KCET 2018 solved Biology paper is a perfect resource which helps the candidates in understanding the question paper blueprint. Candidates can download the previous year question papers of KCET to figure out the important concepts and their weightage in the examination. Practising the KCET previous year papers will guide the students to predict the type of questions that can appear in the exam. It will motivate the students to face the exam with more confidence. Solving these papers will make the students know the time required for each question, which in turn assists them to allocate time in the main examination.
KCET 2018 - Biology
Question 1: The correct sequence of the taxonomic hierarchy is
- a. Genus → Family → Class → Order Phylum → Kingdom → Species
- b. Species → Genus → Family → Order → Class → Phylum → Kingdom
- c. Species → Family → Genus → Kingdom → Order → Class → Phylum
- d. Species → Genus → Family → Class → Order Phylum → Kingdom
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Taxonomic hierarchy is the process of arranging various organisms into successive levels of the biological classification either in a decreasing or an increasing order from kingdom to species and vice versa.” Each of this level of the hierarchy is called the taxonomic category or rank. There are seven main taxonomic ranks: kingdom, phylum or division, class, order, family, genus, species. In ascending order the correct sequence is species – genus – family – order – class – phylum – kingdom.
Question 2: Match the animals of Column I with their respective classes in Column II and choose the correct answer.
|
Column-I |
Column-II |
|
1. Aptenodytes |
I. Aves |
|
2. Hemidactylus |
II. Chondrichthyes |
|
3. Carcharodon |
III. Mammalia |
|
4. Pteropus |
IV. Reptilia |
|
V. Osteichthyes |
Select the code for the correct answer from the options given below:
- a. 1 - V, 2 - II, 3 - IV, 4 - I
- b. 1 - I, 2 - IV, 3 - III, 4 - II
- c. 1 - V, 2 - I, 3 - II, 4 - III
- d. 1 -I, 2 - IV, 3 - II, 4 - III
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Column-I
Column-II
1. Aptenodytes
I. Aves
2. Hemidactylus
II. Osteichthyes
3. Carcharodon
III. Chondrichthyes
4. Pteropus
IV. Mammalia
Question 3: Choose the correct floral formula of the given floral diagram.


Solution:
Answer: (c)

Brassicaceae or Cruciferae is a medium-sized and economically important family of flowering plants, commonly known as mustards, the crucifers or the cabbage family. In Brassicaceae, the flowers are actinomorphic (radial symmetry), bisexual (possess both male and female flowers), sepals 4 and they are dimerous (arranged in two whorls), petals 4 and they are arranged in a single whorl, stamens 6 and they are tetradynamous (two lateral stamens are smaller and four median stamens are larger), carpels are 2 (bicarpellary) syncarpous, ovary superior.
Question 4: In which type of vascular bundles are Xylem and Phloem present at the same radius?
- a. Radial
- b. Closed
- c. Conjoint
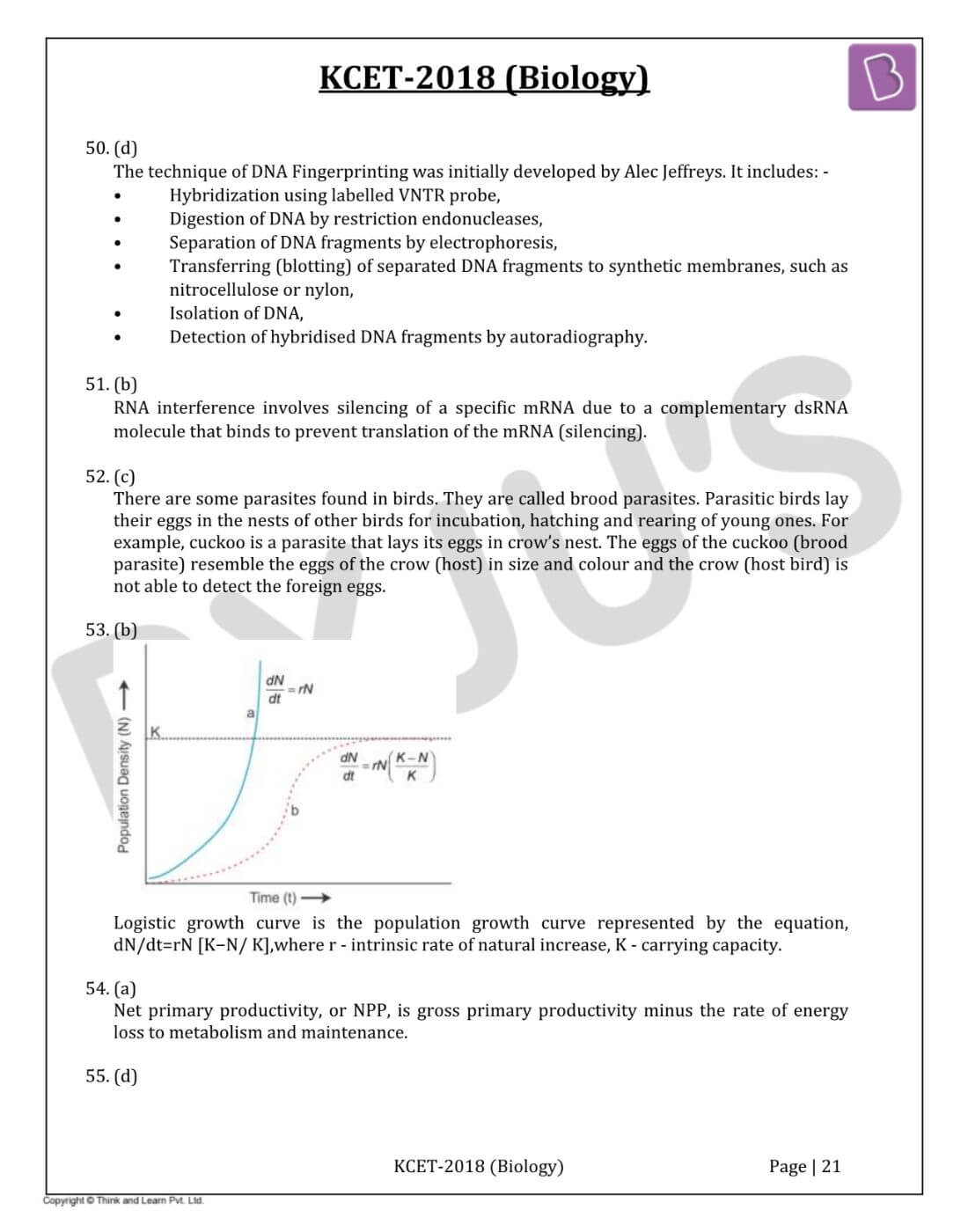
- d. Exarch
Solution:
Answer: (c)
When xylem and phloem are situated on the same radii of vascular bundles, the arrangement is called as conjoint and the vascular bundle is called as conjoint vascular bundles. Such vascular bundles are common in the stem and leaves of dicots and monocots.
