NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 – Free PDF Download
NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes are premier study material required for the students to score good marks in Class 10 CBSE examinations as well as to avoid difficulty in understanding the concepts to be taught in higher secondary and graduation courses. The Class 10 Exemplar provided here consists of MCQs, fill in the blanks, practice questions, value-based questions, and previous years’ questions on Life Processes.
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 mainly deals with the maintenance processes in living organisms. In this chapter, students will learn to identify vital life processes and understand different types of nutrition as well as the respiratory organs and their mechanism, excretion, digestion, etc. To make learning more interesting and easy, we provide NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 – Life Processes in PDF here.
Download the PDF of NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 – Life Processes
Access Answers to NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 – Life Processes
Multiple-choice Questions
1. Which of the following statements about autotrophs is incorrect?
(a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll
(b) They store carbohydrates in the form of starch
(c) They convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates in the absence of sunlight
(d) They constitute the first trophic level in food chains
Soln:
The answer is (c) They convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates in the absence of sunlight
Explanation:
They need sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates.
2. In which of the following groups of organisms, food material is broken down outside the body and absorbed?
(a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba
(b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
(c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta
(d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
Soln:
The answer is (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
Explanation:
Yeast, mushroom and bread moulds are saprophytes, and Saprophytes break the food material outside their body and absorbed it.
3. Select the correct statement
(a) Heterotrophs do not synthesise their own food
(b) Heterotrophs utilise solar energy for photosynthesis
(c) Heterotrophs synthesise their own food
(d) Heterotrophs are capable of converting carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates
Soln:
The answer is (a) Heterotrophs do not synthesise their own food
Explanation:
Heterotrophs are either dependent on Phototrophs or other organisms for their food.
4. Which is the correct sequence of parts in the human alimentary canal?
(a) Mouth → stomach → small intestine → oesophagus → large intestine
(b) Mouth →oesophagus → stomach → large intestine → small intestine
(c) Mouth → stomach → oesophagus → small intestine → large intestine
(d) Mouth → oesophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine
Soln:
The answer is (d) Mouth → oesophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine
5. If salivary amylase is lacking in the saliva, which of the following events in the mouth cavity will be affected?
(a) Proteins breaking down into amino acids
(b) Starch breaking down into sugars
(c) Fats breaking down into fatty acids and glycerol
(d) Absorption of vitamins
Soln:
The answer is (b) Starch breaking down into sugars
Explanation:
The Salivary Amylase enzyme present in the saliva breaks down Starch into simpler sugar and helps in digesting them. Hence the breakdown of starch will be affected if salivary amylase is lacking in the saliva.
6. The inner lining of the stomach is protected by one of the following from hydrochloric acid. Choose the correct one (a) Pepsin
(b) Mucus
(c) Salivary amylase
(d) Bile
Soln:
The answer is (b) Mucus
7. Which part of the alimentary canal receives bile from the liver?
(a) Stomach
(b) Small intestine
(c) Large intestine
(d) Oesophagus
Soln:
The answer is (b) Small intestine
Explanation:
Bile goes to the small intestine from the gall bladder through hepta pancreatic duct.
8. A few drops of iodine solution were added to rice water. The solution turned blue-black in colour. This indicates that rice water contains
(a) complex proteins
(b) simple proteins
(c) fats
(d) starch
Soln:
The answer is (d) starch
Explanation
Starch is made up of two components Amylose and Amylopectin. When we add iodine to starch-containing water Amylose reacts with iodine to form a blue colour complex. Here solution gives blue-black colour on adding Iodine which confirms the presence of starch in the rice water.
9. In which part of the alimentary canal is food finally digested?
(a) Stomach
(b) Mouth cavity
(c) Large intestine
(d) Small intestine
Soln:
The answer is (d) Small intestine
Explanation:
Although the primary digestion process is conducted in mouth and stomach most of the digestion process occurs in the small intestine and large intestine digestion process will not take place.
10. Choose the function of the pancreatic juice from the following
(a) trypsin digests proteins and lipase carbohydrates
(b) trypsin digests emulsified fats and lipase proteins
(c) trypsin and lipase digest fats
(d) trypsin digests proteins and lipase emulsified fats
Soln:
The answer is (d) trypsin digests proteins and lipase emulsified fats
Explanation:
Trypsin breaks down proteins into polypeptides and Lipase digest emulsified fat molecules into fatty acids and glycerol.
11. When air is blown from the mouth into a test-tube containing lime water, the lime water is turned milky due to the presence of
(a) oxygen
(b) carbon dioxide
(c) nitrogen
(d) water vapour
Soln:
The answer is (b) carbon dioxide
Explanation:
Carbon dioxide reacts with lime water and turns the lime water milky.
12. The correct sequence of anaerobic reactions in yeast is

Soln:
The answer is d)
Explanation:
In Yeast cytoplasm, Glucose is breakdown in anaerobic condition to produce Pyruvate which is further breakdown to Ethanol and carbon-di-oxide
13. Which of the following is most appropriate for aerobic respiration?

Soln: Answer is Option (B)
14. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) true about respiration?
(i) During inhalation, ribs move inward and diaphragm is raised
(ii) In the alveoli, exchange of gases takes place i.e., oxygen from alveolar air diffuses into blood and carbon dioxide from the blood into the alveolar air
(iii) Haemoglobin has a greater affinity for carbon dioxide than oxygen
(iv) Alveoli increase surface area for exchange of gases
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Soln:
The answer is (d) (ii) and (iv)
Explanation:
Statement i) is wrong because ribs move outward and the diaphragm is lowered during inhalation. Similarly Option iii) is wrong because Hemoglobin has greater affinity for Oxygen than CO2.
15. Which is the correct sequence of air passage during inhalation?
(a) Nostrils →larynx →pharynx →trachea →lungs
(b) Nasal passage →trachea →pharynx →larynx →alveoli
(c) larynx →nostrils →pharynx →lungs
(d) Nostrils →pharynx →larynx →trachea →alveoli
Soln:
The answer is (d) Nostrils →pharynx →larynx →trachea→alveoli
Explanation:
Air enter respiratory system through nostrils, passes to pharynx, larynx, trachea and then to alveoli. After inhalation diaphragm and intercoastal muscles contract along with expansion of thoracic muscles which creates enough space for the air to enter into the lungs.
16. During respiration exchange of gases take place in
(a) trachea and larynx
(b) alveoli of lungs
(c) alveoli and throat
(d) throat and larynx
Soln:
The answer is (b) alveoli of lungs
Explanation:
Trachea, Larynx provide a passage for the movement of air. Gas exchange takes place in Alveoli of lungs. From alveoli, oxygen diffuses into blood and Carbon-di-oxide exhaled out of blood.
