Table of Contents:
A. GS1 Related:
B. GS2 Related:
1. Beijing unveils doctrine to counter U.S. ‘Pivot’
2. India should send Marine to Italy, U.N. arbitration court rules
C. GS3 Related:
1. Parliament clears mines Bill
2. Robust transmission service for renewable energy mooted
3. Newly discovered planets may boost search for life beyond Earth
D. GS4 Related
E. Important Editorials : A Quick Glance
2. A long and hot summer ahead
3. Everybody loves a good quota
1. PIB update
2. The Economic Times : SWIFT sounds good for boosting exports
3. The Economic times : Show more sense on spectrum utilization
4. Economy-Data
F. Concepts-in-News: Related Concepts to Revise/Learn:
G. Fun with Practice Questions 🙂
H. Archives
.
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Useful News Articles
A. GS1 Related
Nothing here for today folks!
B. GS2 Related
1. Beijing unveils doctrine to counter U.S. ‘Pivot’
Topic: India’s Neighbourhood Category: China Location: The Hindu Key points:
- China formally invited itsneighbours to pursue a regional security doctrine that is led by Beijing, and not the United States, during last week’s foreign ministerial Conference on Interaction and Confidence Building Measures in Asia (CICA) in the Chinese capital
- the Chinese have also launched a regional diplomatic offensive to reinforce that an Asian homegrown solution was the best way to resolve SCS disputes, rather than interference by “outside” powers
- China’s diplomatic exertions have also paid off well with Russia, whose Foreign Minister stressed in Beijing on Friday that the SCS issue should not be “internationalized”
Tags: foreign ministerial Conference on Interaction and Confidence Building Measures in Asia (CICA)
2. India should send Marine to Italy, U.N. arbitration court rules
Topic: International Relations Category: India-Italy Relations Location: The Hindu Key points:
- Two Italian marines who are facing the charge of murdering two Indian fishermen in 2012 off the Kerala coastcould return home on bail in the wake of a decision of the PCA (Permanent Court of Arbitration, The Hague)
- Italy had approached the PCA in June 2015
- The Tribunal left it to the Supreme Court of India to fix the precise conditions of the bail
Tags:Permanent Court of Arbitration, The Hague, Supreme Court
C. GS3 Related
1. Parliament clears mines Bill
Topic: Economy Category: Mining Location: The Business Standard Key points:
- Transfer of captive mines in cases of mergers and acquisitions would now be possible with Parliament on Monday clearing an amendment to the mining law
- Major deals among cement companies like UltraTech, Reliance Cements and Lafarge were stuck because the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Act, 2015 permitted transfer of mining leases only for auctioned mines
- It would also help in checking the stressed and non-performing assets of banks by allowing them to liquidate assets where a firm or its captive mining lease is mortgaged
Tags: Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Act, 2015, NPA
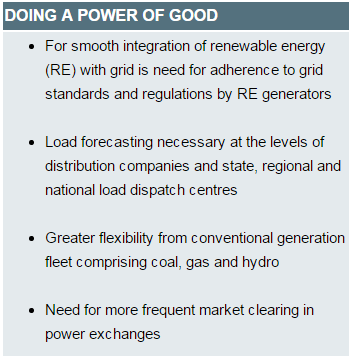
2. Robust transmission service for renewable energy mooted
Topic: Economy Category: Energy sector Location: The Hindu Key points:
- A high level committee appointed by the Union Power Ministry for effective integration of renewable energy (RE) with grid
- The committee headed by special secretary constituted in April 2015 submitted its report last month when the Centre already launched an ambitious plan to increase the renewable capacity to 1,75,000 Mw by 2022 from the present level of over 40,000 Mw
 Tags: Renewable Energy
Tags: Renewable Energy
3. Newly discovered planets may boost search for life beyond Earth
Topic: S&T Category: Space Location: The Hindu Key points:
- Three earth-sized planets are orbitinga small, dim star, located in the constellation Aquarius relatively close to Earth at 40 light years awaywere discovered by astronomers
- They orbit their parent star at a distance that provides the right amount of heat for there to be liquid water on their surface, a condition scientists believe may be critical for fostering life
- The discovery was made using Europe’s Transiting Planets and Planetesimals Small Telescope, or TRAPPIST, located at the La Silla Observatory in Chile.