Question 5: Conjunctive tissue is present between (i) and (ii) in (iii).
- a. (i) Pericycle (ii) Endodermis (iii) Dicot root
- b. (i) Xylem (ii) Phloem (iii) Dicot root
- c. (i) Palisade parenchyma (ii) Spongy parenchyma (iii) Dicot leaf
- d. (i) Xylem (ii) Phloem (iii) Dicot stem
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Parenchyma present between xylem and phloem in the vascular bundles of roots is called conjunctive tissue. In the anatomy of dicot root, parenchyma present between xylem and phloem is called conjunctive tissue. It is concerned in the formation of vascular cambium and storage of food and water.
Question 6: Identify the major site of biosynthesis of lipids.
- a. Golgi apparatus
- b. Mitochondria
- c. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
- d. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
Solution:
Answer: (c)
The endoplasmic reticulum is a type of organelle in the cells of eukaryotic organisms that forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs or tubes known as cisternae. The endoplasm is the inner core of the cytoplasm and the membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum, rough and smooth. The outer (cytosolic) face of the rough endoplasmic reticulum is studded with ribosomes that are the sites of protein synthesis, whereas active smooth endoplasmic reticulum lacks ribosomes and functions in lipid metabolism and biosynthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, etc.
Question 7: The following graph shows the concentration of substrate on enzyme activity:

What does the Y-axis represent?
- a. Temperature
- b. Velocity of reaction
- c. pH
- d. Pressure
Solution:
Answer: (b)

The substrate - enzyme activity is represented by Michelis Menton equation which represents Velocity of reaction on the y-axis and substrate concentration on the x-axis, with the increase in substrate concentration, the velocity of the enzymatic reaction at first. The reaction ultimately reaches a maximum velocity (Vmax) which is not exceeded by any further rise in the concentration of the substrate molecules and after saturation of these molecules, there are no free enzyme molecules to bind with the additional substrate molecules.
Question 8: In the maize plant, CO2 fixation occurs in both mesophyll and bundle sheath cells. The enzymes involved in these cells for the process respectively are
- a. RuBisCO and PEP Kinase
- b. PEP Kinase and Pepsin
- c. RuBisCO and PEP Carboxylase
- d. PEP Carboxylase and RuBisCO
Solution:
Answer: (d)
In the C4 cycle, carbon dioxide fixation in mesophyll cells by PEP Carboxylase and synthesis of sugars in bundle sheath cells by RuBISCO. For example, in maize plants, CO2 fixation occurs in both mesophyll and bundle sheath cells.
Question 9: In the following reaction, identify X and Y respectively:

- a. Water, Acetyl CoA
- b. Acetyl CoA, Pyruvate dehydrogenase
- c. Pyruvate dehydrogenase, Acetyl CoA
- d. Pyruvate dehydrogenase, Oxalo-acetic acid
Solution:
Answer: (c)
The pyruvate which is formed by glycolysis enters into mitochondrial matrix undergoes oxidative decarboxylation by a catalyst called pyruvate dehydrogenase. During this process, two molecules of NADH are produced from the metabolism of two molecules of pyruvic acid. This reaction can be shown by the following equation:

Enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase brings about decarboxylation of pyruvic acid to form two molecules of Acetyl CoA which is further utilized in the Krebs cycle. So X is a pyruvate dehydrogenase and Y Acetyl CoA.
Question 10: Which of the following factors are favourable for the formation of oxyhaemoglobin in the alveoli human lungs?
- a. High pCO2
- b. Lower temperature
- c. High H+ concentration
- d. Low pO2
Solution:
Answer: (b)
The normal temperature favours the binding of haemoglobin with oxygen. The high temperature is responsible for the dissociation of the oxygen from haemoglobin. In the alveoli, where there is high pO2, low pCO2, lesser H+ concentration and lower temperature, the factors are all favourable for the formation of oxyhaemoglobin.
Question 11: Digestion of both starch and proteins is carried out by enzymes of
- a. Gastric juice
- b. Saliva
- c. Bile juice
- d. Pancreatic juice
Solution:
Answer: (d)
• Gastric juice-protein digestion partially.
• Saliva-carbohydrate digestion partially.
• Bile juice has no enzymes.
• Pancreatic juice has enzymes for digesting proteins, carbohydrates and fats. The pancreatic enzymes include amylase that digests the remaining complex carbohydrates into monosaccharides; trypsin, chymotrypsin and elastase all digest proteins; lipase digests triglycerides into fatty acids and monoglycerides. Hence, without pancreas starch protein and fat digestion cannot take place.
Question 12: The type of epithelium found in the inner lining of PCT is
- a. Squamous epithelium
- b. Cuboidal epithelium
- c. Glandular epithelium
- d. Ciliated epithelium
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Simple squamous epithelia are found in capillaries, alveoli, glomeruli etc. This epithelium is associated with filtration and diffusion. The type of epithelium found in the inner lining of PCT is known as the cuboidal epithelium. They consist of a monolayer of epithelial cells which appear square-shaped in cross-section with large, round, centrally located nuclei. Glandular epithelium forms the covering of all major glands. It is also present in the intestinal lining. Ciliated epithelia are found in the airways, the uterus and Fallopian tubes, the efferent ducts of the testes, and the ventricular system of the brain.
