: For the preparation of Alkanes, the aqueous solution of sodium or potassium salt of the carboxylic acid is subjected to
- a. Hydrolysis
- b. Oxidation
- c. Hydrogenation
- d. Electrolysis
Solution:
Answer: (d)
In electrolysis of salts, a new bond is created.
The reaction is

So, aqueous solutions of sodium and potassium salts of carboxylic acid undergo electrolysis for preparation of alkenes.
Question 17: Which one of the following is not a common component of photochemical smog?
- a. Ozone
- b. Acrolein
- c. Peroxy acetyl nitrate
- d. Chlorofluorocarbons
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Ozone, nitrogen, PAN, oxygen and some organic compounds are the pollutants in photochemical smog. Photochemical smog does not include chlorofluorocarbons.
Question 18: Which of the following crystals has unit cells such that a ≠ b ≠ c and α ≠ β ≠ 90°?
- a. K2Cr2O7
- b. NaNO3
- c. KNO3
- d. K2SO4
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Given that a ≠ b ≠ c and α ≠ β ≠ γ ≠ 90°.
Then the unit cell must be triclinic.
∵ K2Cr2O7 has a triclinic unit cell then.
a ≠ b ≠ c and α ≠ β ≠ γ ≠ 90°.
Question 19: The correct statement regarding a defect in solids is
- a. Frenkel defect is usually favoured by a very small difference in the sizes of cations and anions.
- b. Frenkel defect is a dislocation defect.
- c. Trapping of protons in the lattice leads to the formation of F-centers.
- d. Schottky defect has no effect on the physical properties of solids.
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Since, in Frenkel defect, the smallest ion gets dislocated to its interstitial site hence, Frenkel defect is termed as dislocation defect as well.
Question 20: In a face centred cubic arrangement of A and B atoms in which ‘A’ atoms are at the corners of the unit cell and ‘B’ atoms are at the face centres. One of the ‘A’ atoms is missing from one corner in the unit cell. The simplest formula of the compound is
- a. A7B24
- b. A7B8
- c. AB3
- d. A7B3
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Given that it is a face centred cubic cell and A atoms are at the corners of the unit cell.
∵ One of A atom is missing from one corner in the unit cell then, there are 7A atoms with a total contribution.
7 * (1 / 8) = 7 / 8
B atoms are at face centres.
∵ There are 6 face centres. Each contributes 1 / 2.
So, the total contribution will be 6 * (1 / 2) = 3
A:B = (7 / 8):3 => 7:24
The simplest formula of the compound is A7B24.
Question 21: Which of the following aqueous solutions has the highest freezing point?
- a. 0.1 molal Al2 (SO4)3
- b. 0.1 molal BaCl2
- c. 0.1 molal AlCl3
- d. 0.1 molal NH4Cl
Solution:
Answer: (d)
NH4Cl dissociation in aqueous solution is as follows:
NH4Cl → NH4+ + Cl–
Lesser the number of particles available higher will be the freezing point.
Here i = 2 which is least among all so it has the highest freezing point.
Question 22: The Vant Hoff’s factor ‘i’ accounts for
- a. extent of the solubility of solute
- b. extent of dissociation of solute
- c. extent of dissolution of solute
- d. extent of the mobility of solute
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Vant-Hoff’s factor ‘i’ accounts for the extent of dissociation of solute.
Question 23: When the pure solvent diffuses out of the solution through the semipermeable membrane then the process is called
- a. Osmosis
- b. Reverse osmosis
- c. Sorption
- d. Dialysis
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Reverse osmosis is the process in which pure solvent diffuses out of the solution through the semipermeable membrane.
Question 24: The standard reduction potential at 298 K for the following half cell reaction
Zn(aq)2+ + 2e -> Zn(s) E° = – 0.762 V
Cr(aq)3+ + 3e -> Cr(s) E° = 0.740 V
2H(aq)+ + 2e -> H2(g) E° = 0.0 V
F2(g) + 2e -> 2F(aq)− E° = 2.87 V
Which of the following is the strongest reducing agent?
- a. Zn(s)
- b. Cr(s)
- c. H2(g)
- d. F2(g)
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The reducing agent will be stronger when its reduction potential is more negative. ∴ zinc is the strongest reducing agent as its value of reducing potential is highly negative (0.762 v)
Question 25: By passing electric current, NaClO3 is converted into NaClO4 according to the following equation NaClO3 + H2O → NaClO4 + H2
How many moles of NaClO4 will be formed when three Faradays of charge is passed through NaClO3?
