KCET 2018 solved question paper is a perfect resource for the candidates who are appearing for KCET to have an idea of the difficulty level of the exam. The solutions are prepared in such a way that the candidates can have a crystal clear understanding of the KCET question paper. The solutions uploaded here will also enable the students to obtain a fair idea about the distribution of marks with respect to each topic. Practising these questions will help them understand the amount of preparation required to face the examination.
KCET 2018 - Chemistry
Question 1: 1.0 g of Mg is burnt with 0.28 g of O2 in a closed vessel. Which reactant is left in excess and how much?
- a. Mg, 5.8 g
- b. Mg, 0.58 g
- c. O2, 0.24 g
- d. O2, 2.4 g
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Given:
Amount of Mg = 1.0g
Amount of O2 = 0.25g
Balanced chemical reaction
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
Atomic weight of Mg = 24
Atomic weight of O = 16
Moles of Mg = given mass / atomic mass
= [1g] / [24g / mol]
= 0.0416 moles
Moles of O2 = [0.28g] / [32g / mol]
= 0.00875 moles
In this chemical reaction, O2 acts as limiting reagent.
1 mole O2 react with 2 mole Mg
0.0875 Mole O2 react with = 2 × 0.00875 moles of mg
= 0.0175 mole Mg
Number of moles of Mg left after reaction with oxygen
= 0.0416 - 0.0175
= 0.0241 moles
Weight of Mg left in excess = moles × atomic weight
= 0.0241×24
= 0.578
≈ 0.58 g
Question 2: The orbital nearest to the nucleus is
- a. 4f
- b. 5d
- c. 4s
- d. 7p
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Penetration power of the electron describes how much it is closer to the nucleus. Penetration power of an electron follows:
1S > 2S > 2P > 3S > 3P > 4S > 3d > 4P > 5S > 4d > 5P > 6S
Sub shell penetration power follows:
S > P > D > F
So, 4S orbital is closer to the nucleus among the other 4f, 5d, 7p orbital.
Question 3: Which of the following is the correct order of radius?
- a. H– > H > H+
- b. Na+ > F– > O2–
- c. F– > O2– > Na+
- d. Al3+ > Mg2+ > N3–
Solution:
Answer: (a)
The correct order of radius:
H– > H > H+
Size of an atom is directly proportional to the atomic radius if size increases, the atomic radius also increases. Addition of an extra electron in an atom increases the size of the atom as compared to neutral atom and removal of an electron (cation) makes the atom size shorter than the parent atom.
Question 4: The intramolecular hydrogen bond is present in
- a. Phenol
- b. o-Nitrophenol
- c. p-Nitrophenol
- d. p-Cresol
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding:
When H - atom of one molecule forms a bond with an atom of the electronegative element. Intramolecular H-bonding presents in O – nitrophenol.

Intramolecular hydrogen –bonding
Question 5: The state of hybrid orbitals of carbon in CO2, CH4 and CO32- respectively is
- a. sp3, sp2 and sp
- b. sp3, sp and sp2
- c. sp, sp3 and sp2
- d. sp2, sp3 and sp
Solution:
Answer: (c)
According to VSEPR theory, we can use the steric number to determine the hybridization of an atom. SN = number of lone pairs + number of atoms directly attached to the central atom.
For

SN = 0 + 2 = 2 = S P hybridization
That means one S and one P hybrid orbital participate in hybridization.
For CH4:

SN = 0 + 4 = SP3 hybridization
Here, one S and three P hybrid orbitals participate in hybridization.
For CO32-:

SN = 0 + 3 = SP2 hybridization
In CO32- ions
That means one S and two P hybrid orbitals participate in hybridization.
Question 6: For an ideal gas, the compressibility factor is
- a. 0
- b. 1
- c. –1
- d. +2
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Compressibility factors of an ideal gas to describe the deviation of a real gas behaviour from an ideal gas, compressibility factor represented by Z.
Z= PV / nRT
For an ideal gas, the value of Z is always unity = 1.
Question 7: The relationship between Kp and Kc is Kp = Kc(RT)Δn. What would be the value of Δn for the reaction, NH4Cl(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + HCl(g)?
- a. 1
- b. 0.5
- c. 1.5
- d. 2
Solution:
Answer: (d)
For the reaction: NH4Cl(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + HCl(g)
Δng = Number of moles of gaseous product – Number of moles of reactant
Δng = 2 – 0
Δng = 2
Question 8: Acidity of BF3 can be explained on which of the following concepts?
- a. Arrhenius concept
- b. Bronsted-Lowry concept
- c. Lewis concept
- d. Bronsted-Lowry as well as Lewis concept
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Lewis concept:
According to Lewis acid-base theory bases are lone pair donors and acids are lone pair acceptors.
BF3 molecules are electron deficient.
Electronic configuration of boron = 1S2, 2S2, 2P1
Excited state electronic configuration of boron = 1S2, 2S2, 2P1x, 2P1y, Pz
After bond formation with the fluorine atom, boron has one vacant P-orbitals which makes the molecule electron deficient. BF3 very energetically reacts with water and ammonia that has available lone pairs.
Question 9: For the redox reaction
xMnO4– + yH2C2O4 + zH+ → mMn2+ + n CO2 + pH2O
- a. 10, 2, 5, 2
- b. 2, 5, 2, 10
- c. 6, 4, 2, 5
- d. 3, 5, 2, 10
Solution:
Answer: (b)
For redox reaction
xMnO4– + yH2C2O4 + zH+ → mMn2+ + n CO2 + pH2O
Skeletal equation
(1) MnO4- + H2C2O4 → Mn+2 + CO2
C oxidized, +3 → +4 ∴ H2C2O4 is the reducing agent
Mn reduced, +7 → +2 ∴ MnO4– is the oxidizing agent
(2) Balancing the equation other than H and O.
Oxidized; H2C2O4 → 2CO2
Reduction: MnO4– → Mn+2
(3) Balance oxygen by addition of H2O
Oxidation: H2C2O4 → 2CO2 + 2H+
Reduction: MnO4– → Mn+2 + 4H2O
(4) Balance hydrogen by adding H+
Oxidation: H2C2O4 → 2CO2 + 2H+
Reduction: 8H+ + MnO4– → Mn+2 + 4H2O
(5) Balance charge by addition of electrons.
Oxidation: H2C2O4 → 2CO2 + 2H+ + 2e–
Reduction: 5e– + 8H+ + MnO4– → Mn+2 + 4H2O
(6) 5× [Oxidation: H2C2O4 → 2CO2 + 2H+ + 2e–] 2 × [reduction: 5e– + 8H+ + MnO4– → Mn+2 + 4H2O]
Add half reactions together, simplify (cancel species that are same on the both sides of the equation);
5H2C2O4 + 10e– + 16H+ + 2MnO4– → 10CO2 + 10H+ + 10e– + 2Mn+2 + 8H2O
So, the final balanced redox reaction:
5H2C2O4(aq) + 2MnO4–(aq) + 6H+(aq) → 10CO2 (g) + 2Mn+2 (aq) + 8H2O (l)
Question 10: H2O2 is
- a. An oxidizing agent
- b. A reducing agent
- c. Both oxidizing and reducing agent
- d. Neither oxidizing nor reducing agent
Solution:
Answer: (c)
H2O2 acts as both oxidizing and reducing agent oxygen of H2O2 (-1 oxidation state) is reduced to H2O (–2 oxidation state) acts as an oxidizing agent. When the oxygen of H2O2 (-1 oxidation state) is oxidized to (0) oxidation state acts as a reducing agent.
Question 11: Dead burnt plaster is
- a. CaSO4
- b. CaSO4 · (1 / 2) H2O
- c. CaSO4 · H2O
- d. CaSO4 · 2H2O
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Plaster of Paris (CaSO4 . 1 / 2 H2O) is heated above 393K, it’s half water molecule last to crystallization and anhydrous calcium sulphate is left which is called as dead burnt plaster (CaSO4).
Question 12: Identify the following compound which exhibits geometrical isomerism:
- a. But-2-ene
- b. But-1-ene
- c. Butane
- d. Isobutane
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Geometrical isomerism (cis-trans isomerism):-
This isomerism occurs where restricted rotation is found in a molecule. Usually, involve the carbon-carbon double bond containing compound.