Question 13: Select the correct Rh-blood groups of the parents, whose child is affected with erythroblastosis foetalis.
- a. Both Father and Mother are Rh +ve
- b. Mother is Rh +ve and Father is Rh –ve
- c. Both Father and Mother are Rh –ve
- d. Father is Rh +ve and Mother is Rh –ve
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Erythroblastosis fetalis also called hemolytic disease of the newborn, type of anaemia in which the red blood cells (erythrocytes) of a fetus are destroyed in a maternal immune reaction resulting from a blood group incompatibility between the fetus and its mother. This happens during the second pregnancy when the mother's immune system is already sensitized to Rh+ antigens present on the blood cells of the foetus during the first pregnancy i.e. incompatible blood group of mother and foetus. When the mother is Rh-negative while the father is Rh-positive. Since the antigen producing gene is dominant, therefore expressed in the progeny and so the foetus is Rh+. Since the mother is Rh− the antigen present on the child's RBC can cause antibody reaction, a condition called erythroblastosis fetalis.
Question 14: In which of the following groups do the male and female gametophytes have independent, free-living existence?
- a. Bryophytes and Gymnosperms
- b. Bryophytes and Pteridophytes
- c. Pteridophytes and Gymnosperms
- d. Algae and Gymnosperms
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Algae, bryophytes, and pteridophytes have independent gametophytes. Gymnosperms and angiosperms have dependent gametophytes. In gymnosperms, the male and the female gametophytes do not have an independent free-living existence and remain within the sporangia retained on the sporophytes. For example; cedrus.
Question 15: The hormones of "Fright, Fight and Flight" are
- a. Thyroxin and Oxytocin
- b. Thyroxin and Melatonin
- c. Adrenaline and Nor-adrenaline
- d. Gastrin and Secretin
Solution:
Answer: (c)
• Hormones of fright, fight and the flight is called adrenaline or epinephrine it is secreted by the adrenal cortex. Helps the organism to offend, defend or run away from a threatening situation.
• Adrenaline is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands during high stress or exciting situations.
• This powerful hormone is part of the human body's acute stress response system, also called the fight or flight response. It works by stimulating the heart rate, contracting blood vessels, and dilating air passages, all of which work to increase blood flow to the muscles and oxygen to the lungs.
• Additionally, it is used as a medical treatment for some potentially life-threatening conditions including anaphylactic shock.
Question 16: In the given options, which one cannot propagate by vegetative means?
- a. A marginal piece of bryophyllum leaf
- b. A middle piece of sugarcane internode
- c. A piece of potato tuber with eyes
- d. A piece of ginger rhizome
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Vegetative propagation is a form of asexual reproduction of a plant. Here, only one plant is involved and the offspring is the result of one parent. The new plant is genetically identical to the parent. The plant that cannot be propagated by vegetative means is sugarcane internode as buds are absent.
Question 17: Among the following statements related to pollens, choose the correct one.
Statement I: In 40% of angiosperms pollen grains are shed at the 3-celled stage. Statement II: Intine is made of cellulose and pectin and it is discontinuous with germ pores.
- a. Both I and II are correct
- b. Both I and II are incorrect
- c. I is correct and II is incorrect
- d. I is incorrect and II is correct
Solution:
Answer: (c)
In over 60 % of angiosperms, pollen grains are shed at this 2-celled stage tube cell or vegetative cell, generative cell. In the remaining species, the generative cell divides mitotically to give rise to the two male gametes before pollen grains are shed tube cell or vegetative cell two male gametes 3-celled stage. The pollen grain is protected by two layers, the outer exine and the inner intine. The exine is made of chemical substance sporopollenin, while the intine contains in parts cellulose and hemicellulose. It is continuous with the germ pore, while exine is discontinuous with the germ pore.
Question 18: Match the animals of Column I with Column II and select the correct options among the following:
|
Column-I |
Column II |
|
1. DNA replication |
I. RNA polymerase |
|
2. Translation |
II. DNA polymerase |
|
3. Transcription |
III. Reverse transcriptase |
|
4. Reverse transcription |
IV. Aminoacyl synthetase |
Select the code for the correct answer from the options given below:
- a. 1 - II, 2 - IV, 3 - III, 4 - I
- b. 1 - II, 2 - IV, 3 - I, 4 - III
- c. 1 - II, 2 - III, 3 - IV, 4 - I
- d. 1 - II, 2 - I, 3 - IV, 4 - III
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Column-I
Column II
1. DNA replication
DNA polymerase
2. Translation
Amino acyl synthetase
3. Transcription
RNA polymerase
4. Reverse transcription
Reverse transcriptase
Question 19: When pollen grain is shed at the 3-celled stage, name the cells it contains.
- a. 1 vegetative cell and 2 male gametes
- b. 2 vegetative cells and 1 male gamete
- c. 2 generative cells and 1 male gamete
- d. 2 male gametes and 1 generative cell
Solution:
Answer: (a)
A pollen grain with pollen tube carrying male gametes represents mature male gametophyte. Generative cell divides, forming two male gametes and hence at 3 celled stages, the pollen grain contains two male gametes and one vegetative cell.
Question 20: Even in the absence of pollinators, assured seed set will be there in
- a. Chasmogamous flowers
- b. Geitonogamy
- c. Cleistogamous flowers
- d. Xenogamy
Solution:
Answer: (c)
• Chasmogamous flowers are the flowers which have exposed anthers and stigma and thus, both self-pollination and cross-pollination can occur. Chasmogamous flowers may also depend on external agencies for cross-pollination.
• Geitonogamous flowers are the flowers in which pollen are transferred from the anther to the stigma of another flower on the same plant. These flowers also need external agencies for pollination.
• Cleistogamy is the phenomenon, where flowers never open and in such flowers, only self-pollination occurs within the bud (unopened flower). Bisexual flowers which do not open at all are called cleistogamous. In such flowers, anthers and stigma lie close to each other. When the anthers dehisce in the flower buds, pollen grains come in contact with the stigma and pollination occurs. Cleistogamous flowers are not dependent on external agencies for pollination. Hence, seed setting is not dependent on pollinators. Hence, assured seed set is possible even in the absence of pollinators when the flower is Cleistogamous.
