In this article, let us discuss two important mechanical equipment that are widely used, generators and transformers. A generator converts one form of energy into another. Let us know in detail the working principle of transformer, types and applications of generators and transformers.
What is a Generator?
A generator a piece of mechanical equipment that converts a mechanical form of energy into electrical energy. Generators find applications in agricultural and industrial production. The most widely used principle for construction a generator is based on the law of electromagnetic force. In this session, let us know in detail about generators and transformers.
What is the Working Principle of Generator?
It consists of a rectangular coil with a number of copper wires wound over an iron core. The coil is called the armature. It is used to increase the magnetic flux. A strong permanent magnet is placed, and the armature is rotated between the magnets where the magnetic lines are perpendicular to the axis of the armature. There are two slip rings connected to the arms of the armature. They are used to provide movable contact. Two metallic brushes are connected to the slip rings to pass current from the armature to the slip rings. The current is passed through a load resistance, which is connected across the slip rings.
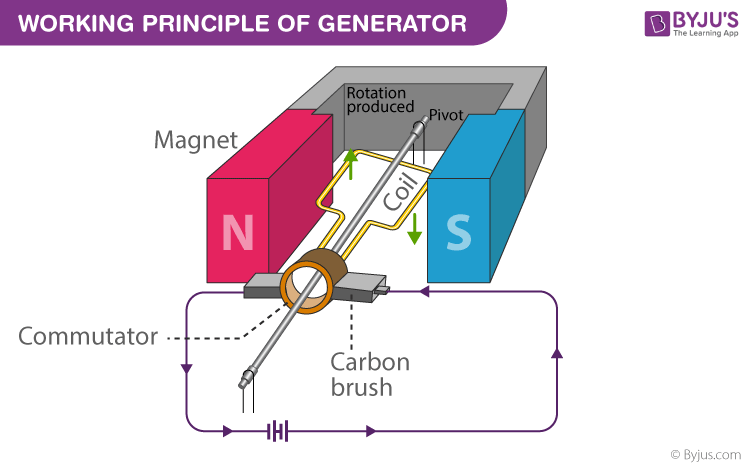
At different time intervals, the position of the armature keeps changing. When the magnetic field lines are perpendicular to the coil, the coil is rotated in the magnetic field, and the induced e.m.f produced increases. This happens in this position because of the number of intercepting magnetic field lines maximum.
What are the Types of Generators?
Following are the types of generators:
- AC generator
- DC generator
AC Generators
What are AC generators?
AC generators are also known as alternators which convert mechanical energy into electrical energy in the form of alternating current. Kilo volt-amperes is the unit used for rating the AC generator.
Read More: AC Generators
What is the Working Principle of AC Generator?
The AC generator working principle is based on electromagnetic induction. The armature rotates between the poles of the magnet, which is perpendicular to the magnetic field. As there is a change in the flux produced by the armature, emf is induced to produce electric current with the help of a galvanometer, slip rings, and brushes. The flow of alternating current through the galvanometer can be observed when the galvanometer oscillates between positive and negative poles.
What are the Types of AC Generators?
There are two types of AC generators:
- Synchronous generators
- Induction generators
Related Article:
What are the Advantages of AC Generators?
Advantages of AC generators are:
- The time spent on maintenance is very less as there are no brushes.
- When compared to DC generator, the size of A generators are small.
- Minimal amount of losses are there.
- The breakers used are relatively smaller when compared to DC generators.
Questions on AC Generator
Q1. What happens when the number of turns is increased in an AC generator?
Ans: As the number of turns increases, emf will also increase for the AC generator.
Q2. Name the parameter on which the emf of the AC generator depends.
Ans: Emf of the AC generator depends on the length of the rotating wire.
Q3. What is the use of armature in an AC generator?
Ans: Armature is used for producing an output voltage.
DC Generator
What is DC generator?
A DC generator is used for converting mechanical energy onto direct current electricity.
What is the Working Principle of DC Generator?
The DC generator works on the principle of Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction. When a conductor is placed in a varying field, an emf is induced in the conductor. The magnitude of the emf induced can be calculated with the help of the emf equation of the DC generator. The circulation of induced current takes place within the closed path. With the help of Fleming’s right-hand rule, the direction of the induced current can be determined.
Emf equation of DC generator is given as
\(\begin{array}{l}Eg=\frac{P\phi NZ}{60A}\end{array} \) |
Where,
- P is the number of field poles.
- Φ is the flux produced per pole in Weber.
- Z is the total number of armature conductors.
- A is the number of parallel paths in the armature.
- N is the rotational speed of the armature in rpm.
What are the Types of DC Generators?
Following are the types of SC generators:
- Permanent magnet DC generator
- Separately excited DC generator
- Self-excited Dc generator
- Series wound generator
- Shunt-wound generator
- Compound wound generator
What are the Advantages of DC Generators?
Following are the advantages of a DC generator:
- Cable cost will be less as there is no shielding from radiation.
- The fluctuations in the generator can be reduced by the constant arrangement of the coils.
- The operating characteristics of a DC generator depend on the field winding.