(The telescope finds planets by looking for changes in the amount of light coming from a star that may be caused by a planet passing by the telescope’s line of sight. The smaller the background star, the easier it is to detect and measure these transiting planets) Tag: TRAPPIST, Aquarius
D. GS4 Related
E. Important Editorials: A Quick Glance
The Hindu
Topic: Governance Category: Environmental Conservation Key points:
- Western Himalayan region, with its mix of colourful forests, including moist deciduous, tropical dry deciduous, temperate and sub-Alpine types is a precious natural heritage of India
- A dry season is almost always followed by forest fires that ravage this spectacular heritage.Garhwal and Kumaon hills are more prone to fires
- What should be done to prevent them in the future?
- Whatever little research has gone into the fires in this area points to accidental or intentional involvement of people in starting the blaze, most frequently in the chir pine forests (Setting the vegetation afire in some forests helps produce richer grazing lands by bringing about better botanical diversity on the ground)
- Some of the studies reported by organisations affiliated to the Union Environment Ministry point to the effective intervention of community-led ‘vanpanchayats’ (forest councils) in preventing fires
- Progress can be made also by providing environmental education to local residents and officials
- Significantly, the use of biomass alternatives, including cooking gas, has had a beneficial impact on fire risk, and this must be expanded
- Equally, the clearing of ecologically important natural oak forests can be reduced by tapping the plantation sector, which could give preference to growing useful fodder and timber trees.
- Stopping further spread of pine trees(they burn in no time) planted over several decades for narrow economic reasons, are crucial for the health of the Western Himalayas
- It is possible that the changing patterns of climate may be exacerbating the problem; more research is required to conclude whether the El Niño that set in last year, marked by a lack of pre-monsoon showers, also played a part in intensifying the fires
Tags: moist deciduous, tropical dry deciduous, temperate, sub-Alpine, chir pine, forest councils, El Niño, pre-monsoon showers Note: Our forests are to be preserved and nurtured. Suggest ways to prevent forest fires.
2. A long and hot summer ahead
Topic: Governance Category: climate change Key Points:
- The Paris Agreement which emerged out of the 21st Conference of the Parties (COP-21) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is indeed historic
- The Paris Agreement represents only a skeletal framework which will now have to be fleshed out in post-Paris negotiations
- For example, take the concept of “transparency”. Developed countries claim that transparency requires a “common and unified system” to compare climate action undertaken as Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) by Parties. Developing countries, on the other hand, point to the “flexibilities” available to them in recognition of the principle of “common but differentiated responsibilities and respective capabilities” (the well-known CBDR principle) and insist that this should be reflected in the application of the transparency provision
- Since India, along with other developing countries, agreed to drop the key principle of “historical responsibility” enshrined in the UNFCCC from the Paris Agreement, the responsibility of the developed industrialised countries for the largest proportion of GHG emissions accumulated in the Earth’s atmosphere, and which is what is responsible for global warming, will be ignored in comparing mitigation contributions. Only current emissions will be the basis for this exercise
- With the concept of carbon budget out of the way, it is current emissions alone which will become the focus in the new climate change regime and create inevitable pressures on India for enhanced mitigation pledges — as we saw in Paris itself
- While trying to impose specific and onerous commitments on developing countries, the developed countries continue to evade providing any clarity on what they intend to contribute by way of finance, technology and capacity building to fulfill their Paris Agreement pledges
- On technology transfer, there is already an offensive by the U.S. corporate sector to ensure that in the post-Paris negotiations there is no concession on intellectual property (IP) issues
- India has already made substantial concessions to enable a consensus and successful outcome at Paris.We must ensure that India’s vital interests are safeguarded and the principle of equity and equitable burden-sharing is reflected across this architecture
Tags:Paris Agreement, the 21st Conference of the Parties (COP-21) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), GHG, IP issues, NDC, CBDR principle
3. Everybody loves a good quota
Topic:Polity Category: Art 15(4) Key Points:
- How do you dismantle the Quota Raj?