In one case, the CH3 groups are on opposite sides of the double bond and in the other case, they are on the same side.
Question 13: During the fusion of organic compound with sodium metal, nitrogen present in the organic compound is converted into
- a. NaNO2
- b. NaNH2
- c. NaCN
- d. NaNC
Solution:
Answer: (c)
When an organic compound reacts with sodium (Na) metal, its nitrogen is converted in sodium cyanide.
Chemical reaction:

Question 14: The reagent ‘X’ used for the following reaction is

- a. Ni
- b. Pd/C
- c. LiAlH4
- d. Na/Liquid NH3
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Hydrogenation of an alkyne with Pd/C gives cis alkane.

Lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4) does not reduce alkynes, reducing only if an alcohol group is nearby.
Question 15: Which of the following ions will cause hardness in water?
- a. Ca2+
- b. Na+
- c. Cl–
- d. K+
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Hardness in water:
Calcium and magnesium carbonates or bicarbonates dissolved in the water are the two most common minerals that make water "hard".
Water which does not give lather with soap is hard water.
Question 16: Which of the following oxides shows electrical properties like metals?
- a. SiO2
- b. MgO
- c. SO2(s)
- d. CrO2
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Transition metal oxides show electrical properties like metals. CrO2 (chromium oxides) is a good conductor of electricity. It is ferromagnetic at room temperature. The Curie temperature is 118° C and the material readily is demagnetized with little energy input. The electrical conductivity of this black compound is quite high.
Question 17: Which of the following aqueous solutions should have the highest boiling point?
- a. 1.0 M NaOH
- b. 1.0 M Na2SO4
- c. 1.0 M NH4NO3
- d. 1.0 M KNO3
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Colligative properties of solutions are properties that depend upon the concentration of solute molecules or ions but not the identity of the solute. Concentrations of all the solutions are the same given one. So, colligative property (elevation in boiling point) depends only on the number of ions or molecules. The boiling point increases as the number of ions increases in the aqueous solutions.
1M NaOH gives the number of ions = 2
1M Na2SO4 gives the number of ions = 3
1M NH4SO4 gives the number of ions = 2
1M KNO3 gives the number of ions = 2
So, 1M Na2SO4 has the maximum boiling point among them all.
Question 18: The charge required for the reduction of 1 mole of MnO4− to MnO2 is
- a. 1 F
- b. 3 F
- c. 5 F
- d. 7 F
Solution:
Answer: (b)

Change is oxidation state = 7 – 4 = + 3
The amount of electric charge carried by one mole of electrons (6.02 × 1023 electrons) is called the Faraday (F) and is equal to 96,500 coulombs.
1-mole e– required 1F electric charge
3 mole e– required 3F electric charge
To reduce MnO4− to MnO2 we require 3 moles of the electron charge.
Question 19: For the reaction, 2SO2 + O2 ⇌ 2SO3, The rate of disappearance of O2 is 2 × 10–4 mol L–1 s–1. The rate of appearance of SO3 is
- a. 2 × 10–4 mol L–1 s–1
- b. 4 × 10–4 mol L–1 s–1
- c. 1 × 10–1 mol L–1 s–1
- d. 6 × 10–4 mol L–1 s–1
Solution:
Answer: (b)
For the reaction
2SO2 + O2 ⇌ 2SO3
Rate of reaction
(-1 / 2) {d [SO2] / dt} = {-d [O2] / dt} = (1 / 2) {d [SO3] / dt}
Rate of disappearance of O2 = 2 × 10–4 mol L–1 S–1
Then,
{-d [O2] / dt} = (1 / 2) {d [SO3] / dt}
2 × 10–4 = (1 / 2) {d [SO3] / dt}
{d [SO3] / dt} = 4 × 10–4 mol L–1 s–1
Rate of appearance of SO3 = 4 × 10–4 mol L–1 s–1
Question 20: Which of the following electrolytes will have maximum coagulating value for AgI / Ag+ sol?
- a. Na2S
- b. Na3PO4
- c. Na2SO4
- d. NaCl
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Different electrolytes have different coagulation values. Smaller the coagulation value of the electrolyte larger is its coagulating or precipitating power.
Coagulating power ∝ (1 / Coagulation value or flocculation value)
According to Hardy-Schulze law, the greater the charge on anion greater the coagulating power.
Electrolyte
Anion
Charge
Na2S
S2-
2
Na3PO4
PO43-
3
Na2SO4
SO42-
2
NaCl
Cl-
1
So, NaCl has lowest anionic charge and maximum coagulating power.
Question 21: Electrolytic refining is used to purify which of the following metals?
- a. Cu and Zn
- b. Ge and Si
- c. Zr and Ti
- d. Zn and Hg
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Electrolytic refining:
It is a process of refining a metal (mainly copper and Zinc) by the process of electrolysis.
During electrolysis, impure metal is used as anode with a thin strip of pure metal at the cathode. In this setup, an electrolyte (metal salt aqueous solution) depending on the metal is after use.
The pure metal is obtained at the cathode when the electric current of a sufficient voltage is applied by dissolving metal to the anode. It is about 99.95% pure which makes it a good product.
Question 22: Dry ice is
- a. Solid CO
- b. Solid SO2
- c. Solid CO2
- d. Solid O2
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Dry ice: Dry ice is a common name for solid carbon dioxide (CO2). It gets this name because it does not melt into a liquid when heated; Instead, it changes directly into a gas (a process known as sublimation).
Question 23: Which of the following is an amphoteric oxide?
- a. V2O5, Cr2O3
- b. Mn2O7, Cr2O3
- c. CrO, V2O5
- d. V2O5, V2O4
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Amphoteric oxides can react with both acids and bases to form salt and water as the main products.
The element that forms amphoteric oxides has some metals and some of the nonmetals characteristics.
Amphoterism based on oxide's oxidation state.
Both Cr2O3 and V2O5 are amphoteric in nature because of their high oxidation state.
V2O5 reacts with alkalies as well as acids to give VO43– and VO4+ respectively.
Cr2O3 (chromium (III) oxide) insoluble in water but dissolves in acid to produce hydrated chromium ions,[Cr(H2O)6]+3 which react with a base to give slat of [Cr(OH)6]3–
It dissolved in concentrated alkali to yield chromite ions [CrO2]–.
Question 24: The IUPAC name of [Co(NH3)4Cl(NO2)] Cl is
- a. tetraamminechloridonitrito-N-cobalt(III) chloride
- b. tetraamminechloridonitrocobalt(II) chloride
- c. tetraamminechloridonitrocobalt(I) chloride
- d. tetraamminechloridodinitrocobalt(III) chloride
Solution:
Answer: (a)
First, write the name of the cationic part and then anionic part. After that ligands name in alphabetical order and then the name of the metal atom.
For ambidentate ligands here we use –N– before the name of metal ion, because the nitrogen of – NO2 ligand is directly attached to the cobalt metal.
After the name of metal ion with its oxidation state in roman number and then anionic ligand name [Co(NH3)4Cl(NO2)] Cl
x+ (0) 4 + (–1) + (–1) = +1
x = + 3
IUPAC name of this complete is tetraamminechloridonitrito –N–cobalt (III) chloride.
Question 25: Which of the following statements is true in the case of alkyl halides?
- a. They are polar in nature
- b. They can form hydrogen bonds
- c. They are highly soluble in water
- d. They undergo addition reactions
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Polarity results from the uneven partial charge distribution between various atoms in a compound. More the electronegativity difference between two atoms more will be the polarity of that compound. In alkyl halide, the carbon-hydrogen bond is polar because all the halogen is more electronegative than carbon. Due to high electronegativity of halogens, they pull electrons of carbon towards them so, on carbon, a small positive charge (δ+) and on halogen partial negative charge (δ–) developed. As the Alkyl halides have a polar bond they are not soluble in water not form H-bond also.
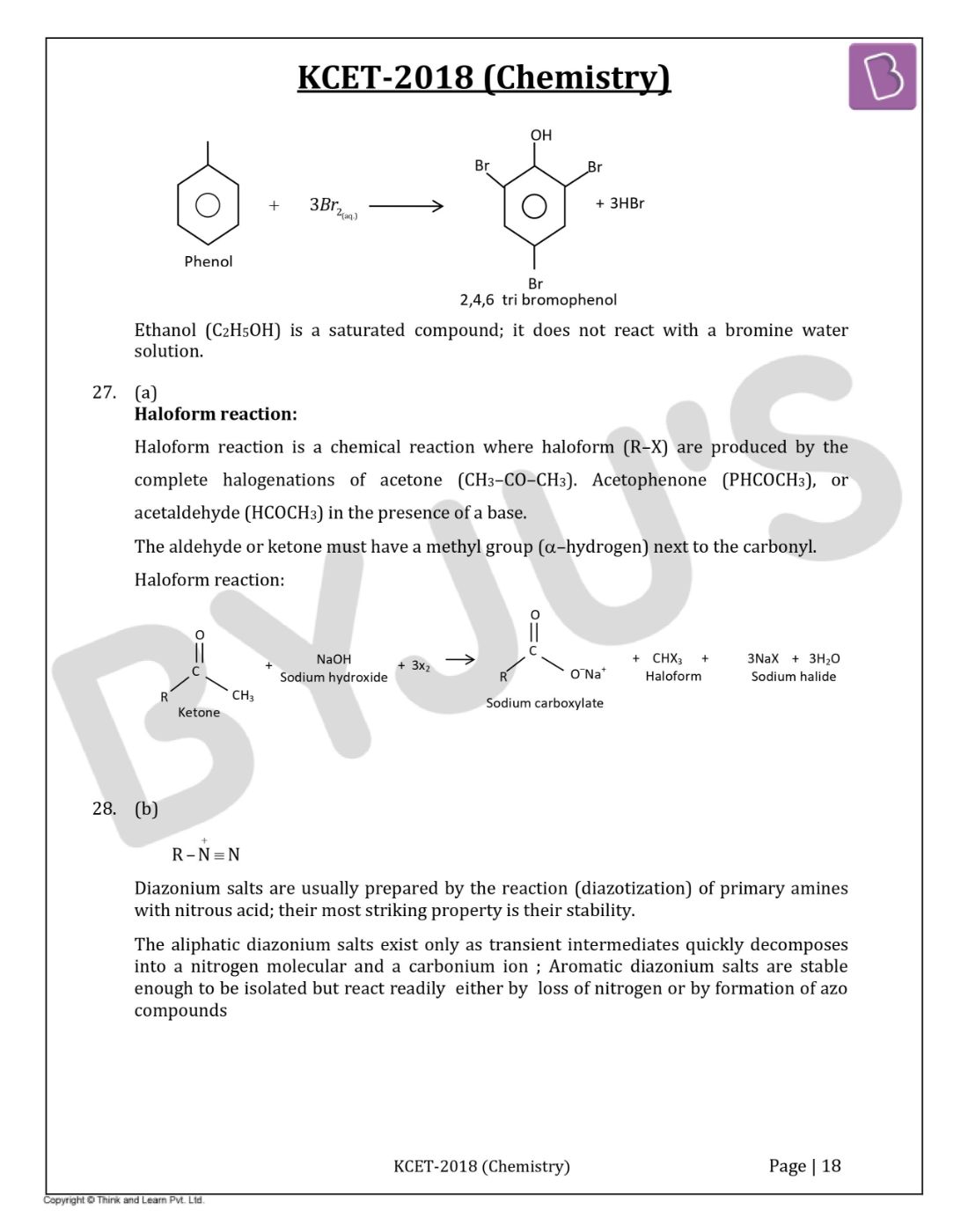
Question 26: Phenol can be distinguished from ethanol by the reagent
- a. Bromine water
- b. Sodium metal
- c. Iron metal
- d. Chlorine water
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Bromine water test (Saturation test):- The bromine water test used to identify the alkene or alkane functional groups. phenols undergo substitution reaction in the presence of bromine water to give a brominated product. During the process, bromine water is decolourized and gives white precipitate.