- a. 0.75
- b. 1.0
- c. 1.5
- d. 3.0
Solution:
Answer: (c)
The reaction is
NaClO3 + H2O → NaClO4 + H2
Here, the oxidation number changes from +5 to +7 so, two electrons are involved in the reaction.
Thus, 2 Faraday of charge will form one mole of NaClO4.
∴ 3 Faraday of charge will form [1 / 2] × 3 = 1.5 mole of NaClO4.
Question 26: In the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride solution, which of the half cell reactions will occur at the anode?
- a. Na(aq)+ + e– → Na(s) E0 = –2.71 volts
- b. 2H2O(l) → O2 + 4H+ + 4e– E0cell = 1.23 volts
- c. H(aq)+ + e– → (1 / 2) H2 E0cell = 0.00 volts
- d. Cl(aq)− → (1 / 2) Cl2 + e– E0cell = 1.36 volts
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Half cell reduction reaction at the cathode is
H2O (l) + e– → (1 / 2) H2 + OH–
The standard reduction potential of the above reaction is 0 volts.
The half cell oxidation reaction at the anode is shown below.
Cl– (aq) → (1 / 2) Cl2 + e–
The standard reduction potential of the above reaction is 1.36 volts.
Question 27: Which of the following statements is in accordance with the Arrhenius equation?
- a. Rate of a reaction increases with increase in temperature
- b. Rate of a reaction increases with a decrease in activation energy
- c. Rate constant decreases exponentially with an increase in temperature
- d. Rate of reaction does not change with an increase in activation energy
Solution:
Answer: (a, b)
The expression for the Arrhenius equation is k = Ae-𝜺a/RT
By seeing the above equation we can conclude that the rate of reaction depends upon activation energy and temperature. It is clear that the rate of reaction will increase as the activation energy decreases and temperature increases.
The rate of reaction depends upon activation energy and temperature, increases with increase in temperature & decrease in activation energy.
Question 28: Which of the following statements is incorrect?
- a. The rate law for any reaction cannot be determined experimentally
- b. Complex reactions have fractional order.
- c. Biomolecular reactions involve a simultaneous collision between two species
- d. Molecularity is only applicable to the elementary reaction.
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The rate law for a chemical reaction is the equation that links the initial reaction rate with the concentration of reactants. For many reactions the initial rate is given by Vo = k[A]x [B]y hence, rate law for any reaction can be determined experimentally.
Question 29: For a reaction (1 / 2) A → 2B rate of disappearance of A is related to the rate of appearance of B by the expression
- a. -d[A] / dt = 4 [d[B] / dt]
- b. -d[A] / dt = (1 / 4) [d[B] / dt]
- c. -d[A] / dt = (1 / 2) [d[B] / dt]
- d. -d[A] / dt = [d[B] / dt]
Solution:
Answer: (b)
The given equation is (1 / 2) A → 2B.
The rate of reaction is
Rate of disappearance of products = Rate of formation of products.
Rate = -2 [d[A] / dt] = (1 / 2) [d[B] / dt]
Rate of disappearance of A is -d[A] / dt = (1 / 4) [d[B] / dt].
Question 30: The process which is responsible for the formation of the delta at a place where rivers meet the sea is
- a. Coagulation
- b. Colloid formation
- c. Emulsification
- d. Peptization
Solution:
Answer: (a)
When the river meets the sea the colloidal particles are coagulated by electrolyte available in the sea, due to which the colloidal particles settle down during meet time. So, coagulation occurs.
Question 31: Hydrogenation of vegetable oils in presence of finely divided nickel as a catalyst. The reaction is
- a. Heterogeneous catalysis
- b. Homogeneous catalysis
- c. Enzyme catalysed reaction
- d. Liquid catalysed reaction
Solution:
Answer: (a)
For finding the solution, we have to write the equation of hydrogenation of vegetable oils

Here, we can see that the phases of reactant and catalyst are different, so the reaction is heterogeneous catalysis.
Question 32: Which of the following is not a favourable condition for physical adsorption?
- a. High-temperature
- b. High-pressure
- c. Higher critical temperature of adsorbate
- d. Low temperature
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Since physical adsorption is an exothermic process so it is favoured at low temperature. Further Le chatelier's principle states that with the increase in temperature, the extent of adsorption decreases. So, high temperature is not favourable for physical adsorption.