- The reserved category certificate should not be treated as a currency that is hoarded by groups who no longer need it. This involves periodic recertification into the reserved category
- Unfortunately, the current system has an established, if imperfect, procedure for notification of new groups into the reserved category but not for moving groups out of the reserved category
- A first step towards establishing such a process may be to ensure that we collect data on caste/tribe affiliation along with data on basic demographic and housing characteristics in the 2021 population census
- This would allow us to move past the exclusive reliance on the 1931 census and obtain information on the current socio-economic conditions of all castes and communities in India.
- Collecting data on thousands of castes is difficult, but it is by no means impossible.The Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India ORGI should not shirk from that, anticipating difficulty
- National interest demands that caution be put aside to develop a long-term solution to an issue that has gained such visibility
- While we are destined for periodic eruptions of demand for reservations by groups like the Jats, without timely and accurate data we have no way of developing a rational system for responding to these demands.
Tags:ORGI
Topic: Governance Category: Defence Procurement Key Points:
- Many a defence deal India signed with other countries is marred with bribes
- As India grew in its status as a moneyed shopper in the international arms bazaar, middlemen and shady operators all began to crowd into New Delhi
- India drew up a comprehensive Defence Procurement Procedure (DPP), and made “integrity clause” a must for all deals, but it did not end corruption
- India continues to perpetuate scams on the military and honest taxpayer. Nobody gets punished.The CBI was not able to send any high-profile individual to jail
- All defence scandals have an international dimension to them. Though the money paid originates from the government exchequer, it is paid abroad, and commissions are distributed across secretive tax havens
- Black money, including that from arms deals, has a powerful role in Indian politics. Political parties, except for a couple of exceptions, suck in massive amounts of black money to sustain their operations and their lavish election-time spending. Arms deals continue to be a key source of such illegal funding
- For India to come out of this cycle of scams, of which Choppergate is only the latest, some important aspects need to be addressed
- It must stop being the world’s largest importer of arms and take a strategic turn towards indigenous procurement. To create a robust military-industrial complex in India, a restructuring of its engineering curriculum, its procurement procedures, military research systems, etc. are required.
- ‘Make in India’ is a good first step, but for now it is a mere slogan. Painful decisions, including abandoning some ongoing expensive procurements from abroad, are important to help push Indian private sector into the procurement cycle
Tags:DPP
Indian Express:
1. Banking on Bharat
Topic: Governance Category: Financial Inclusion Key Points:
- Rural households constitute 55-60 per cent of India’s population. The key to India’s prosperity thus lies in increasing the affluence of this so-called Bharat
- But rural bank lending has historically been driven by regulation through the mandated priority sector lending commitments rather than by a genuine search for business
- A good rural strategy is to provide a complete range of appropriate products for rural customers and replace the moneylender who has traditionally charged crippling rates for the rural poor, perpetuating a vicious cycle of debt
- But to achieve this, the entire paradigm of product design, sales and collection would have to be turned on its head
- For wheat farmers, the time taken between delivering the produce to the agent at the time of grain procurement and his final payment through a cheque or draft typically took 15 to 20 days. With digitisation, this process can be crunched to just 48 hours. The key steps in this dramatic shortening of turnaround time would include the issuance of a smart card to procurement agents, installation of an electronic data machine (EDM) at the mandi backed by the e-payment system RuPay, quick generation of MIS and reports and, finally, e-approvals by the procurement agency
- Comparable solutions can enable quick payment to other segments like milk producers, by leveraging the technology of Point of Sale terminals for small operations and full-scale ATMs for larger dairy societies
- Rural banking is not just about providing customised innovations. There’s a large market for an entire suite of products — car loans, two-wheeler loans, tractor loans, light commercial vehicle loans, small working capital loans to traders, personal loans, gold loans, commodity finance, along with the more conventional agricultural credit
- Digitisation of banking has helped access a wider range of customers in rural India. For a rural population that is mobile-enabled to a large extent, digital applications (wallets, mobile-to-mobile payments) are adding to transaction traffic by leaps and bounds
- Any credit disbursal at the grassroots level must have a holistic approach. Along with timely credit, it’s critical to conduct financial literacy and credit counsellingprogrammes
- The right mix of technology, business model and outreach through targeted programmes to tap these opportunities is the need of the hour
Others:
1. PIB update :
- Changes in Foreign Investment Rules
- To improve the Ease of Doing business GOI has taken many steps to open up more FDI in key areas like insurance, construction, defence, railways and medical devices.
