The subject of Indian Polity and Constitution has occupied a dominant space at all 3 stages of the IAS exam, be it Prelims, Mains or Interview. Apart from mastering the Indian Constitution, being well aware about the basics of our political functioning is quintessential for the candidates who strive to compete in the civil services exam. Even when one gets into the service, the significance of the subject is carried forward.
Polity for UPSC
- The Constitution is undoubtedly the most important topic under Indian Polity but it also includes topics like various policies of the government, centre-state relations, new bills, laws, governance issues, social justice, etc.
- It is crucial for a candidate to be abreast with the local happenings and this way it creates a sense of awareness about one’s rights, duties and responsibilities and helps one take an informed decision.
- A good understanding and a proper approach for Indian Polity is a must if you wish to clear the UPSC 2023.
- Polity is one of the easiest of all the subjects to score as the syllabus is factual and concise.
- One can expect a lot of straight forward questions and can get most of the answers right in Polity section in the UPSC Prelims if revised thoroughly.
- Indian Polity questions appearing in the Prelims can cover both static as well as the dynamic part.
- A significant number of questions can be expected in this section. Over the years, the questions have been found to be mostly direct and they range from easy to moderate on the difficulty level.
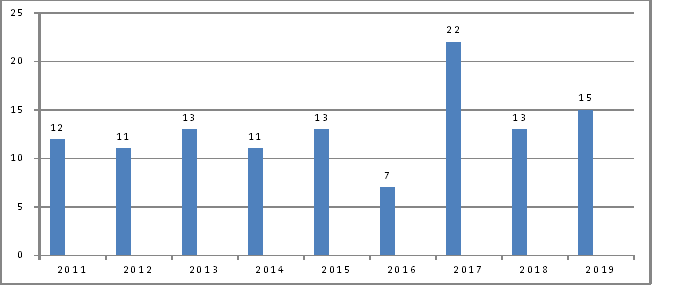
From the above data, we can incur that on an average 15% of the questions come from this section. One can easily judge the importance of this subject because of the significance of weightage given in the IAS exam.
The graph below shows the number of questions asked from polity in the IAS prelims through the years 2011 to 2019.
UPSC Books for Polity
- Class IX NCERT textbook – Democratic Politics-I
- Class X NCERT textbook – Democratic Politics-II
- Class XI NCERT textbook – Indian Constitution at work
- Indian Polity – M. Laxmikanth
- Introduction to the Constitution of India – D.D. Basu
- India Year Book
You can download NCERT Polity Books from the link below:
How to study polity for UPSC Prelims
- The lucidity and simplicity of NCERT textbooks make them an interesting read and gives a good insight for beginners. They don’t take up much of a candidate’s preparation time. To begin one can start with the NCERT of class IX, Democratic Politics-I and move on to Class X NCERT, Democratic Politics-II, where one can get conceptual clarity about the politics and some concepts relevant to the understanding of the constitution. Finally, move on to the NCERT textbook of Class XI, Indian Constitution at work which is a must read and acts as a prerequisite to reading other standard books. It is advised to read NCERT’s thoroughly and cultivate a habit of highlighting important points as you read for future reference.
- The next logical step which can enhance one’s preparation is to refer to India Polity by M. Laxmikanth, which alone can aid a candidate to score higher marks in this section in the Prelims stage. It happens to be the most resourceful and comprehensive book to prepare for Indian Polity for prelims. Almost all the topics mentioned in the syllabus are covered in this book. The language used in the book is lucid and even a beginner finds it easy to comprehend. However, owing to the factual nature of the subject, one needs to do multiple revisions. For more on how to read Laxmikanth for Polity, click here.
- Introduction to the Constitution of India by D.D. Basu can be extremely useful for mains and gives a candidate an in-depth analysis of the subject. Beginners will find the language of this book quite complex.
- Candidates need not mug up all the articles of the Indian Constitution. Only a few important articles are necessary. Most relevant articles would automatically get registered if one is clear with the basics and has revised the subject sufficient number of times.
- It is vital to go through a national daily like The Hindu or The Indian Express and while reading these, pay special attention to news items and editorials that are either related to the Indian Constitution or the national as well as international political systems, in one way or the other. All new bills, acts, policies and any related provisions should be noted down.
- Polity questions in prelims can get tricky as in the first look of it, all options look similar and this may lead to confusion and ambiguity. Regular revisions and practising MCQ’s can help strengthen the basics and boost one’s confidence in the subject. Solving previous year prelims question papers can aid a candidate in understanding the nature of questions and prepare accordingly.
For more UPSC Polity Notes, click on the linked article.
Basic Areas to Focus in Polity
Preamble
- Features of preamble
- 42nd Amendment
- Swaran Singh committee
Schedules
- Basic idea about 12 schedules
Constitution of India
- Basic idea about All articles
- Historical Background
- Drafting committee and the making of the Constitution
- Influence of other constitutions
- Its salient features
- Union and its Territory
-
- Basic idea about Article 1-4
- State reorganization and different Commissions
- Federal nature
- Recent issues
- Citizenship
-
- Basic idea about Article 5-11
- PIO, NRI, OCI and Pravasi Bharathiya Divas
- Privileges available for Indian citizens and foreigners
- Citizenship Amendment Act of 2016
- New policies, schemes and recent changes in voting.