• Xenogamous flowers are the flowers in which pollen are transferred from the anther to the stigma of a different flower on a different plant. Xenogamous flowers are cross-pollinated and depend on external agencies for pollination.
Question 21: The process of conversion of non-motile spermatids into motile spermatozoa is called
- a. Spermiogenesis
- b. Oogenesis
- c. Sporogenesis
- d. Spermatogenesis
Solution:
Answer: (a)
• The process of Differentiation of immature no motile spermatids to motile sperms are called spermiogenesis.
• Oogenesis is the growth process, in which the primary egg cell (or ovum) becomes a mature ovum.
• Sporogenesis is the production of spores.
• Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis.
Question 22: Several mammary ducts join to form a wider structure called
- a. Lactiferous duct
- b. Mammary lobe
- c. Mammary ampulla
- d. Mammary tubules
Solution:
Answer: (c)
A Functional mammary gland is characteristic of all female mammals. The mammary glands are paired structures (breasts) that contain glandular tissue and a variable amount of fat. The glandular tissue of each breast is divided into 15-20 mammary lobes containing a cluster of cells called alveoli. The cells of alveoli open into mammary tubules. The tubules of each lobe join to form a mammary duct which joins to form a wider mammary ampulla. The mammary ampulla is connected to the lactiferous duct through which milk is sucked out.
Question 23: The signals for the population process originate from
- a. Muscles of uterus
- b. Fully developed foetus and placenta
- c. Placenta
- d. Hormones of ovaries and uterus
Solution:
Answer:
BONUS
Question 24: Match the following Column I with Column II:
|
Column-I |
Column II |
|
1. Surgical methods |
I. Condom |
|
2. Barrier methods |
II. Pills |
|
3. Natural methods |
III. Tubectomy |
|
4. Chemical methods |
IV. Lactational amenorrhea |
Select the code for the correct answer from the options given below:
- a. 1 - III, 2 - I, 3 - IV, 4 - II
- b. 1 - III, 2 - IV, 3 - I, 4 - II
- c. 1 - IV, 2 - III, 3 - II, 4 - I
- d. 1 - II, 2 - I, 3 - III, 4 - IV
Solution:
Answer: (a)
• Tubectomy is a major surgical procedure in which the fallopian tubes are cut open and clipped or tied up to block the passage of the egg into the uterus.
• Barrier methods are used only when you have sexual intercourse. Barrier methods include the condom, diaphragm and cervical cap.
• The lactational amenorrhea method is a natural method of family planning for women who breastfeed their infants.
• Pill is the same as taking other tablets. It is the chemical methods.
Question 25: The following factors indicate improved reproductive health of society. Choose the correct option.
1. Better detection and cure of disease
2. Better post-natal care
3. Medically assisted deliveries
4. Increased MMR
Select the code for the correct answer from the options given below:
- a. 2, 3 and 4 only
- b. 1, 2 and 3 only
- c. 1, 3 and 4 only
- d. 1, 2 and 4 only
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Reproductive health in society can be improved by better awareness about sex-related matters, increased number of medically assisted deliveries and better post-natal care leading to decreased maternal and infant mortality rates, increased number couples with small families, better detection and cure of STDs and overall increased medical facilities for all sex-related problems, etc. all indicate improved reproductive health of the society.
Question 26: ABO blood type in man is an example of
1. Pleiotropy
2. Incomplete dominance
3. Co-dominance
4. Multiple allelism
Select the code for the correct answer from the options given below:
- a. 1, 2 and 3 only
- b. 1, 3 and 4 only
- c. 3 and 4 only
- d. 1, 2 and 4 only
Solution:
Answer: (c)
• Human blood group inheritance is governed by three alleles namely IA, IB and i. When both recessive and dominant traits are expressed in a heterozygous genotype; it is codominance. Alleles IA and IB show codominance as 'IA IB' genotype produce AB blood group that exhibits characters of both IA and IB alleles. Allele 'i' is recessive to both 'IA' and 'IB'; IAi and IBi phenotypes exhibit A and B blood groups respectively.
• Presence of more than two alleles for a gene is called Multiple alleles. These are present on the same locus of homologous chromosomes. Eg: ABO blood group.
Question 27: The codon on mRNA are CAU — CCU — AAA — CUG
Identify the correct sequence of amino acids.
- a. His — Pro — Lys — Leu
- b. Pro — His — Lys — Leu
- c. His — Pro — Leu — Lys
- d. Pro — Leu — Lys — His
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The correct sequence of amino acids is CAU-Histidine, CCU-Proline, AAA-Lysine and CUGLeucine.
Question 28: Choose the possible genotypes responsible for lightest skin colour in human beings.
- a. AABBCC
- b. AaBbCc
- c. aabbcc
- d. AABbCc
Solution:
Answer: (c)
In humans, skin colour is controlled by more than 1 gene. The human genotype of aabbcc has the lowest amount of melanin and has very light skin. Polygenic trait and quantitative inheritance, more recessive genes are lighter skin.
Question 29: Both male and female have a normal vision though their fathers were colour blind, and mothers did not have any gene for colour blindness. The probability of their daughter becoming colour blind is
- a. 0%
- b. 15%
- c. 25%
- d. 50%
Solution:
Answer: (a)
If both male and female have normal vision. Father and mother have normal vision, the probability of daughter becoming colour blindness is 0% because in both parents no presence of genes for colour blindness.
Question 30: Find the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA which codes for the sequence of amino acids - `Met - Leu - Val - Arg - Ala' and choose the correct option from below:
- a. AUG - GAU - GAA - UAU - UGU
- b. AUG - GAU - GAA - CGU - GCC
- c. AUG - CUA - GUG - UAU - UGU
- d. AUG - CUA - GUG - CGU - GCC
Solution:
Answer: (d)
The correct sequence of amino acids is AUG-Methionine, CUA - Leucine, GUG- Valine, CGUArginine and GCC- Alanine.