- Procedures are being simplified and digital technology is being used to eliminate multiple approvals. A predictable, stable and competitive tax regime is being built.
- As per the extant FDI policy, any non-resident entity can invest in India, subject to the FDI Policy except in those sectors/ activities which are prohibited.
- However, a citizen of Bangladesh or an entity incorporated in Bangladesh can invest only under the Government route.
- Further, a citizen of Pakistan or an entity incorporated in Pakistan can invest, only under the Government route, in sectors/ activities other than defence, space and atomic energy and sectors/ activities prohibited for foreign investment.
2.Startup India
- An Action Plan for Startup India to build a strong eco-system to nurture innovation and Startups in the country was launched in January 2016.
- Some of the salient features of the scheme include
- Simple Compliance Regime for startups based on Self-certification
- Relaxed norms of public procurement for startups
- Tax exemption to startups for 3 years
- Launch of Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) with Self –Employment and Talent Utilization (SETU) Program of NITI Aayog
Please click here to read more the salient features of the scheme from BEST of PIB Section.
- Manufacturing Sectorand NIMZs
- To boost manufacturing sector under ‘ Make in India’ programme 22 thrust sectors have been identified and various steps were taken to create ease of doing business like
- Setting up of an investor facilitation cell.
- Launch of e-biz portal and
- Liberalising policy for industrial license for defence industries.
- For creation of state-of-art infrastructure, Government is implementing Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) project
- National Investment and Manufacturing Zones (NIMZs) are impartment instrumentalities of the National Manufacturing Policy (NMP).
- Government has approved Eight Investment Regions along the Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) project as NIMZs.
- Both Domestic as well as foreign investors can participate in various tender packages being issued by DMICDC and can also set up a manufacturing base in these cities.
- Industrial Corridor Nodes : DMIC
(Note: Aspirants should try to locate the below places in India map and get some familiarity. No need to memorise)
- Ahmedabad-Dholera Investment Region, Gujarat
- Pithampur-Dhar-Mhow Investment Region, Madhya Pradesh
- Shendra-Bidkin Industrial Park , Maharashtra
- Dighi Port Industrial Area, Maharashtra
- Manesar-Bawal Investment Region, Haryana
- Khushkhera-Bhiwadi-Neemrana Investment Region, Rajasthan
- Jodhpur-Pali-Marwar Region in Rajasthan
To read more about other corridors and NMIZ’s please click here for BEST of PIB section 4.Patent of Ayurvedic system of medicine
- Under Trade Related Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement, to which India is committed, every country is required to accord to the nationals of other members, treatment which is no less favourable than it accords to its own nationals with regard to the protection of intellectual property.
- The Government has taken measures to safeguard the national interest in respect of grant of patents based on indigenous medicinal / herbal products / plants, besides exclusions provided for in the Patents Act 1970.
- These exclusions and measures are outlined below:Patents cannot be granted to plants, including medicinal/ herbal plants, or any part thereof including seeds, varieties and species and essentially biological processes for production or propagation of plants as per section 3 (j) of the Patents Act, 1970.• An invention, which in effect, is traditional knowledge or which is an aggregation or duplication of known properties of traditionally known component or components, is not patentable under Section 3(p) of the Patents Act, 1970.
- The Government has established the Traditional Knowledge Digital Library (TKDL) with the objective of preventing misappropriation of Indian traditional knowledge on Ayurveda, Unani and Siddha medicinal systems.
- The TKDL has been prepared in five languages, namely English, French, German, Japanese and Spanish in patent compatible format.
- It makes available Indian traditional knowledge which are already in public domain, to the patent examiners so that such patent applications which claim Indian traditional knowledge are rejected at the examination stage itself.
- Council of Scientific and Industrial Research files opposition in various patent offices across the world against any patent applications based on Indian Traditional Knowledge.
5.Unnat Bharat Abhiyan
- The Ministry of Human Resource Development has launched Unnat Bharat Abhiyan (UBA) in 2014 to enable higher educational institutions to work with the people of rural India in identifying development challenges and evolving appropriate solutions for accelerating sustainable growth.