Question 33: The metal extracted by leaching with a cyanide
- a. Al
- b. Ag
- c. Cu
- d. Na
Solution:
Answer: (b)
The reactions involved in process of leaching of cyanides are
Ag2S + 4NaCN ⇌ 2Na [Ag (CN)2] + Na2S
2Na [Ag (CN)2] + Zn → Na2 [2n (CN)4] + 2Ag
So, silver is obtained by leaching with cyanide.
Question 34: Extraction of chlorine from brine solution is based on
- a. Oxidation
- b. Chlorination
- c. Reduction
- d. Acidification
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The reaction involved in the extraction of chlorine from brine is
2Cl– + 2H2O → 2OH– + H2 + Cl2
So here oxidation of Cl– ion to chlorine gas occurs.
Question 35: Which of the following elements forms pπ – pπ bond with itself?
- a. N
- b. P
- c. Se
- d. Te
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Since the size of the nitrogen atom is very small.
So it is able to form pπ – pπ bond with itself and can accommodate other atoms of itself.
So, the answer is nitrogen 'N'.
Question 36: Which one of the following metallic oxides exhibits amphoteric nature?
- a. CaO
- b. Na2O
- c. BaO
- d. Al2O3
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Amphoteric oxides are those that can act as acid as well as the base.
When we move down the ‘s’ group the acidic character of the element decreases and basic character increases.
So, Al2O3 is amphoteric in nature.
Question 37: Select the wrong chemical reaction among the following:
- a. MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O
- b. 8NH3 + 3Cl2 → 6NH4Cl + N2
- c. 2NaOH + Cl2 → 2NaCl + H2 + O2
- d. 2Ca(OH)2 + 2Cl2 → Ca(OCl)2 + CaCl2 + 2H2O
Solution:
Answer: (c)
In reaction
2NaOH + Cl2 → 2NaCl + H2 + O2
The products formed are wrong the correct products will be
2NaOH + Cl2 → 2NaCl + + NaOCl + H2O
Question 38: Which one of the following noble gas has an unusual property of diffusing through the materials such as rubber, glass or plastic?
- a. Ne
- b. Ar
- c. Kr
- d. He
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Helium is used for filling balloons and airships since it is light in weight. It has the property of diffusing through the materials such as rubber, glasses or plastic.
Question 39: The magnetic nature of elements depends on the presence of unpaired electrons. Identify the configuration of transition elements which shows the highest magnetic moment?
- a. 3d7
- b. 3d5
- c. 3d8
- d. 3d2
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Magnetic character depends on the number of unpaired electrons. 3d5 has five unpaired electrons. Therefore its magnetic moment is highest.
Question 40: Which of the following statements is wrong regarding Lanthanoids?
- a. Ln(III) compounds are generally colourless.
- b. Ln(III) compounds are predominantly ionic in character
- c. The ionic size of Ln(III) ions decreases with increasing atomic number
- d. Ln(III) hydroxides are mainly basic in nature.
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Lanthanoids are generally colourful since vacant orbitals transition of electrons takes place.