Question 31: Sickle-cell anaemia is due to the following mutant gene:
- a. CTC - CAC
- b. CTC - GAG
- c. CAC - GUG
- d. GAG - GUG
Solution:
Answer: (a, d)
• Sickle cell anaemia is a form of point mutation, where a single nitrogen base (CTC) of the codon for Leucine is changed to (CAC) for Histidine.
• Sickle-cell disease is caused by a single point mutation (a mis-sense mutation) in the beta-haemoglobin gene that converts a GAG codon into GUG, which encodes the amino acid valine rather than glutamic acid.
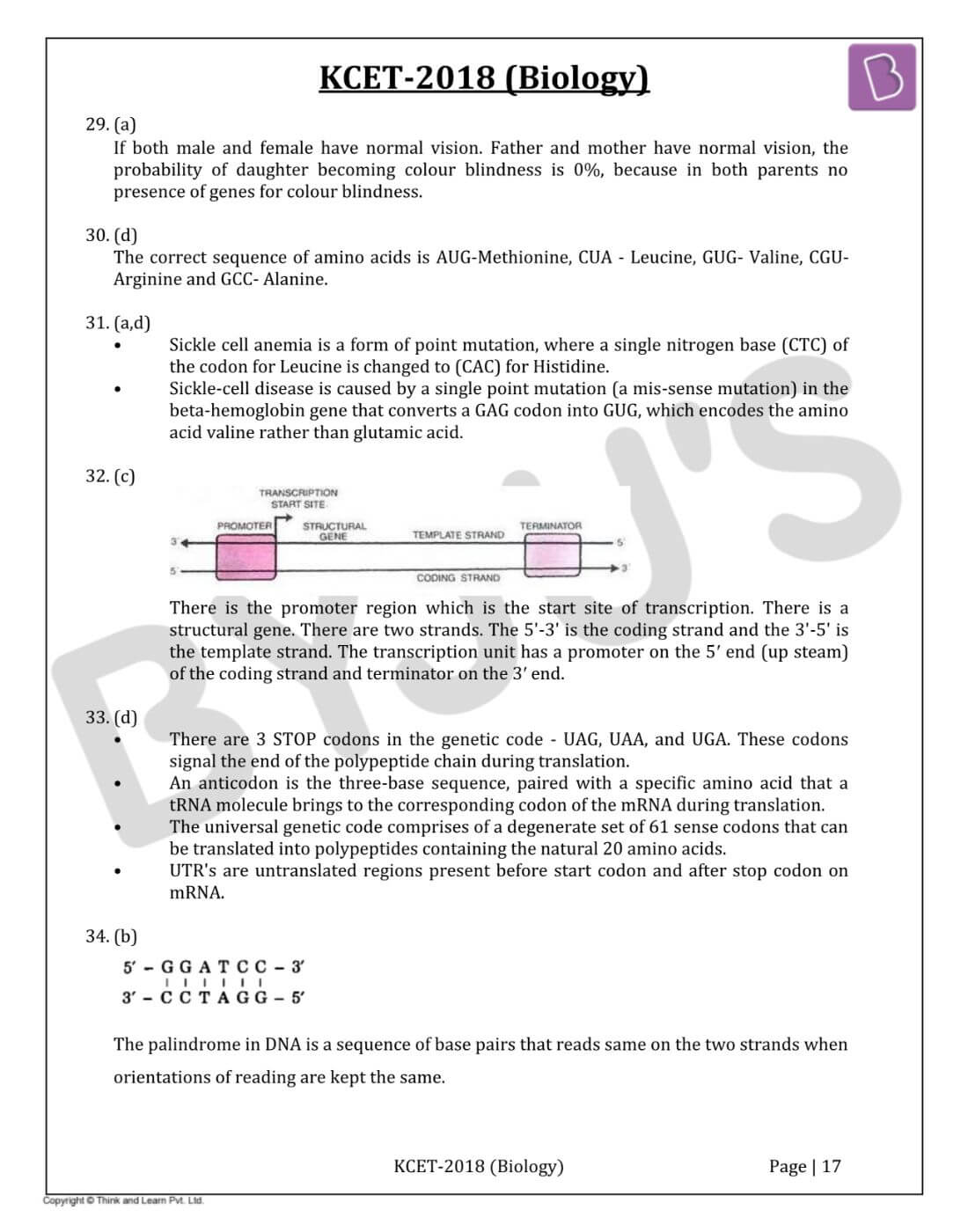
Question 32: In the given transcription unit, identify the regions I and II respectively.

- a. Promoter and Terminator
- b. Rho factor and Sigma factor
- c. Terminator and Promoter
- d. Operator and Inhibitor
Solution:
Answer: (c)

There is the promoter region which is the start site of transcription. There is a structural gene. There are two strands. The 5'-3' is the coding strand and the 3'-5' is the template strand. The transcription unit has a promoter on the 5′ end (up steam) of the coding strand and terminator on the 3′ end.
Question 33: Which of the following sequences of mRNA are required for the translation process but are not translated?
- a. Stop codons
- b. Anticodons
- c. Sense codons
- d. UTR
Solution:
Answer: (d)
• There are 3 STOP codons in the genetic code - UAG, UAA, and UGA. These codons signal the end of the polypeptide chain during translation.
• An anticodon is the three-base sequence, paired with a specific amino acid that a tRNA molecule brings to the corresponding codon of the mRNA during translation.
• The universal genetic code comprises of a degenerate set of 61 sense codons that can be translated into polypeptides containing the natural 20 amino acids.
• UTR's are untranslated regions present before the start codon and after stop codon on mRNA.
Question 34: Identify the palindromic sequence in the following base sequences:

Solution:
Answer: (b)

The palindrome in DNA is a sequence of base pairs that reads the same on the two strands when orientations of reading are kept the same.
Question 35: DNA, present in the nucleus, was named as `Nuclein' by
- a. James Watson and Crick
- b. Friedrich Miescher
- c. Maurice Wilkins
- d. Rosalind Franklin
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Friedrich Meischer was a Swiss physician and was the first to isolate nucleic acid or DNA as a distinct molecule. He named it 'nuclein' that is DNA associated with proteins and isolated it from the cell nuclei.
