The NCERT solutions for Class 8 Maths cover the topics with frequent, focused, engaging Maths challenges and activities that strengthen Maths concepts. Each question of the exercise in NCERT Class 8 Maths Solutions has been carefully solved for the students to understand, keeping the examination point of view in mind.
Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 – Practical Geometry Exercise 4.1 Questions and answers help the students to understand the construction of a quadrilateral with lengths of four sides and a diagonal given. These NCERT Solutions are prepared by BYJU’S subject experts using a step-by-step approach.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 – Practical Geometry Exercise 4.1
Access Other Exercise Solutions of Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 – Practical Geometry
Exercise 4.2 Solutions 1 Question
Exercise 4.3 Solutions 1 Question
Exercise 4.4 Solutions 1 Question
Exercise 4.5 Solutions 4 Questions
Access Answers to Maths NCERT Class 8 Chapter 4 – Practical Geometry Exercise 4.1 Page Number 60
1. Construct the following quadrilaterals.
(i) Quadrilateral ABCD AB = 4.5 cm
BC = 5.5 cm
CD = 4 cm AD = 6 cm AC = 7 cm
Solution:
The rough sketch of the quadrilateral ABCD can be drawn as follows:

(1) ∆ABC can be constructed by using the given measurements as follows:

(2) Vertex D is 6 cm away from vertex A. Therefore, while taking A as the centre, draw an arc of radius 6 cm.

(3) Taking C as the centre, draw an arc of radius 4 cm, cutting the previous arc at point D. Join D to A and C.

ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
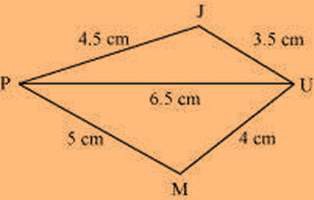
(ii) Quadrilateral JUMP JU = 3.5 cm
UM = 4 cm MP = 5 cm PJ = 4.5 cm PU = 6.5 cm
Solution:
The rough sketch of the quadrilateral JUMP can be drawn as follows:
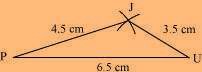
(1) ∆ JUP can be constructed by using the given measurements as follows:
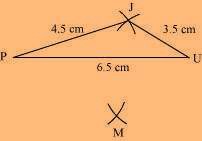
(2) Vertex M is 5 cm away from vertex P and 4 cm away from vertex U. Taking P and U as centres, draw arcs of radii 5 cm and 4 cm, respectively. Let the point of intersection be M.
(3) Join M to P and U.
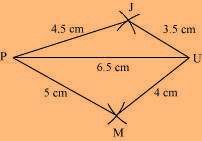
JUMP is the required quadrilateral.
(iii) Parallelogram MORE
OR = 6 cm
Solution:
RE = 4.5 cm
EO = 7.5
We know that opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal in length, and also these are parallel to each other.
i.e., ME = OR, MO = ER
The rough sketch of the parallelogram MORE can be drawn as follows:
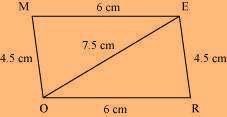
(1) ∆ EOR can be constructed by using the given measurements as follows:
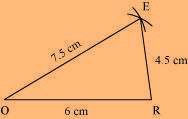
(2) Vertex M is 4.5 cm away from vertex O and 6 cm away from vertex E. Therefore, while taking O and E as centres, draw arcs of 4.5 cm radius and 6 cm radius, respectively. These will intersect each other at point M.
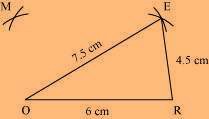
(3) Join M to O and E.
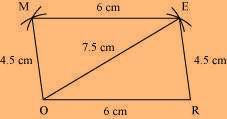
MORE is the required parallelogram.
(iv) Rhombus BEST
BE = 4.5 cm
ET = 6 cm
Solution:
We know that all sides of a rhombus are of the same measure. Hence, BE = ES = ST = TB.
The rough sketch of the rhombus BEST can be drawn as follows:
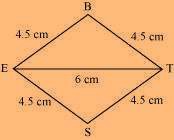
(1) ∆ BET can be constructed by using the given measurements as follows:
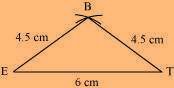
(2) Vertex S is 4.5 cm away from vertex E and also from vertex T. Therefore, while taking E and T as centres, draw arcs of 4.5 cm radius, which will intersect each other at point S.
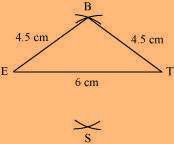
(3) Join S to E and T.
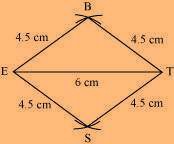
BEST is the required rhombus.
Exercise 4.1 of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 – Practical Geometry is based on the following topics:
- Constructing a Quadrilateral
- When the lengths of four sides and a diagonal are given
Also, explore –





It is Nice