- Two Hundred and One (201) villages have been identified for intervention by institutions of higher education.
- Higher educational institutions have been advised to give special emphasis on issues pertaining to sanitation, drinking water supply, energy, agriculture and allied activities, irrigation, education, health, etc. and to provide innovative solution in consultation with Panchayat Raj Institutions (PRIs).
- Smart Grid Projects
- Government of India (GOI) has launched National Smart Grid Mission (NSGM), to plan and monitor implementation of policies and programmes related to Smart Grid activities in India.
- NSGM envisages implementation of Smart Grid projects in the country to make Indian Power infrastructure cost effective, responsive, reliable and self healing.
- Two smart grid projects for Amravati and Chandigarh have been approved under NSGM, with 30% funding from GoI under NSGM.
- The Budgetary support for NSGM activities for the Financial Year 2016-17 is Rs.30 crore.
7.Erosion of coastlines
- As per data base compiled by the National Institute of Oceanography (NIO) in the year of 2005, around 23% of the Indian coastline is affected by varying degrees of erosion.
- A Shoreline Change Atlas of the Indian Coast prepared by the Space Application Centre (SAC), Ahmadabad in association with the Central Water Commission in May, 2014, indicates that around 45% of the total coastline is under erosion, around 35.7% of coastline is under accretion and rest (18.79%) is under stable category.
Please click here to read more on the steps taken by government to check coastal erosion from Best of PIB section.
2. The Economic Times : SWIFT sounds good for boosting exports
Topic: Economy Category: Exports Key Points
- The proposed new green channel for export of manufactures, which would reportedly reduce cargo clearance to a few hours rather than the norm of an entire week, makes excellent sense
- It would reduce transaction costs, hugely improve ease of doing business and boost our trade competitiveness.
- India stands 133rd in the World Bank’s ease of doing business ranking on the parameter of ‘trading across borders’
- The new facility would be functional at select ports in a month, after the Finance Bill is passed. It would allow export shipment without upfront payment of duties, as proposed in the Budget
- The idea is to remove procedural delays and documentation requirements and move to a system where exporters and importers need file just one form at ports, as per the Single Window Interface for Facilitating Trade, or SWIFT
- The way ahead is to diffuse SWIFT across the board, and address manpower shortage at customs to transparently facilitate trade
- But in tandem, there’s the vital need to correct duty structures that give rise to questionable domestic value addition behind relatively high tariff walls. For instance, a duty of 2.5% on printed circuit boards and of 12.5% on finished handsets really incentivises trading passing itself off as an assembly operation here. And the way forward is to have moderate, uniform duty protection across components and finished products.
- Merchandise exports have fallen from a high of $30.5 billion in March 2013 to a low of 22 billion in March 2016, even as the rupee has depreciated 17% vis-à-vis the dollar. World trade is slowing. We do need strategy and brand-building to boost trade in the entire gamut of skill-intensive services
Tags: SWIFT
3. The Economic times : Show more sense on spectrum utilization
- The Telecom Commission has decided to go ahead with a base price of Rs 57,425 crore for a pan-India chunk of 5 MHz of spectrum in the 700 MHz band
- This is a bad choice from multiple perspectives, ranging from the telecom industry’s capital intensity and tariffs to power consumption by the telecom sector
- The irrationality of the decision is compounded by the proposal to free up swathes of sub-700 MHz spectrum from terrestrial broadcast, to which it currently stands assigned, for unlicensed Wi-Fi connectivity. Better sense should prevail, both on auction prices and spectrum utilization
- Wi-Fi utilises unlicensed spectrum, and to prevent interference when multiple users are on the same spectrum band, uses up huge bandwidth. This problem grows with the area covered by one route
- If a low-frequency band, such as the proposed sub-700 MHz band, is used for Wi-Fi, its ability to spread far and penetrate walls would mean that the area covered would be huge, as would be the swathe of spectrum required to service all the people in the area covered. One way to get around that is to use very low power to transmit those Wi-Fi signals.