Ethanol (C2H5OH) is a saturated compound; it does not react with a bromine water solution.
Question 27: Which of the following compounds undergoes haloform reaction?
- a. CH3COCH3
- b. HCHO
- c. CH3CH2Br
- d. CH3 – O– CH3
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Haloform reaction:
Haloform reaction is a chemical reaction where haloform (R–X) is produced by the complete halogenations of acetone (CH3 – O– CH3). Acetophenone (PHCOCH3), or acetaldehyde (HCOCH3) in the presence of a base.
The aldehyde or ketone must have a methyl group (–hydrogen) next to the carbonyl.
Haloform reaction:

Question 28: Which of the following will be the most stable diazonium salt (RN2+X-)?
- a. CH3 N2+ X–
- b. C6H5 N2+ X–
- c. CH3CH2 N2+ X–
- d. C6H5CH2 N2+ X–
Solution:
Answer: (b)

Diazonium salts are usually prepared by the reaction (diazotization) of primary amines with nitrous acid; their most striking property is their stability.
The aliphatic diazonium salts exist only as transient intermediates quickly decompose into a nitrogen molecular and a carbonium ion; Aromatic diazonium salts are stable enough to be isolated but react readily either by loss of nitrogen or by the formation of azo compounds.

C6H5 N2+ X– is more stable in comparison to C6H5 N2+ X– because resonance stabilized due to direct bond with nitrogen.
Question 29: Which of the following bases is not present in DNA?
- a. Adenine
- b. Guanine
- c. Cytosine
- d. Uracil
Solution:
Answer: (d)
DNA is made up of nucleotides. A nucleotide has two compounds: a backbone, made from the sugar deoxyribose, phosphate groups, and nitrogenous bases, known as cytosine, thymine, adenine, and guanine.
Adenine and Uracil are the main basic building block of RNA.
Question 30: Which one of the following is a polyamide polymer?
- a. Terylene
- b. Nylon-6, 6
- c. Buna-S
- d. Bakelite
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Polyamide polymers are the polycondensation product of a diacid chloride and a diamine.
Nylon-6, 6 is a member of the polyamide group.
The structural unit of polyamide is joined together by an amide

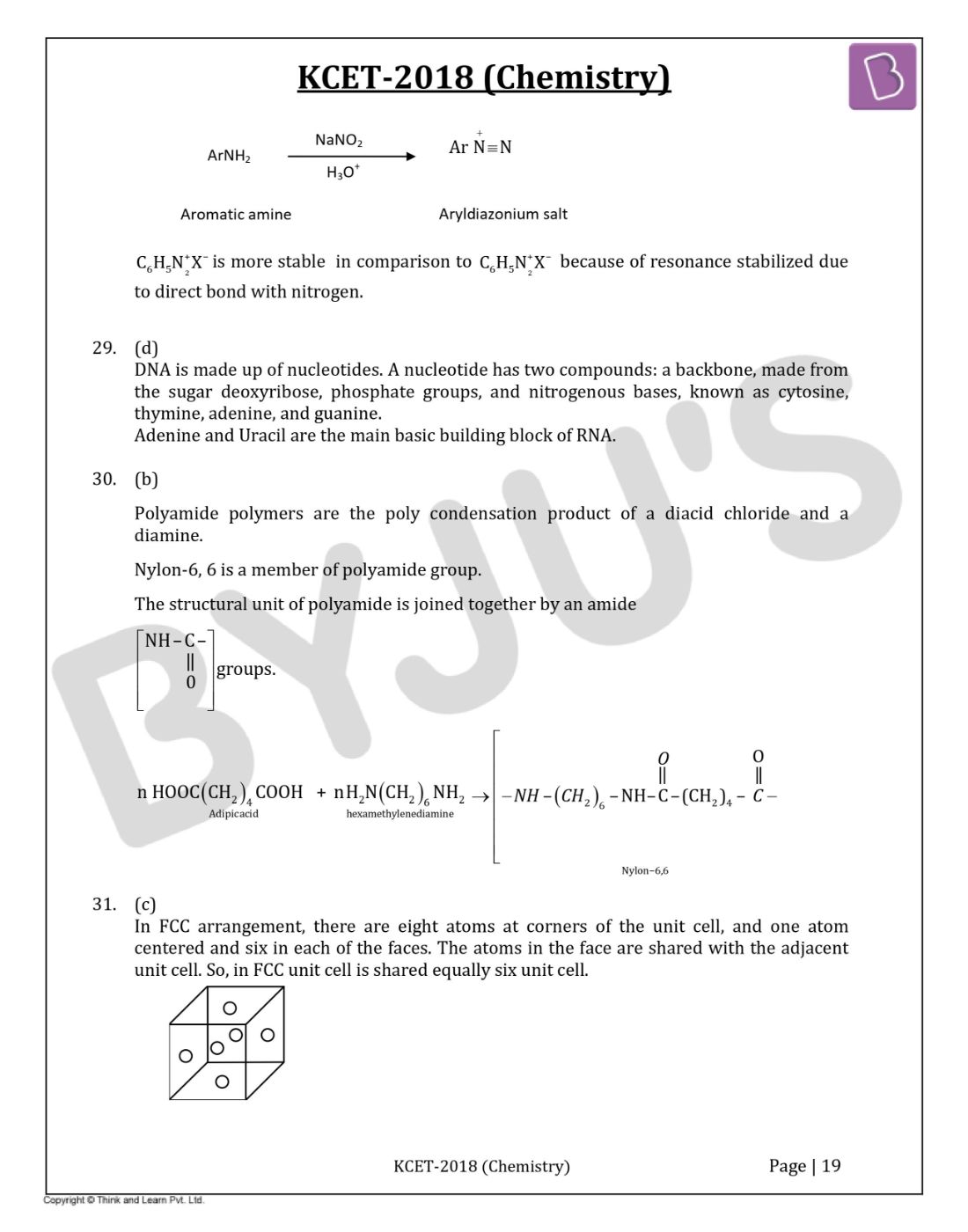
Question 31: In F.C.C. the cell is shared equally by how many unit cells?
- a. 10
- b. 8
- c. 6
- d. 2
Solution:
Answer: (c)
In FCC arrangement, there are eight atoms at corners of the unit cell, and one atom centred and six in each of the faces. The atoms in the face are shared with the adjacent unit cell. So, an FCC unit cell is shared equally by six-unit cell.