17. Which of the following statement (s) is (are) true about the heart?
(i) The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from different parts of the body while the right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from lungs
(ii) Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to different body parts while right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs
(iii) Left atrium transfers oxygenated blood to the right ventricle which sends it to different body parts
(iv) The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from different parts of the body while the left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to different parts of the body
(a) (i)
(b) (ii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Soln:
The answer is (c) (ii) and (iv)
Explanation:
Oxygenated blood circulates through the left part of the heart whereas deoxygenated blood circulates through the right part of the heart. Atrium receives blood and ventricle pumps the blood out of the heart.
18. What prevents backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction?
(a) Valves in heart
(b) Thick muscular walls of ventricles
(c) Thin walls of atria
(d) All of the above
Soln:
The answer is (a) Valves in the heart
Explanation:
Walls in the heart are responsible for only pumping of the blood and they are not responsible for blocking backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction.
19. Single circulation i.e., blood flows through the heart only once during one cycle of passage through the body, is exhibited by
(a) Labeo, Chameleon, Salamander
(b) Hippocampus, Exocoetus, Anabas
(c) Hyla, Rana, Draco
(d) Whale, Dolphin, Turtle
Soln:
The answer is (b) Hippocampus, Exocoetus, Anabas
Explanation:
In Option a) Chameleon is a reptile and Salamander is an amphibian which has 3 chambered hearts and shows partial double circulation. In Option c) all are Amphibians and they show partial double circulation. In option d) Whale is a mammal, but a turtle is a reptile hence option d) is wrong.
20. In which of the following vertebrate group/groups, the heart does not pump oxygenated blood to different parts of the body?
(a) Pisces and amphibians
(b) Amphibians and reptiles
(c) Amphibians only
(d) Pisces only
Soln:
The answer is (d) Pisces only
Explanation:
This is because of the single circulation where deoxygenated blood from all part of the body is pumped into the heart. From the heart, it is pumped to gills where it gets oxygenated and gets transferred to all parts of the body. Hence it proves Pisces will not receive oxygenated blood.
21. Choose the correct statement that describes arteries.
(a) They have thick elastic walls, blood flows under high pressure; collect blood from different organs and bring it back to the heart
(b) They have thin walls with valves inside, blood flows under low pressure and carries blood away from the heart to various organs of the body
(c) They have thick elastic walls, blood flows under low pressure; carry blood from the heart to various organs of the body
(d) They have thick elastic walls without valves inside, blood flows under high pressure and carry blood away from the heart to different parts of the body.
Soln:
The answer is (d) They have thick elastic walls without valves inside, blood flows under high pressure and carries blood away from the heart to different parts of the body.
22. The filtration units of kidneys are called
(a) ureter
(b) urethra
(c) neurons
(d) nephrons
Soln:
The answer is (d) nephrons
Explanation:
Nephron is called as the functional unit of the kidney. It helps in removing the waste products and excess substances from our body.
23. Oxygen liberated during photosynthesis comes from
(a) water
(b) chlorophyll
(c) carbon dioxide
(d) glucose
Soln:
The answer is (a) water
Explanation:
During photosynthesis, water molecule splits to produce Oxygen and Hydrogen Ions. Oxygen is expelled out of plants and Hydrogen is used to reduce Carbon-di-oxide to produce carbohydrates.
24. The blood leaving the tissues becomes richer in
(a) carbon dioxide
(b) water
(c) haemoglobin
(d) oxygen
Soln:
The answer is (a) carbon dioxide
Explanation:
Because of respiration Carbon-di-oxide gets accumulated in tissues. Hence blood leaving the tissues becomes richer in Carbon-di-oxide.
25. Which of the following is an incorrect statement?
(a) Organisms grow with time
(b) Organisms must repair and maintain their structure
(c) Movement of molecules does not take place among cells
(d) Energy is essential for life processes
Soln:
The answer is (c) Movement of molecules does not take place among cells
Explanation:
Movement of molecule is a vital process. Movement of molecules in cells take place in active and passive modes such as Diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion etc.
26. The internal (cellular) energy reserve in autotrophs is
(a) glycogen
(b) protein
(c) starch
(d) fatty acid
Soln:
The answer is (c) starch
Explanation:
Glycogen is the stored energy in animals, Plants stores energy in the form of Starch.
27. Which of the following equations is the summary of photosynthesis?
(a) 6CO2 + 12H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
(b) 6CO2 +H2O + Sunlight→C6H12O6 + O2 + 6H2O
(c) 6CO2 + 12H2O + Chlorophyll + Sunlight→ C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
(d) 6CO2 + 12H2O + Chlorophyll + Sunlight→ C6H12O6 + 6CO2 + 6H2O
Soln:
Answer is (c) 6CO2 + 12H2O + Chlorophyll + Sunlight→ C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
Explanation:
Option a does not show the factors responsible for photosynthesis. Option b) is not a balanced equation. Option d) is wrong as it has CO2 in the products.
28. Choose the event that does not occur in photosynthesis
(a) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
(b) Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates
(c) Oxidation of carbon to carbon dioxide
(d) Conversion of light energy to chemical energy
Soln:
Answer is (c) Oxidation of carbon to carbon dioxide
29. The opening and closing of the stomatal pore depend upon
(a) oxygen
(b) temperature
(c) water in guard cells
(d) concentration of CO2 in stomata
Soln:
The answer is (c) water in guard cells
Explanation:
Opening of guard cells is facilitated by the entry of water inside guard cells. This makes the guard cell turgid. The closing of guard cells is facilitated by water coming out of guard cells. This will make the guard cells flaccid.
30. Choose the forms in which most plants absorb nitrogen
(i) Proteins
(ii) Nitrates and Nitrites
(iii) Urea
(iv) Atmospheric nitrogen
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Soln:
The answer is (b) (ii) and (iii)
Explanation:
Plants cannot absorb atmospheric Nitrogen. They can absorb Nitrogen in the form of Nitrates, Nitrites and Urea present in the soil.
31. Which is the first enzyme to mix with food in the digestive tract?
(a) Pepsin
(b) Cellulase
(c) Amylase
(d) Trypsin
Soln:
Answer is (c) Amylase
Explanation:
Amylase is secreted in mouth and acts on the starch to convert into simpler molecules. Hence Amylase is the first enzyme to mix with food in the digestive tract.
32. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
(i) Pyruvate can be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide by yeast
(ii) Fermentation takes place in aerobic bacteria
(iii) Fermentation takes place in mitochondria
(iv) Fermentation is a form of anaerobic respiration
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Soln:
The answer is(c) (i) and (iv)
Explanation:
Fermentation is carried out by anaerobes in the cytoplasm. Hence option ii) and iii) are wrong.