Question 36: When does the lac-operon in E. coli become "switched on"?
- a. Repressor binds to operator
- b. RNA polymerase binds to operator
- c. Lactose is present and it binds to the repressor
- d. Lactose is present and it binds to RNA polymerase
Solution:
Answer: (c)
The repressor of the operon is synthesized (all-the-time-constitutively) from the ‘i’ gene. The repressor protein binds to the operator region of the operon and prevents RNA polymerase from transcribing the operon. In the presence of an inducer, such as lactose or allolactose, the repressor is inactivated by interaction with the inducer. This allows RNA polymerase access to the promoter and transcription proceeds. Thus, the lac operon gets switched on.
Question 37: The primary gases that were used by Miller in his experiment are
- a. CH4, NH3, H2O, H2
- b. CH4, CO2, N2, SO2
- c. CH4, CO2, N2, NH3
- d. CH4, N2, NH3, H2
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The first experimental support for Oparin-Haldane's theory of the origin of life came from Urey and Miller's experiment. They conducted an experiment on evolution to prove the biochemical origin of life.
In 1953, Miller built an apparatus of glass tubes and flasks in the laboratory. He created an atmosphere containing hydrogen, ammonia, methane and water vapour in one big flask and allowed the condensed liquid to accumulate in another small flask. The ratio of methane, ammonia and hydrogen in the large flask was 2: 1: 2. The energy was supplied to the apparatus by heating the liquid as well as by electric sparks from tungsten's electrodes in the gaseous flask. The conditions of apparatus resembled the atmosphere present on the early earth.
Question 38: From which of the given plants is the drug whose skeletal structure is given below extracted?

- a. Papaver somniferum
- b. Atropa belladonna
- c. Cannabis sativa
- d. Erythroxylum coca
Solution:
Answer: (c)

The Skeletal structure is of cannabinoid molecule. It is obtained from Cannabis sativa.
Question 39: The allele frequency of 'A' and 'a' in a population are 0.6 and 0.4 respectively. The expected frequency of heterozygous individuals is
- a. 48%
- b. 36%
- c. 16%
- d. 24%
Solution:
Answer: (a)
In a stable population, for a gene with two alleles, 'A' (dominant) and 'a' (recessive), if the frequency of 'A' is p and the frequency of 'a' is q, then the frequencies of the three possible genotypes (AA, Aa and aa) can be expressed by the Hardy-Weinberg equation:
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1. Where p2 = Frequency of AA (homozygous dominant) individuals
q2 = Frequency of aa (homozygous recessive) individuals
2pq = Frequency of Aa (heterozygous) individuals.
So, p= 0.6 and q = 0.4 (given)
2pq (frequency of heterozygote) = 2 × 0.6 × 0.4 = 0.48 × 100 = 48%
Question 40: Identify the odd one from the following:
- a. a-Interferon
- b. Oncogenic virus
- c. Proto-oncogenes
- d. UV rays
Solution:
Answer: (a)
• Interferons are used in the treatment of cancer. Rest all are causes of cancer.
• A number of viruses are suspected of causing cancer in animals, including humans, and are frequently referred to as oncogenic viruses.
• Proto-oncogene is a normal gene which, when altered by mutation, becomes an oncogene that can contribute to cancer.
• Damage from UV exposure is cumulative and increases your skin cancer risk over time.
Question 41: During replication of a retrovirus
- a. Viral protein is introduced into the host cell.
- b. Viral RNA is introduced into the host cell.
- c. Viral DNA is introduced into the host cell.
- d. Transcriptase enzyme is introduced into the host cell
Solution:
Answer: (b)
After a retrovirus enters a host cell, reverse transcriptase converts the retroviral RNA genome into double-stranded DNA. This viral DNA then migrates to the nucleus and becomes integrated into the host genome. Viral genes are transcribed and translated.
Question 42: In malignant tumours, the cells divide rapidly and move to distant parts of the body and cause new tumours. This property is called
- a. Metastasis
- b. Metagenesis
- c. Teratogenesis
- d. Mitosis
Solution:
Answer: (a)
• In malignant tumours, the cells divide rapidly and move to distant parts of the body and cause new tumours is called metastasis.
• The alternation of generations between sexual and asexual reproduction is called metagenesis.
• Teratogenesis is prenatal toxicity characterized by structural or functional defects in the developing embryo or fetus.
• Mitosis a type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth.
Question 43: The breeding technique that is useful to expose harmful recessive genes is
- a. Outbreeding
- b. Artificial insemination
- c. Inbreeding
- d. MOET
Solution:
Answer: (c)
When breeding is done between animals of the same breed for 4−6 generations, it is called inbreeding. Inbreeding is necessary if we want to develop a pure line of any animal. It exposes harmful recessive genes that are eliminated by selection. It also helps in the accumulation of superior genes and the elimination of less desirable genes.
Question 44: Germplasm collection refers to
- a. Collection of all alleles for all genes in a crop.
- b. Collection of all alleles for few genes in a crop.
- c. Collection of different alleles for all genes in different crop plants.
- d. Collection of few alleles for all genes in several crop plants.
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The entire collection having all the diverse alleles for all genes in a given crop is called germplasm collection. It is an example of ex-situ conservation of biodiversity. Ex-situ conservation is done by preserving the components of biological diversity outside their natural habitats. It is done by conserving genetic resources, as well as wild and cultivated or species.
Question 45: The microorganisms involved in floc formation during sewage treatment are
- a. Anaerobic bacteria and fungus
- b. Aerobic bacteria and fungus
- c. Autotrophic bacteria and yeast
- d. Fungus and algae
Solution:
Answer: (b)
After the primary treatment of sewage water, primary effluent is passed into large aeration tanks, where it is constantly agitated mechanically, and the air is pumped into it. This allows vigorous growth of useful aerobic microbes into flocs (masses of bacteria associated with fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures). While growing, these microbes consume the major part of the organic matter in the effluent. It reduces the Biochemical Oxygen Demand of the effluent. The effluent is then passed into a settling tank, where the bacterial flocs are allowed to sediment. This sediment is called activated sludge.