Atoms present on the six faces of the face-centred unit cell.
Question 32: At a particular temperature, the ratio of molar conductance to specific conductance of 0.01 M NaCl solution is
- a. 105 cm3mol–1
- b. 103 cm3mol–1
- c. 10 cm3mol–1
- d. 105 cm2mol–1
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Given
Concentration = 0.01 m

Question 33: Isotonic solutions are solutions having the same
- a. Surface tension
- b. Vapour pressure
- c. Osmotic pressure
- d. Viscosity
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Isotonic solution
Two solutions having the same osmotic pressure across a semipermeable membrane is referred to as an isotonic solution.
It has the same osmolarity (solute concentration) as another solution.
Question 34: The temperature coefficient of a reaction is 2. When the temperature is increased from 30° C to 90°C, the rate of reaction is increased by
- a. 150 times
- b. 410 times
- c. 72 times
- d. 64 times
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Given that
Temperature coefficient = 2
T1 = 30°C
T2 = 90° C
Rate of the reaction (R) = (Temperature coefficient) ΔT/10
=2{(90-30)/10}
= 26
R = 64
So, the rate of reaction is increased by 64 times.
Question 35: Gold sol is not a
- a. Lyophobic sol
- b. Negatively charged sol
- c. Macromolecular sol
- d. Multimolecular colloid
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Gold sol is an example of multimolecular colloid. In multimolecular colloids many particles (atoms or small molecules) of the dispersed phase aggregate together to form species having the size of a colloidal particle (1–1000 nm).
Question 36: The common impurity present in bauxite is
- a. CuO
- b. ZnO
- c. Fe2O3
- d. Cr2O3
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Major impurities in bauxite are iron oxides [hematite (Fe2O3) & goethite], silicon dioxide, the clay mineral kaolinite as well as a small amount of anatase (TiO2).
Question 37: Very pure N2 can be obtained by
- a. Thermal decomposition of ammonium dichromate
- b. Treating aqueous solution of NH4Cl and NaNO2
- c. Liquefaction and fractional distillation of liquid airMidbrain
- d. Thermal decomposition of sodium azide
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Thermal decomposition of ammonium dichromate:

Treatment of an aqueous solution of NH4Cl and NaNO2
NH4Cl + NaNO2 → NaCl + N2 ↑ + 2H2O
Thermal decomposition of sodium azide:

From the above decomposition of sodium azide gives maximum and very pure N2 gas.
Question 38: Which of the following oxidation states is common for all lanthanides?
- a. + 2
- b. + 3
- c. + 4
- d. + 5
Solution:
Answer: (b)
The lanthanides consist of the elements in the f-block of period six, in the periodic table. Lanthanides' most common and stable oxidation state is +3. It is obtained by removing three outermost electrons from 6S orbital and one electron from 4f orbital. Removal of one more electron from the 4f subshell is difficult because of high energy difference.
Question 39: The electronic configuration of transition element “X” is +3, the oxidation state is [Ar]3d5. What is its atomic number?
- a. 25
- b. 26
- c. 27
- d. 24
Solution:
Answer: (b)
The electronic configuration of X after removal of three electrons is X+3: [Ar] 3d5. So, before the removal of electrons.
This compound contains X = 18 + 5 + 3 = 26e–.
The atomic number of X is 26.
Question 40: n-Propyl chloride reacts with sodium metal in dry ether to give
- a. CH3-CH2-CH2–CH2–CH2–CH3
- b. CH3-CH2-CH3
- c. CH3-CH2-CH2–CH3
- d. CH3-CH2-CH2–CH2–CH2–CH2–CH3
Solution:
Answer: (a)

n–propyl chloride reacts with sodium metal in presence of dry ether to give n-hexane, this reaction is known as Wurtz reaction.
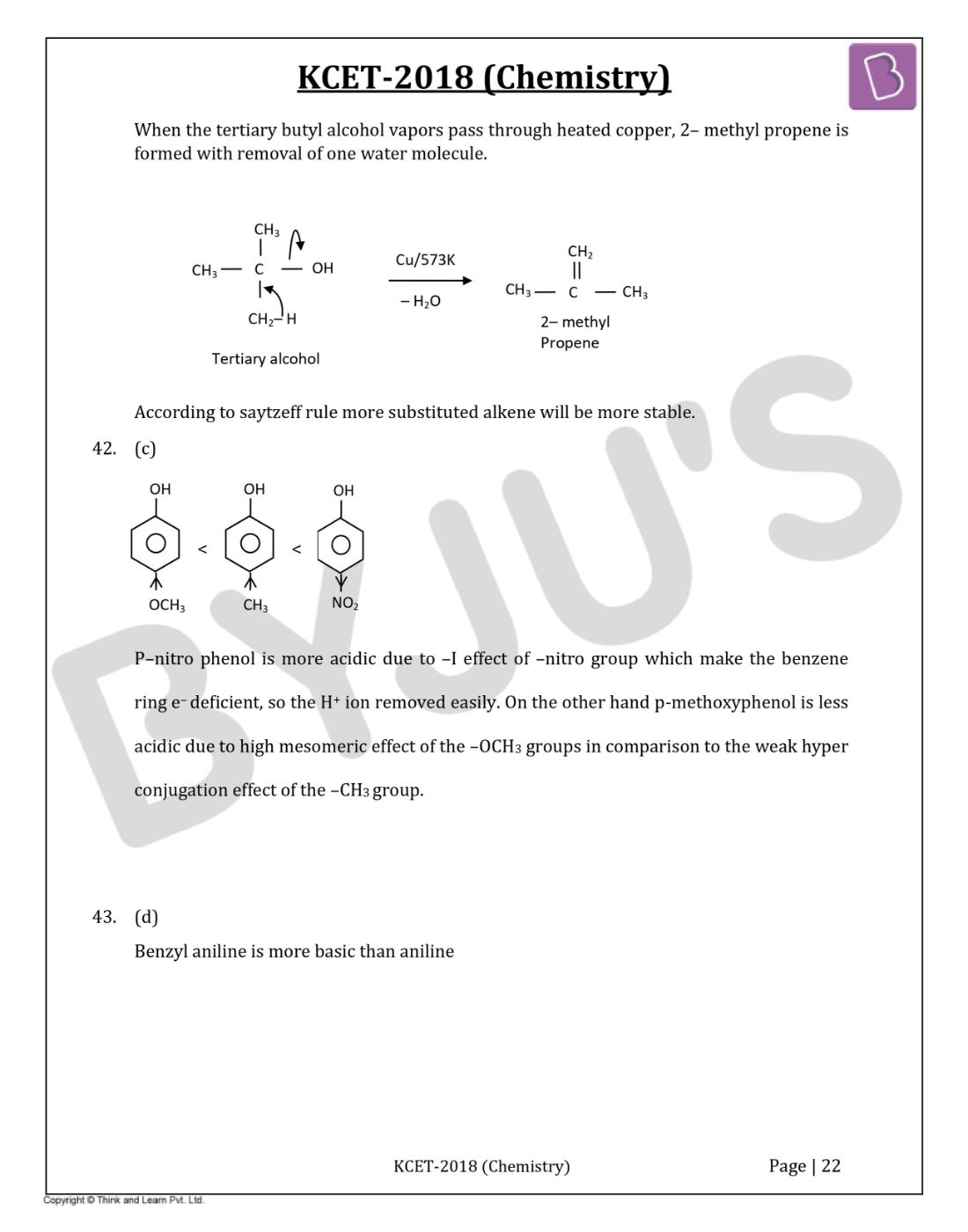
Question 41: When the vapours of tertiary butyl alcohol are passed through heated copper at 573 K, the product formed is
- a. But-2-ene
- b. 2-Butanone
- c. 2-Methyl propene
- d. Butanal
Solution:
Answer: (c)
When the tertiary butyl alcohol vapours pass through heated copper, 2– methyl propene is formed with the removal of one water molecule.