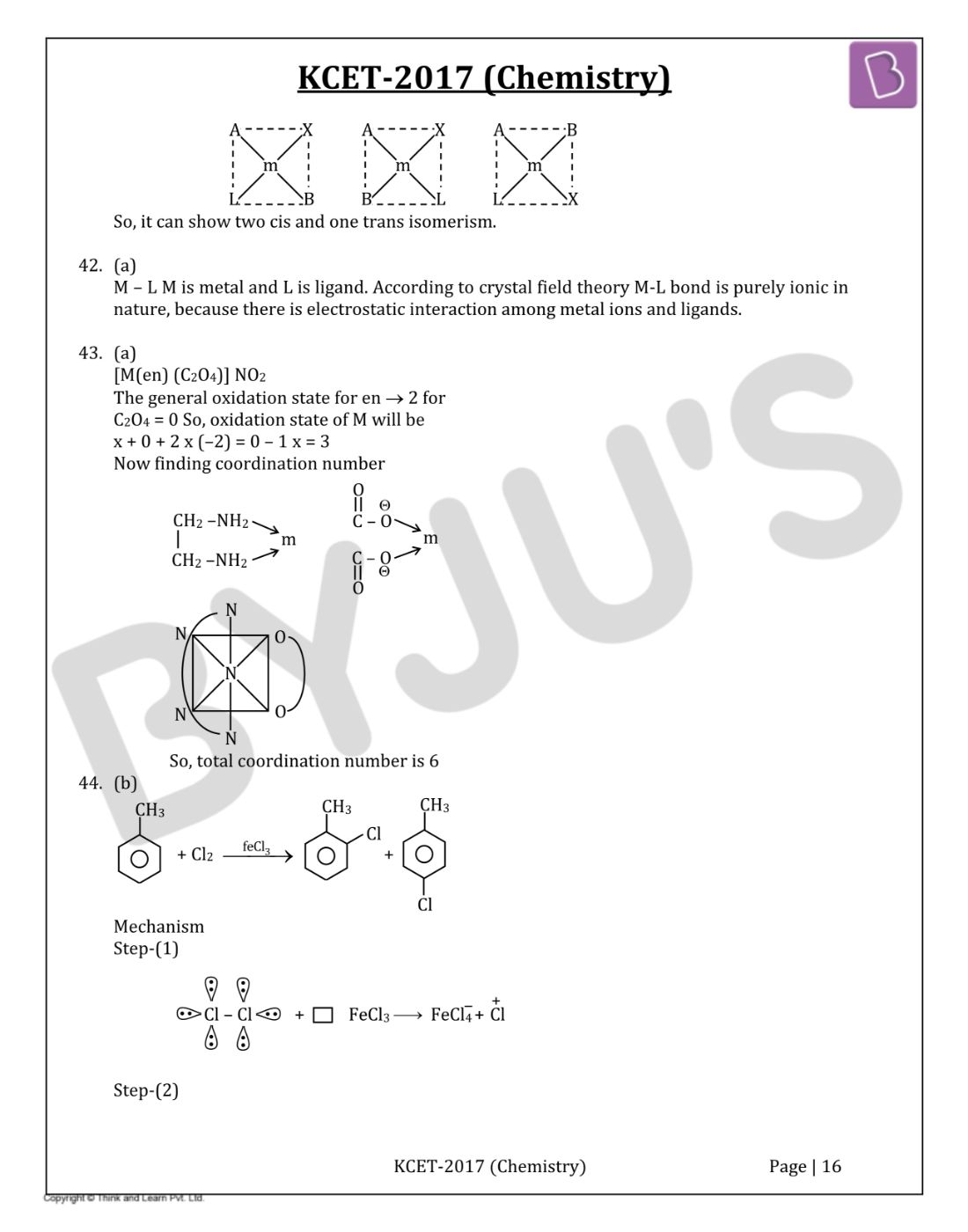
Question 41: Square planar complex of the type MAXBL (where A, B, X and L are unidentate ligands) shows following set of isomers
- a. Two cis and one trans
- b. Two trans and one cis
- c. Two cis and two trans
- d. Three cis and one trans
Solution:
Answer: (a)
MAXBL complex is shown below.

So, it can show two cis and one trans isomerism.
Question 42: According to crystal field theory, the M – L bond in a complex is
- a. Purely ionic
- b. purely covalent
- c. Purely co-ordinate
- d. Partially covalent
Solution:
Answer: (a)
M – L M is metal and L is a ligand. According to crystal field theory, M-L bond is purely ionic in nature, because there is electrostatic interaction among metal ions and ligands.
Question 43: The coordination number and the oxidation state of the element ‘M’ in the complex [M(en)2 (C2O4)] NO2 {where (en) is ethan-1, 2 – diamine} are respectively
- a. 6 and 3
- b. 6 and 2
- c. 4 and 2
- d. 4 and 3
Solution:
Answer: (a)
[M(en)2 (C2O4)] NO2
The general oxidation state for en → 2 for
C2O4 = 0 So, oxidation state of M will be
x + 0 + 2 x (–2) = 0 – 1 x = 3
Now finding coordination number

So, the total coordination number is 6.