33. Lack of oxygen in muscles often leads to cramps among cricketers. This results due to
(a) conversion of pyruvate to ethanol
(b) conversion of pyruvate to glucose
(c) non-conversion of glucose to pyruvate
(d) conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid
Soln:
The answer is (d) conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid
Explanation:
The breakdown of Pyruvate in the presence of oxygen takes place in mitochondria leading to the formation of Lactic acid. Due to workout oxygen is used for the production of energy leading to the lack of oxygen and production of lactic acid.
34. Choose the correct path of urine in our body
(a) kidney → ureter → urethra → urinary bladder
(b) kidney → urinary bladder → urethra → ureter
(c) kidney → ureters → urinary bladder → urethra
(d) urinary bladder → kidney → ureter → urethra
Soln:
Answer is (c) kidney → ureters → urinary bladder → urethra
Explanation:
Urine from nephron is brought to the collecting duct of kidneys where the urine enters the ureters. There are 2 ureters, each opening from one kidney into the urinary bladder. The urinary bladder stores urine and its size increases as the amount of urine collected increases. When the CNS gives a voluntary message the muscles of bladder contract and the bladder sphincter relaxes thus excreting urine out through the urethra.
35. During deficiency of oxygen in tissues of human beings, pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid in the
(a) cytoplasm
(b) chloroplast
(c) mitochondria
(d) Golgi body
Soln:
Answer is (a) cytoplasm
Explanation:
When there is lack of oxygen Breakdown of Pyruvate takes place in the cytoplasm of muscle cells leading to the formation of Lactic acid.
Short Answer Questions
36. Name the following
(a) The process in plants that links light energy with chemical energy
(b) Organisms that can prepare their own food
(c) The cell organelle where photosynthesis occurs
(d) Cells that surround a stomatal pore
(e) Organisms that cannot prepare their own food
(f) An enzyme secreted from gastric glands in the stomach that acts on proteins.
Soln:
- Photosynthesis
- Autotrophs
- Chloroplasts
- Guard cells
- Heterotrophs
- Pepsin
37. “All plants give out oxygen during day and carbon dioxide during the night”. Do you agree with this statement? Give reason.
Soln:
The statement is wrong because plants respire every time and expel out Carbon-di-oxide every time but they give out oxygen only in the daytime as the photosynthesis process can take place only in the presence of sunlight.
38. How do the guard cells regulate the opening and closing of stomatal pores?
Soln:
Opening of guard cells is facilitated by the entry of water inside guard cells. This make the guard cell turgid. The closing of guard cells is facilitated by water coming out of guard cells. This will make the guard cells flaccid.
Entry of water inside guard cells will make the cell turgid leading to the opening of stomata. Similarly, the cell becomes flaccid when water comes out of guard cells, this leads to the closing of the stomata.
39. Two green plants are kept separately in oxygen-free containers, one in the dark and the other in continuous light. Which one will live longer? Give reasons.
Soln:
The plant kept in continuous light live longer because plants release CO2 during respiration. In the case of the plant kept in the dark, CO2 resulting in lack of oxygen and the plant will die earlier.
40. If a plant is releasing carbon dioxide and taking in oxygen during the day, does it mean that there is no photosynthesis occurring? Justify your answer.
Soln:
If a plant is releasing carbon dioxide and taking in oxygen during the day means plant is respiring; it does not mean that there is no photosynthesis occurring in the plant. This is because Photosynthesis and respiration are two independent processes.
41. Why do fishes die when taken out of water?
Soln:
Fishes can respire only by using dissolved oxygen. When we take fish out of the water it cannot respire due to lack of dissolved oxygen and they die.
42. Differentiate between an autotroph and a heterotroph
Soln:
| Autotrophs | Heterotrophs |
| They can make their food | They cannot make their food |
| Ex: Plants and certain bacteria | Ex: Animals, Fungi and protozoans |
43. Is ‘nutrition’ a necessity for an organism? Discuss.
Soln:
Nutrition is an absolute necessity for the organisms because nutrition provides energy for carrying out metabolic activities.
44. What would happen if green plants disappear from earth?
Soln:
Green plants are the sources of energy for all the heterotrophs on earth. Plants convert solar and chemical energy into viable food sources. If plants get disappeared from the earth, it leads to an imbalance in the ecosystem and heterotrophs may die without food.
45. Leaves of a healthy potted plant were coated with vaseline. Will this plant remain healthy for long? Give reasons for your answer.
Soln:
Coating vaseline to the leaves of a healthy plant will clog its stomata pores and stops the respiration of plants and the plants die.
46. How does aerobic respiration differ from anaerobic respiration?
Soln:
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
| Takes place in the presence of Oxygen | Takes place in the absence of Oxygen |
| Carbon-di-oxide and water are the end products | Carbon-di-oxide and Lactic acid/ethanol are the end products |
| More efficient in energy production | Less efficient in energy production |
| Takes Place in animals and plants | Takes place in unicellular organisms |
47. Match the words of Column (A) with that of Column (B)
| Column A | Column B |
| Phloem | (i) Excretion |
| Nephron | (ii) Translocation of food |
| Veins | (iii) Clotting of blood |
| Platelets | (iv) Deoxygenated blood |
Soln:
| Column A | Column B |
| Phloem | (ii) Translocation of food |
| Nephron | (i) Excretion |
| Veins | (iv) Deoxygenated blood |
| Platelets | (iii) Clotting of blood |
48. Differentiate between an artery and a vein.
Soln:
Artery has thick walls whereas Veins has thin walls.
Arteries carry blood away from the heart but veins carry blood to the heart.
In arteries valves are absent and in veins they are present
In arteries, blood flows under pressure but in veins, there will be no pressure.
49. What are the adaptations of leaf for photosynthesis?
Soln:
Adaptation of leaf for photosynthesis are as follows
- The surface of the leaf is flat to allow greater exposure of light.
- Presence of chlorophyll to trap sunlight
- Presence of stomata on the lower surface for easy transpiration
50. Why is small intestine in herbivores longer than in carnivores?
Soln:
Food of herbivores contains mostly cellulose. To digest cellulose herbivores need help of certain bacteria. To accommodate the microbes and to facilitate digestion of food herbivores has longer small intestine than carnivores.
51. What will happen if the mucus is not secreted by the gastric glands?
Soln:
Mucus prevent the inner lining of the stomach from HCL. Mucus prevents drying of the inner lining of the stomach. Mucus helps in easy movement of food particles through the digestive system. If the mucus is not secreted food will not easily be moved through the digestive system. HCL will damage the stomach lining and the digestion process will not take place.