According to the Saytzeff rule, more substituted alkene will be more stable.
Question 42: What is the increasing order of acidic strength among the following?
(i) p-methoxy phenol
(ii) p-methyl phenol
(iii) p-nitro phenol
- a. ii < iii <i
- b. iii < ii <i
- c. i< ii < iii
- d. i< iii < ii
Solution:
Answer: (c)

P–nitrophenol is more acidic due to –I effect of –nitro group which makes the benzene ring e– deficient, so the H+ ion is removed easily. On the other hand, p-methoxy phenol is less acidic due to the high mesomeric effect of the –OCH3 groups in comparison to the weak hyperconjugation effect of the –CH3 group.
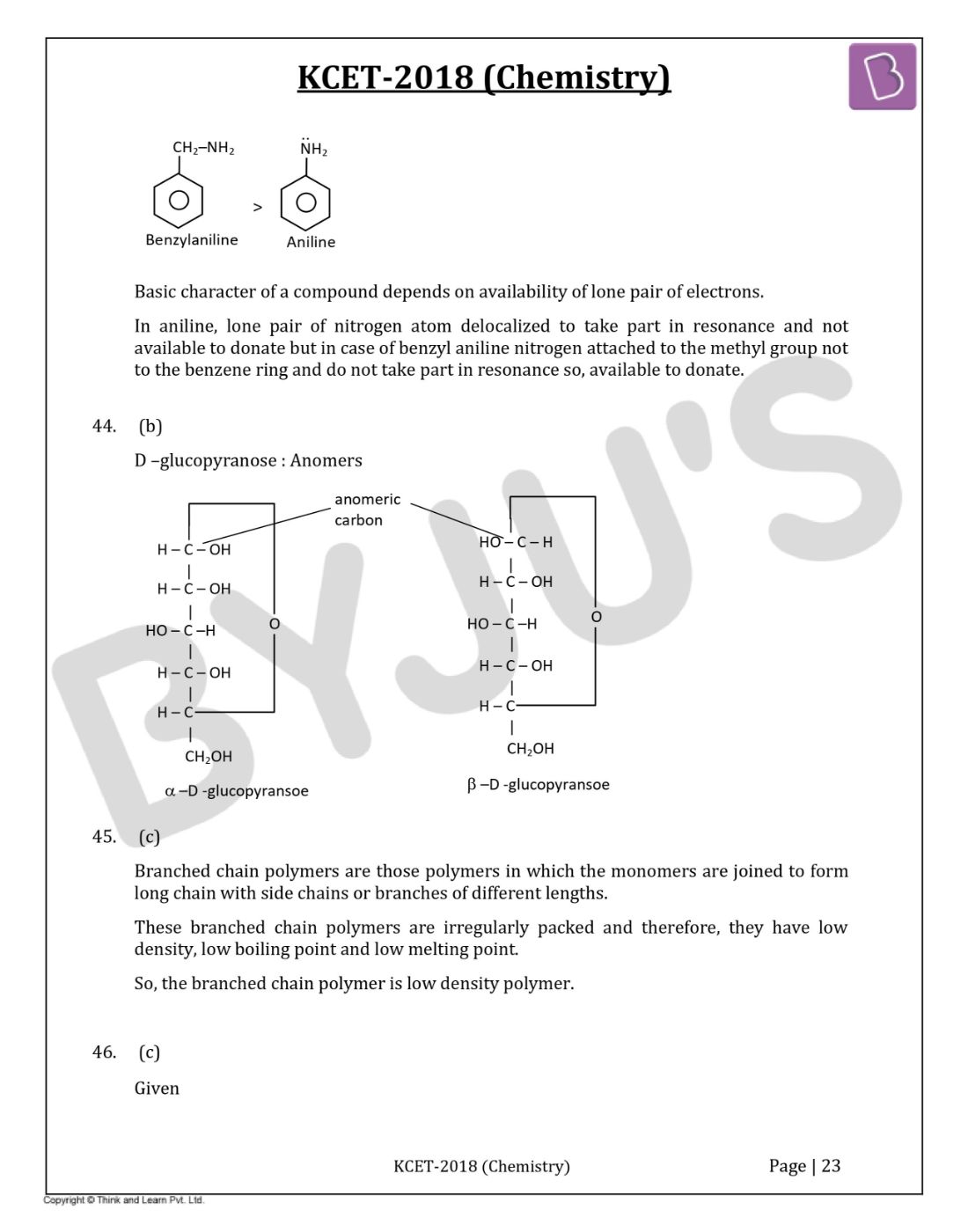
Question 43: Which of the following is more basic than aniline?
- a. Diphenylamine
- b. Triphenylamine
- c. p-nitroaniline
- d. Benzylamine
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Benzyl aniline is more basic than aniline.

The basic character of a compound depends on the availability of a lone pair of electrons.
In aniline, lone pair of nitrogen atom delocalized to take part in resonance and not available to donate but in case of benzyl aniline nitrogen attached to the methyl group, not to the benzene ring and do not take part in resonance so, available to donate.
Question 44: The two forms of D-Glucopyranose are called
- a. Diastereomers
- b. Anomers
- c. Epimers
- d. Enantiomers
Solution:
Answer: (b)
D –glucopyranose: Anomers