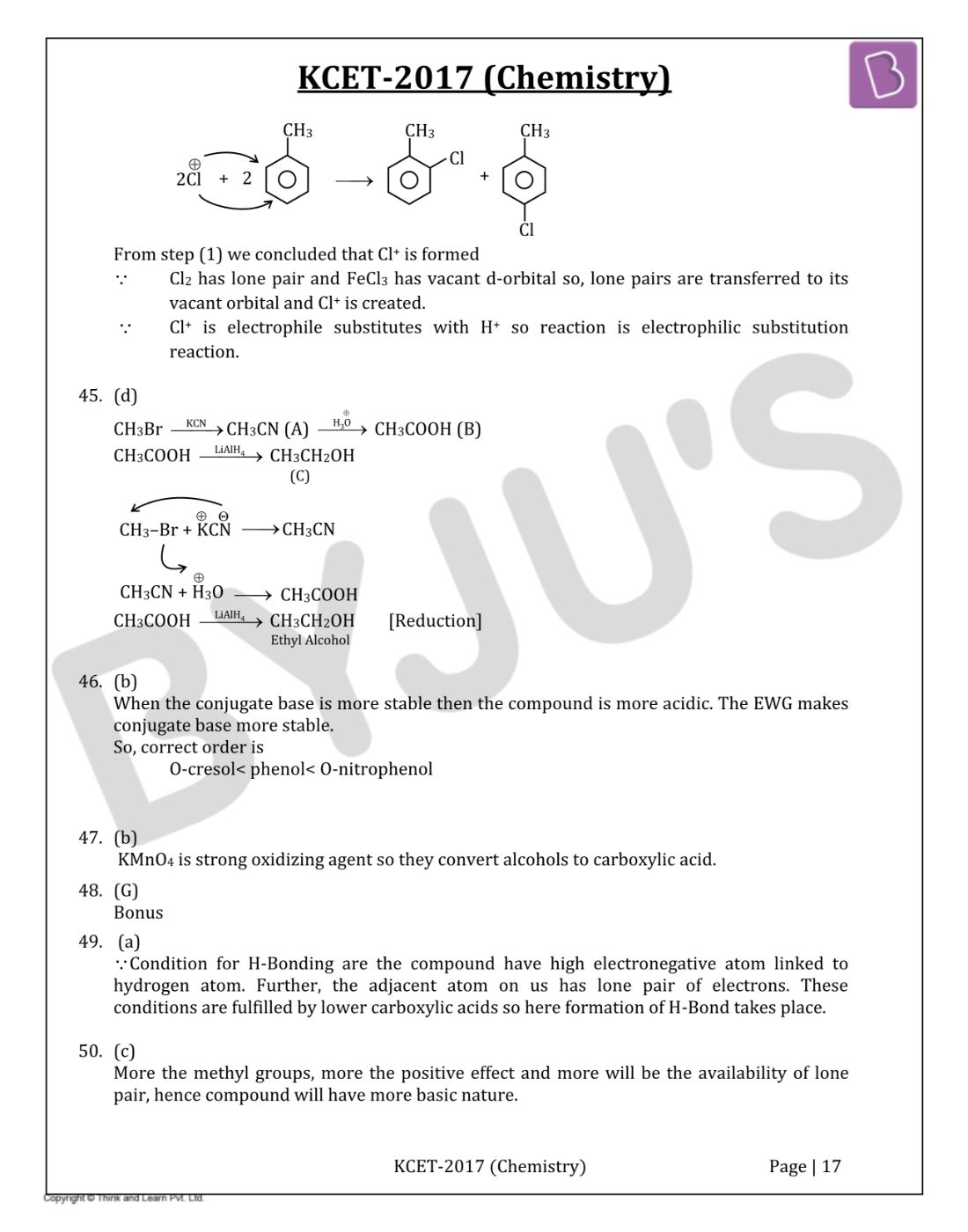
Question 44: Toluene reacts with halogen in presence of Iron (III) chloride giving ortho and para halo compounds. The reaction is
- a. Electrophilic elimination reaction
- b. Electrophilic substitution reaction
- c. Free radical addition reaction
- d. Nucleophilic substitution reaction
Solution:
Answer: (b)

From step (1) we concluded that Cl+ is formed
∵ Cl2 has lone pairs and FeCl3 has vacant d-orbital so, lone pairs are transferred to its vacant orbital and Cl+ is created.
∵ Cl+ is electrophile substitutes with H+ so reaction is electrophilic substitution reaction.
Question 45: In the following sequence of reactions

The end product C is
- a. Acetone
- b. Methane
- c. Acetaldehyde
- d. Ethyl Alcohol
Solution:
Answer: (d)

Question 46: Which of the following orders is true regarding the acidic nature of phenol?