52. What is the significance of the emulsification of fats?
Soln:
Emulsification is a process of breakage of larger fats molecules into digestible fat globules. Emulsification aids action enzymes on fats by breaking larger fat molecules.
53. What causes movement of food inside the alimentary canal?
Soln:
Peristalsis is the process that cause movement of food inside the alimentary canal.
54. Why does the absorption of digested food occur mainly in the small intestine?
Soln:
Small intestine has specialized structures that facilitate the absorption of digested food. Small intestine has several folds that increase the area of absorption. Small intestine also has fingerlike projection called microvilli which are richly supplied by blood vessels.
55. Match Group (A) with Group (B)
| Group A | Group B |
| (a) Autotrophic nutrition | (i) Leech |
| (b) Heterotrophic nutrition | (ii) Paramecium |
| (c) Parasitic nutrition | (iii) Deer |
| (d) Digestion in food vacuoles | (iv) Green plant |
Soln:
| Group A | Group B |
| (a) Autotrophic nutrition | (iv) Green plant |
| (b) Heterotrophic nutrition | (iii) Deer |
| (c) Parasitic nutrition | (i) Leech |
| (d) Digestion in food vacuoles | (ii) Paramecium |
56. Why is the rate of breathing in aquatic organisms much faster than in terrestrial organisms?
Soln:
Rate of breathing in aquatic organisms much faster than in terrestrial organisms because the availability of oxygen is less in water than on land, hence to obtain required oxygen aquatic organisms has to work hard.
57. Why is blood circulation in the human heart called double circulation?
Soln:
In Humans blood flow in two directions simultaneously in one cardiac cycle. Oxygenated blood comes to the heart from the lungs and at the same time, de-oxygenated blood goes from Heart towards the lungs. Because of this double movement is blood circulation in the human heart called double circulation.
58. What is the advantage of having a four-chambered heart?
Soln:
Four chambered heart has the following advantages
- Clear cut division of labours among different chambers
- Segregation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in the heart.
- Efficiency of the heart will increase.
59. Mention the major events during photosynthesis
Soln:
Major events of Photosynthesis are
- Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
- Conversion of light energy into chemical energy
- Splitting of water molecules into Hydrogen and Oxygen
- Reduction of CO2 to form carbohydrates.
60. In each of the following situations what happens to the rate of photosynthesis?
(a) Cloudy days
(b) No rainfall in the area
(c) Good manuring in the area
(d) Stomata get blocked due to dust
Soln:
- Rate of photosynthesis will reduce due to the availability of sunlight.
- Rainfall will not affect the rate of Photosynthesis
- Manuring will not affect the rate of Photosynthesis
- Blockage of stomata will reduce the rate of photosynthesis because blockage will affect availability pf Carbon-di-oxide.
61. Name the energy currency in the living organisms. When and where is it produced?
Soln:
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy currency in the living organisms. It is produced in Mitochondria during respiration.
62. What is common for Cuscuta, ticks and leeches?
Soln:
These all are parasite. They live on or inside another body to obtain food from the host. In obtaining food parasites always harm their host.
63. Explain the role of the mouth in digestion of food.
Soln:
Role of mouth in digestion of food.
- Ingestion of food
- Breakage of food by Mastication
- Saliva aids easy swallowing of food
- Salivary amylase breaks starch into simpler carbohydrates.
64. What are the functions of gastric glands present in the wall of the stomach?
Soln:
Hydrochloric acid, pepsin and mucus are secreted by gastric gland present in the stomach. They have following functions.
HCL Kills germs present in the food and it decreases PH of the stomach which is essential for the working of digestive enzymes.
Pepsin digests protein.
Mucus protects the stomach’s inner line from HCL.
65. Match the terms in Column (A) with those in Column (B)
| Column (A) | Column (B) |
| (a) Trypsin | (i) Pancreas |
| (b) Amylase | (ii) Liver |
| (c) Bile | (iii) Gastric glands |
| (d) Pepsin | (iv) Saliva |
Soln:
| Column (A) | Column (B) |
| (a) Trypsin | (i) Pancreas |
| (b) Amylase | (iv) Saliva |
| (c) Bile | (ii) Liver |
| (d) Pepsin | (iii) Gastric glands |
66. Name the correct substrates for the following enzymes
(a) Trypsin
(b) Amylase
(c) Pepsin
(d) Lipase
Soln:
- Protein
- Starch
- Protein
- Lipid
67. Why do veins have thin walls as compared to arteries?
Soln:
Blood flow through veins does not exert pressure on walls of veins hence they have thin walls. Blood flow in arteries exerts high pressure on arterial walls hence they need thick walls.
68. What will happen if platelets were absent in the blood?
Soln:
Platelets are responsible for the clotting of the blood. If platelets are absent blood will not clot. In case of injuries, blood flow cannot be stopped without clotting and this may prove fatal for the person.
69. Plants have low energy needs as compared to animals. Explain.
Soln:
Most of the transport in plants occurs through passive transport which does not require energy and plants standstill at one place and they will not travel in search of food Hence Plants require low energy compared to animals.
70. Why and how does water enter continuously into the root xylem?
Soln:
Water should enter the root xylem continuously to assist the various process such as photosynthesis. Continuous flow of water into root xylem is due to transpiration pull.
71. Why is transpiration important for plants?
Soln:
Transpiration is important for plants because of the following reasons.
(a) It creates transpiration pull to facilitate the ascent of sap.
(b) Ascent of sap is necessary to make water available for photosynthesis.
(c) It helps a plant to get rid of excess water.
72. How do leaves of plants help in excretion?
Soln:
Leaves plays an important role in excretion in plants because CO2 is expelled out through pores of stomata present in the leaf. Plants shed leaves to get rid of excretory products deposited on them.
Long Answer Questions
73. Explain the process of nutrition in Amoeba.
Soln:
Amoeba shows holozoic nutrition which is comprised of Ingestion, Digestion, Absorption, Assimilation and Egestion.
Ingestion:
Ameoba traps food particles through fingerlike projections called pseudopodia. Pseudopodia present outside its body and helps in taking food along with water
Digestion:
Food vacuoles are made after ingesting the food. Enzymes are released in the food vacuole for digestion.
Absorption:
After digestion, nutrients enter the cytoplasm through osmosis.
Assimilation:
Nutrients are utilized by the cell for various purposes.
Egestion:
Food vacuole goes near the cell membrane to empty its contents outside the cell. This results in the expulsion of waste materials from the cell.