Question 45: Among the following, the branched-chain polymer is
- a. Polyvinyl chloride
- b. Bakelite
- c. Low-density polythene
- d. High-density polythene
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Branched-chain polymers are those polymers in which the monomers are joined to form a long chain with side chains or branches of different lengths.
These branched-chain polymers are irregularly packed and therefore, they have low density, low boiling point and low melting point.
So, the branched-chain polymer is a low-density polymer.
Question 46: Edge length of a cube is 300 pm. Its body diagonal would be
- a. 600 pm
- b. 423 pm
- c. 519.6 pm
- d. 450.5 pm
Solution:
Answer: (c)
Given
Edge length of a cube (a) = 300 pm.
Body = √3.a.
Diagonal = √3 . 300
= 1.732 × 300
= 519.6 pm
Body diagonal would be 519.6 pm.
Question 47: Which of the following is not a conductor of electricity?
- a. Solid NaCl
- b. Cu
- c. Fused NaCl
- d. Brine solution
Solution:
Answer: (a)
To conduct electricity compound must-have free electrons or ions. In solid-state NaCl, the compound has a fixed composition of ions. So these ions do not move from their place to conduct electricity. But in molten states (moist) ions are free to move to conduct electricity. So, in the molten state, they are a good conductor of electricity.
Question 48: For a cell reaction involving two-electron changes, E0cell = 0.3 V at 25° C. The equilibrium constant of the reaction is
- a. 10–10
- b. 3 × 10–2
- c. 10
- d. 1010
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Nernt’s equation
For a cell reaction:
F (faraday) = 96500
R = gas constant (8.314 J mol–1 k–1)
T = Temperature (k)
n = charge
E0cell = (2.303RT / nF) log k
E0cell = {(2.303 * 8.314 * 298) / (2 * 96500)} log k
= (0.059 / 2) log k
Given
E0cell = 0.3 V
0.3 = 0.0295 log k or
0.3 = 0.03 log k
k = antilog 10
k = 1010
Equilibrium constant of the reaction is 1010.
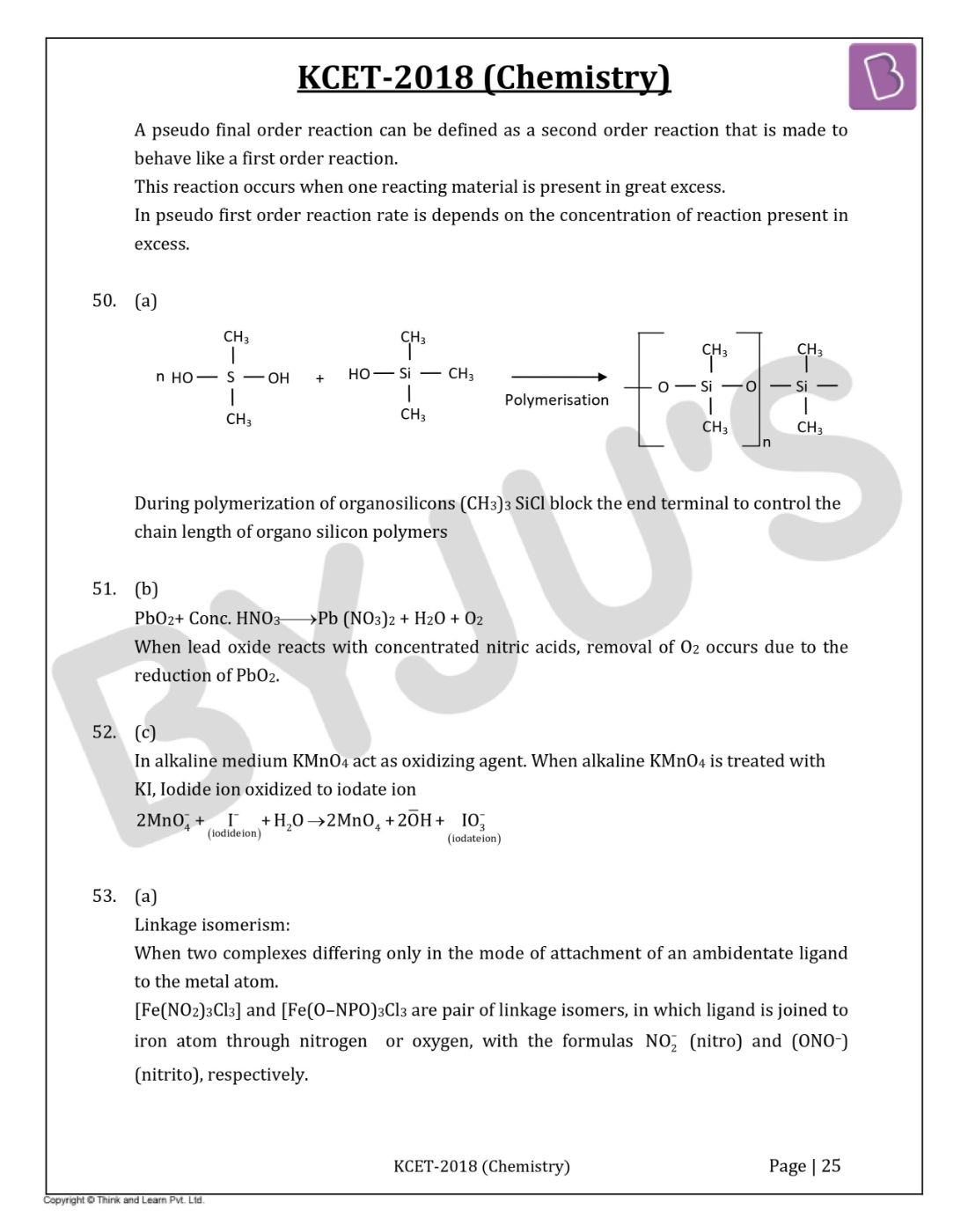
Question 49: The value of rate constant of a pseudo-first-order reaction
- a. Depends only on temperature
- b. Depends on the concentration of reactants present in small amounts
- c. Depends on the concentration of reactants present in excess
- d. Is independent of the concentration
Solution:
Answer: (c)
A pseudo final order reaction can be defined as a second-order reaction that is made to behave like a first-order reaction.
This reaction occurs when one reacting material is present in great excess.
In pseudo-first-order reaction rate depends on the concentration of reaction present in excess.
Question 50: (CH3)3SiCl is used during polymerization of organosilicons because
- a. The chain length of organosilicon polymers can be controlled by adding (CH3)SiCl
- b. (CH3)3SiCl does not block the end terminal of silicone polymer
- c. (CH3)3SiCl does not block the end terminal of silicone polymer
- d. (CH3)3SiCl acts as a catalyst during polymerisation
Solution:
Answer: (a)

During polymerization of organosilicons (CH3)3SiCl block the end terminal to control the chain length of organosilicon polymers.
Question 51: When PbO2 reacts with concentrated HNO3, the gas evolved is
- a. NO2
- b. O2
- c. N2
- d. N2O
Solution:
Answer: (b)
PbO2 + Conc. HNO3 → Pb (NO3)2 + H2O + O2
When lead oxide reacts with concentrated nitric acids, removal of O2 occurs due to the reduction of PbO2.
Question 52: KMnO4 acts as an oxidizing agent in alkaline medium. When alkaline KMnO4 is treated with KI, iodide ion is oxidized to
- a. I2
- b. IO–
- c. IO3−
- d. IO4–
Solution:
Answer: (c)
In the alkaline medium KMnO4 acts as an oxidizing agent. When alkaline KMnO4 is treated with KI, Iodide ion is oxidized to iodate ion.