- a. Phenol > O-cresol > O-nitrophenol
- b. O-cresol< phenol< O-nitrophenol
- c. Phenol < O-cresol > O-nitrophenol
- d. Phenol < O-cresol > O-nitrophenol
Solution:
Answer: (b)
When the conjugate base is more stable then the compound is more acidic. The EWG makes the conjugate base more stable.
So, the correct order is O-cresol< phenol< O-nitrophenol
Question 47: Which of the following reagents cannot be used to oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes?
- a. CrO3 in anhydrous medium
- b. KMnO4 in acidic medium
- c. Pyridinium chlorochromate
- d. Heating in presence of Cu at 573 K
Solution:
Answer: (b)
KMnO4 is a strong oxidizing agent so they convert alcohols to a carboxylic acid.
Question 48: Cannizzaro’s reaction is an example of auto-oxidation
- a. It is a typical reaction of aliphatic aldehyde
- b. It is a reaction answered only by aromatic aldehydes
- c. It is a reaction answered by all aldehydes.
- d. It is a reaction answered by only aldehydes containing -hydrogen.
Solution:
Answer: (G)
Bonus
Question 49: Lower members of aliphatic carboxylic acid are soluble in water. This is due to
- a. Formation of hydrogen bonds with water.
- b. Van der-Waals interaction with water molecules
- c. Water is non-electrolyte
- d. Due to London forces
Solution:
Answer: (a)
∵ Condition for H-bonding is that the compound has a high electronegative atom linked to the hydrogen atom. Further, the adjacent atom on us has a lone pair of electrons. These conditions are fulfilled by lower carboxylic acids so here formation of H-bond takes place.
Question 50: The correct order of increasing basic nature for the bases NH3, CH3NH2 and (CH3)2 NH in aqueous solutions
- a. CH3NH2 < NH3 < (CH3)2 NH
- b. (CH3)2NH < NH3 < CH3NH2
- c. NH3 < CH3NH2 < (CH3)2NH
- d. CH3NH2 < (CH3)2 NH < NH3
Solution:
Answer: (c)
More the methyl groups, more the positive effect and more will be the availability of lone pairs, hence compounds will have more basic nature.
NH3 < CH3NH2 < (CH3)2NH
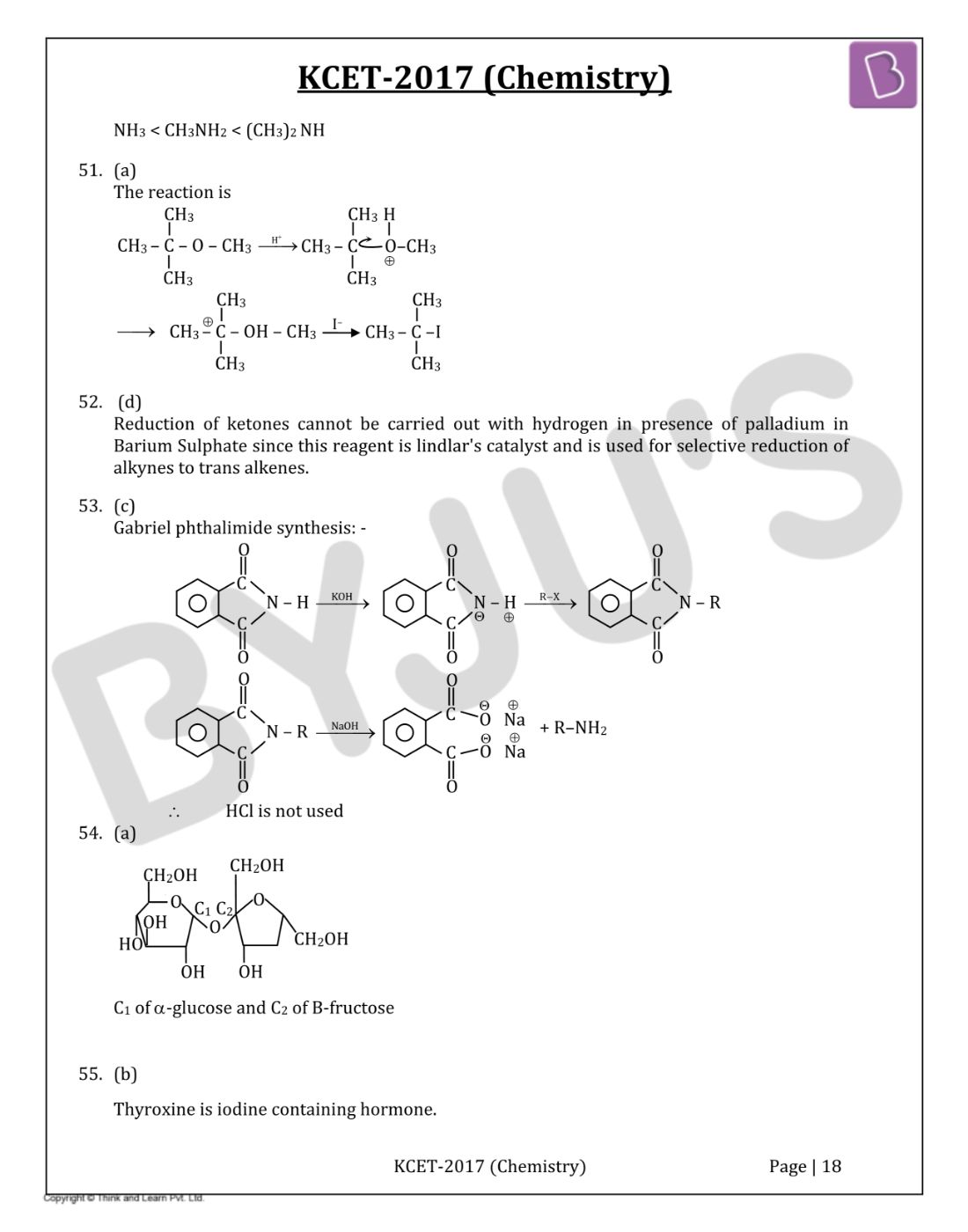
Question 51: The product formed during the following reaction is