- Fundamental Rights (FR)
-
- Basic idea about Article 12-35
- A thorough understanding of Articles 14- 30 and Article 32
- Rights and privileges available to citizens of India only to the citizens and both to citizens and foreigners
- 44th amendment act
- Different types of Writs
- Enforcement and Exceptional cases with regard to FR’s
- RTE and recent issues related to FR
- Fundamental Duties(FD)
-
- Article 51A
- Difference between FR and FD
- Significance and Criticism
- Enforcement of FD’s
- Recent issues about FD
- Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP)
-
- Basic idea about Article and Article 36-51 and Article 368
- Sources and key features of DPSP
- Classification of DPSP
- Comparison/ conflicts between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles
- Keshavananda Bharathi, Minerva Mills, Golaknath Case, Maneka Gandhi case.
- Important Amendments – 42nd Amendment, 44th Amendment, and 97th amendment
- Union
-
- Basic idea about Article 52-73
- Qualification and Election
- Function and Powers- (Executive, Legislative, Financial, Judicial, Diplomatic, Military and Emergency Powers)
- Resignation and impeachment
- Role and responsibilities and relationship with Prime minister, Council of Minister, Cabinet ministers.
- Prime minister and council of ministers- Basic idea about Article 74-75
- Powers and Functions
- Resignation and Removal
- Attorney general
- Parliament
-
- Basic idea about Article related
- Role and functions of the Parliament
- Sessions, Motions, Parliamentary procedure – Summoning, Prorogation, Joint sitting
- Parliamentary proceedings like Question Hour, Zero Hour, and Adjournment Motion, etc.
- Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha,
- Special powers of Rajya Sabha
- Anti-defection law and 10th schedule
- Parliamentary Privileges
- Bill and lawmaking procedure
- Budget, funds and its summary
- Parliamentary Committees
- Judiciary
-
- Basic idea about Article related to the judiciary.
- Powers of Supreme court and high court
- Qualification and appointment
- Removal procedure
- Recent controversy, verdicts, and constitutional provisions.
- State Government- State Executive
-
- Governor- appointment, removal and special powers.
- Executive, Legislative, Financial, Judicial powers and discretionary of the governor
- 7th constitutional amendment
- Chief minister and council of ministers
- Power of chief minister
- State Legislature
-
- State legislature compared to the Parliament with regard to composition, powers, and functions.
- Bicameral legislatures
- Creation and abolition of the Legislative councils
- Administration of Union Territories (UT)
-
- Special provision for Delhi
- Administration and jurisdiction in UT’s
- Administration of Special Areas
-
- Basic idea about 5thSchedule 6th Schedule
- Recent issues related to Administration of Special Areas
- Special provision for Jammu and Kashmir-Article 370
- Difference between constitutional provisions related to Jammu and Kashmir
- Emergency Provisions
-
- National emergency- Article 352
- President’s rule or State emergency- Article 356
- Financial emergency- Article 360
- 44th Amendment Act
- Effects and implications of emergency
- Role of President in emergency time
- The State of FR, Lok Sabha, and Rajya Sabha
- Revoking emergency
- State-Centre and interstate relations
-
- Basic idea about Articles 262 and 263
- Composition and functions of Interstate council and Zonal council
- Inter-State trade and Commerce
- Recent disputes between states, controversies etc
- New policies or schemes which impact interstate relations
- Panchayati Raj and municipalities
-
- Elections, auditing, powers and authority of panchayats
- 3 tier structure
- 73rd Amendment Act and 74th Amendment Act
- Relation with FR and DPSP
- Schemes introduced
- Metropolitan planning committee and urban development
- Reservation
- Constitution Bodies
-
- Election Commission
- UPSC
- SPSC
- JPSC
- Finance Commission
- National Commission for SCs and ST’s,
- Composition, Powers and Functions, Removal of the Constitutional bodies
- Non-Constitutional Bodies
-
- Basic idea about Composition, Functions, Working of the Non-Constitutional bodies such as National Human Rights Commission, Central Information Commission, Central Vigilance Commission, Central Bureau of Investigation, State Human Rights Commission, State Information Commission etc
- Tribunals
-
- Basic idea about Article 323A and tribunals under Article 323B
- Recent controversial issues related to tribunals
- Different tribunals and importance
- Special Provisions for SC’s, ST’s, Backward Classes, Minorities and Anglo-Indians
-
- Privileges and right issued to SC’s, ST’s, Backward Classes, Minorities and Anglo-Indians
- Issues related to vulnerable sections like women, child, SC’s, ST’s, Backward Classes, Minorities and Anglo-Indians
- Current affairs
-
- Recent issues related to above-mentioned categories
- Important schemes, programs, missions, laws, and policies launched by the government.
- Recent Government Bills and Governance- actions
Take a look at a few example questions from the UPSC Prelims 2019 that came from the polity and governance segment:
Q1. With reference to the constitution of India, consider the following statements:
- No High Court shall have the jurisdiction to declare any central law to be constitutionally invalid.
- An amendment to the Constitution of India cannot be called into question by the Supreme Court of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: d
Q2. In the context of polity, which one of the following would you accept as the most appropriated definition of liberty?
a) Protection against the tyranny of political rulers
b) Absence of restraint
c) Opportunity to do whatever one likes
d) Opportunity to develop oneself fully
Answer: b
Q3. Consider the following statements:
- Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB) is the first regulatory body set up by the government of India.
- One of the tasks of PNGRB is to ensure competitive markets for gas.
- Appeals against the decisions of PNGRB go before the Appellate Tribunals for Electricity.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: b
Related Links:
Comments