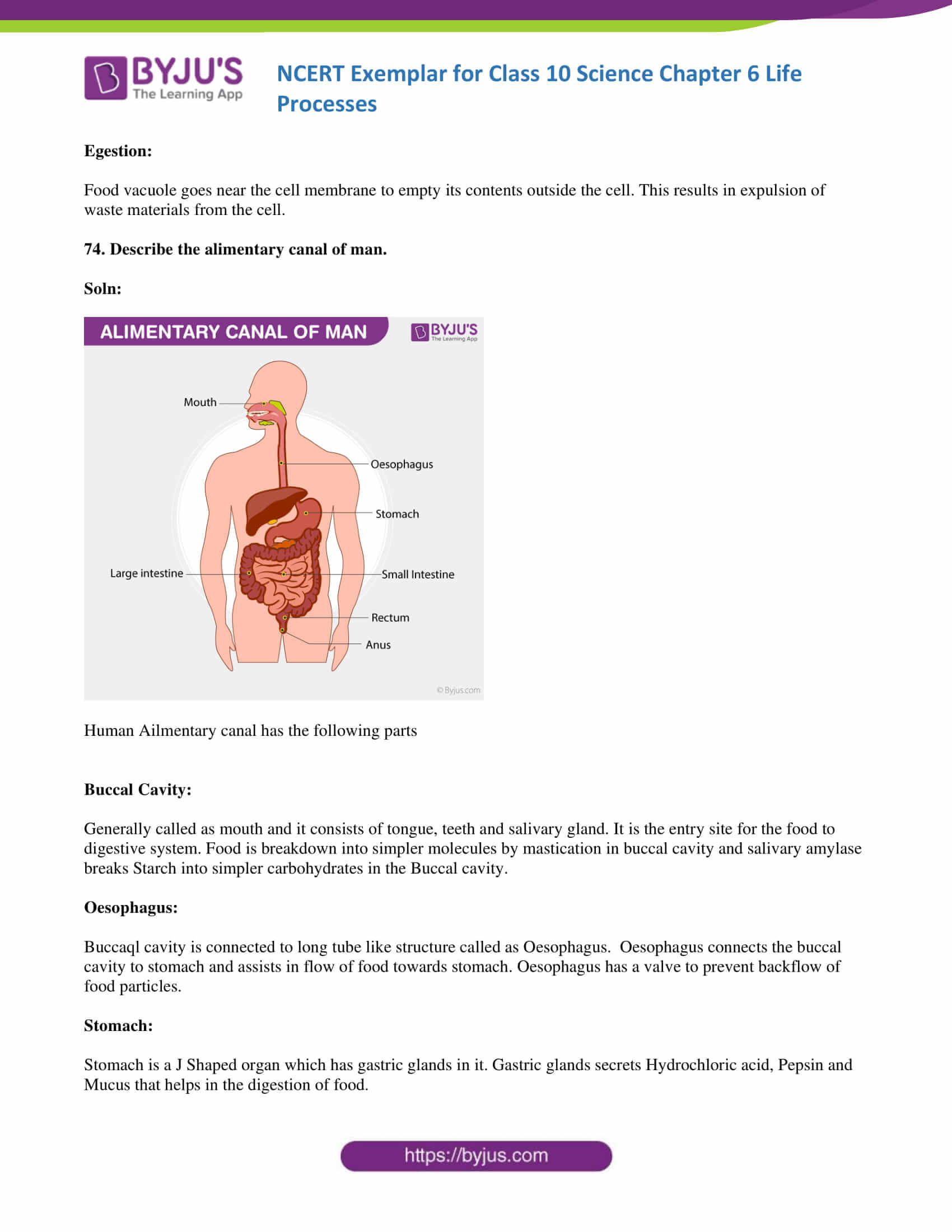
74. Describe the alimentary canal of man.
Soln:

Human Alimentary canal has the following parts
Buccal Cavity:
Generally called as mouth and it consists of tongue, teeth and salivary gland. It is the entry site for the food to the digestive system. Food is breakdown into simpler molecules by mastication in the buccal cavity and salivary amylase breaks Starch into simpler carbohydrates in the Buccal cavity.
Oesophagus:
Buccal cavity is connected to the long tube-like structure called as Oesophagus. Oesophagus connects the buccal cavity to the stomach and assists the inflow of food towards the stomach. Oesophagus has a valve to prevent backflow of food particles.
Stomach:
Stomach is a J Shaped organ which has gastric glands in it. Gastric glands secrets Hydrochloric acid, Pepsin and Mucus that helps in the digestion of food.
Small Intestine:
Small intestine is highly coiled long structure. Small intestine performs major of the food absorption. Small intestine has specialized structures that facilitate the absorption of digested food. Small intestine has several folds that increase the area of absorption. Small intestine also has fingerlike projection called microvilli which are richly supplied by blood vessels.
Large Intestine :
This is shorter than the small intestine and its lumen is larger than that of Small intestine. The major function of the large intestine is to absorb water from the remaining indigestible food matter and transmit the useless waste material from the body.
Rectum:
Large Intestine open into rectum. Waste materials and undigested food are stored in the rectum.
Anus:
It is the opening at the end of the alimentary canal. Solid waste materials leave the body through Anus.
75. Explain the process of breathing in man
Soln:
Breathing in Humans has two processes 1) Inhalation 2) Exhalation
Inhalation:
Inhalation is the process of taking oxygen. During this process, ribs come out and the diaphragm moves down. This increases the volume of the lungs and decreases the pressure. This will make the air move towards the lungs.
Exhalation:
Exhalation is a process of throwing out carbon-dioxide. During this process, ribs go down and the diaphragm moves up. This decreases the volume of the lungs and increases the pressure. As a result, air moves out of the lungs.
76. Explain the importance of soil for plant growth.
Soln:
Soil is very important for the growth of the plant for the following reasons.
- Soil provides the base for the growth of the plants and provides a platform for the penetration of roots.
- It acts as a reservoir of the water.
- Soil has different minerals essential for the growth of the plant. Soil is the only medium from which soil obtain nutrients.
- Soil has organic materials essential for the growth of the plants.
- Soil has microorganisms that have a symbiotic relationship with the plant and these microbes assist the plant in their growth and life processes.