Question 53: [Fe(NO2)3 Cl3] and [Fe(O–NO)3 Cl3] shows
- a. Linkage isomerism
- b. Geometrical isomerism
- c. Optical isomerism
- d. Hydrate isomerism
Solution:
Answer: (a)
Linkage isomerism: When two complexes differ only in the mode of attachment of an ambidentate ligand to the metal atom. [Fe(NO2)3Cl3] and [Fe(O–NPO)3Cl3 are pair of linkage isomers, in which ligand is joined to iron atom through nitrogen or oxygen, with the formulas NO2– (nitro) and (ONO–) (nitrito), respectively.
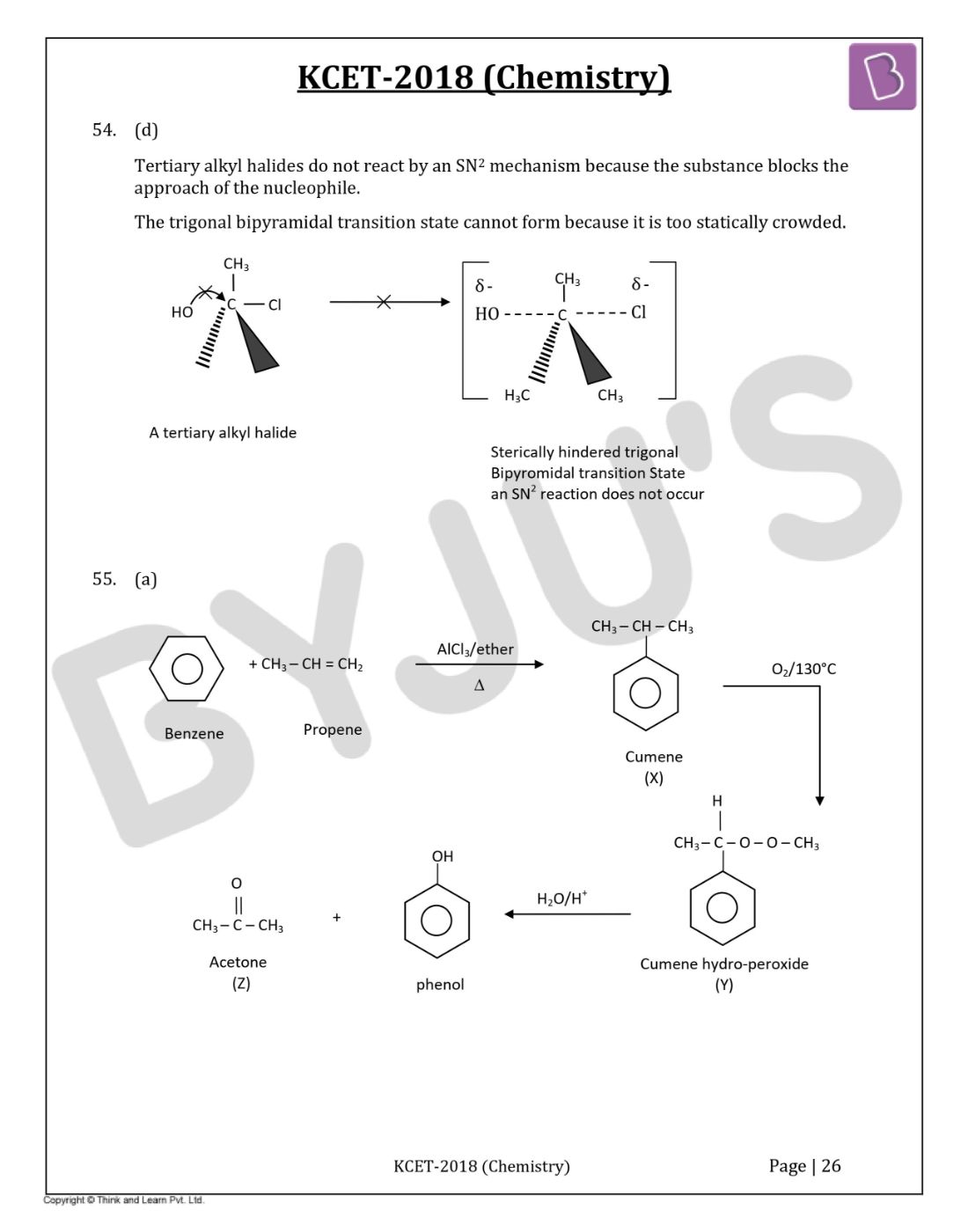
Question 54: Tertiary alkyl halide is practically inert to substitution by SN2 mechanism because of
- a. Insolubility
- b. Instability
- c. Inductive effect
- d. Steric hindrance
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Tertiary alkyl halides do not react by an SN2 mechanism because the substance blocks the approach of the nucleophile.
The trigonal bipyramidal transition state cannot form because it is too statically crowded.

Question 55: The products X and Z in the following reaction sequence are

- a. Isopropyl benzene and acetone
- b. Cumene peroxide and acetone
- c. Isopropyl benzene and isopropyl alcohol
- d. Phenol and acetone
Solution:
Answer: (a)

Question 56: The appropriate reagent for the following transformation is

- a. Zn–Hg/HCl
- b. H2N–NH2, KOH/ethylene glycol
- c. Ni/H2
- d. NaBH4
Solution:
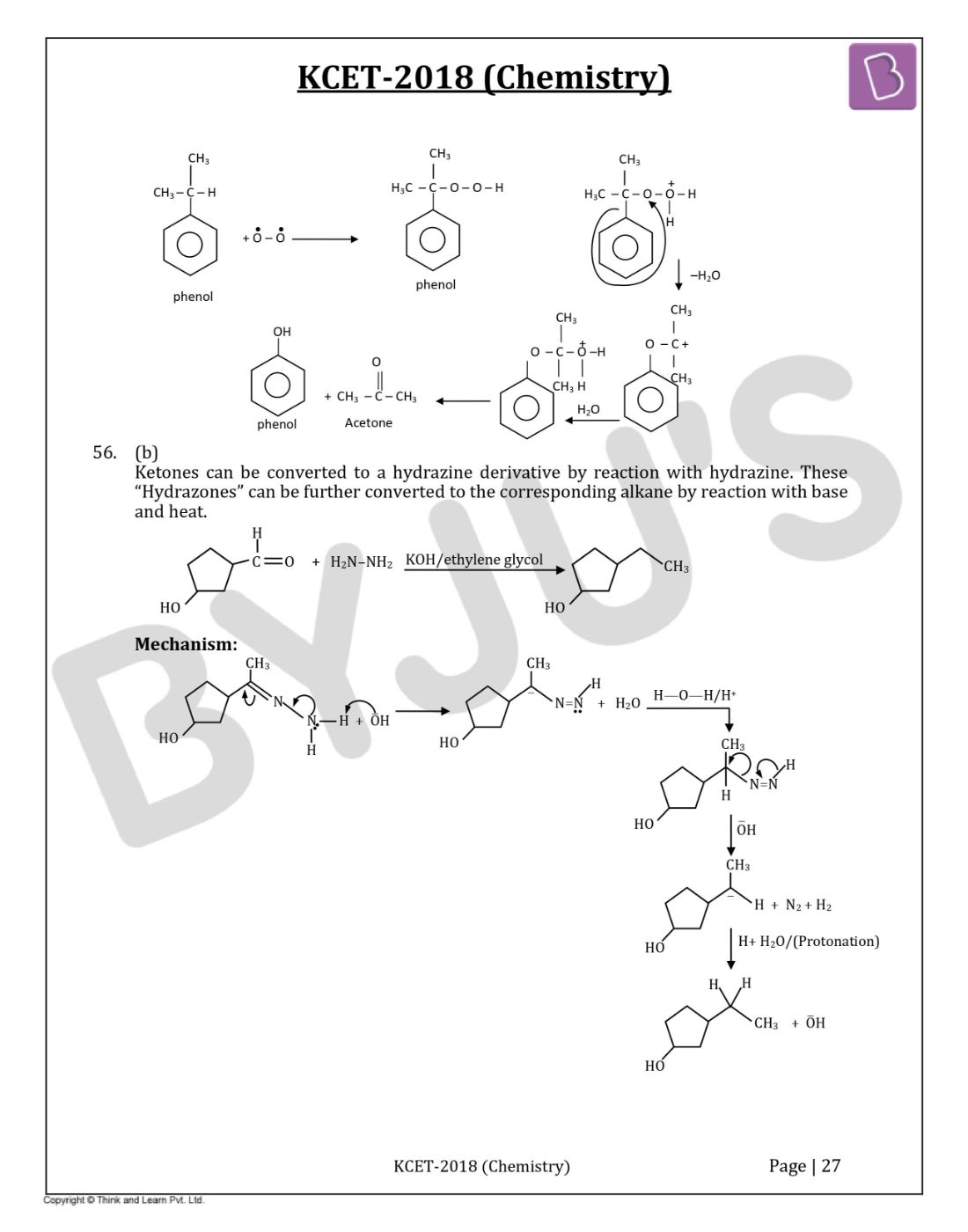
Answer: (b)
Ketones can be converted to a hydrazine derivative by reaction with hydrazine. These “Hydrazones” can be further converted to the corresponding alkane by reaction with base and heat.