Solution:
Answer: (a)
The reaction is

Question 52: Reduction of ketones cannot be carried out with which of the following reagents?
- a. Sodium borohydride or Lithium Aluminum hydride
- b. Zinc amalgam and concentrated HCl
- c. Hydrazine and KOH in ethylene glycol
- d. Hydrogen in presence of palladium in Barium sulphate and quinoline
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Reduction of ketones cannot be carried out with hydrogen in presence of palladium in Barium Sulphate since this reagent is lindlar's catalyst and is used for selective reduction of alkynes to trans alkenes.
Question 53: Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is used in the preparation of primary amine from phthalimide, which of the following reagent is not used during the process?
- a. KOH
- b. NaOH
- c. HCl
- d. Alkyl Halides
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Gabriel phthalimide synthesis:-

∴ HCl is not used.
Question 54: The Glycosidic linkage present in sucrose is between
- a. C – 1 of α - glucose and C – 2 of β - fructose
- b. C – 1 of α - glucose and C – 4 of α - glucose
- c. C – 1 of β - galactose and C – 4 of α - glucose
- d. C – 1 of α - glucose and C – 4 of β - fructose
Solution:
Answer: (a)

C – 1 of α - glucose and C – 2 of β - fructose
Question 55: Hormones are secreted by ductless glands of the human body. Iodine containing hormone is
- a. Insulin
- b. Thyroxine
- c. Testosterone
- d. Adrenaline
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Thyroxine is an iodine-containing hormone.
Question 56: Pick the wrong statement from the following :
- a. Sources of Vitamin B1 are yeast, milk, green vegetables and cereals
- b. Deficiency of Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) results in convulsions
- c. Consumption of citrus fruits and green leafy vegetables in food prevents scurvy
- d. Deficiency of vitamin D causes xerophthalmia
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Due to the deficiency of vitamin D, rickets is caused. Deficiency of vitamin A causes xerophthalmia. Vitamin A is also known as retinol.
