NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Exercise 3.2 Chapter 3 Linear Equations In Two Variables is the best way students can prepare the concept. These NCERT Solutions have all the solutions to the questions provided in the exercise on page no. 73. The answers provided by our subject experts are accurate and have been prepared after a lot of brainstorming.
Solutions to all the exercises mentioned in the textbook are provided in the NCERT Solutions of Class 10 Maths. It also contains several other questions for practice. These questions will help the students prepare well for the board examinations. NCERT Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 3 – Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables is an important chapter from the examination perspective. The students need to be thorough with the basic concepts to solve the problems related to this chapter.
Solutions of NCERT act as a guide during preparation for the examinations. The students can refer to them in case of any doubts. They can practise and evaluate themselves and work on their weak points thereafter.
Download PDF for NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 – Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise 3.2
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 – Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise 3.2
1. Form the pair of linear equations in the following problems, and find their solutions graphically.
(i) 10 students of Class X took part in a Mathematics quiz. If the number of girls is 4 more than the number of boys, find the number of boys and girls who took part in the quiz.
(ii) 5 pencils and 7 pens together cost 50, whereas 7 pencils and 5 pens together cost 46. Find the cost of one pencil and that of one pen.
Solution:
(i) Let there be x number of girls and y number of boys. As per the given question, the algebraic expression can be represented as follows.
x +y = 10
x– y = 4
Now, for x+y = 10 or x = 10−y, the solutions are;

For x – y = 4 or x = 4 + y, the solutions are;

The graphical representation is as follows;

From the graph, it can be seen that the given lines cross each other at point (7, 3). Therefore, there are 7 girls and 3 boys in the class.
(ii) If 1 pencil costs Rs. x and 1 pen costs Rs. y.
According to the question, the algebraic expression cab be represented as;
5x + 7y = 50
7x + 5y = 46
For, 5x + 7y = 50 or x = (50-7y)/5, the solutions are;

For 7x + 5y = 46 or x = (46-5y)/7, the solutions are;

Hence, the graphical representation is as follows;