Question 57: In the following reaction

The compound Z is
- a. Benzoic acid
- b. Benzaldehyde
- c. Acetophenone
- d. Benzene
Solution:
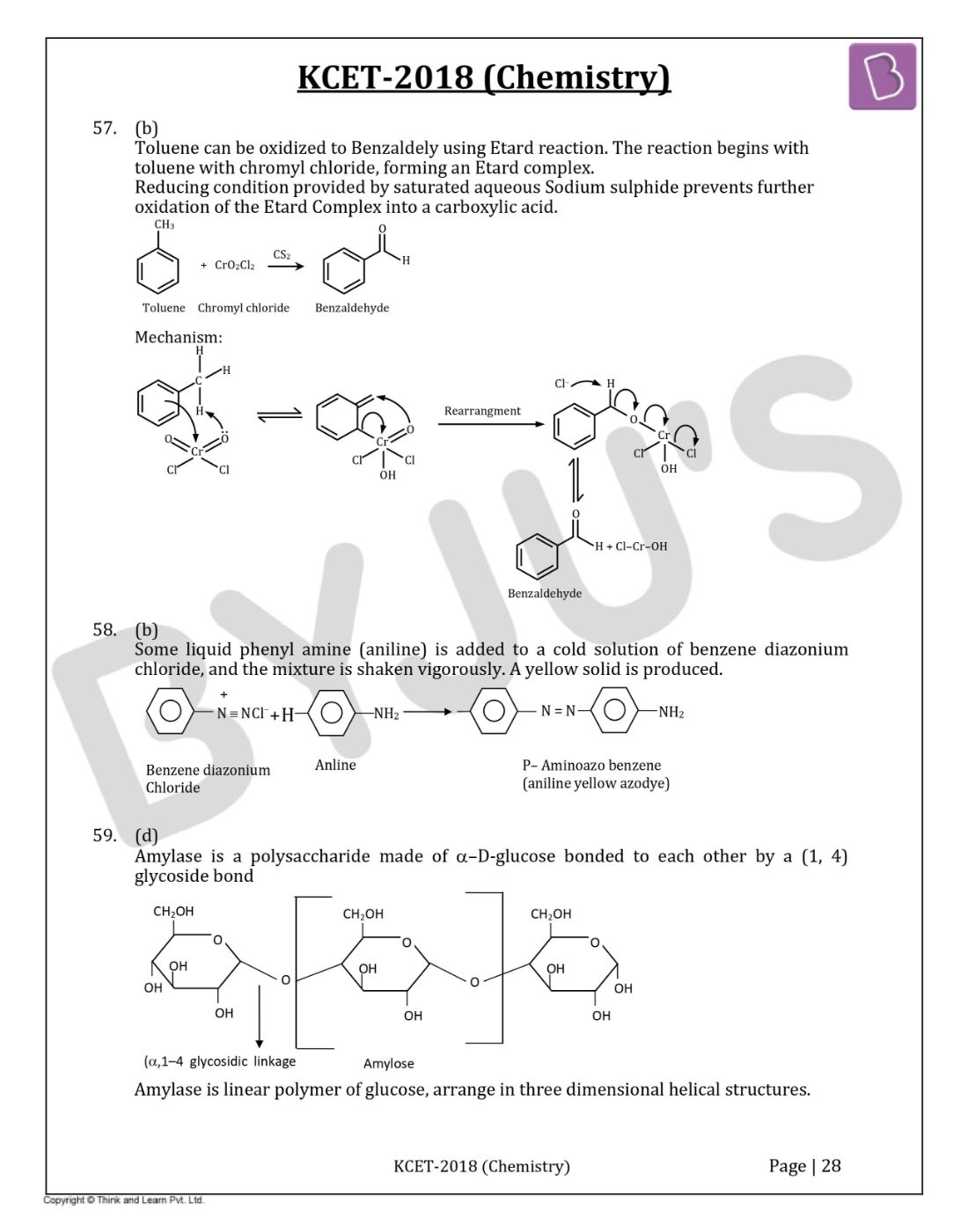
Answer: (b)
Toluene can be oxidized to Benzaldely using Etard reaction. The reaction begins with toluene with chromyl chloride, forming an Etard complex. Reducing conditions provided by saturated aqueous Sodium sulphide prevents further oxidation of the Etard Complex into a carboxylic acid.

Question 58: The reaction of Benzene diazonium chloride with aniline yields a yellow dye. The name of the yellow dye is
- a. p-Hydroxyazobenzene
- b. p-Aminoazobenzene
- c. p-Nitroazobenzene
- d. o-Nitroazobenzene
Solution:
Answer: (b)
Some liquid phenylamine (aniline) is added to a cold solution of benzene diazonium chloride, and the mixture is shaken vigorously. A yellow solid is produced.

Question 59: The glycosidic linkage involved in linking the glucose units in amylose part of the starch is
- a. C1 – C4β-linkage
- b. C1 – C6α-linkage
- c. C1 – C6β-linkage
- d. C1 – C4α-linkage
Solution:
Answer: (d)
Amylase is a polysaccharide made of α–D-glucose bonded to each other by a (1, 4) glycoside bond.

Amylase is a linear polymer of glucose, arranged in three-dimensional helical structures.
Question 60: Ziegler-Natta catalyst is used to prepare
- a. Low-density polythene
- b. Teflon
- c. High-density polythene
- d. Nylon-6
Solution:
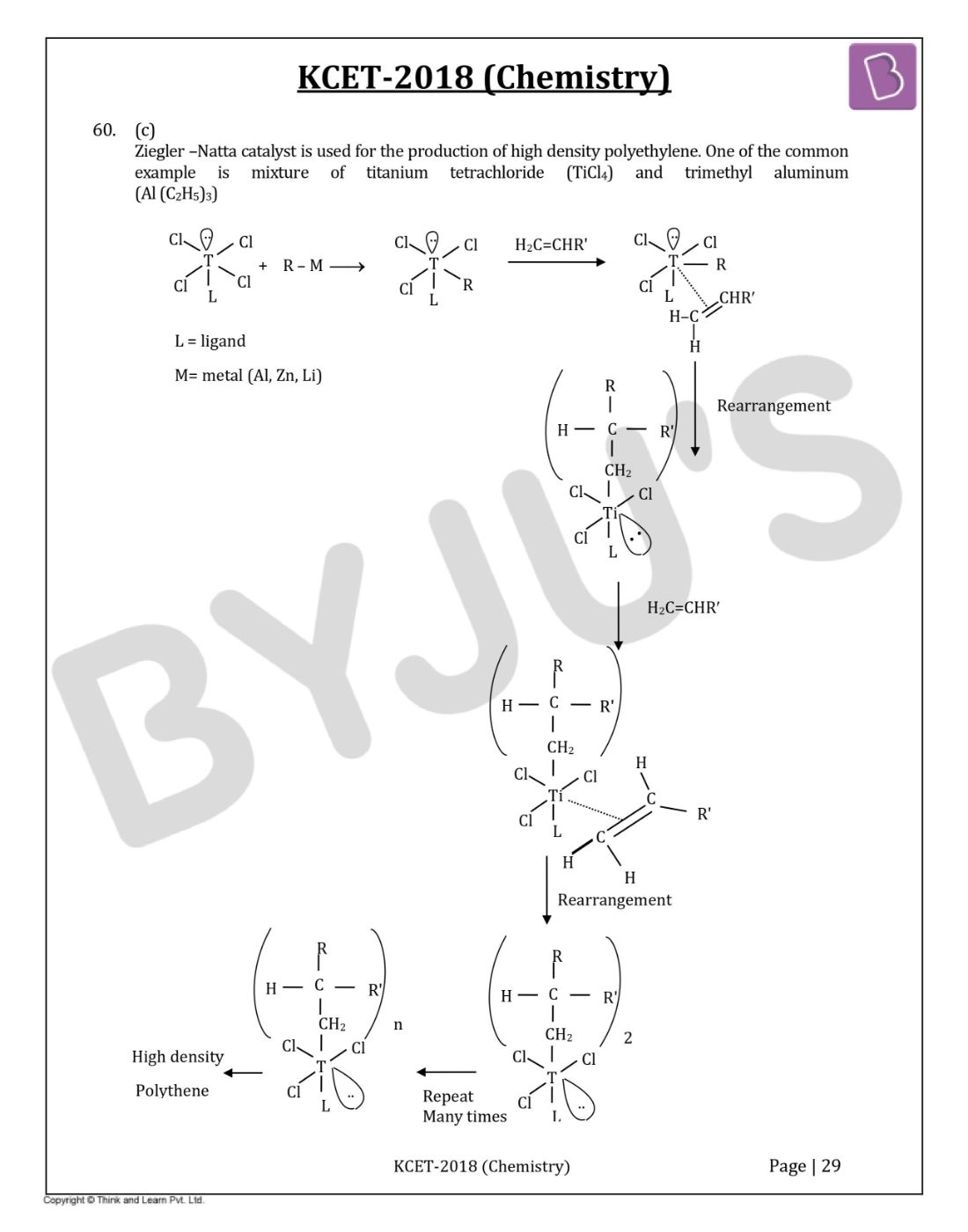
Answer: (c)
Ziegler –Natta catalyst is used for the production of high-density polyethylene. One of the common examples is a mixture of titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) and trimethylaluminum (Al (C2H5)3).