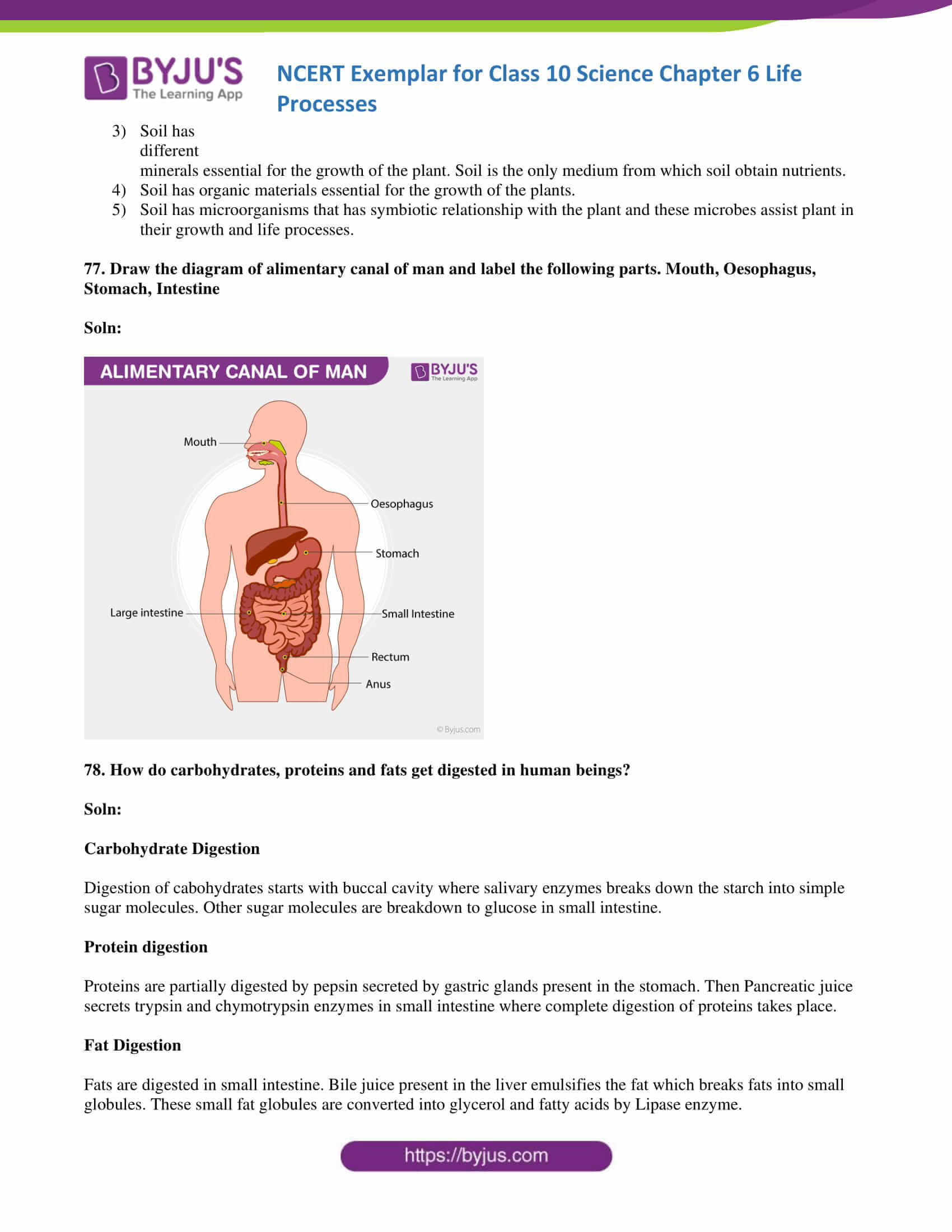
77. Draw the diagram of the alimentary canal of man and label the following parts. Mouth, Oesophagus, Stomach, Intestine
Soln:

78. How do carbohydrates, proteins and fats get digested in human beings?
Soln:
Carbohydrate Digestion
Digestion of carbohydrates starts with buccal cavity where salivary enzymes break down the starch into simple sugar molecules. Other sugar molecules are breakdown to glucose in the small intestine.
Protein digestion
Proteins are partially digested by pepsin secreted by gastric glands present in the stomach. Then Pancreatic juice secrets trypsin and chymotrypsin enzymes in the small intestine where complete digestion of proteins takes place.
Fat Digestion
Fats are digested in the small intestine. Bile juice present in the liver emulsifies the fat which breaks fats into small globules. These small fat globules are converted into glycerol and fatty acids by Lipase enzyme.
79. Explain the mechanism of photosynthesis
Soln:
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants produce their own food by utilizing sunlight, CO2 and water. CO@ and water are converted to carbohydrates with the evolution of oxygen. Photosynthesis reaction can be given by the following reaction.