From the graph, it is can be seen that the given lines cross each other at point (3, 5).
So, the cost of a pencil is 3/- and cost of a pen is 5/-.
2. On comparing the ratios a1/a2 , b1/b2 , c1/c2, find out whether the lines representing the following pairs of linear equations intersect at a point, are parallel or coincident:
(i) 5x – 4y + 8 = 0
7x + 6y – 9 = 0
(ii) 9x + 3y + 12 = 0
18x + 6y + 24 = 0
(iii) 6x – 3y + 10 = 0
2x – y + 9 = 0
Solutions:
(i) Given expressions;
5x−4y+8 = 0
7x+6y−9 = 0
Comparing these equations with a1x+b1y+c1 = 0
And a2x+b2y+c2 = 0
We get,
a1 = 5, b1 = -4, c1 = 8
a2 = 7, b2 = 6, c2 = -9
(a1/a2) = 5/7
(b1/b2) = -4/6 = -2/3
(c1/c2) = 8/-9
Since, (a1/a2) ≠ (b1/b2)
So, the pairs of equations given in the question have a unique solution and the lines cross each other at exactly one point.
(ii) Given expressions;
9x + 3y + 12 = 0
18x + 6y + 24 = 0
Comparing these equations with a1x+b1y+c1 = 0
And a2x+b2y+c2 = 0
We get,
a1 = 9, b1 = 3, c1 = 12
a2 = 18, b2 = 6, c2 = 24
(a1/a2) = 9/18 = 1/2
(b1/b2) = 3/6 = 1/2
(c1/c2) = 12/24 = 1/2
Since (a1/a2) = (b1/b2) = (c1/c2)
So, the pairs of equations given in the question have infinite possible solutions and the lines are coincident.
(iii) Given Expressions;
6x – 3y + 10 = 0
2x – y + 9 = 0
Comparing these equations with a1x+b1y+c1 = 0
And a2x+b2y+c2 = 0
We get,
a1 = 6, b1 = -3, c1 = 10
a2 = 2, b2 = -1, c2 = 9
(a1/a2) = 6/2 = 3/1
(b1/b2) = -3/-1 = 3/1
(c1/c2) = 10/9
Since (a1/a2) = (b1/b2) ≠ (c1/c2)
So, the pairs of equations given in the question are parallel to each other and the lines never intersect each other at any point, and there is no possible solution for the given pair of equations.
3. On comparing the ratio, (a1/a2) , (b1/b2) , (c1/c2), find out whether the following pair of linear equations are consistent, or inconsistent.
(i) 3x + 2y = 5 ; 2x – 3y = 7
(ii) 2x – 3y = 8 ; 4x – 6y = 9
(iii)(3/2)x+(5/3)y = 7; 9x – 10y = 14
(iv) 5x – 3y = 11 ; – 10x + 6y = –22
(v)(4/3)x+2y = 8 ; 2x + 3y = 12
Solutions:
(i) Given : 3x + 2y = 5 or 3x + 2y -5 = 0
and 2x – 3y = 7 or 2x – 3y -7 = 0
Comparing these equations with a1x+b1y+c1 = 0
And a2x+b2y+c2 = 0
We get,
a1 = 3, b1 = 2, c1 = -5
a2 = 2, b2 = -3, c2 = -7
(a1/a2) = 3/2
(b1/b2) = 2/-3
(c1/c2) = -5/-7 = 5/7
Since, (a1/a2) ≠ (b1/b2)
So, the given equations intersect each other at one point and they have only one possible solution. The equations are consistent.
(ii) Given 2x – 3y = 8 and 4x – 6y = 9
Therefore,
a1 = 2, b1 = -3, c1 = -8
a2 = 4, b2 = -6, c2 = -9
(a1/a2) = 2/4 = 1/2
(b1/b2) = -3/-6 = 1/2
(c1/c2) = -8/-9 = 8/9
Since , (a1/a2) = (b1/b2) ≠ (c1/c2)
So, the equations are parallel to each other and they have no possible solution. Hence, the equations are inconsistent.
(iii) Given (3/2)x + (5/3)y = 7 and 9x – 10y = 14
Therefore,
a1 = 3/2, b1 = 5/3, c1 = -7
a2 = 9, b2 = -10, c2 = -14
(a1/a2) = 3/(2×9) = 1/6
(b1/b2) = 5/(3× -10)= -1/6
(c1/c2) = -7/-14 = 1/2
Since, (a1/a2) ≠ (b1/b2)
So, the equations are intersecting each other at one point and they have only one possible solution. Hence, the equations are consistent.
(iv) Given, 5x – 3y = 11 and – 10x + 6y = –22
Therefore,
a1 = 5, b1 = -3, c1 = -11
a2 = -10, b2 = 6, c2 = 22
(a1/a2) = 5/(-10) = -5/10 = -1/2
(b1/b2) = -3/6 = -1/2
(c1/c2) = -11/22 = -1/2
Since (a1/a2) = (b1/b2) = (c1/c2)
These linear equations are coincident lines and have infinite number of possible solutions. Hence, the equations are consistent.
(v) Given, (4/3)x +2y = 8 and 2x + 3y = 12
a1 = 4/3 , b1= 2 , c1 = -8
a2 = 2, b2 = 3 , c2 = -12
(a1/a2) = 4/(3×2)= 4/6 = 2/3
(b1/b2) = 2/3
(c1/c2) = -8/-12 = 2/3
Since (a1/a2) = (b1/b2) = (c1/c2)
These linear equations are coincident lines and have infinite number of possible solutions. Hence, the equations are consistent.
4. Which of the following pairs of linear equations are consistent/inconsistent? If consistent, obtain the solution graphically:
(i) x + y = 5, 2x + 2y = 10
(ii) x – y = 8, 3x – 3y = 16
(iii) 2x + y – 6 = 0, 4x – 2y – 4 = 0
(iv) 2x – 2y – 2 = 0, 4x – 4y – 5 = 0
Solutions:
(i) Given, x + y = 5 and 2x + 2y = 10
(a1/a2) = 1/2
(b1/b2) = 1/2
(c1/c2) = 1/2
Since (a1/a2) = (b1/b2) = (c1/c2)
∴ The equations are coincident and they have infinite number of possible solutions.
So, the equations are consistent.
For, x + y = 5 or x = 5 – y

For 2x + 2y = 10 or x = (10-2y)/2

So, the equations are represented in graphs as follows:

From the figure, we can see, that the lines are overlapping each other.
Therefore, the equations have infinite possible solutions.
(ii) Given, x – y = 8 and 3x – 3y = 16
(a1/a2) = 1/3
(b1/b2) = -1/-3 = 1/3
(c1/c2) = 8/16 = 1/2
Since, (a1/a2) = (b1/b2) ≠ (c1/c2)
The equations are parallel to each other and have no solutions. Hence, the pair of linear equations is inconsistent.
(iii) Given, 2x + y – 6 = 0 and 4x – 2y – 4 = 0
(a1/a2) = 2/4 = ½
(b1/b2) = 1/-2
(c1/c2) = -6/-4 = 3/2
Since, (a1/a2) ≠ (b1/b2)
The given linear equations are intersecting each other at one point and have only one solution. Hence, the pair of linear equations is consistent.
Now, for 2x + y – 6 = 0 or y = 6 – 2x

And for 4x – 2y – 4 = 0 or y = (4x-4)/2

So, the equations are represented in graphs as follows:

From the graph, it can be seen that these lines are intersecting each other at only one point (2,2).
(iv) Given, 2x – 2y – 2 = 0 and 4x – 4y – 5 = 0
(a1/a2) = 2/4 = ½
(b1/b2) = -2/-4 = 1/2
(c1/c2) = 2/5
Since, a1/a2 = b1/b2 ≠ c1/c2
Thus, these linear equations have parallel and have no possible solutions. Hence, the pair of linear equations are inconsistent.
5. Half the perimeter of a rectangular garden, whose length is 4 m more than its width, is 36 m. Find the dimensions of the garden.
Solutions: Let us consider.
The width of the garden is x and length is y.
Now, according to the question, we can express the given condition as;
y – x = 4
and
y + x = 36
Now, taking y – x = 4 or y = x + 4