What is a Transformer?
For many purposes, it is necessary to change (or transform) an alternating voltage from one to another of greater or smaller value. This is done with a device called a transformer using the principle of mutual induction. Let us understand the nuances of transformers in detail in this section.

It consists of two coils named, a Primary coil and a Secondary coil which is wound on a soft iron core. The soft iron core is laminated to minimise eddy currents. The alternating current is applied across the primary coil, and the output is obtained across the secondary coil.
Working Principle of Transformer
After knowing what a transformer is, let us now learn the principle of transformer. The main working principle of the transformer is based on the mutual inductance between the two circuits that are linked by a common magnetic flux. A transformer consists of two coils that are electrically separated but magnetically linked through a path of reluctance.
What are the Types of Transformers?
There are two types of transformers:
- Step-up Transformer
- Step-down Transformer
A step-up transformer converts a low voltage into a high voltage. The number of turns in the primary coil is less than the number of turns in the secondary coil, i.e.
- NP < Ns
A step-down Transformer converts a high voltage when current decreases into a low voltage when current increases. The number of turns in the primary coil is greater than the number of turns in the secondary coil, i.e.
- Np > Ns
According to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, the induced e.m.f is given by:
- e = – (dΦ/dt)
- ep = – (dΦp/dt)
- es = – (dΦs/dt)
By using the above equations, we get,
- es = NsNpep
The ratio
- NsNp = k
There are different types of transformers based on various parameters, and they are listed below:
- Based on design
- Core-type transformer
- Shell-type transformer
- Based on cooling method
- Oil filled self-cooled type
- Oil filled water cooled type
- Air blast type
Applications of Transformer
There are three basic applications of transformer and they are:
- To step up the current and voltage.
- To step down the current and voltage.
- Prevention of DC to the next circuit in the DC transformers.
Related Articles:
Hope you understood the working principle of the generator and the principle of the transformer. Stay tuned with BYJU’S to know about various science and math concepts.
Frequently Asked Questions
When can two DC generators be operated simultaneously?
When the dropping voltage characteristics of both DC generators are the same, then the two Dc generators can be operated simultaneously.
What is the use of lap winding in a DC generator?
Lap winding is used for maintaining low voltage and high current in a DC generator.
Define critical resistance in a DC generator.
Critical resistance is defined as the resistance offered by the field.
Name the important parts of a transformer.
The important parts of a transformer are a magnetic circuit with a laminated iron core and clamping structures, a primary and secondary winding, a tank with insulating oil, a vent pipe, a winding temperature indicator, an oil temperature indicator, and a radiator.
What is the use of primary and secondary winding?
The primary winding is the winding to which the supply is provided, and the secondary winding is where the supply is taken for load connecting.
How to reduce the magnetic leakage in a transformer?
The magnetic leakage is reduced by sectionalising and by interleaving the primary and secondary windings.

Nice notes
I like these notes very much