6CO2 + 6H2O Sunlight energy C6H12O6 + 6O2
Process of Photosynthesis is divided into 4 processes
- Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
- Conversion of light energy into chemical energy
- Splitting of water molecules into Hydrogen and Oxygen
- Reduction of CO2 to produce carbohydrates
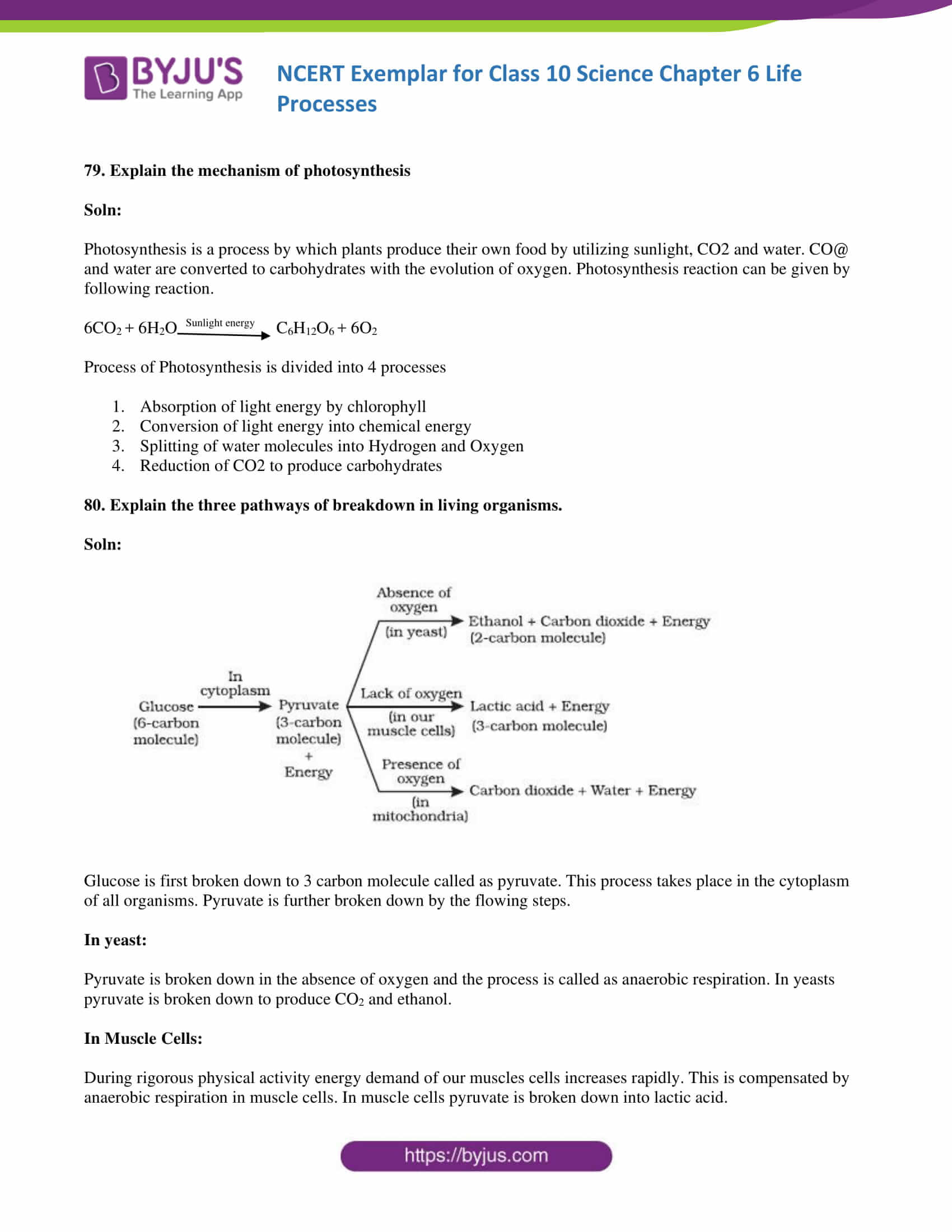
80. Explain the three pathways of breakdown in living organisms.
Soln:

Glucose is first broken down to 3 carbon molecule called pyruvate. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of all organisms. Pyruvate is further broken down by the flowing steps.
In yeast:
Pyruvate is broken down in the absence of oxygen and the process is called anaerobic respiration. In yeasts, pyruvate is broken down to produce CO2 and ethanol.
In Muscle Cells:
During rigorous physical activity, the energy demand of our muscles cells increases rapidly. This is compensated by anaerobic respiration in muscle cells. In muscle cells, pyruvate is broken down into lactic acid.
In Mitochondria:
In case of aerobic respiration( in presence of oxygen) pyruvate is broken down in mitochondria. Here Pyruvate is broken down to produce H2O and CO2. Aerobic respiration is most common in most of the organisms.
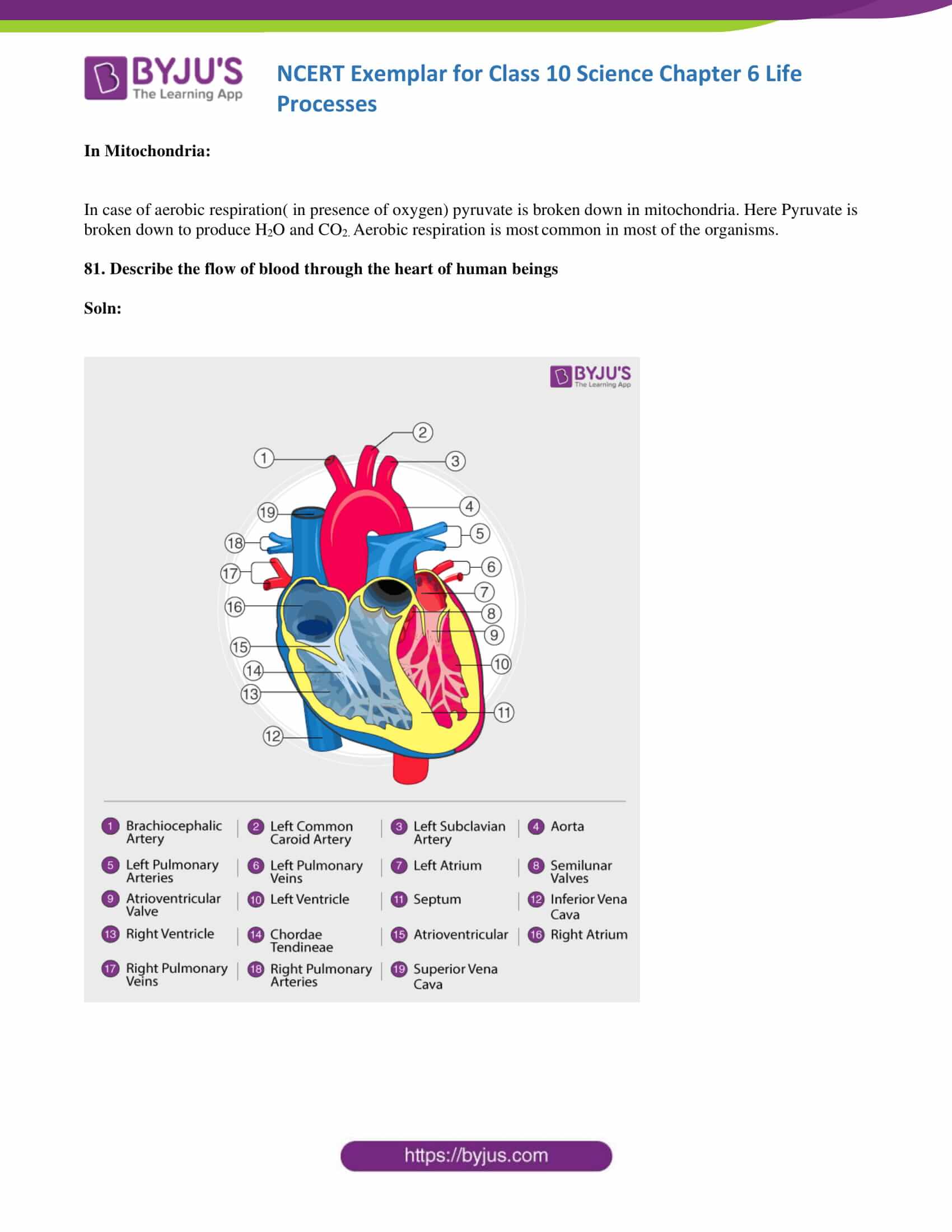
81. Describe the flow of blood through the heart of human beings
Soln:

• Deoxygenated blood from different organs comes to the right atrium through the vena cava.
• From the right atrium, blood goes to the right ventricle. The tricuspid valve between the right atrium and right ventricle prevents the backflow of blood.
• From the right ventricle, blood goes to the lungs through the pulmonary artery. Inside the lungs, carbon dioxide is removed from the blood and oxygen enters the blood.
• From the lungs, blood goes to the left atrium through the pulmonary vein.