- The ideal Wi-Fi spectrum is 5, 6, 7 and 8 GHz. Transmission at such frequencies attenuates fast, reducing the coverage area of each Wi-Fi hotspot and allowing efficient use of the spectrum. The government should delicense spectrum in these frequency ranges and make them available for Wi-Fi.
- The same qualities that make sub-700 MHz ill-suited for Wi-Fi make it splendid spectrum for 4G networks. Low-frequency data networks would call for fewer towers and base stations, as compared to high-frequency networks and would significantly lower the energy drained by the telecom sector
- All these considerations warrant a serious reconsideration of spectrum use. Stop letting terrestrial broadcast hoard the best spectrum suited for wireless broadband. Make it available for telecom.
- Trust spectrum usage charges and data-fuelled economic growth to generate revenue, rather than jack up base prices for spectrum auctions.
Tags: spectrum auction, telecom commission
Quick bits
4. Economy-Data
a) Manufacturing PMI slows to 4-month low
- The Nikkei Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) slowed to 50.5 in April from 52.4 in March
- “PMI data indicated that Indian manufacturers raised output at a slower pace in April as new business inflows were broadly unchanged during the month,” according to a statement from Nikkei
b) Core sector output acceleratesto 16-month high of 6.4 %
- India’s infrastructure sectors clocked their highest growth in 16 months in March 2016, with the index for core industries climbing 6.4 per cent, buoyed by a sharp uptick in the output of cement, electricity, fertilisers and refinery products
(“One can’t say conclusively that the economy is on the mend. Investment is happening, activity is happening on government-led capital expenditure (capex) in road, rail and defence. But private capex is not really happening.” Another reason why the jubilation over a recovery might be premature is that the strong growth in March 2016 could likely be a result of a base effect brought on by the contraction seen in the index in March 2015” says experts) 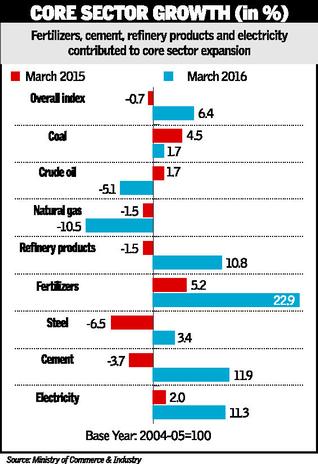 Tags:PMI, core sector
Tags:PMI, core sector
F. Concepts-in-News: Related Concepts to Revise/Learn:
- PMI
- Spectrum Auction
- TRAPPIST
- Paris Agreement
- Mines bill
- Pre-monsoon showers
G. Fun with Practice Questions 🙂
Question 1:Which of the following is/are correctly matched( name of pre monsoon shower and state)?
- Mango Showers – Kerala
- Cherry Blossom – Karnataka
- Kalbaisakhi -West Bengal
- Bardoichila – Assam
a) 1 and 2 b) 1, 2 and 3 c) 1, 2 and 4 d) All the Above
Question 2: Which of the following country(ies) surround(s) the South China Sea?
- Taiwan
- Australia
- Japan
- Indonesia
a) 2 and 3 only b) 1,2 and 3 c) 1 and 4 d) All the Above
Question 3:Which of the following indicators are included in the Purchasing Managers’ Index ?
- inventory levels
- new orders
- supplier deliveries
- employment environment
a) 1,2 and 3 b) 2 and 3 c) 1 and 2 d) All the Above
Question 4:Which of the following statements is/are true?
-
- Joint forest management programincludesafforestation schemes in disused farm lands, degraded forests or other wasteland
- Social forestry programincludes designation of marked areas in reserved forests and protected forests of India as a communal forest
a) 1 only b) 2 only c) Both 1 and 2 d) Neither 1 nor 2
Question 5:Which of the following forest type(s) are found in the Himalayan region?
- Which of the following forest type(s) are found in the Himalayan region?>
- Temperate Moist deciduous forest
- Tropical Evergreen forest
- Alpine forest
- TemperateMontane forest
a) 1 and 3 b) 1,3 and 4 c) 2 and 3 d) All the Above
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Online Current Affairs Crash Course’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
H. Archives:
You can check out some more recent News Analysis sections to build even more context
2nd May 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
1st May 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
Practice More: Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series
Comments