For y + x = 36, y = 36 – x

The graphical representation of both the equation is as follows;
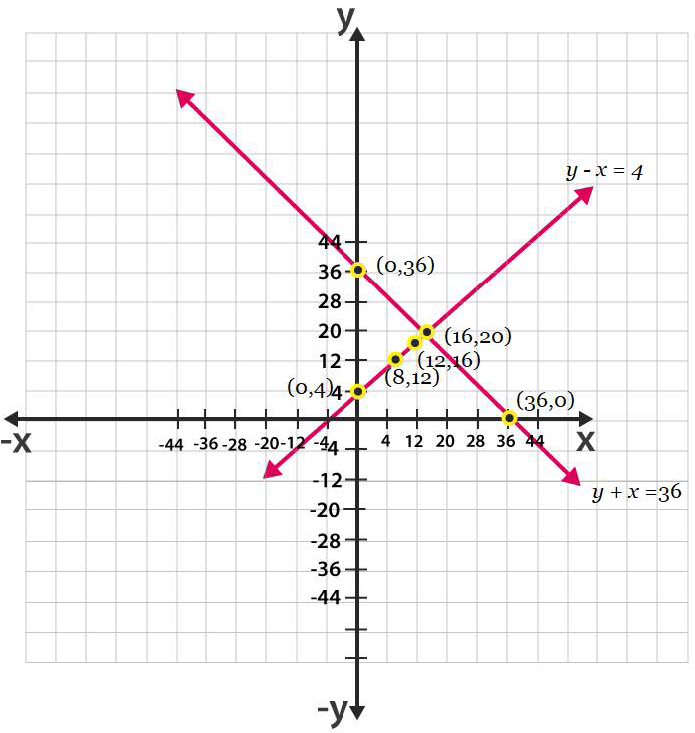
From the graph you can see, the lines intersect each other at a point (16, 20). Hence, the width of the garden is 16 and length is 20.
6. Given the linear equation 2x + 3y – 8 = 0, write another linear equation in two variables such that the geometrical representation of the pair so formed is:
(i) Intersecting lines
(ii) Parallel lines
(iii) Coincident lines
Solutions:
(i) Given the linear equation 2x + 3y – 8 = 0.
To find another linear equation in two variables such that the geometrical representation of the pair so formed is intersecting lines, it should satisfy the below condition;
(a1/a2) ≠ (b1/b2)
Thus, another equation could be 2x – 7y + 9 = 0, such that;
(a1/a2) = 2/2 = 1 and (b1/b2) = 3/-7
Clearly, you can see another equation satisfies the condition.
(ii) Given the linear equation 2x + 3y – 8 = 0.
To find another linear equation in two variables such that the geometrical representation of the pair so formed is parallel lines, it should satisfy the below condition;
(a1/a2) = (b1/b2) ≠ (c1/c2)
Thus, another equation could be 6x + 9y + 9 = 0, such that;
(a1/a2) = 2/6 = 1/3
(b1/b2) = 3/9= 1/3
(c1/c2) = -8/9
Clearly, you can see another equation satisfies the condition.
(iii) Given the linear equation 2x + 3y – 8 = 0.
To find another linear equation in two variables such that the geometrical representation of the pair so formed is coincident lines, it should satisfy the below condition;
(a1/a2) = (b1/b2) = (c1/c2)
Thus, another equation could be 4x + 6y – 16 = 0, such that;
(a1/a2) = 2/4 = 1/2 ,(b1/b2) = 3/6 = 1/2, (c1/c2) = -8/-16 = 1/2
Clearly, you can see another equation satisfies the condition.
7. Draw the graphs of the equations x – y + 1 = 0 and 3x + 2y – 12 = 0. Determine the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines and the x-axis, and shade the triangular region.
Solution: Given, the equations for graphs are x – y + 1 = 0 and 3x + 2y – 12 = 0.
For, x – y + 1 = 0 or x = -1+y

For, 3x + 2y – 12 = 0 or x = (12-2y)/3

Hence, the graphical representation of these equations is as follows;

From the figure, it can be seen that these lines are intersecting each other at point (2, 3) and x-axis at (−1, 0) and (4, 0). Therefore, the vertices of the triangle are (2, 3), (−1, 0), and (4, 0).
This is the second exercise of the chapter. It has a total of 7 questions. The solutions to these questions are provided in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 – Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise 3.2. The students can refer to this page for solutions. The solutions are provided stepwise by the subject experts and are accurate.
Key Features of NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 – Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise 3.2
- The questions are solved by subject experts.
- The answers are provided after a lot of brainstorming and are accurate.
- These will help in scoring well in the examinations.
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 – Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables includes the solutions to the exercises given in the textbook.















good_responce_from_byjus…..👍🏻
i_like_this_website…..👌🏻
👍 byjus is best app for study .