• From the left atrium, blood goes to the left ventricle.
• From the left ventricle, blood is pumped into the aorta so that it can be supplied to different organs.
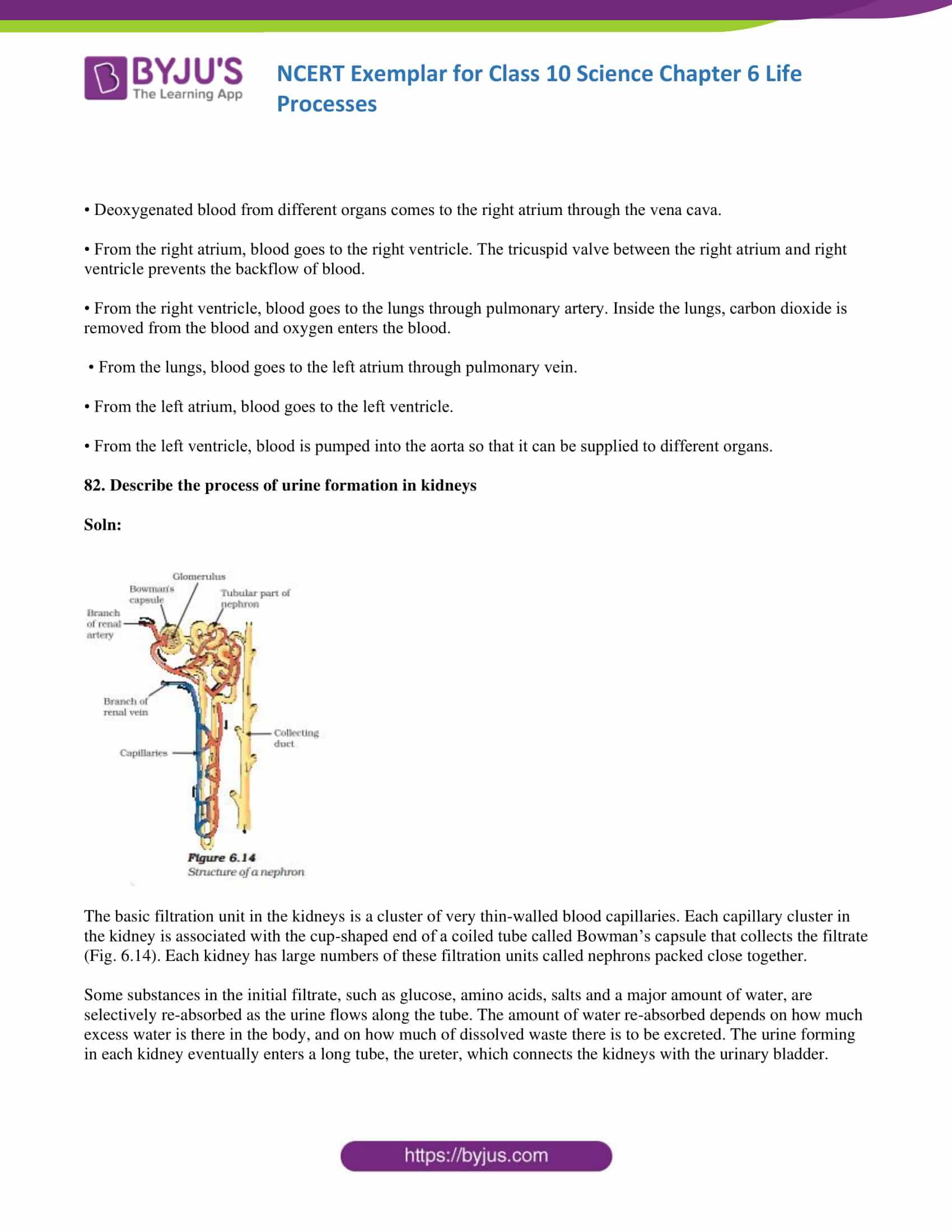
82. Describe the process of urine formation in kidneys
Soln:

The basic filtration unit in the kidneys is a cluster of very thin-walled blood capillaries. Each capillary cluster in the kidney is associated with the cup-shaped end of a coiled tube called Bowman’s capsule that collects the filtrate (Fig. 6.14). Each kidney has large numbers of these filtration units called nephrons packed close together.
Some substances in the initial filtrate, such as glucose, amino acids, salts and a major amount of water, are selectively re-absorbed as the urine flows along the tube. The amount of water re-absorbed depends on how much
excess water is there in the body and on how much of dissolved waste there is to be excreted. The urine forming in each kidney eventually enters a long tube, the ureter, which connects the kidneys with the urinary bladder.
Urine is stored in the urinary bladder until the pressure of the expanded bladder leads to the urge to pass it out through the urethra. The bladder is muscular, so it is under nervous control.
| Also Access |
| NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 |
| CBSE Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 |
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes NCERT Exemplar
These Exemplars will help students gain insights into all the important chapter questions as well as develop a better understanding of each topic. Additionally, using these exemplars will enable students to study effectively and be well-prepared to answer any type of question that can be asked in the board exam.
Class 10 Science NCERT Life Process Important Topics
- What Is Life Process?
- Nutrition
-
- Autotrophic Nutrition
- Heterotrophic Nutrition
- How Do Organisms Obtain Their Nutrition?
- Nutrition in Human Beings
- Respiration
- Transportation
- Excretion
- Excretion in Human Beings
- Excretion in Plants
NCERT Exemplar Solutions, provided on BYJU’S website, will boost your exam preparation by providing you with the additional knowledge required to understand the concepts clearly. Students are recommended to study these Exemplar Solutions and NCERT Solutions thoroughly to excel in CBSE Class 10 examination. To score good marks in the Class 10 examinations, students can access and download the study materials provided at BYJU’S in PDFs for free. To access the study material, you can visit BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S – The Learning App.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6
Why are BYJU’S NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 important?
What concepts will I learn from the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6?
1. What Is the Life Process?
2. Nutrition
a. Autotrophic Nutrition
b. Heterotrophic Nutrition
c. How Do Organisms Obtain Their Nutrition?
d. Nutrition in Human Beings
3. Respiration
4. Transportation
5. Excretion
a. Excretion in Human Beings
b. Excretion in Plants
What are the advantages of using the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 from BYJU’S?
2. The important questions, shortcut techniques and other information can be obtained easily by the students.
3. The expert faculty has designed the solutions which cover all the fundamental concepts and questions which are important for the exam.
4. These solutions are arranged in a systematic manner which develops comprehensive learning among students.
5. The important definitions and examples are explained in an interactive manner to make learning interesting for the students.
Also Read























Comments