Question 46: Match the following bacteria of List - I with their commercial products of List - II:
|
List - I |
List - II |
|
1. Lactobacillus |
I. Butyric acid |
|
2. Aspergillus niger |
II. Acetic acid |
|
3.Acetobacteraceae |
III. Lactic acid |
|
4. Clostridium butyricum |
IV. Citric acid |
Select the code for the correct answer from the options given below:
- a. 1 - III, 2 - II, 3 - IV, 4 - I
- b. 1 - I, 2 - IV, 3 - III, 4 - II
- c. 1 - III, 2 - IV, 3 - II, 4 - I
- d. 1 - III, 2 - IV, 3 - I, 4 - II
Solution:
Answer: (c)
• Lactobacilli belong to the lactic acid bacteria; they produce lactic acid and derive energy from the fermentation of lactose, glucose and other sugars to lactate.
• Citric acid is the most important organic acid produced mainly by submerged fermentation using Aspergillus Niger.
• Acetic acid is a group of Gram-negative bacteria which oxidize sugars or ethanol and produce acetic acid during fermentation. The acetic acid bacteria consist of family Acetobacteraceae.
• Clostridium butyricum is a strictly anaerobic endospore-forming Gram-positive butyric acid-producing.
Question 47: The technique of bombarding plant cells with high-velocity microparticle's of gold or tungsten, coated with DNA, is
- a. Microinjection
- b. Biolistic method
- c. Heat shock method
- d. By disarmed pathogen vector
Solution:
Answer: (b)
• Micro-injection is a method used to inject a recombinant DNA into the nucleus of an animal cell. This is the only way to introduce alien DNA into host cells.
• Biolistic or gene gun method is used for bombarding gold or tungsten coated with DNA into a plant cell.
• E. coli using the heat shock method is a basic technique of molecular biology. It consists of inserting a foreign plasmid or ligation product into bacteria.
• When the disarmed pathogen infects the cell, it transfers the recombinant DNA into the host.
Question 48: Choose the bacterium which is not a source of REN:
- a. Haemophilus influenzae
- b. Escherichia coli
- c. Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- d. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens
Solution:
Answer: (c)
The restriction enzymes are isolated from the bacterial sources and are named according to the name of the bacterial species. REN is isolated from the haemophilus influenza, E. coli and bacillus amyloliquefaciens. But no REN is extracted from Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
Question 49: Silencing of a specific mRNA translation could be achieved through
- a. Antisense RNA
- b. RNA interference technique
- c. Both (A) and (B)
- d. Microinjection
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Silencing of the gene could achieve through the use of short interfering RNA and antisense RNA because antisense RNA is a single-stranded oligonucleotide complementary to a protein-coding mRNA. It forms a ds structure with the mRNA Thus, blocking the process of translation RNA interference technique silences the targeted mRNA molecule using ds RNA.
Question 50: In which of the following steps in the DNA fingerprinting technique are labelled VNTR probes used?
- a. During isolation of DNA
- b. During digestion of DNA by REN
- c. During electrophoresis
- d. During hybridization
Solution:
Answer: (d)
The technique of DNA Fingerprinting was initially developed by Alec Jeffreys. It includes:-
• Hybridization using labelled VNTR probe,
• Digestion of DNA by restriction endonucleases,
• Separation of DNA fragments by electrophoresis,
• Transferring (blotting) of separated DNA fragments to synthetic membranes, such as nitrocellulose or nylon,
• Isolation of DNA,
• Detection of hybridised DNA fragments by autoradiography.
Question 51: dsRNA is used to develop pest-resistant tobacco plant by a technique called
- a. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
- b. RNA interference (RNAi)
- c. Electrophoresis
- d. Insertional Activation
Solution:
Answer: (b)
RNA interference involves silencing of a specific mRNA due to a complementary dsRNA molecule that binds to prevent translation of the mRNA (silencing).
Question 52: The interaction between "Cuckoo and Crow" is an example of
- a. Competition
- b. Predation
- c. Brood parasitism
- d. Mutualism
Solution:
Answer: (c)
There are some parasites found in birds. They are called brood parasites. Parasitic birds lay their eggs in the nests of other birds for incubation, hatching and rearing of young ones. For example, the cuckoo is a parasite that lays its eggs in crow’s nest. The eggs of the cuckoo (brood parasite) resemble the eggs of the crow (host) in size and colour and the crow (host bird) is not able to detect the foreign eggs.
Question 53: Verhulst-Pearl logistic growth is described by the equation dN/ dt = rN ([K - N] / K) where ‘r’ and ‘K' represent
- a. r - intrinsic rate of natural decrease, K - carrying capacity
- b. r - intrinsic rate of natural increase, K - carrying capacity
- c. r - extrinsic rate of natural increase, K - productive capacity
- d. r - extrinsic rate of natural decrease, K - carrying capacity
Solution:
Answer: (b)

The logistic growth curve is the population growth curve represented by the equation, dN / dt = rN [K − N / K], where r - the intrinsic rate of natural increase, K - carrying capacity.
Question 54: Net primary productivity (NPP) in an ecosystem is
- a. GPP - R = NPP
- b. GPP + R = NPP
- c. GPP - NPP = R
- d. R - NPP = GPP
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Net primary productivity, or NPP, is gross primary productivity minus the rate of energy loss to metabolism and maintenance.
Question 55: Which among the following is not a functional unit of the ecosystem?
- a. Decomposition
- b. Nutrient cycling
- c. Energy flow
- d. Pollution
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that causes adverse change. It is not a functional unit of the ecosystem.