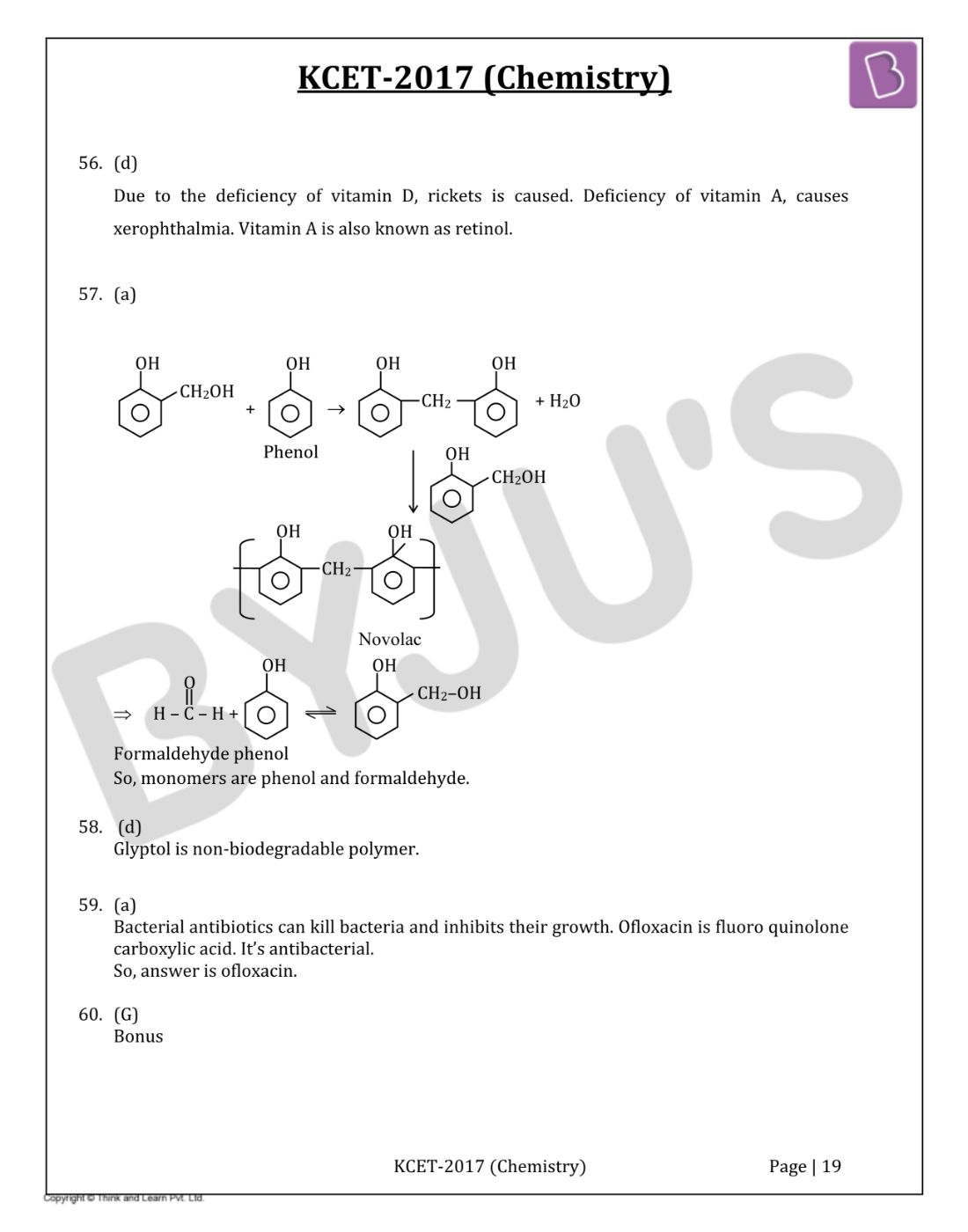
Question 57: The monomer used in Novolac, a polymer used in paints
- a. Phenol and Formaldehyde
- b. Melamine and Formaldehyde
- c. Butadiene and Styrene
- d. Butadiene and Acrylo Nitrile
Solution:
Answer: (a)

Formaldehyde phenol.
So, monomers are phenol and formaldehyde.
Question 58: Which of the following is not a biodegradable polymer?
- a. Polyhydroxy butyrate – CO- hydroxy valerate
- b. pHBV
- c. Nylon 2-Nylon-6
- d. Glyptol
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Glyptol is a non-biodegradable polymer.
Question 59: Bactericidal antibiotics among the following is
- a. Ofloxacin
- b. Erythromycin
- c. Tetracycline
- d. Chloramphenicol
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Bacterial antibiotics can kill bacteria and inhibit their growth. Ofloxacin is fluoroquinolone carboxylic acid. It’s antibacterial.
So, the answer is ofloxacin.
Question 60: Pick the correct statement among the following:
- a. Cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide is a popular cationic detergent used in air conditioner
- b. Non-ionic detergents are formed when polyethylene glycol reacts with adipic acid
- c. Sodium dodecylbenzene sulphonate used in toothpaste is a cationic detergent.
- d. Sodium lauryl sulphate forms an insoluble scum with hard water.
Solution:
Answer: (G)
Bonus