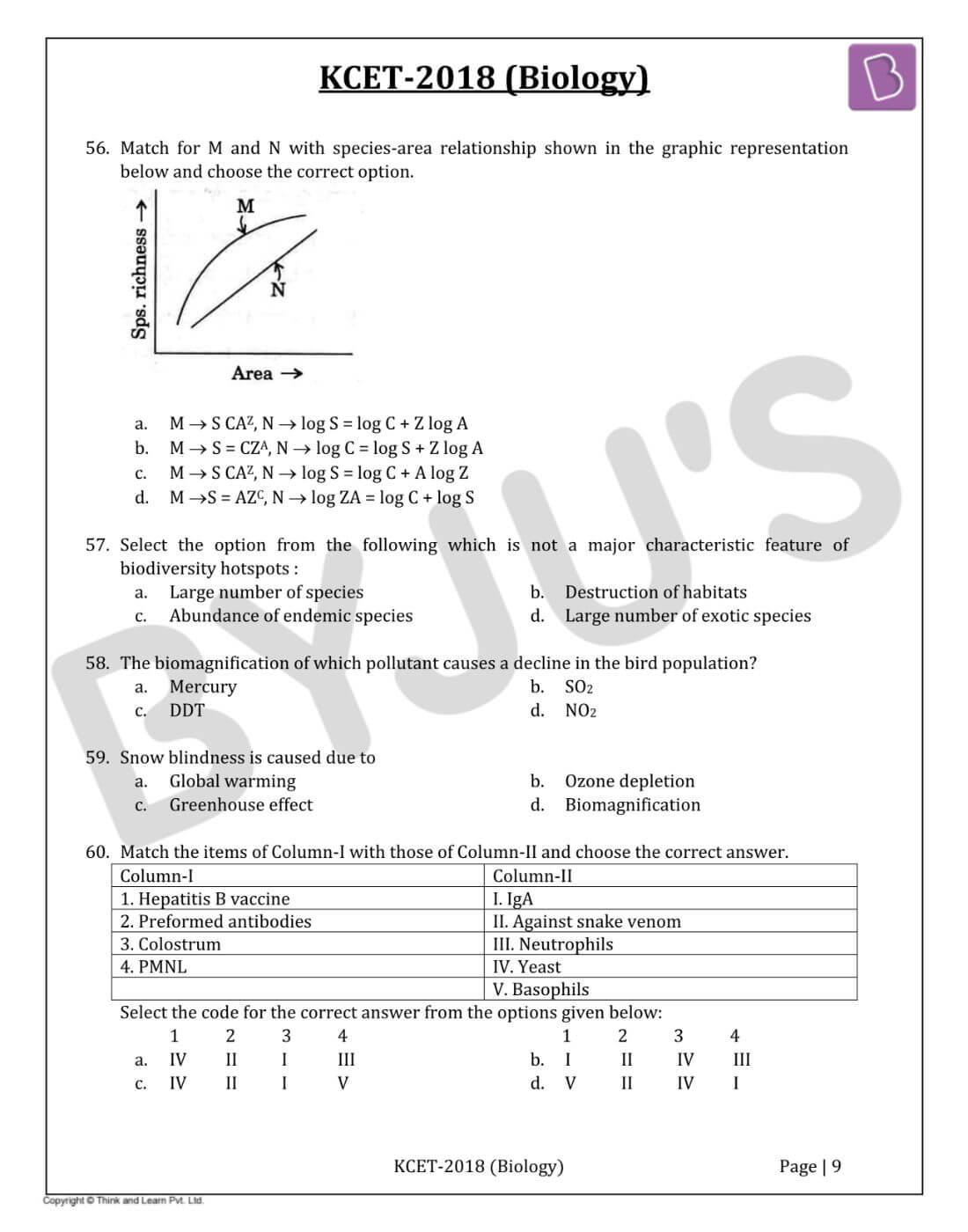
Question 56: Match for M and N with the species-area relationship shown in the graphic representation below and choose the correct option.

- a. M → S CAZ, N → log S = log C + Z log A
- b. M → S = CZA, N → log C = log S + Z log A
- c. M → S CAZ, N → log S = log C + A log Z
- d. M →S = AZC, N → log ZA = log C + log S
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The species-area relationship describes the relationship between the area of a habitat and the number of species found within that area is “M → S = CAZ, N → log S = log C + ZlogA”.
Question 57: Select the option from the following which is not a major characteristic feature of biodiversity hotspots:
- a. Large number of species
- b. Destruction of habitats
- c. Abundance of endemic species
- d. Large number of exotic species
Solution:
Answer: (b)
A Biodiversity Hotspot is an area containing a large number of species, the abundance of endemic species and a larger number of exotic species. Habitat destruction is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species is not a major feature of biodiversity hotspots.
Question 58: The biomagnification of which pollutant causes a decline in the bird population?
- a. Mercury
- b. SO2
- c. DDT
- d. NO2
Solution:
Answer: (c)
DDT is a crystalline compound which is used as an insecticide. DDT on runoff from the fields reaches the water bodies and gets accumulated in the bodies of fishes. When fishes are eaten by birds, it gets accumulated in the body of birds and hence, in this way it enters the food chain. The high concentration of DDT leads to a decline in their population.
Question 59: Snow blindness is caused due to
- a. Global warming
- b. Ozone depletion
- c. Greenhouse effect
- d. Biomagnification
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Snow blindness is the condition of loss of vision due to overexposure of UV light0074. When the layer of ozone gets depleted a large amount of UV radiation starts reaching to the earth's atmosphere and increased dose of UV radiation causes diseases.
Question 60: Match the items of Column-I with those of Column-II and choose the correct answer.
|
Column-I |
Column-II |
|
1. Hepatitis B vaccine |
I. IgA |
|
2. Preformed antibodies |
II. Against snake venom |
|
3. Colostrum |
III. Neutrophils |
|
4. PMNL |
IV. Yeast |
|
V. Basophils |
Select the code for the correct answer from the options given below:
- a. 1 - IV, 2- II, 3 - I, 4 - III
- b. 1 - I, 2 - II, 3 - IV, 4 - III
- c. 1 - IV, 2 - II, 3 - I, 4 - V
- d. 1 - V, 2 - II, 3 - IV, 4 - I
Solution:
Answer: (a)
• Human hepatitis B virus vaccine was prepared using antigen produced by recombinant technology in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae).
• Snake antivenom is a medication made up of antibodies used to treat snake bites by venomous snakes.
• Colostrum contains large numbers of antibodies called (IgA) that help protect the mucous membranes in the throat, lungs, and intestines of the infant.
• Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell i.e. leucocyte (PMNL) that helps heal damaged tissues and resolve infections.